Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Outcomes of Liver Resection and Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Multinodular BCLC-A Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jiwon Yang, Won-Mook Choi, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Deok-Bog Moon, Dong-Hwan Jung, Jonggi Choi
- Received March 3, 2024 Accepted March 25, 2024 Published online April 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.25 [Accepted]
- 333 Views
- 27 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to compare the outcomes of liver resection (LR) and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with multinodular hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) within the Milan criteria who were not eligible for liver transplantation.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 483 patients with multinodular HCC within the Milan criteria, who underwent either LR or TACE as an initial therapy between 2013 and 2022. The overall survival (OS) in the entire population and recurrence-free survival (RFS) in patients who underwent LR and TACE and achieved a complete response were analyzed. Propensity score (PS) matching analysis was also used for a fair comparison of outcomes between the two groups.
Results
Among the 483 patients, 107 (22.2%) and 376 (77.8%) underwent LR and TACE, respectively. The median size of the largest tumor was 2.0 cm, and 72.3% of the patients had two HCC lesions. The median OS and RFS were significantly longer in the LR group than in the TACE group (p <0.01 for both). In the multivariate analysis, TACE (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.81 and aHR, 2.41) and large tumor size (aHR, 1.43 and aHR, 1.44) were significantly associated with worse OS and RFS, respectively. The PS-matched analysis also demonstrated that the LR group had significantly longer OS and RFS than the TACE group (PS <0.05).
Conclusion
In this study, LR showed better OS and RFS than TACE in patients with multinodular Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A HCC. Therefore, LR can be considered an effective treatment option for these patients.

Review Articles
- Changing etiology and epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: Asia and worldwide
- Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):62-70. Published online March 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.13
- 729 Views
- 59 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
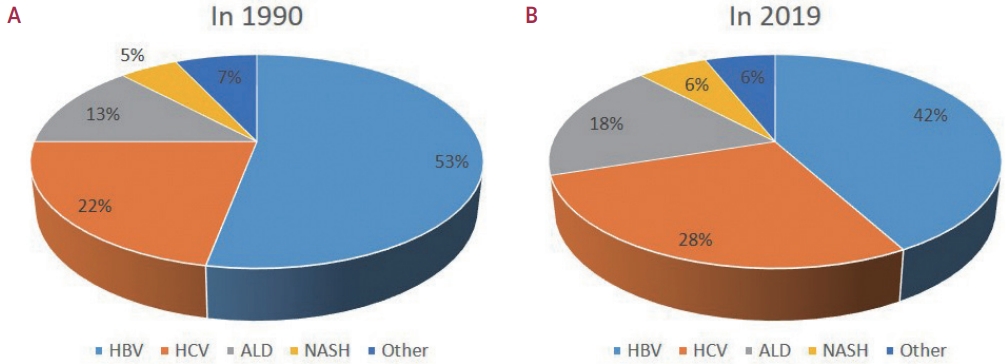
PDF - Approximately 80% of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cases arise in sub-Saharan Africa and Eastern Asia, following a similarly high prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) carriers in these regions. The etiology and epidemiology of HCC have recently changed worldwide. Although HBV infection is the main contributor to HCC development, a slow but continuous decline in HBV infection rates has been reported since 1990. Owing to the widespread use of direct-acting antivirals, the incidence of hepatitis C virus-related HCC has remarkably decreased in Japan and European countries. In Korea, Taiwan, and Singapore, the incidence of HBV-related HCC has significantly decreased owing to vaccination against HBV. Globally, while HBV accounted for more than half of HCCs in 1990, this had decreased to 42% in 2019. In contrast, the proportion of patients with alcoholic- and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) increased from 13% to 18% and from 5% to 6%, respectively. NASH-related HCC has characteristics that differ from those of virus-associated HCC. Compared with other etiologies, patients with NASHassociated HCC are older, have a higher body mass index, and have higher rates of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and cardiovascular disease. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)-associated HCC is also known to develop in the absence of cirrhosis, unlike alcohol-related and autoimmune liver diseases. Because patients with NAFLD usually have diabetes or obesity, surveying this population is challenging. Optimal selection of the target population and surveillance tools among patients with NAFLD needs to be determined.

- Multidisciplinary approach for hepatocellular carcinoma patients: current evidence and future perspectives
- Joo Hyun Oh, Dong Hyun Sinn
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):47-56. Published online March 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.02.27

- 526 Views
- 45 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Management of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is challenging due to the complex relationship between underlying liver disease, tumor burden, and liver function. HCC is also notorious for its high recurrence rate even after curative treatment for early-stage tumor. Liver transplantation can substantially alter patient prognosis, but donor availability varies by each patient which further complicates treatment decision. Recent advancements in HCC treatments have introduced numerous potentially efficacious treatment modalities. However, high level evidence comparing the risks and benefits of these options is limited. In this complex situation, multidisciplinary approach or multidisciplinary team care has been suggested as a valuable strategy to help cope with escalating complexity in HCC management. Multidisciplinary approach involves collaboration among medical and health care professionals from various academic disciplines to provide comprehensive care. Although evidence suggests that multidisciplinary care can enhance outcomes of HCC patients, robust data from randomized controlled trials are currently lacking. Moreover, the implementation of a multidisciplinary approach necessitates increased medical resources compared to conventional cancer care. This review summarizes the current evidence on the role of multidisciplinary approach in HCC management and explores potential future directions.

Original Article
- Comparison of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
- Jeayeon Park, Yun Bin Lee, Yunmi Ko, Youngsu Park, Hyunjae Shin, Moon Haeng Hur, Min Kyung Park, Dae-Won Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Kyung-Hun Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Su Jong Yu, Tae-Yong Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Tae-You Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):81-91. Published online January 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.12.25
- 992 Views
- 133 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
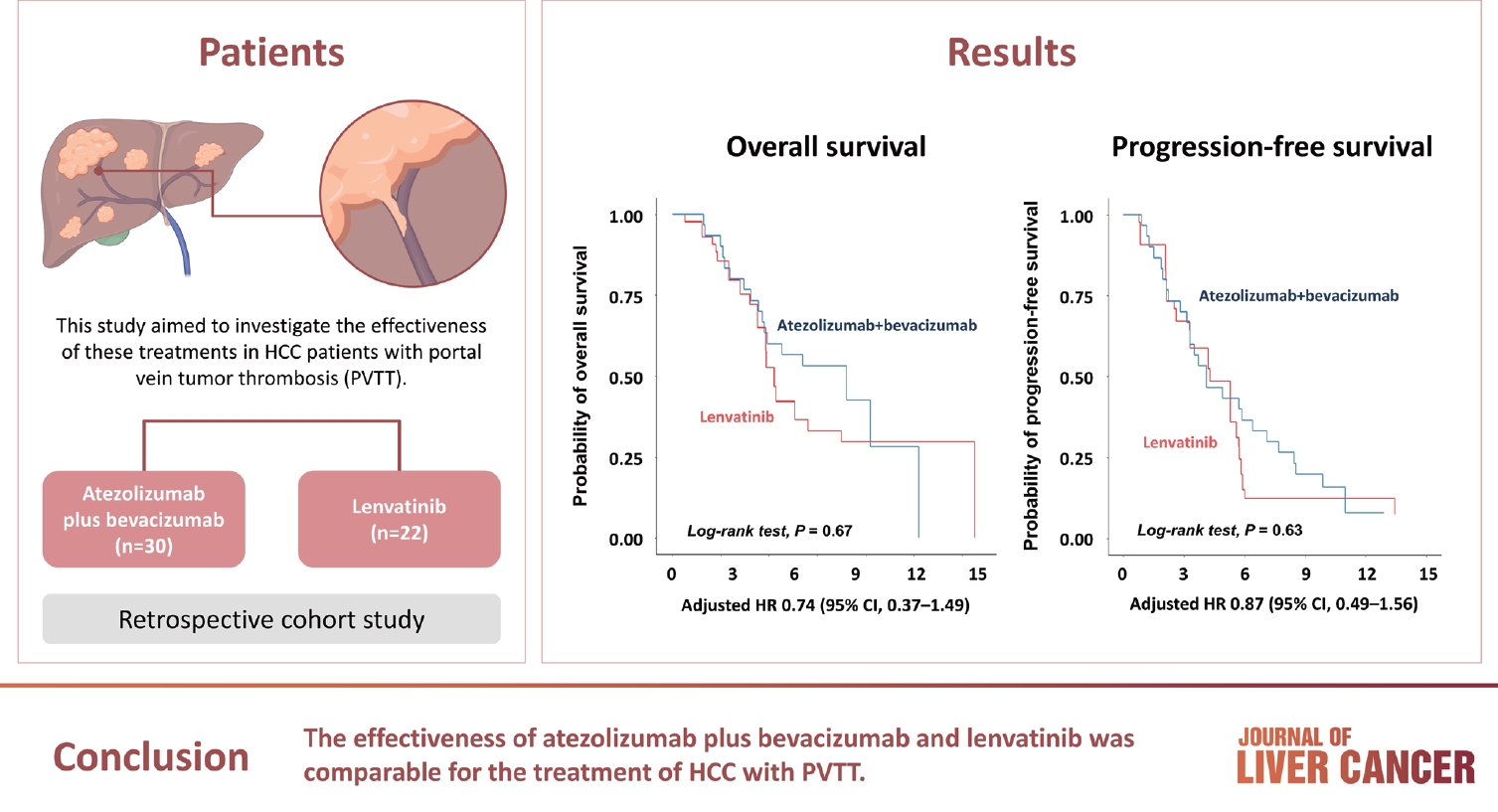
Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib are currently available as first-line therapy for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, comparative efficacy studies are still limited. This study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of these treatments in HCC patients with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT).
Methods
We retrospectively included patients who received either atezolizumab plus bevacizumab or lenvatinib as first-line systemic therapy for HCC with PVTT. Primary endpoint was overall survival (OS), and secondary endpoints included progressionfree survival (PFS) and disease control rate (DCR) determined by response evaluation criteria in solid tumors, version 1.1.
Results
A total of 52 patients were included: 30 received atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and 22 received lenvatinib. The median follow-up duration was 6.4 months (interquartile range, 3.9-9.8). The median OS was 10.8 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 5.7 to not estimated) with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and 5.8 months (95% CI, 4.8 to not estimated) with lenvatinib (P=0.26 by log-rank test). There was no statistically significant difference in OS (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.71; 95% CI, 0.34-1.49; P=0.37). The median PFS was similar (P=0.63 by log-rank test), with 4.1 months (95% CI, 3.3-7.7) for atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and 4.3 months (95% CI, 2.6-5.8) for lenvatinib (aHR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.51-1.69; P=0.80). HRs were similar after inverse probability treatment weighting. The DCRs were 23.3% and 18.2% in patients receiving atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib, respectively (P=0.74).
Conclusion
The effectiveness of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib was comparable for the treatment of HCC with PVTT.

Review Article
- Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: histological diversity and the role of the pathologist
- Mina Komuta
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):17-22. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.12.11
- 761 Views
- 95 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
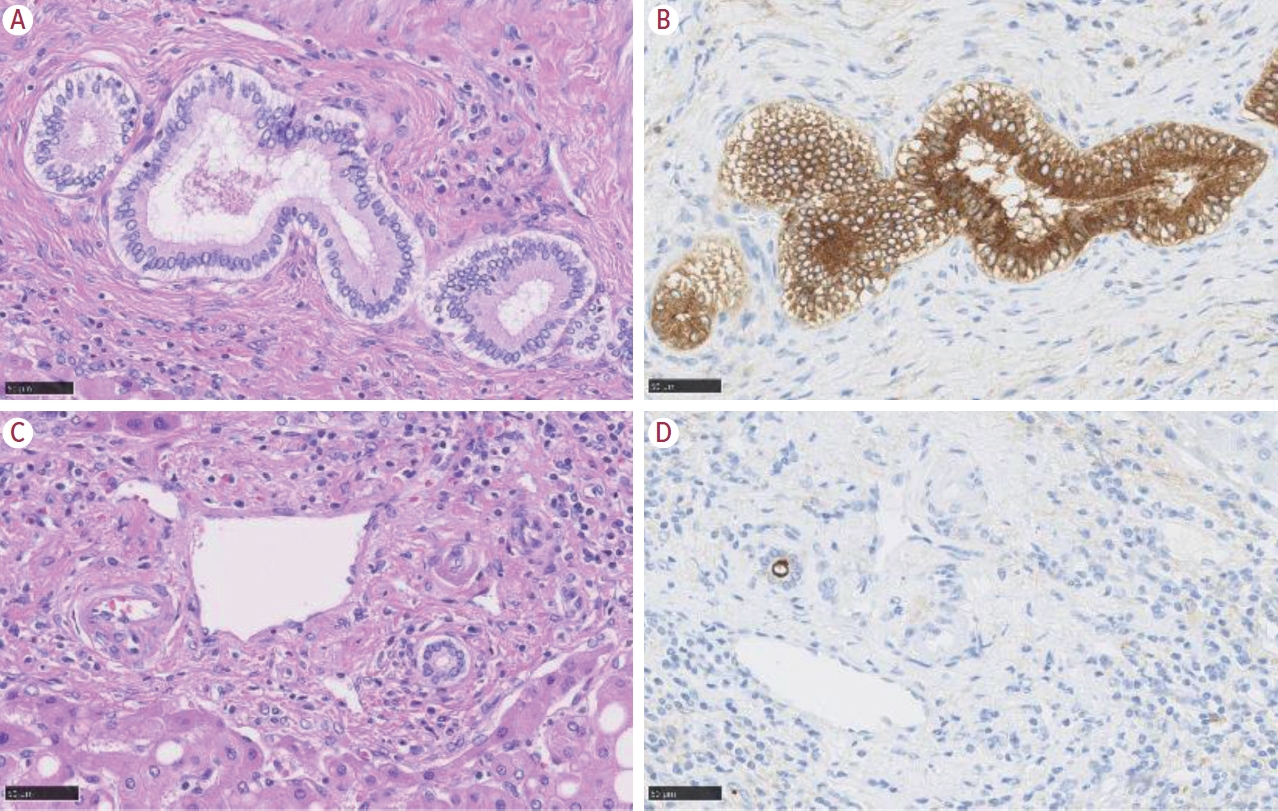
PDF - Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) is one of the primary liver cancers and presents with tumor heterogeneity. About 50% of iCCAs comprise actionable mutations, which completely change patient management. In addition, the precise diagnosis of iCCA, including subtype, has become crucial, and pathologists play an important role in this regard. This review focuses on iCCA heterogeneity; looking at different perspectives to guide diagnosis and optimal treatment choice.

Case Report
- Metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis confirmed on blind liver biopsy
- Hun Kim, Tae Hoon Roh, Jun Seop Lee, Min Seong Kim, Beom Kyung Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):113-117. Published online November 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.11.05
- 825 Views
- 80 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
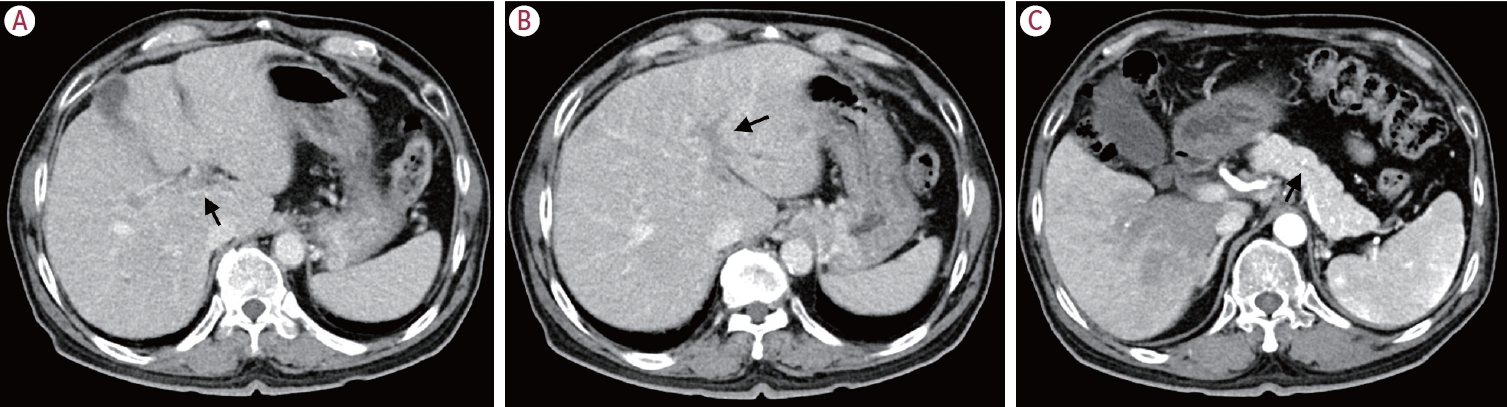
PDF - Portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) is an uncommon condition in which tumor cells expand into the vessels, causing blood clot formation in the portal vein. PVTT is mainly associated with hepatocellular carcinoma, leading to an unfavorable prognosis; however, it can also develop in patients with other cancer types. Herein, we report a case of metastatic renal cell carcinoma diagnosed by a blind liver biopsy in a patient with dynamic computed tomography-confirmed portal vein thrombosis and cholangiopathy. This case illustrates the importance of systematic surveillance with routine laboratory tests and contrast-enhanced imaging studies on patients with cancer to detect potential liver infiltration of metastatic cancer.

Review Article
- Management of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: challenges and strategies for optimal outcomes
- Jae Hyun Yoon, Sung Kyu Choi
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):300-315. Published online September 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.08.27
- 2,164 Views
- 144 Downloads
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
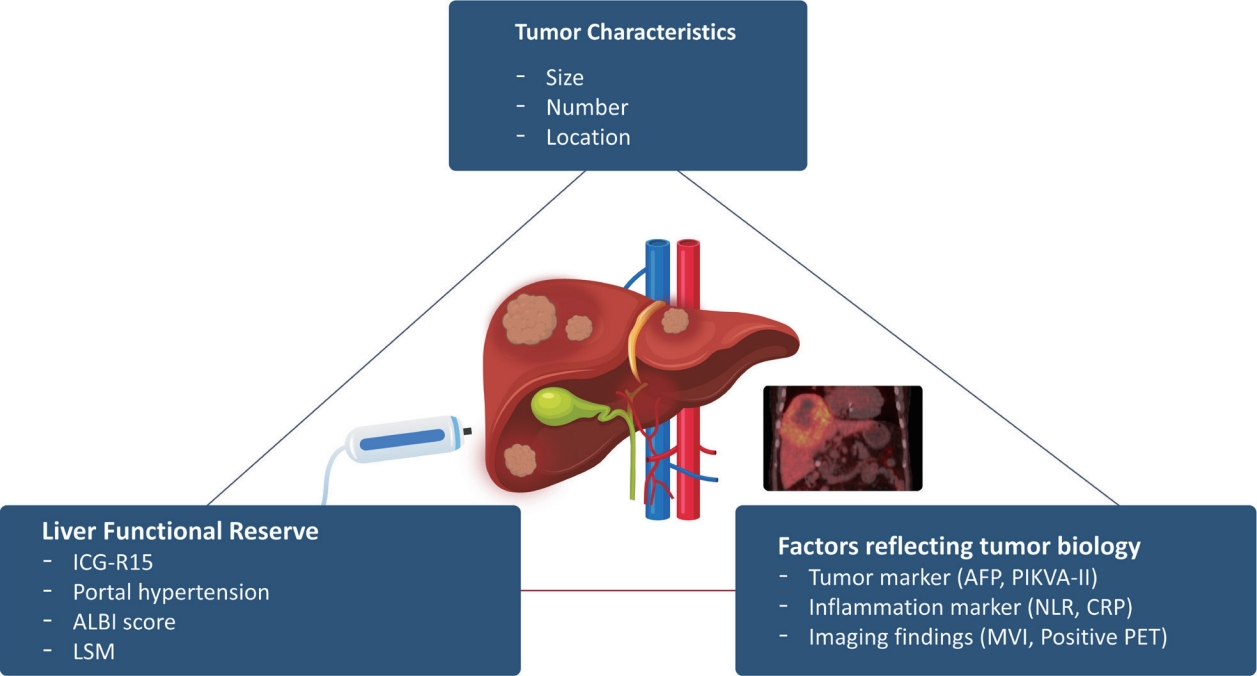
PDF - Although hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is associated with a poor prognosis, management of early-stage HCC is often successful with highly efficacious treatment modalities such as liver transplantation, surgical resection, and radiofrequency ablation. However, unfavorable clinical outcomes have been observed under certain circumstances, even after efficient treatment. Factors that predict unsuitable results after treatment include tumor markers, inflammatory markers, imaging findings reflecting tumor biology, specific outcome indicators for each treatment modality, liver functional reserve, and the technical feasibility of the treatment modalities. Various strategies may overcome these challenges, including the application of reinforced treatment indication criteria with predictive markers reflecting tumor biology, compensation for technical issues with up-to-date technologies, modification of treatment modalities, downstaging with locoregional therapies (such as transarterial chemotherapy or radiotherapy), and recently introduced combination immunotherapies. In this review, we discuss the challenges to achieving optimal outcomes in the management of early-stage HCC and suggest strategies to overcome these obstacles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diosgenin potentiates the anticancer effect of doxorubicin and volasertib via regulating polo-like kinase 1 and triggering apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Eman H. Yousef, Mohamed E. El-Mesery, Maha R. Habeeb, Laila A. Eissa
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef - Radiofrequency for hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 3 cm: potential for applications in daily practice
Ji Hoon Kim, Pil Soo Sung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Efficacy of Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) for Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Moonhyung Lee, Hyun Phil Shin
Medicina.2023; 59(12): 2174. CrossRef
- Diosgenin potentiates the anticancer effect of doxorubicin and volasertib via regulating polo-like kinase 1 and triggering apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells

Case Reports
- Adult hepatoblastoma: making the challenging distinction from hepatocellular carcinoma
- Allison Kaye L. Pagarigan, Paulo Giovanni L. Mendoza
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):219-224. Published online March 13, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.24

- 766 Views
- 48 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatoblastoma is an exceptionally rare malignancy in adults with just over 70 non-pediatric cases reported in literature. Recounted is a case of a 49-year-old female who presented with acute right upper quadrant abdominal pain, elevated serum alpha fetoprotein and a large liver mass on imaging. Hepatectomy was performed under clinical suspicion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Immunomorphologic characteristics of the tumor proved consistent with hepatoblastoma of mixed epithelial and mesenchymal type. Hepatocellular carcinoma remains to be the primary differential diagnosis for adult hepatoblastoma, however, distinguishing between these two neoplasms requires close histomorphologic assessment and immunohistochemical profiling as clinical, radiologic and gross pathologic findings typically overlap. Making this distinction is highly crucial in the timely initiation of surgical and chemotherapeutic interventions for this inherently aggressive and rapidly fatal disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Blastomas of the digestive system in adults: A review
Yu Liu, Tony El Jabbour, Jonathan Somma, Yukihiro Nakanishi, Saverio Ligato, Hwajeong Lee, Zhi-Yan Fu
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2024; 16(4): 1030. CrossRef
- Blastomas of the digestive system in adults: A review

- Parenchymal-sparing hepatectomy for multiple bilobar colorectal liver metastases in a Jehovah’s witness: a case report
- Shehan Ratnayake, Duminda Subasinghe, Vihara Dassanayake, Sivasuriya Sivaganesh
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):202-205. Published online February 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.01.27
- 1,473 Views
- 68 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
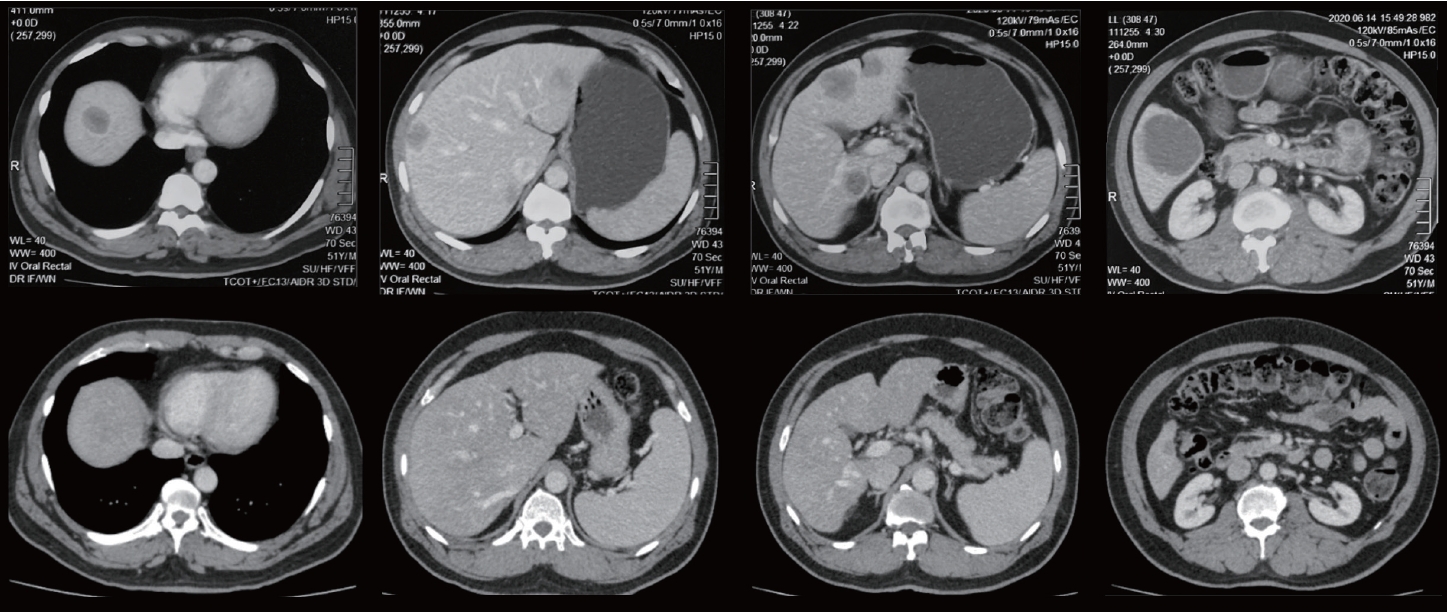
PDF - Parenchymal-sparing hepatectomy (PSH), though technically challenging, is emerging as a choice of treatment for colorectal liver metastases (CRLM). PSH in Jehovah’s witness (JW) patients, for whom transfusion is not an option, involves complex surgical and medicolegal issues. A 52-year-old JW male with synchronous, multiple, bilobar liver metastases from a rectal adenocarcinoma was referred following neoadjuvant chemotherapy. At surgery, 10 metastatic deposits were observed and confirmed by intraoperative ultrasonography. Parenchymal-sparing non-anatomical resections were performed using a cavitron ultrasonic aspirator with the application of intermittent Pringle maneuvres. Histology confirmed multiple CRLMs with tumor-free resection margins. PSH is increasingly employed for CRLMs to preserve residual liver volume and minimize morbidity without compromising oncological outcomes. It is technically challenging, especially in the presence of bilobar, multi-segmental disease. This case illustrates the feasibility of performing complex hepatic surgery in special patient groups by meticulous planning and preparation involving multiple specialties and the patient.

Review Article
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma
- Darine Daher, Karim Seif El Dahan, Amit G. Singal
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):127-142. Published online February 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.12.30
- 3,200 Views
- 168 Downloads
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
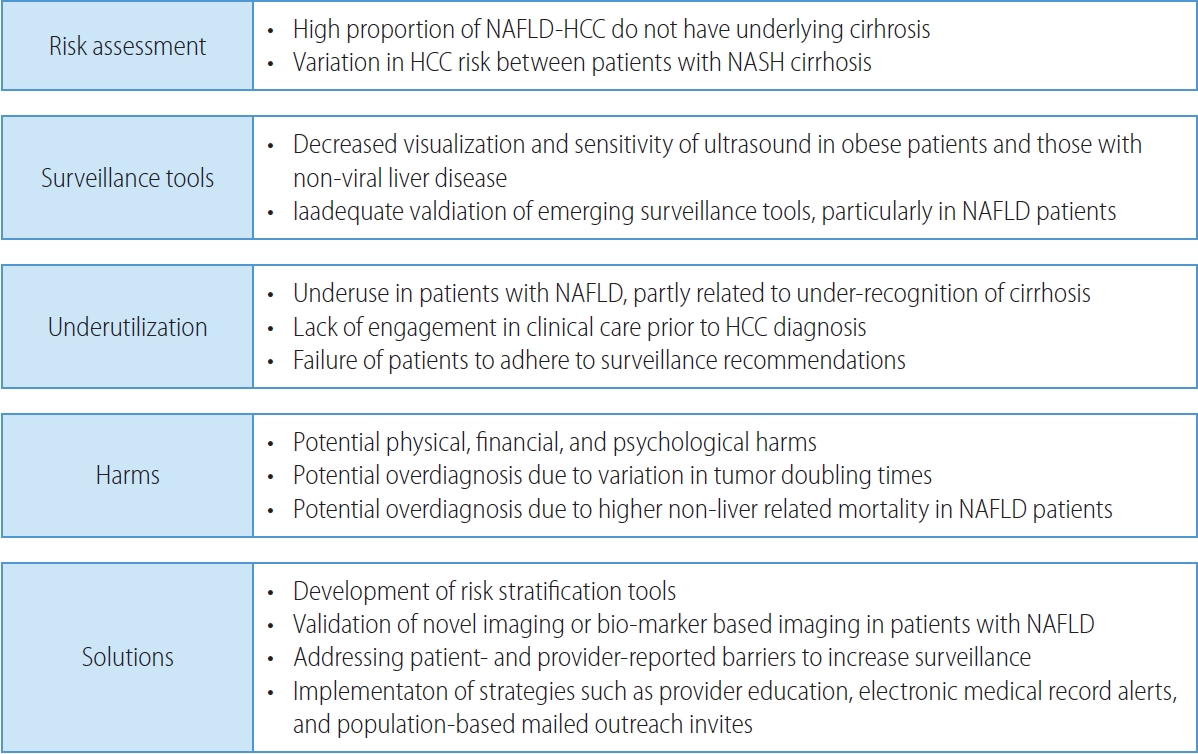
PDF - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), one of the most common causes of liver disease, is an increasingly common cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Several demographic, clinical, and genetic factors contribute to HCC risk in NAFLD patients, which may inform risk stratification scores. Proven efficacious approaches to primary prevention approach in patients with non-viral liver disease remain an area of need. Semi-annual surveillance is associated with improved early tumor detection and reduced HCC-related mortality; however, patients with NAFLD have several challenges to effective surveillance, including under-recognition of at-risk patients, low surveillance utilization in clinical practice, and lower sensitivity of current tools for early-stage HCC detection. Treatment decisions are best made in a multidisciplinary fashion and are informed by several factors including tumor burden, liver dysfunction, performance status, and patient preferences. Although patients with NAFLD often have larger tumor burden and increased comorbidities compared to counterparts, they can achieve similar post-treatment survival with careful patient selection. Therefore, surgical therapies continue to provide a curative treatment option for patients diagnosed at an early stage. Although there has been debate about the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with NAFLD, current data are insufficient to change treatment selection based on liver disease etiology.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Overnutrition and Lipotoxicity: Impaired Efferocytosis and Chronic Inflammation as Precursors to Multifaceted Disease Pathogenesis
Vivek Mann, Alamelu Sundaresan, Shishir Shishodia
Biology.2024; 13(4): 241. CrossRef - Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Steatotic Liver Disease and Its Newly Proposed Subclassification
Byeong Geun Song, Aryoung Kim, Myung Ji Goh, Wonseok Kang, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Dong Hyun Sinn
Liver Cancer.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Smoking Increases the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Man Young Park, Eun Ju Cho, Su Jong Yu, Sang Gyune Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Young Seok Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3336. CrossRef - Reply: Validation of MELD 3.0 scoring system in East Asian patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim
Liver Transplantation.2023; 29(11): E38. CrossRef - Unraveling the Janus-Faced Role of Autophagy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Implications for Therapeutic Interventions
Thi Ha Nguyen, Tuan Minh Nguyen, Dinh Thi Minh Ngoc, Taesik You, Mi Kyung Park, Chang Hoon Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(22): 16255. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter, Propensity Score Study
Ji Kim, Hee-Chul Nam, Chang-Wook Kim, Hee Cho, Jae-Sung Yoo, Ji Han, Jeong Jang, Jong Choi, Seung Yoon, Hyun Yang, Si Bae, Suho Kim, Jung Oh, Ho Chun, Chang Jeon, Jaegyoon Ahn, Pil Sung
Cancers.2023; 15(17): 4233. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Overnutrition and Lipotoxicity: Impaired Efferocytosis and Chronic Inflammation as Precursors to Multifaceted Disease Pathogenesis

Original Article
- Indications for open hepatectomy in the era of laparoscopic liver resection: a high volume single institutional study
- Sung Jun Jo, Jinsoo Rhu, Jong Man Kim, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):146-157. Published online September 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.08.22
- 2,303 Views
- 60 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
Since the introduction of laparoscopy for liver resection in the 1990s, the performance of laparoscopic liver resection (LLR) has been steadily increasing. However, there is currently no data on the extent to which laparoscopy is used for liver resection. Herein, we investigated the extent to which laparoscopy is performed in liver resection and sought to determine whether surgeons prefer laparoscopy or laparotomy in the posterosuperior (PS) segment.
Methods
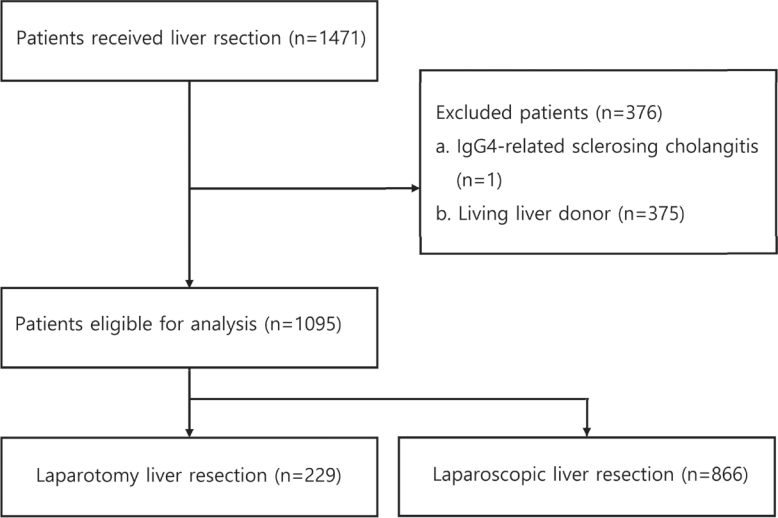
For this retrospective observational study, we enrolled patients who had undergone liver resection at the Samsung Medical Center between January 2020 and December 2021. The proportion of LLR in liver resection was calculated, and the incidence and causes of open conversion were investigated.
Results
A total of 1,095 patients were included in this study. LLR accounted for 79% of the total liver resections. The percentage of previous hepatectomy (16.2% vs. 5.9%, P<0.001) and maximum tumor size (median 4.8 vs. 2.8, P<0.001) were higher in the open liver resection (OLR) group. Subgroup analysis revealed that tumor size (median 6.3 vs. 2.9, P<0.001) and surgical extent (P<0.001) in the OLR group were larger than those in the LLR group. The most common cause of open conversion (OC) was adhesion (57%), and all OC patients had tumors in the PS.
Conclusions
We investigated the recent preference of practical surgeons in liver resection, and found that surgeons preferred OLR to LLR when treating a large tumor located in the PS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sujin Koo, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Seungeun Ryoo, Jungeun Park, Dong Ah Park
Current Oncology.2024; 31(1): 324. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis of blood transfusion rates during liver resection by country
Seonju Kim, Yun Kyung Jung, Kyeong Geun Lee, Kyeong Sik Kim, Hanjun Kim, Dongho Choi, Sumi Lee, Boyoung Park
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2023; 105(6): 404. CrossRef
- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

Case Report
- Hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosed in a patient who had Fontan operation 30 years ago: a case report
- Moon Haeng Hur, Haeryoung Kim, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):188-193. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.08.17
- 2,262 Views
- 61 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
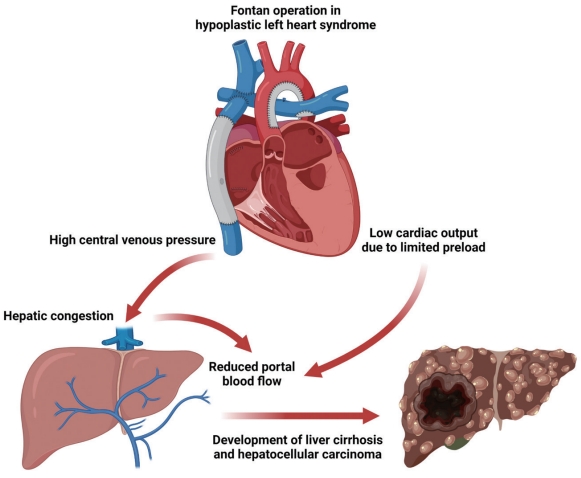
PDF - The Fontan operation is performed in patients with a single ventricle. As the systemic venous return is directly connected to the pulmonary circulation during this procedure, chronic hepatic congestion is induced, leading to Fontan-associated liver disease (FALD) including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In this report, we present a case of HCC diagnosed in a patient who underwent the Fontan operation 30 years ago. The patient underwent regular surveillance for FALD, which revealed a 4 cm-sized hepatic mass with elevated serum alpha-fetoprotein. After surgical treatment, there was no evidence of HCC recurrence during 3 years of follow-up. As the risk of HCC and Fontan-associated liver cirrhosis increases with the duration elapsed since the operation, regular surveillance should be emphasized. Serial follow-up of serum alpha-fetoprotein levels and abdominal imaging are necessary to achieve early and accurate diagnosis of HCC in post-Fontan patients.

Original Article
- The effects of immune checkpoint modulators on the clinical course of patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma
- Jihyun An, Hyo Jeong Kang, Eunsil Yu, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):40-50. Published online March 17, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.06

- 3,341 Views
- 112 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
Immune checkpoint proteins regulating T-cell mediated anti-tumor immunity have been reported to affect clinical outcomes in multiple malignancies. This study aimed to investigate the prognostic effect of histological expression of immune checkpoint proteins in patients with resected hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
A total of 221 patients with HCC who underwent curative resection were included. Expression of programmed-cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) in tumor cells (tPD-L1) and tumor infiltrating mononuclear cells (TIMCs) (iPD-L1), programmed-cell death-1 in TIMCs (iPD-1), and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 in TIMCs (iCTLA-4) were measured immunohistochemically.
Results
Histo-positivity for iCTLA-4, iPD-1, iPD-L1, and tPD-L1 was 32.1%, 42.5%, 35.3%, and 14.9%, respectively. Multivariate logistic analyses revealed that male sex and tumor >5 cm were variables related to iCTLA-4 positivity (odds ratio [OR], 0.46 and 1.94, respectively; P<0.05). Poor differentiation was related to PD-L1 expression in both tumor cells and TIMCs (OR, 2.88 and 3.46, respectively; P<0.05). Microvascular invasion was significantly associated only with iPD-L1 (OR, 2.24; P<0.05). In time-dependent outcome analyses, expression of immune checkpoint proteins in TIMCs (i.e., iCTLA-4, iPD-1, and iPD-L1) was significantly related to longer overall survival and non-cancer-related survival (all P<0.05), but not to time-to-recurrence or cancer-specific deaths. Concurrent activation of the PD-1:PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways predicted improved outcomes in terms of overall survival and non-cancer related survival (P=0.06 and P=0.03, respectively).
Conclusions
Immune checkpoint proteins upregulated in TIMCs in HCC tissues have individual and additive effects in prolonging the survival of patients, specifically in terms of survival not related to cancer recurrence.

Case Report
- Curative liver transplantation after lung resection for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with lung metastasis and inferior vena cava tumor thrombosis: a case report
- Dong Jin Joo, Do Young Kim, Jinsil Seong, Hyun Jeong Kim, Jae Geun Lee, Dai Hoon Han, Gi Hong Choi, Myoung Soo Kim, Jin Sub Choi, Soon Il Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):181-186. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.08

- 3,616 Views
- 91 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with distant metastasis is an absolute contraindication for liver transplantation (LT). However, it is still unclear whether LT is feasible or acceptable in such patients, albeit after being treated with a multidisciplinary approach and after any metastatic lesion is ruled out. We report one such successful treatment with living donor LT (LDLT) after completely controlling far-advanced HCC with inferior vena cava tumor thrombosis and multiple lung metastases. The patient has been doing well without HCC recurrence for eight years since LDLT. The current patient could be an anecdotal case, but provides a case for expanding LDLT indications in the context of advanced HCC and suchlike.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inferior Vena Cava Thrombectomy and Stenting as Bridge to Liver Transplantation After Radiotherapy-Induced Thrombosis
Raphael PH Meier, Shani Kamberi, Josue Alvarez-Casas, Barton F. Lane, Chandra S. Bhati, Saad Malik, William Twaddell, Kirti Shetty, Adam Fang, Hyun S. Kim, Daniel G. Maluf
Progress in Transplantation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inferior Vena Cava Thrombectomy and Stenting as Bridge to Liver Transplantation After Radiotherapy-Induced Thrombosis

Review Article
- Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
- Sang Jin Kim, Jong Man Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):105-112. Published online September 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.03.17

- 5,000 Views
- 221 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traditionally, liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis is not recommended. However, with recent developments in locoregional therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma, more aggressive treatments have been attempted for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Recently, various studies on locoregional therapies for downstaging followed by living donor liver transplantation reported inspiring overall survival and recurrence-free survival of patients. These downstaging procedures included three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy, trans-arterial chemoembolization, stereotactic body radiation therapy, trans-arterial radioembolization, hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy and combinations of these therapies. Selection of the optimal downstaging protocol should depend on tumor location, biology and background liver status. The risk factors affecting outcome include pre-downstaging alpha-fetoprotein values, delta alpha-fetoprotein values, disappearance of portal vein tumor thrombosis on imaging and meeting the Milan criteria or not after downstaging. For hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis, downstaging procedure with liver transplantation in mind would be helpful. If the reaction of the downstaged tumor is good, liver transplantation may be performed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis confirmed on blind liver biopsy
Hun Kim, Tae Hoon Roh, Jun Seop Lee, Min Seong Kim, Beom Kyung Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 113. CrossRef - Refining MRI-based criteria for portal vein invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: improving sensitivity beyond portal vein tumor thrombosis
Jeongju Kim, Woo Kyoung Jeong, Jong Man Kim, Sang Yun Ha, Kyunga Kim
Abdominal Radiology.2023; 49(2): 437. CrossRef - Prediction models of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver transplantation: A comprehensive review
Sang Jin Kim, Jong Man Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 739. CrossRef
- Metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis confirmed on blind liver biopsy


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter