Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Complications of immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
- Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):9-16. Published online November 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.11.21
- 2,115 Views
- 122 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
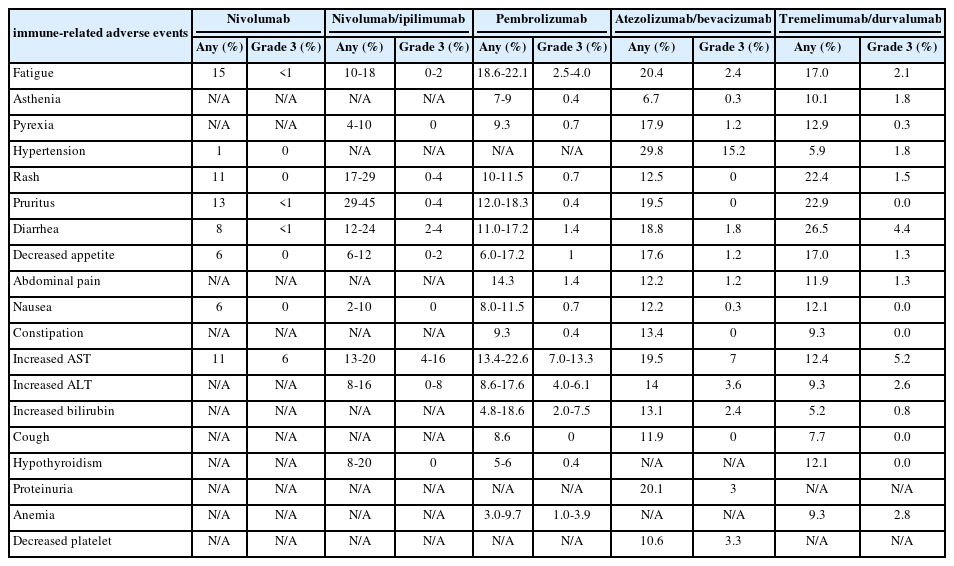
PDF - Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are highly effective in cancer treatment. However, the risks associated with the treatment must be carefully balanced against the therapeutic benefits. Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) are generally unpredictable and may persist over an extended period. In this review, we analyzed common irAEs reported in highly cited original articles and systematic reviews. The prevalent adverse reactions include fatigue, pyrexia, rash, pruritus, diarrhea, decreased appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, constipation, hepatitis, and hypothyroidism. Therefore, it is crucial to conduct evaluations not only of gastrointestinal organs but also of cardiac, neurologic, endocrine (including the frequently affected thyroid), and ophthalmic systems before commencing ICIs. This review further explores commonly reported types of irAEs, specific irAEs associated with each ICI agent, rare yet potentially fatal irAEs, and available treatment options for managing them.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intrahepatic IgA complex induces polarization of cancer-associated fibroblasts to matrix phenotypes in the tumor microenvironment of HCC
Jong Geun Park, Pu Reun Roh, Min Woo Kang, Sung Woo Cho, Suhyun Hwangbo, Hae Deok Jung, Hyun Uk Kim, Ji Hoon Kim, Jae-Sung Yoo, Ji Won Han, Jeong Won Jang, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Young Kyoung You, Ho Joong Choi, Jae Yong Ryu, Pil Soo Sung
Hepatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Bleeding in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Young-Gi Song, Kyeong-Min Yeom, Eun Ae Jung, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Liver Cancer.2024; : 1. CrossRef
- Intrahepatic IgA complex induces polarization of cancer-associated fibroblasts to matrix phenotypes in the tumor microenvironment of HCC

Original Articles
- Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: a large-scale multicenter study
- Sun Hong Yoo, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Han-Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim, Do Seon Song, Seong Hee Kang, Moon Young Kim, Young-Hwan Ahn, Jieun Han, Young Seok Kim, Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, Jeong-Ju Yoo
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):189-201. Published online March 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.03.11
- 2,005 Views
- 71 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
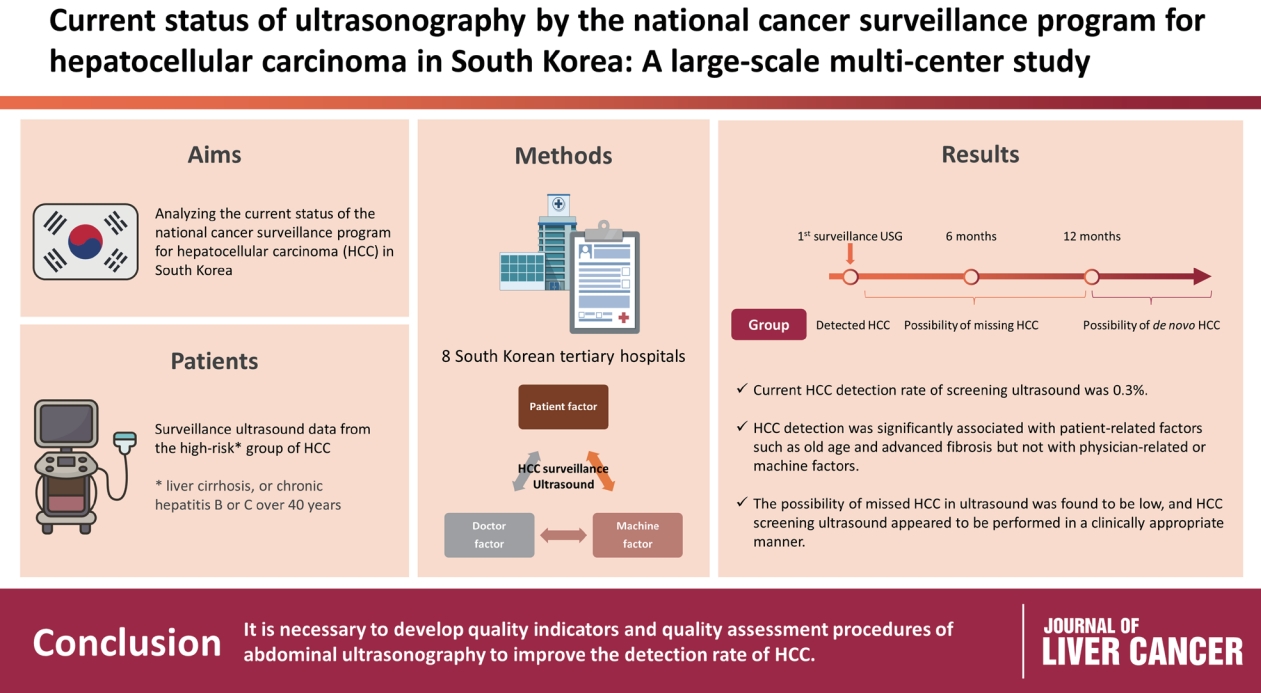
Abdominal ultrasonography (USG) is recommended as a surveillance test for high-risk groups for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study aimed to analyze the current status of the national cancer surveillance program for HCC in South Korea and investigate the effects of patient-, physician-, and machine-related factors on HCC detection sensitivity.
Methods
This multicenter retrospective cohort study collected surveillance USG data from the high-risk group for HCC (liver cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis B or C >40 years of age) at eight South Korean tertiary hospitals in 2017.
Results
In 2017, 45 experienced hepatologists or radiologists performed 8,512 USG examinations. The physicians had a mean 15.0±8.3 years of experience; more hepatologists (61.4%) than radiologists (38.6%) participated. Each USG scan took a mean 12.2±3.4 minutes. The HCC detection rate by surveillance USG was 0.3% (n=23). Over 27 months of follow-up, an additional 135 patients (0.7%) developed new HCC. The patients were classified into three groups based on timing of HCC diagnosis since the 1st surveillance USG, and no significant intergroup difference in HCC characteristics was noted. HCC detection was significantly associated with patient-related factors, such as old age and advanced fibrosis, but not with physician- or machine-related factors.
Conclusions
This is the first study of the current status of USG as a surveillance method for HCC at tertiary hospitals in South Korea. It is necessary to develop quality indicators and quality assessment procedures for USG to improve the detection rate of HCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis
Log Young Kim, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Young Chang, Hoongil Jo, Young Youn Cho, Sangheun Lee, Dong Hyeon Lee, Jae Young Jang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term HBsAg Titer Kinetics with Entecavir/Tenofovir: Implications for Predicting Functional Cure and Low Levels
Soon Kyu Lee, Soon Woo Nam, Jeong Won Jang, Jung Hyun Kwon
Diagnostics.2024; 14(5): 495. CrossRef
- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis

- The diagnostic value of circulating tumor DNA in hepatitis B virus induced hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, Hyuksoo Eun, Young‑Sun Lee, Do Seon Song, Su Jong Yu, Sae Hwan Lee, Won Kim, Hyun Woong Lee, Sang Gyune Kim, Seongho Ryu, Suyeon Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):167-177. Published online September 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.09.19
- 2,926 Views
- 83 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
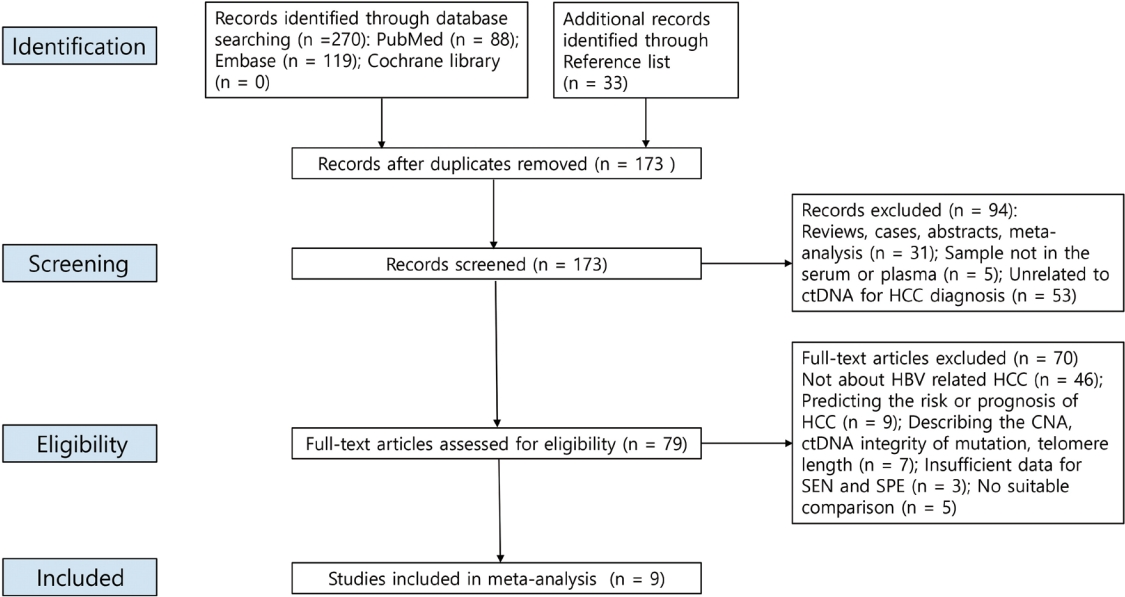
New biomarkers are urgently needed to aid in the diagnosis of early stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We performed a meta-analysis on the diagnostic utility of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) levels in patients with hepatitis B virus-induced HCC.
Methods
We retrieved relevant articles from PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library up to February 8, 2022. Two subgroups were defined; one subset of studies analyzed the ctDNA methylation status, and the other subset combined tumor markers and ctDNA assays. Pooled sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and area under the summary receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) were analyzed.
Results
Nine articles including 2,161 participants were included. The overall SEN and SPE were 0.705 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.629-0.771) and 0.833 (95% CI, 0.769-0.882), respectively. The DOR, PLR, and NLR were 11.759 (95% CI, 7.982-17.322), 4.285 (95% CI, 3.098- 5.925), and 0.336 (0.301-0.366), respectively. The ctDNA assay subset exhibited an AUC of 0.835. The AUC of the combined tumor marker and ctDNA assay was 0.848, with an SEN of 0.761 (95% CI, 0.659-0.839) and an SPE of 0.828 (95% CI, 0.692-0.911).
Conclusions
Circulating tumor DNA has promising diagnostic potential for HCC. It can serve as an auxiliary tool for HCC screening and detection, especially when combined with tumor markers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 16S rRNA Next-Generation Sequencing May Not Be Useful for Examining Suspected Cases of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
Chan Jin Yang, Ju Sun Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Keun Woo Park, Jina Yun, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(2): 289. CrossRef - Methylated circulating tumor DNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive analysis of biomarker potential and clinical implications
Qian Zhu, Jiaqi Xie, Wuxuan Mei, Changchun Zeng
Cancer Treatment Reviews.2024; 128: 102763. CrossRef
- 16S rRNA Next-Generation Sequencing May Not Be Useful for Examining Suspected Cases of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis

Case Reports
- Rare Case of Pyogenic Brain Abscess after Transarterial Chemoembolization in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Case Report and Literature Review
- Jun-Ho Myeong, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):81-86. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.81

- 3,046 Views
- 70 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a useful treatment option for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). TACE can particularly be used as a treatment for localized HCC, where surgical resection is impossible due to decreased liver function. However, TACE is associated with several complications, including vascular complications, liver failure, non-target embolization, infection, and death. The main risk factor for complications after TACE is decreased liver function. There have been only few reports of brain abscesses after TACE that are difficult to be distinguished from hepatic encephalopathy. Here, we report a rare case of brain abscess caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae that occurred after TACE.

- Early Experience of Oncolytic Virus Injection Combined with Sorafenib in a Patient with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Portal Vein Thrombosis
- Hyun Ho Jo, Seong Joon Chun, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Min Hee Lee, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):177-182. Published online September 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.177

- 3,632 Views
- 72 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - JX-594 is a modified oncolytic poxvirus designed to selectively replicate in and destroy cancer cells. In a pilot study, JX-594 injection followed by sorafenib was well-tolerated in three patients and associated with objective tumor responses. In this study, we report a case in which a patient with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein thrombosis was treated with a combination of JX-594 and sorafenib.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent progress in combination therapy of oncolytic vaccinia virus
Seyedeh Nasim Mirbahari, Miles Da Silva, Abril Ixchel Muñoz Zúñiga, Nika Kooshki Zamani, Gabriel St-Laurent, Mehdi Totonchi, Taha Azad
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Recent progress in combination therapy of oncolytic vaccinia virus

- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis Treated by Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy
- Jin Yong Lee, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Seong Joon Chun, Sun Hyun Bae, Jae Myeong Lee, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):78-83. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.78
- 5,079 Views
- 99 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
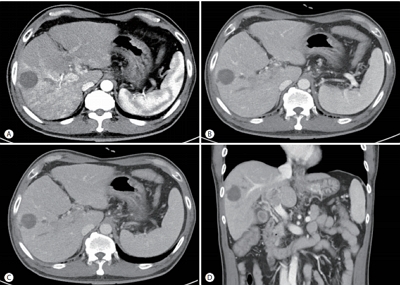
PDF - Sorafenib is the standard treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein thrombosis (PVT). Additionally, hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy has been used as a treatment option for advanced HCC. Here, we report a case of sustained partial response in a patient with advanced HCC with PVT after hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy and radiation therapy.

Review Article
- Clinical Application of Liver Stiffness Measurement for Assessing the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jeong-Ju Yoo, Eun-Ae Jung, Sang Gyune Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(1):12-18. Published online March 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.1.12

- 4,382 Views
- 101 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The most significant risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the presence of cirrhosis or advanced fibrosis of the liver. Liver biopsy was traditionally considered the gold standard for assessing the liver fibrosis burden. Recently, non-invasive methods, particularly transient elastography (TE), have proven effective at measuring fibrosis and determining cirrhosis. Clinical application of TE ranges from measuring fibrosis to predicting long-term prognosis and treatment response. Here, we focus on recent studies on the prognostic value of TE for predicting HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma
Byeong Geun Song, Sung Chul Choi, Myung Ji Goh, Wonseok Kang, Dong Hyun Sinn, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Seung Woon Paik
JHEP Reports.2023; : 100810. CrossRef
- Metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma

Case Reports
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Pulmonary Metastasis Who Showed Complete Response by Cytotoxic Chemotherapy after Sorafenib Failure
- Hwa-Sun Park, Jae Young Jang, Min Young Baek, Yong Kwon Kim, Hyun Jin Youn, Su Young Back, Soung Won Jeong, Sae Hwan Lee, Sang Gyune Kim, Sang Woo Cha, Young Seok Kim, Young Deok Cho, Hong Soo Kim, Boo Sung Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):72-76. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.72
- 2,224 Views
- 26 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the 2nd most common cause of cancer related death in Korea and well-known malignancy with poor prognosis. Sorafenib is the first-line molecular targeted agent in patients with extra-hepatic spread of HCC. However, complete response is extremely rare in patients treated with sorafenib and the disease control rate is only 43%. We report a 53-year-old man with advanced HCC with pulmonary metastasis who showed complete response by cytotoxic chemotherapy with doxorubicin and cisplatin with relatively tolerable adverse effects after failure of treatment with sorafenib.

- A Case of Management for Early Recurrence after Hepatic Resection for the Treatment of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Kyung Woo Park, Young Seok Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, Hong Soo Kim, Sae Hwan Lee, Boo Sung Kim, Jun Cheol Jeong, Min Hee Lee, Jae Myeong Lee, Hee Kyung Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2015;15(2):122-125. Published online September 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.15.2.122
- 1,180 Views
- 8 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - For a small hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), liver resection shows most favorable outcome in
case
which liver transplantation is not available, although it has also substantial recurrence rate. Here, we report a case of recurred HCC with multiple intrahepatic metastasis at 5 months after surgical resection for small HCC was done. A 55-year-old man with chronic HBV infection received subsegmentectomy for HCC less than 2 cm. A follow-up computed tomography (CT) at 5 months from operation revealed that there were multiple enhancing nodules in entire remnant liver. Intra-arterial injections of adriamycin mixed lipiodol and gelfoam particles were instituted through hepatic artery. We assume that poorly differentiated cellular feature would be attributable to this kind of very early and aggressive recurrence of HCC. (J Liver Cancer 2015;15:122-125)

Original Articles
- Follow-up of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Transarterial Chemoembolization; The Concordance of Contrast Enhanced Ultrasonography and Lipiodol CT
- Gene Hyun Bok, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, Sae Hwan Lee, Sang Gyune Kim, Sang-Woo Cha, Young Seok Kim, Young Deok Cho, Hong Soo Kim, Boo Sung Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2014;14(2):115-119. Published online September 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.14.2.115
- 955 Views
- 4 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
The aim of this study is to evaluate the concordance of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) and lipiodol computed tomography (L-CT) for the assessment of viable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after transarterial chemoembolization (TACE).
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the post-TACE CEUS and L-CT images of 65 consecutive HCCs in 41 patients to assess the presence of viable tumor tissue. Forty-seven HCCs in 31 patients that underwent post-TACE L-CT within 4 weeks of the CEUS examination were included. The degree of concordance between CEUS and L-CT and factors related to concordance were analyzed.
Results
The overall concordance of CEUS and LDCT was 78.7% (37/47). The concordance with L-CT for viable tumor and non-viable tumor tissue on CEUS was 95.2%, and 65.4% respectively (P<0.013). Diffuse tumors had a tendency for non-concordance (P=0.066). Although 3 of 4 lesions located in the hepatic dome were non-concordant, the sample size was too small to establish significance. The mean tumor size for concordant and non-concordant tumors was 2.9 and 3.0 cm, with no significant difference.
Conclusions
Although the concordance of CEUS and L-CT for viable tumor tissue was high, the concordance for non-viable tumor tissue was relatively low. Prospective studies using angiography as a gold standard should be performed in the future. (J Liver Cancer 2014;14:115-119)

- The Comparison of Overall Survival between Child C with Early Stage HCC and Child A with Advanced Stage HCC
- Eui Ju Park, Jae Young Jang, Soung Won Jeong, Jin Woo Choo, Jin Nyoung Kim, Soon Ha Kwon, Byoung Moo Lee, Sae Hwan Lee, Sang Gyune Kim, Sang-Woo Cha, Young Seok Kim, Young Deok Cho, Hong Soo Kim, Boo Sung Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2013;13(2):136-144. Published online September 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.13.2.136
- 1,029 Views
- 5 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
The prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is affected by stage as well as liver function. We analyzed the survival outcome of early stage HCC in Child class C patients and advanced HCC in Child class A patients.
Methods
Among 453 HCC patients with good performance status, Group A included 33 consecutive Child class C patients with early stage (I, II) HCC, and Group B included 45 consecutive Child class A patients with advanced stage (III, IV) HCC. We investigated the clinical characteristics, cirrhotic complications, and prognostic factors related with survival in each group, and compared overall survival between two groups.
Results
Age, prothrombin time, total bilirubin and Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) scores were significantly higher in Group A. Male sex, platelet count, albumin, sodium (Na), hepatitis B virus, alpha fetoprotein (AFP) and portal vein thrombosis were significantly higher in Group B. Complications of cirrhosis such as variceal bleeding, ascites, and hepatic encephalopathy were increased in Group A (P<0.05). Patients with an elevated AFP (>400 ng/mL) tended to exhibit poor survival as it increased in Group A (P=0.084). MELD scores>15 (Hazard ratio[HR] 17.84, 95% confidence interval [CI] 3.70-85.93, P<0.001), stage IV (HR:3.27, 95% CI 1.10-9.75, P=0.033), and absence of HCC treatment (HR: 3.70, 95% CI 1.06-12.50, P=0.040) were independent poor prognostic factors in Group B. Median overall survival was 24.6 months (95% CI 10.6-38.4) for Group A and 13.5 months (95% CI 4.6-22.3) for Group B (P=0.278). In the HCC treatment group, there were no significant differences of median overall survival between Group A and Group B, respectively (27.1 vs. 15.7 months, P=0.338). In patients with conservative treatment, Group A and Group B had a significantly different median overall survival of 13.6 and 2.5 months, respectively (P=0.012). In patients of Group B, median overall survival was significantly higher in patients who received treatment of HCC compared to those who did not, respectively (15.7 vs. 2.5 months, P<0.001).
Conclusions
Overall median survival was not different between both groups. However, in Child class A patients with advanced stage HCCs, the cumulative median survival was higher in patients who received treatment of HCC compared to those who did not. Therefore, advanced stage HCC patients with good liver function should be considered for HCC treatments.

- Occurrence Rates of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Adefovir-rescue Therapy for Lamivudine-Resistant Chronic Hepatitis B
- Jihyun Kim, Sae Hwan Lee, Kanghyug Choi, Yun Nah Lee, Soung won Jeong, Sang Gyune Kim, Jae Young Jang, Young Seok Kim, Hong Soo Kim, Boo Sung Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2013;13(2):130-135. Published online September 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.13.2.130
- 1,131 Views
- 5 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
Suboptimal virological response to adefovir (ADV) rescue therapy was commonly experienced in patient with lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B. The aim of this study is to compare occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) of patients with adefovir rescue therapy to naïve patients with entecavir.
Methods
Electronic medical records of 156 patients with lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B who treated with ADV and of 186 naïve-patients who received entecavir 0.5 mg, as control group, were reviewed retrospectively. Study subjects were matched using estimated propensity score and 107 matched subjects in each group were analyzed. Cumulative occurrence of HCC was evaluated during antiviral therapy and the association between clinical variables and development of HCC were analyzed using Kaplan-Meyer curve and risk factor for HCC was evaluated with Cox-proportional hazard model.
Results
Age, gender, Child-Pugh score, underlying cirrhosis, HBeAg, and HBV DNA level were not different in both groups, except treatment duration with ADV or entecavir (mean 52.6±17.5 vs 46.7±11.4 months, P=0.004). Cumulative virological response rates were 16% and 42% in patient with ADV rescue therapy and 68% and 85% in naïve-patients received entecavir at 1 and 3 years (P<0.001), respectively. HCC were diagnosed in 6 of 107 patients with lamivudine-resistance and 9 of 107 naïve-patients during follow-period and cumulative occurrence rates of HCC was not different between both group (P=0.308). Cumulative occurrence rates of HCC in total 214 subjects were 2.3%, 4.8%, and 9.6% at 1, 3, and 5 years, respectively. Age, underlying cirrhosis, and baseline HBV DNA level were associated with the occurrence of HCC, however gender, HBeAg status, ADV rescue therapy, and cumulative virological response were not correlated in univariate analysis. In multivariate analysis, age (P=0.008) and underlying cirrhosis (P=0.002) were independent risk factors for occurrence of HCC.
Conclusions
Long-term ADV rescue therapy in patients with lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B did not increase the occurrence rates of HCC.

Case Reports
- A Case of Good Responsed Bile Duct Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma on Cyberknife Therapy
- Dae Han Choi, Jae Young Jang, Soung Won Jeong, Sae Hwan Lee, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim, Hong Soo Kim, Boo Sung Kim, A ram Jang
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2013;13(1):70-73. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.13.1.70
- 1,071 Views
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the common tumor worldwide and recorded as third most common cause of cancer-related deaths. Invasion of the portal and hepatic veins by HCC is common. But intrabiliary invasion is rare. Radiotherapy (RT) is considered appropriate for unresectable, locally advanced HCC without extrahepatic metastasis. With the conventional RT, it is not possible to deliver a high radiation dose to a treatment volume in a short time and narrow lesion. Recent technological developments in radiation therapy, such as stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), make it possible to deliver a substantial dose of radiation to the tumor and avoid radiosensitive normal liver in the vincinity. We report a patient who were treated by cyberknife therapy for bile duct invasion of progressing HCC despite of treatment.

- A Case of Refractory Hepatocellular Carcinoma Presented with Brain Metastasis
- Eui Bae Kim, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, Sae Hwan Lee, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim, Hong Soo Kim, Boo Sung Kim, A ram Jang
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(2):151-154. Published online September 30, 2012
- 574 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common tumor worldwide and the third leading cause of tumor mortality. The majority of tumors are diagnosed when advanced and then a 5-year survival rate of HCC is below 5%. However, recent progress in the diagnosis and treatment of HCC has made it possible for the patient to survive longer, and as a result, distant metastasis from HCC has increased and attracted more attention than before. HCC can be metastasized to all organs through blood and lymphatic channel. Of the various metastatic sites, the most common site is the lungs, followed by the lymph nodes, musculoskeletal, adrenal and omentum. Also, spleen, small bowel, large bowel and esophagus can be invloved. Brain metastasis can be occurred rarely, and then it is regarded to oncologic emergency. We report a patient who present with brain metastasis of progressing HCC despite of treatment.

- A One cm Sized Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma in a Patient with Chronic Hepatiits B Misdiagnosed as Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Gene Hyun Bok, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, Kwang Yeun Shim, Sae Hwan Lee, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim, Hong Soo Kim, Boo Sung Kim, So Young Jin, Sung Sook Hong, Yong Jae Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(1):23-27. Published online February 28, 2012
- 569 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Morphologically, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) presents as a parenchymal mass, and it is occasionally resectable and potentially curable. In some cases, differentiation from other hepatic neoplasms such as metastatic lesions and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can be extremely difficult, both clinically and histologically, and definitive diagnosis often needs correlation with clinical and radiologic finding.Contrasted computed tomography (CT) is useful in the diagnosis of ICC and in determining the extent of tumor involvement. Although the majority of liver tumors can be diagnosed by modern imaging modalities such as contrast CT, some cases of ICC show tumor enhancement in the arterial phase the same as that in HCC, or a biliary dilatation without stenosis by intraductal tumor growth. Differences in these patterns of tumor enhancement and status of the bile ducts in ICC may also reflect differences in cellular characteristics, clinical features, and prognosis after treatment. We present a case of a small ICC showing similar clinical and radiologic characteristics to HCC.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter