Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Articles
- Management of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: challenges and strategies for optimal outcomes
- Jae Hyun Yoon, Sung Kyu Choi
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):300-315. Published online September 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.08.27
- 2,905 Views
- 167 Downloads
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
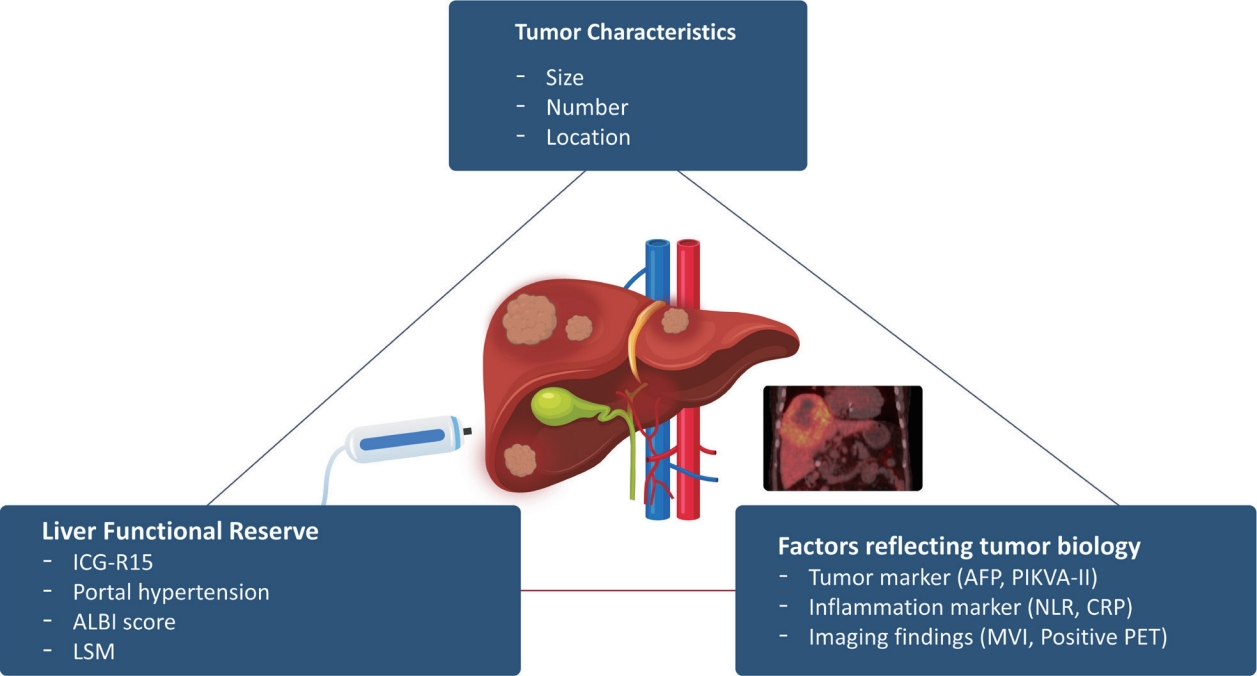
PDF - Although hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is associated with a poor prognosis, management of early-stage HCC is often successful with highly efficacious treatment modalities such as liver transplantation, surgical resection, and radiofrequency ablation. However, unfavorable clinical outcomes have been observed under certain circumstances, even after efficient treatment. Factors that predict unsuitable results after treatment include tumor markers, inflammatory markers, imaging findings reflecting tumor biology, specific outcome indicators for each treatment modality, liver functional reserve, and the technical feasibility of the treatment modalities. Various strategies may overcome these challenges, including the application of reinforced treatment indication criteria with predictive markers reflecting tumor biology, compensation for technical issues with up-to-date technologies, modification of treatment modalities, downstaging with locoregional therapies (such as transarterial chemotherapy or radiotherapy), and recently introduced combination immunotherapies. In this review, we discuss the challenges to achieving optimal outcomes in the management of early-stage HCC and suggest strategies to overcome these obstacles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diosgenin potentiates the anticancer effect of doxorubicin and volasertib via regulating polo-like kinase 1 and triggering apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Eman H. Yousef, Mohamed E. El-Mesery, Maha R. Habeeb, Laila A. Eissa
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2024; 397(7): 4883. CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef - Radiofrequency for hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 3 cm: potential for applications in daily practice
Ji Hoon Kim, Pil Soo Sung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma outcomes and potential implications for surveillance in elderly patients
Aryoung Kim, Goeun Park, Myung Ji Goh, Byeong Geun Song, Wonseok Kang, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Dong Hyun Sinn
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in alcohol use and alcoholic liver disease in South Korea: a nationwide cohort study
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Dong Hyeon Lee, Young Chang, Hoongil Jo, Young Youn Cho, Sangheun Lee, Log Young Kim, Jae Young Jang
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) for Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Moonhyung Lee, Hyun Phil Shin
Medicina.2023; 59(12): 2174. CrossRef
- Diosgenin potentiates the anticancer effect of doxorubicin and volasertib via regulating polo-like kinase 1 and triggering apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells

- Imaging prognostication and tumor biology in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Diana Kadi, Marilyn F. Yamamoto, Emily C. Lerner, Hanyu Jiang, Kathryn J. Fowler, Mustafa R. Bashir
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):284-299. Published online September 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.08.29

- 2,534 Views
- 122 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver malignancy, and represents a significant global health burden with rising incidence rates, despite a more thorough understanding of the etiology and biology of HCC, as well as advancements in diagnosis and treatment modalities. According to emerging evidence, imaging features related to tumor aggressiveness can offer relevant prognostic information, hence validation of imaging prognostic features may allow for better noninvasive outcomes prediction and inform the selection of tailored therapies, ultimately improving survival outcomes for patients with HCC.

Original Article
- Nomogram for predicting overall survival in patients with large (>5 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma based on real-world practice
- Nalee Kim, Jeong Il Yu, Hee Chul Park, Jung Yong Hong, Ho Yeong Lim, Myung Ji Goh, Yong-Han Paik
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):350-361. Published online September 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.08.10

- 1,184 Views
- 54 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
Patients with large (>5 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have limited treatment options, thus necessitating the identification of prognostic factors and the development of predictive tools. This study aimed to identify prognostic factors and to construct a nomogram to predict survival outcomes in patients with large HCC.
Methods
A cohort of 438 patients, who were diagnosed with large HCC at a tertiary hospital between 2015 and 2018, was analyzed. Cox proportional hazards models were used to identify key prognosticators of overall survival (OS), and an independent set of prognostic factors was used to develop a nomogram. The discrimination and calibration abilities of the nomogram were assessed and internal validation was performed using cross-validation and bootstrapping methods.
Results
During a median follow-up of 9.3 months, the median OS was 9.9 months, and the 1-year OS rate was 43.9%. Multivariable Cox regression analysis revealed that performance status, modified albumin-bilirubin grade, tumor size, extent of portal vein tumor thrombosis, and initial treatment significantly affected OS. The newly developed nomogram incorporating these variables demonstrated favorable accuracy (Harrell’s concordance index, 0.807).
Conclusions
The newly developed nomogram facilitated the estimation of individual survival outcomes in patients with large HCC, providing an acceptable level of accuracy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prognostic Role of Basal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Suitable for Curative Treatment
Stefano Mazza, Chiara Frigerio, Daniele Alfieri, Aurelio Mauro, Francesca Torello Viera, Davide Scalvini, Chiara Barteselli, Carmelo Sgarlata, Letizia Veronese, Marco Bardone, Laura Rovedatti, Simona Agazzi, Elena Strada, Lodovica Pozzi, Marcello Maestri,
Medicina.2024; 60(5): 692. CrossRef
- Prognostic Role of Basal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Suitable for Curative Treatment

Review Article
- Radiologic features of hepatocellular carcinoma related to prognosis
- Shin Hye Hwang, Hyungjin Rhee
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):143-156. Published online March 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.16

- 2,430 Views
- 126 Downloads
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The cross-sectional imaging findings play a crucial role in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent studies have shown that imaging findings of HCC are not only relevant for the diagnosis of HCC, but also for identifying genetic and pathologic characteristics and determining prognosis. Imaging findings such as rim arterial phase hyperenhancement, arterial phase peritumoral hyperenhancement, hepatobiliary phase peritumoral hypointensity, non-smooth tumor margin, low apparent diffusion coefficient, and the LR-M category of the Liver Imaging-Reporting and Data System have been reported to be associated with poor prognosis. In contrast, imaging findings such as enhancing capsule appearance, hepatobiliary phase hyperintensity, and fat in mass have been reported to be associated with a favorable prognosis. Most of these imaging findings were examined in retrospective, single-center studies that were not adequately validated. However, the imaging findings can be applied for deciding the treatment strategy for HCC, if their significance can be confirmed by a large multicenter study. In this literature, we would like to review imaging findings related to the prognosis of HCC as well as their associated clinicopathological characteristics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiomics and machine learning based on preoperative MRI for predicting extrahepatic metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with transarterial chemoembolization
Gang Peng, Xiaojing Cao, Xiaoyu Huang, Xiang Zhou
European Journal of Radiology Open.2024; 12: 100551. CrossRef - A Nomogram Based on MRI Visual Decision Tree to Evaluate Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hanting Dai, Chuan Yan, Wanrong Huang, Yifan Pan, Feng Pan, Yamei Liu, Shunli Wang, Huifang Wang, Rongping Ye, Yueming Li
Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Parameters Work Well as Predictive Factors for Atezolizumab and Bevacizumab Treatment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ji Yeon Lee, Pil Soo Sung
Gut and Liver.2024; 18(4): 558. CrossRef - Imaging prognostication and tumor biology in hepatocellular carcinoma
Diana Kadi, Marilyn F. Yamamoto, Emily C. Lerner, Hanyu Jiang, Kathryn J. Fowler, Mustafa R. Bashir
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 284. CrossRef
- Radiomics and machine learning based on preoperative MRI for predicting extrahepatic metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with transarterial chemoembolization

Original Article
- Clinical characteristics and prognosis of Korean patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with respect to etiology
- Wonjoon Jang, Hye Won Lee, Jae Seung Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):158-166. Published online September 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.09.18
- 3,140 Views
- 72 Downloads
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
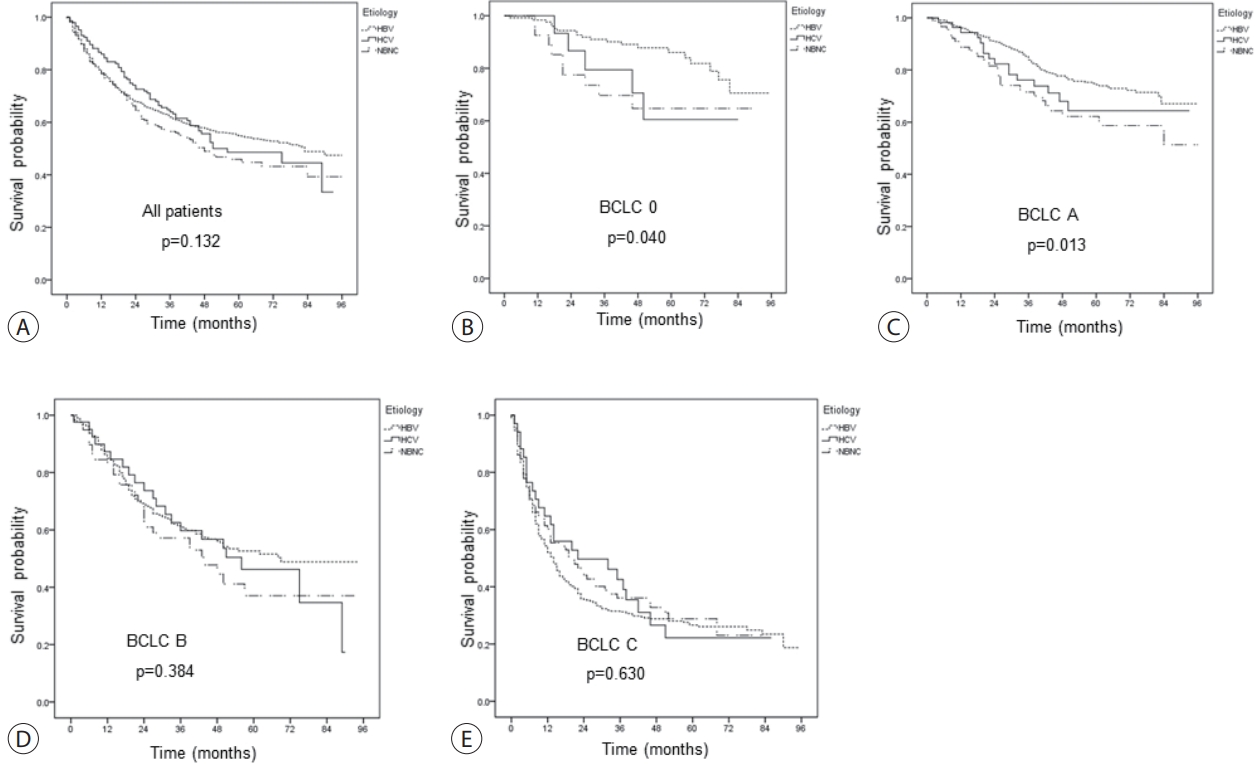
The profile of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has changed globally; the role of etiology in predicting prognosis of HCC patients remains unclear. We aimed to analyze the characteristics and prognosis of Korean patients with HCC according to disease etiology.
Methods
This retrospective observational study included patients diagnosed with HCC between 2010 and 2014 in a single center in Korea. Patients with HCC aged <19 years old, had coinfection with other viral hepatitis, had missing follow-up data, were Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage D, or died before 1 month were excluded.
Results
A total of 1,595 patients with HCC were analyzed; they were classified into the hepatitis B virus (HBV) group (1,183 [74.2%]), hepatitis C virus (HCV) group (146 [9.2%]), and non-B non-C (NBNC) group (266 [16.7%]). The median overall survival of all patients was 74 months. The survival rates at 1, 3, and 5 years were 78.8%, 62.0% and 54.9% in the HBV group; 86.0%, 64.0%, and 48.6% in the HCV group; and 78.4%, 56.5%, and 45.9% in the NBNC group, respectively. NBNC-HCC has a poorer prognosis than other causes of HCC. Survival was significantly longer in the HBV group with early-stage HCC than in the NBNC group. Furthermore, survival was shorter in patients with early-stage HCC and diabetes mellitus (DM) than in those without DM.
Conclusions
The etiology of HCC affected clinical characteristics and prognosis to some extent. NBNC-HCC patients showed shorter overall survival than viral-related HCC patients. Additionally, the presence of DM is an additional important prognostic factor in patients with early-stage HCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis
Log Young Kim, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Young Chang, Hoongil Jo, Young Youn Cho, Sangheun Lee, Dong Hyeon Lee, Jae Young Jang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef - Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis Followed by Acute Hepatitis A Infection: Case Report
Min-Woo An, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jin Kuk Kim, Ahrim Moon, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Medicina.2023; 59(5): 819. CrossRef - Validation of MELD 3.0 scoring system in East Asian patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jong-In Chang, Ji Eun Moon, Dong Hyun Sinn, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Liver Transplantation.2023; 29(10): 1029. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Statin use and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with chronic hepatitis B: an emulated target trial using longitudinal nationwide population cohort data
Dong Hyun Sinn, Danbee Kang, Yewan Park, Hyunsoo Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Juhee Cho, Geum-Youn Gwak
BMC Gastroenterology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Addition of Kidney Dysfunction Type to MELD-Na for the Prediction of Survival in Cirrhotic Patients Awaiting Liver Transplantation in Comparison with MELD 3.0 with Albumin
Kyeong-Min Yeom, Jong-In Chang, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Ji Eun Moon, Dong Hyun Sinn, Young Seok Kim, Sang Gyune Kim
Diagnostics.2023; 14(1): 39. CrossRef
- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis

Review Article
- A clinical and pathological update on hepatocellular carcinoma
- Salvatore Lorenzo Renne, Luca Di Tommaso
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):14-22. Published online March 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.18

- 8,994 Views
- 536 Downloads
- 12 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It is estimated that more than 1 million individuals will be affected annually by hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by 2025. HCC can be broadly grouped into two major molecular subgroups, each of which is characterized by specific morphological and phenotypic features that mirror the genetic background. The use of these tissue biomarkers in the daily practice of pathologists promises to better allocate patients with HCC with adequate treatments. In turn, this will likely boost the attitude of clinicians toward obtaining a pre-treatment biopsy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sujin Koo, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Seungeun Ryoo, Jungeun Park, Dong Ah Park
Current Oncology.2024; 31(1): 324. CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef - Enhancing liver cirrhosis varices and CSPH risk prediction with spleen stiffness measurement using 100-Hz probe
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sun Ah Maeng, Young Chang, Sae Hwan Lee, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, Gab Jin Cheon, Young Seok Kim, Hong Soo Kim, Sang Gyune Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of gallbladder cancer by direct near-infrared measurement of raw bile combined with two-trace two-dimensional correlation analysis
Eunjin Jang, Woosuk Sohng, Dongho Choi, Hoeil Chung
The Analyst.2023; 148(2): 374. CrossRef - Measurement of Heavy Metal and Antioxidant-Oxidant Levels in Tissues Obtained From Three Different Localizations of Explant Hepatectomy of Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Cemalettin Koc, Sami Akbulut, Kemal Baris Sarici, Muhammed Mehdi Uremis, Ufuk Gunay Dogan, Zeynep Kucukakcali, Ibrahim Umar Garzali, Ertugrul Karabulut, Yusuf Turkoz, Sezai Yilmaz
Transplantation Proceedings.2023; 55(5): 1262. CrossRef - Adding MRI as a Surveillance Test for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis Can Improve Prognosis
Su Jong Yu, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Dong Ho Lee, Su Jin Kim, Eun Ju Cho, Se Hyung Kim, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Yoon Jun Kim, Jeong Min Lee, Jae Young Lee, Jung-Hwan Yoon
Biomedicines.2023; 11(2): 382. CrossRef - Development of a sorafenib-loaded solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system: Formulation optimization and characterization of enhanced properties
Chaemin Lim, Dayoon Lee, Mikyung Kim, Subin Lee, Yuseon Shin, Jacob D. Ramsey, Han-Gon Choi, Eun Seong Lee, Yu Seok Youn, Kyung Taek Oh
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2023; 82: 104374. CrossRef - Validation of MELD 3.0 scoring system in East Asian patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jong-In Chang, Ji Eun Moon, Dong Hyun Sinn, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Liver Transplantation.2023; 29(10): 1029. CrossRef - Higher Number of Tumor-Infiltrating PD-L1+ Cells Is Related to Better Response to Multikinase Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ji Won Han, Ji Hoon Kim, Dong Hyun Kim, Jeong Won Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Jaegyoon Ahn, Hyun Yang, Pil Soo Sung
Diagnostics.2023; 13(8): 1453. CrossRef - Risk of dyslipidemia in chronic hepatitis B patients taking tenofovir alafenamide: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Eui Gwon Hwang, Eun-Ae Jung, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Hepatology International.2023; 17(4): 860. CrossRef - Recent application of artificial intelligence on histopathologic image-based prediction of gene mutation in solid cancers
Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Kyung Jin Seo, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Kwangil Yim, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang, Chan Kwon Jung, Yosep Chong
Briefings in Bioinformatics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of pelitinib in the regulation of migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via inhibition of Twist1
Sewoong Lee, Eunjeong Kang, Unju Lee, Sayeon Cho
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

Original Articles
- The effects of immune checkpoint modulators on the clinical course of patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma
- Jihyun An, Hyo Jeong Kang, Eunsil Yu, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):40-50. Published online March 17, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.06

- 3,734 Views
- 121 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
Immune checkpoint proteins regulating T-cell mediated anti-tumor immunity have been reported to affect clinical outcomes in multiple malignancies. This study aimed to investigate the prognostic effect of histological expression of immune checkpoint proteins in patients with resected hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
A total of 221 patients with HCC who underwent curative resection were included. Expression of programmed-cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) in tumor cells (tPD-L1) and tumor infiltrating mononuclear cells (TIMCs) (iPD-L1), programmed-cell death-1 in TIMCs (iPD-1), and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 in TIMCs (iCTLA-4) were measured immunohistochemically.
Results
Histo-positivity for iCTLA-4, iPD-1, iPD-L1, and tPD-L1 was 32.1%, 42.5%, 35.3%, and 14.9%, respectively. Multivariate logistic analyses revealed that male sex and tumor >5 cm were variables related to iCTLA-4 positivity (odds ratio [OR], 0.46 and 1.94, respectively; P<0.05). Poor differentiation was related to PD-L1 expression in both tumor cells and TIMCs (OR, 2.88 and 3.46, respectively; P<0.05). Microvascular invasion was significantly associated only with iPD-L1 (OR, 2.24; P<0.05). In time-dependent outcome analyses, expression of immune checkpoint proteins in TIMCs (i.e., iCTLA-4, iPD-1, and iPD-L1) was significantly related to longer overall survival and non-cancer-related survival (all P<0.05), but not to time-to-recurrence or cancer-specific deaths. Concurrent activation of the PD-1:PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways predicted improved outcomes in terms of overall survival and non-cancer related survival (P=0.06 and P=0.03, respectively).
Conclusions
Immune checkpoint proteins upregulated in TIMCs in HCC tissues have individual and additive effects in prolonging the survival of patients, specifically in terms of survival not related to cancer recurrence. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role of PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway in cancer pathogenesis and treatment: a systematic review
Amirhosein Sabaghian, Shahnam Shamsabadi, Saghar Momeni, Mobina Mohammadikia, Kiarash Mohebbipour, Samira Sanami, Sajjad Ahmad, Nahid Akhtar, Neeta Raj Sharma, Raja Babu Singh Kushwah, Yash Gupta, Ajit Prakash, Hamidreza Pazoki-Toroudi
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The role of PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway in cancer pathogenesis and treatment: a systematic review

- Serum PD-1 Levels Change with Immunotherapy Response but Do Not Predict Prognosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Hye Won Lee, Kyung Joo Cho, Soon Young Shin, Ha Yan Kim, Eun Ju Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):108-116. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.108
- 5,651 Views
- 154 Downloads
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aims
Programmed death receptor 1 (PD-1) is a promising new target for treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A high expression level of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a possible prognostic indicator for poor outcome in other malignancies. Here, we investigated the clinical significance of PD-1 and PD-L1 in patients with HCC.
Methods
We enrolled patients with HCC who underwent surgical resection at Severance Hospital between 2012 and 2017 and investigated the levels of PD-L1 in HCC tissues (tPD-L1) and PD-L1/PD-1 in serum (sPD-L1/sPD-1). We also aimed to determine whether expression levels correlated with clinical and histological features.
Results
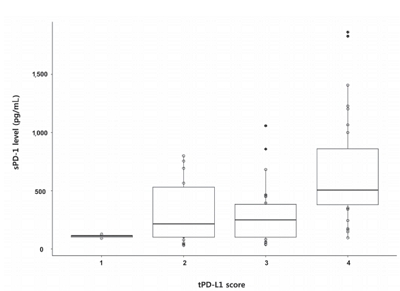
A total of 72 patient samples were analyzed. The median sPD-L1 and sPD-1 levels were 25.72 and 341.44 pg/mL, respectively. A positive correlation was detected between tPD-L1 and sPD-1 levels (R2=0.426, P<0.001). The median sPD-1 level increased linearly with tPD-L1 score (P=0.002). During the follow-up period, HCC recurred in eight (11.1%) patients and liverrelated mortality occurred in eight (11.1%) patients. Higher sPD-L1 levels (≥19.18 pg/mL) tended to be associated with liver-related mortality (hazard ratio 6.866; 95% confidence interval, 0.804-58.659, P=0.078). sPD-1 levels of patients treated with nivolumab as a second-line therapy changed serially, and a >50% reduction in sPD-1 levels was observed immediately after nivolumab administration. However, sPD-1 level was not associated directly with prognosis in patients with advanced HCC.
Conclusions
The results demonstrated that PD-L1 and PD-1 levels changed according to the immunotherapy. However, no significant association with clinical outcome in patients with HCC was detected. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Blood-based biomarkers for immune-based therapy in advanced HCC: Promising but a long way to go
Pil Soo Sung, Isaac Kise Lee, Pu Reun Roh, Min Woo Kang, Jaegyoon Ahn, Seung Kew Yoon
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum levels of soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1): A possible biomarker in predicting post-treatment outcomes in patients with early hepatocellular carcinoma
Tudor Mocan, Maria Ilies, Iuliana Nenu, Rares Craciun, Adelina Horhat, Ruxandra Susa, Iulia Minciuna, Ioana Rusu, Lavinia-Patricia Mocan, Andrada Seicean, Cristina Adela Iuga, Nadim Al Hajjar, Mihaela Sparchez, Daniel-Corneliu Leucuta, Zeno Sparchez
International Immunopharmacology.2021; 94: 107467. CrossRef - Interfacial interactions of SERS-active noble metal nanostructures with functional ligands for diagnostic analysis of protein cancer markers
Han-Jung Ryu, Won Kyu Lee, Yoon Hyuck Kim, Jae-Seung Lee
Microchimica Acta.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Status and Future Direction of Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What Do the Data Suggest?
Hye Won Lee, Kyung Joo Cho, Jun Yong Park
Immune Network.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Nivolumab for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Multiple Lung Metastases after Sorafenib Failure
Jaewoong Kim, Jin Won Chang, Jun Yong Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(1): 72. CrossRef
- Blood-based biomarkers for immune-based therapy in advanced HCC: Promising but a long way to go

Review Article
- Tumor Response Evaluation after Treatment and Post-treatment Surveillance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Yoon, Jun Sik , Park, Soo Young
- J Liver Cancer. 2018;18(1):9-16. Published online March 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.18.1.9
- 8,730 Views
- 212 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma is one of the most prevalent malignancies and frequent causes of death worldwide. Treatment options of hepatocellular carcinoma consist of locoregional therapy, surgical resection, liver transplantation, and systemic therapy. Assessment of tumor response is required in patients receiving locoregional and systemic therapy. The Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.1 is widely used tumor response evaluation criteria. However, the RECIST does not reflect the extent of tumor necrosis after some locoregional therapies and molecular targeted agents. The Modified RECIST (mRECIST), which has the concept of viable tumor, was introduced in order to overcome this problem. The mRECIST were developed on the basis of RECIST version 1.1 and only tumoral tissue showing contrast uptake in arterial phase of dynamic radiologic imaging techniques was measured to assess tumor response. Recently, immune checkpoint inhibitors have emerged as a promising therapeutic modality for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. To identify tumor response after immunotherapy, immune RECIST (iRECIST) has been proposed as consensusbased criteria. After achieving complete response after curative treatment, optimal surveillance was needed to detect recurrence. Individualized surveillance schedule should be considered, taking into consideration the risk factors of the patient and the risk associated with the treatment modalities.

Original Article
- Factors Affecting Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis: Implications for Future Therapeutic Strategies
- Sang Jun Suh, Hyung Joon Yim, Dong Won Lee, Jong Jin Hyun, Young Kul Jung, Ji Hoon Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun, Soon Ho Um
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):60-71. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.60
- 2,289 Views
- 25 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) exhibits poor prognosis. The aim of this study is to evaluate factors associated with survival of HCC patients with PVTT to suggest better therapeutic options.
Methods
Patients with HCC which were newly diagnosed at three tertiary hospitals between January 2004 and December 2012, were reviewed retrospectively. Among them, Barcelona Clinic of Liver Cancer stage C patients with PVTT were identified. Factors affecting overall survival (OS) were analyzed and efficacies of the treatment modalities were compared.
Results
Four hundred sixty five patients with HCC and PVTT were included. Liver function, tumor burden, presence of extrahepatic tumor, alfa fetoprotein, and treatment modalities were significant factors associated with OS. Treatment outcomes were different according to the initial modalities. OS of the patients who received hepatic resection, radiofrequency ablation (RFA), transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC), sorafenib, systemic cytotoxic chemotherapy, radiation therapy (without combination), and supportive care were 27.8, 7.1, 6.7, 5.3, 2.5, 3.0, 1.8, and 0.9 months, respectively (P<0.001). Curative-intent treatments such as hepatic resection or RFA were superior to noncurativeintent treatments (P<0.001). TACE or HAIC was superior to sorafenib or systemic chemotherapy (P<0.001). Combining radiotherapy to TACE or HAIC did not provide additional benefit on OS (P=0.096).
Conclusions
Treatment modalities as well as baseline factors significantly influenced on OS of HCC patients with PVTT. Whenever possible, curative intent treatments should be preferentially considered. If unable, locoregional therapy would be a better choice than systemic therapy in HCC patients with PVTT. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Value of surgical resection compared to transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A meta-analysis of hazard ratios from five observational studies
Keera Kang, Sung Kyu Song, Chul-Woon Chung, Yongkeun Park
Annals of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery.2020; 24(3): 243. CrossRef
- Value of surgical resection compared to transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A meta-analysis of hazard ratios from five observational studies

Case Reports
- A Case of Complete Response by Multidisciplinary Management in a Patient with Solitary Bone Metastasis after Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Seawon Hwang, Hyun Yang, Hae Lim Lee, Jeong Won Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(1):52-56. Published online March 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.1.52
- 1,093 Views
- 14 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Despite recent advances in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the prognosis of patients with extrahepatic metastasis from HCC still remains dismal. The current study presents a case of HCC that was metastatic to the pelvis and describes successful treatment with multidisciplinary approach to the skeletal metastasis. The patient was a 67-year-old male who presented with right pelvic pain 28 months following right hepatectomy for HCC. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging indicated a solitary bone metastasis without intrahepatic recurrence. Complete response was achieved with multidisciplinary management including sorafenib, transarterial embolization, surgery to remove the metastatic mass and radiotherapy after surgery. A post-operative follow-up 15 months later found that the patient remained in good health with maintained complete response. This case suggests that a multidisciplinary approach can achieve long-term cancer-free survival and prolonged life expectancy beyond palliative care for patients with solitary bone metastasis after curative surgery for HCC.

- A Case of Rapid Progressive Extrahepatic Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Surgical Resection for Huge Single Mass
- Eun Sun Jang, Haeryoung Kim, Young Rok Choi, Jai Young Cho, Yoo-Seok Yoon, Ho-Seong Han, Ji Hyun Kim, Jin-Wook Kim, Sook-Hyang Jeong
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(1):42-46. Published online March 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.1.42
- 950 Views
- 14 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) shows a poor prognosis with high recurrence rate even after surgical resection. To improve prognosis of HCC patient, regular surveillance for high-risk group is recommended, but cost-benefit of the surveillance under 40 years old Asian male with hepatitis B infection is unclear. We share a 39-year-old male case which showed early recurrence and rapid extrahepatic metastasis after surgical resection for single huge HCC. Based on the pathologic finding, this case was diagnosed with ‘stemness’-related markerexpressing HCC. Further molecular classification for HCC could be beneficial to estimate individual risk for HCC recurrence and to predict prognosis.

Original Articles
- Subclassification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Intermediate Stage
- Hye Won Lee, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Snag Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Beom Kyung Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(1):17-22. Published online March 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.1.17
- 1,435 Views
- 15 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) intermediate stage includes a highly heterogeneous population. Here, we aimed to subclassify hepatocellular carcinoma with BCLC intermediate stage for better prognostification.
Methods
Between 2003 and 2008, 325 patients who were newly diagnosed as HCC with BCLC intermediate stage were considered eligible. Tumor factor and liver function were used for sub-classification. Overall survival (OS) was analyzed using Kaplan-Meier method with a comparison by log-rank test.
Results
A total of 325 patients with intermediate stage HCC were analyzed. Patients with tumor size ≥7 cm, tumor number ≥4 and Child-Pugh class B had the worse OS compared to those with tumor size <7 cm, tumor number <4 and Child-pugh class A, respectively (all P<0.05). These three variables affected the OS independently from multivariate Cox regression analysis (all P<0.05). So, using these three variables, patients were finally sub-classified as those with fulfilling none of three factors (B-a), one of three factors (B-b), two of three factors (B-c) and all of three factors (B-d) with the median OS of 39.2, 20.6, 12.0 and 8.3 months with statistical significances (all P<0.05 between B-a and B-b, between B-b and B-c, and between B-c and B-d), respectively.
Conclusions
Sub-classification of HCC with BCLC intermediate stage may be useful in not only prognostification but also guidance of treatment strategies. (J Liver Cancer 2016;16:17-22)

- Loss of Liver Fatty Acid Binding Protein Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinomas is Associated with a Decreased Recurrence-Free Survival
- Haeryoung Kim, Hyejung Lee, Young Nyun Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2015;15(1):30-35. Published online March 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.15.1.30
- 1,165 Views
- 23 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
Loss of liver fatty acid binding protein (LFABP) expression by immunohistochemistry is a useful marker for the identification of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α (HNF1α)- inactivated hepatocellular adenomas; however, the expression status of LFABP in hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) is still unclear. We aimed to investigate the expression status of LFABP in HCCs and examine the clinicopathological characteristics of LFABP-negative HCCs.
Methods
Immunohistochemical stains LFABP, K19 (mouse monoclonal, Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) and EpCAM (mouse monoclonal, Calbiochem, Darmstadt, Germany) were performed on tissue microarray sections from 188 surgically resected HCCs, and the association between LFABP expression status and the clinicopathological features, survival and “stemness”-related marker expression status were analyzed.
Results
Loss of LFABP expression was noted in 30 (16%) out of 188 HCCs. LFABP-negative HCCs were associated with a decreased recurrence-free survival (LFABP-negative: 17.0 ± 4.84 months [95% confidence interval [CI]: 7.5–26.5 months] versus LFABP-positive: 51.0 ± 8.7 months [95% CI: 34.0–68.0 months]; P=0.004). HCCs with LFABP expression loss were more frequently larger and showed more frequent vascular invasion, although not statistically significant; and an inverse correlation was seen between LFABP expression and K19 expression status (P=0.001).
Conclusions
Loss of LFABP expression is seen in HCCs, and is associated with a decreased recurrence-free survival. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hepatocellular adenomas: recent updates
Haeryoung Kim, Young Nyun Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2021; 55(3): 171. CrossRef
- Hepatocellular adenomas: recent updates

Review Article
- The Issues for Improving Prognosis in Intermediate Stage of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Yang Jae Yoo, Ji Hoon Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2014;14(2):80-88. Published online September 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.14.2.80
- 1,138 Views
- 8 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of major malignant tumor with heterogeneity and poor prognosis. In contrast to other solid malignant tumors, the prognosis of HCC is affected by not only progression of tumor itself but also residual liver function. Therefore, diverse staging systems are developed in HCC and there was no universal consensus for best staging system. However, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) system, which was endorsed by Western expert guidelines, is most commonly used staging system. BCLC system defined intermediate stage as single tumor more than 5cm, 2-3 tumor more than 3cm or ≥ 4 tumor at any size with Child-Pugh A or B and performance status 0-1 and allocated transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) as primary treatment for this stage. Intermediate stage include heterogeneous patients population and inevitably showed diverse prognosis. Among HCC patients, about 20% belonged to intermediate stage and intermediate stage means relatively little progressed stage, fair liver function and performance status. Therefore, improvement of survival of intermediate HCC patients may be a cornerstone leading improvement of survival of overall HCC patients. Hence, the strategy for optimal classification and treatment modality for intermediate HCC patients at pre and post treatment to improve prognosis in this patients will be discussed in this review. (J Liver Cancer 2014;14:80-88)


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter