Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Outcomes of Liver Resection and Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Multinodular BCLC-A Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jiwon Yang, Won-Mook Choi, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Deok-Bog Moon, Dong-Hwan Jung, Jonggi Choi
- Received March 3, 2024 Accepted March 25, 2024 Published online April 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.25 [Accepted]

- 760 Views
- 51 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to compare the outcomes of liver resection (LR) and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with multinodular hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) within the Milan criteria who were not eligible for liver transplantation.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 483 patients with multinodular HCC within the Milan criteria, who underwent either LR or TACE as an initial therapy between 2013 and 2022. The overall survival (OS) in the entire population and recurrence-free survival (RFS) in patients who underwent LR and TACE and achieved a complete response were analyzed. Propensity score (PS) matching analysis was also used for a fair comparison of outcomes between the two groups.
Results
Among the 483 patients, 107 (22.2%) and 376 (77.8%) underwent LR and TACE, respectively. The median size of the largest tumor was 2.0 cm, and 72.3% of the patients had two HCC lesions. The median OS and RFS were significantly longer in the LR group than in the TACE group (p <0.01 for both). In the multivariate analysis, TACE (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.81 and aHR, 2.41) and large tumor size (aHR, 1.43 and aHR, 1.44) were significantly associated with worse OS and RFS, respectively. The PS-matched analysis also demonstrated that the LR group had significantly longer OS and RFS than the TACE group (PS <0.05).
Conclusion
In this study, LR showed better OS and RFS than TACE in patients with multinodular Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A HCC. Therefore, LR can be considered an effective treatment option for these patients.

Review Article
- Advancing Korean nationwide registry for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic sampling approach utilizing the Korea Central Cancer Registry database
- Bo Hyun Kim, E Hwa Yun, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Geun Hong, Jun Yong Park, Ju Hyun Shim, Eunyang Kim, Hyun-Joo Kong, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Suk Lim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):57-61. Published online March 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.03
- 1,021 Views
- 38 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
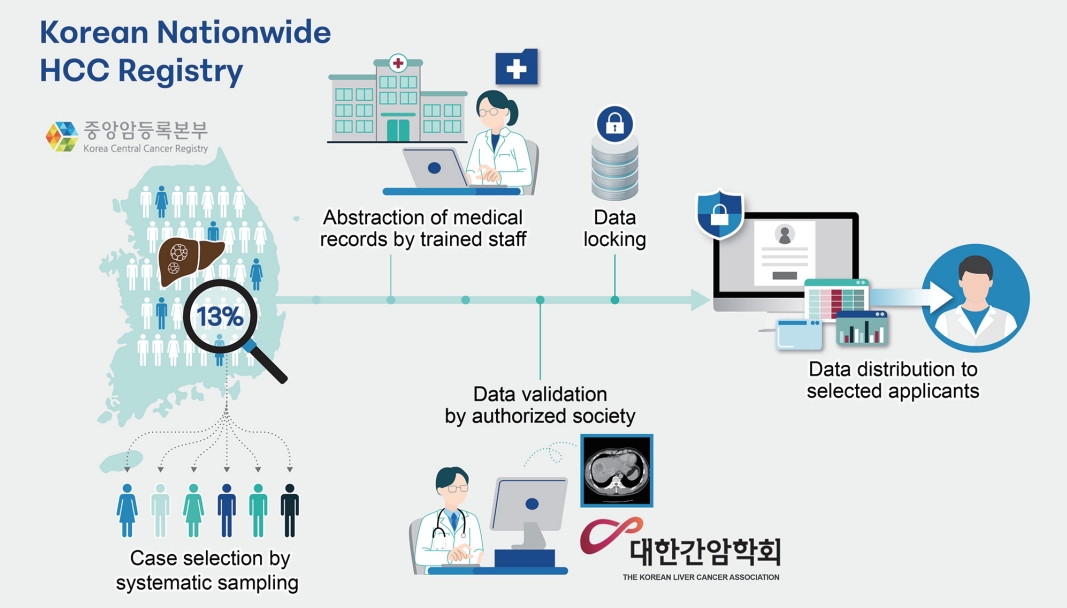
Supplementary Material - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presents a substantial public health challenge in South Korea as evidenced by 10,565 new cases annually (incidence rate of 30 per 100,000 individuals), in 2020. Cancer registries play a crucial role in gathering data on incidence, disease attributes, etiology, treatment modalities, outcomes, and informing health policies. The effectiveness of a registry depends on the completeness and accuracy of data. Established in 1999 by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, the Korea Central Cancer Registry (KCCR) is a comprehensive, legally mandated, nationwide registry that captures nearly all incidence and survival data for major cancers, including HCC, in Korea. However, detailed information on cancer staging, specific characteristics, and treatments is lacking. To address this gap, the KCCR, in partnership with the Korean Liver Cancer Association (KLCA), has implemented a systematic approach to collect detailed data on HCC since 2010. This involved random sampling of 10-15% of all new HCC cases diagnosed since 2003. The registry process encompassed four stages: random case selection, meticulous data extraction by trained personnel, expert validation, anonymization of personal data, and data dissemination for research purposes. This random sampling strategy mitigates the biases associated with voluntary reporting and aligns with stringent privacy regulations. This innovative approach positions the KCCR and KLCA as foundations for advancing cancer control and shaping health policies in South Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of modifiable metabolic risk factors and lifestyle with all-cause mortality in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Hwi Young Kim, Hye Ah Lee, Pompilia Radu, Jean-François Dufour
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of modifiable metabolic risk factors and lifestyle with all-cause mortality in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma

Original Articles
- The efficacy of treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly patients
- Han Ah Lee, Sangheun Lee, Hae Lim Lee, Jeong Eun Song, Dong Hyeon Lee, Sojung Han, Ju Hyun Shim, Bo Hyun Kim, Jong Young Choi, Hyunchul Rhim, Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):362-376. Published online September 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.08.03
- 1,734 Views
- 87 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
Despite the increasing proportion of elderly patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) over time, treatment efficacy in this population is not well established.
Methods
Data collected from the Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry, a representative cohort of patients newly diagnosed with HCC in Korea between 2008 and 2017, were analyzed. Overall survival (OS) according to tumor stage and treatment modality was compared between elderly and non-elderly patients with HCC.
Results
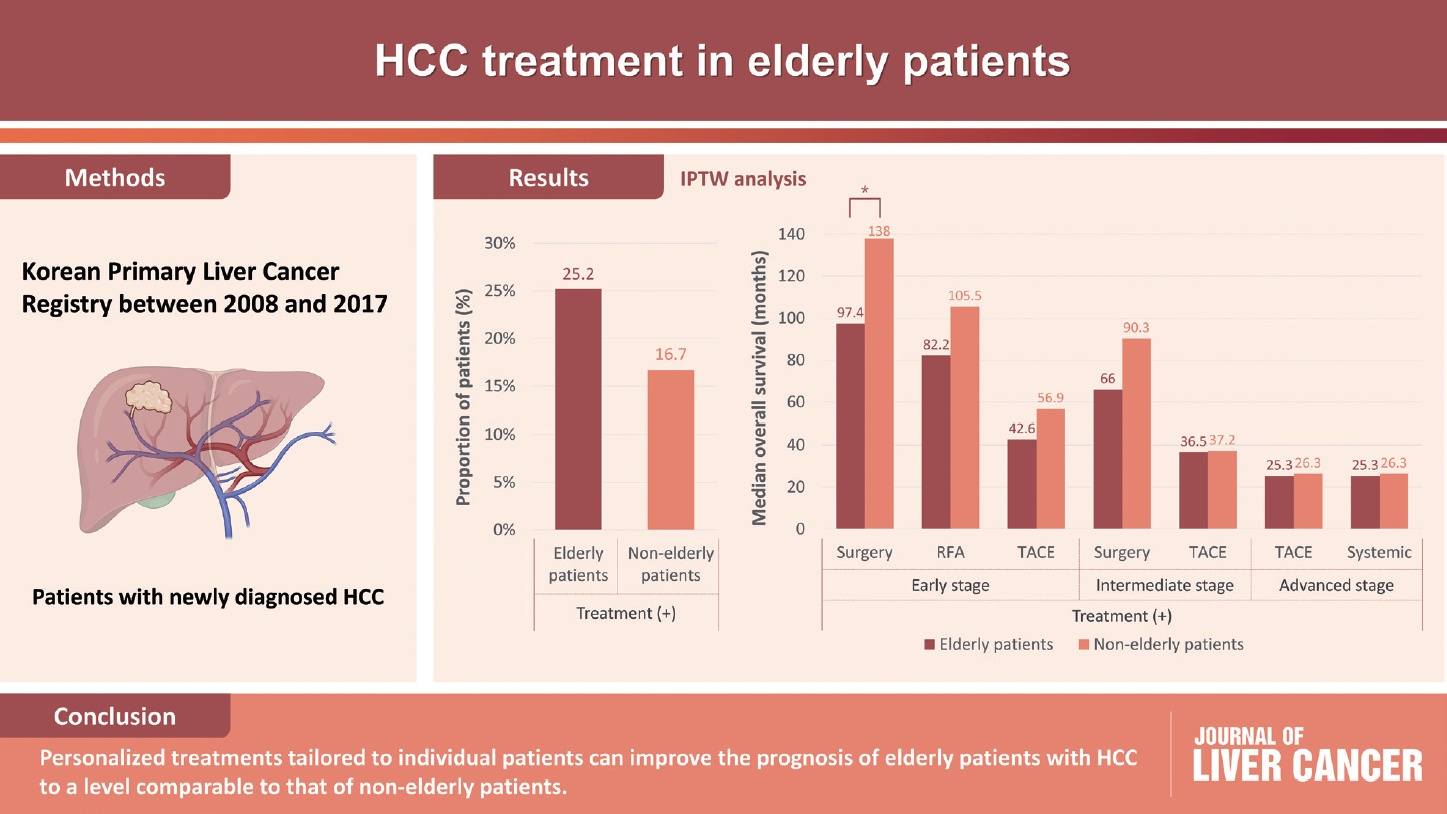
Among 15,186 study patients, 5,829 (38.4%) were elderly. A larger proportion of elderly patients did not receive any treatment for HCC than non-elderly patients (25.2% vs. 16.7%). However, OS was significantly better in elderly patients who received treatment compared to those who did not (median, 38.6 vs. 22.3 months; P<0.001). In early-stage HCC, surgery yielded significantly lower OS in elderly patients compared to non-elderly patients (median, 97.4 vs. 138.0 months; P<0.001), however, local ablation (median, 82.2 vs. 105.5 months) and transarterial therapy (median, 42.6 vs. 56.9 months) each provided comparable OS between the two groups after inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) analysis (all P>0.05). After IPTW, in intermediate-stage HCC, surgery (median, 66.0 vs. 90.3 months) and transarterial therapy (median, 36.5 vs. 37.2 months), and in advanced-stage HCC, transarterial (median, 25.3 vs. 26.3 months) and systemic therapy (median, 25.3 vs. 26.3 months) yielded comparable OS between the elderly and non-elderly HCC patients (all P>0.05).
Conclusions
Personalized treatments tailored to individual patients can improve the prognosis of elderly patients with HCC to a level comparable to that of non-elderly patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and Safety of Surgical Resection in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jin-Soo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Seungeun Ryoo, Jungeun Park, Gi Hong Choi, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Gut and Liver.2024; 18(4): 695. CrossRef - Achieving Sufficient Therapeutic Outcomes of Surgery in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients through Appropriate Selection
Han Ah Lee
Gut and Liver.2024; 18(4): 556. CrossRef
- Efficacy and Safety of Surgical Resection in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

- Subclassification of advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: combined transarterial chemoembolization and radiotherapy as an alternative first-line treatment
- Sujin Jin, Won-Mook Choi, Ju Hyun Shim, Danbi Lee, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Jinhong Jung, Sang Min Yoon, Jonggi Choi
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):177-188. Published online March 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.03.04

- 1,921 Views
- 96 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
The Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) guidelines recommend systemic therapy as the only first-line treatment for patients with BCLC stage C hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) despite its heterogeneity of disease extent. We aimed to identify patients who might benefit from combined transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radiation therapy (RT) by subclassifying BCLC stage C.
Methods
A total of 1,419 treatment-naïve BCLC stage C patients with macrovascular invasion (MVI) who were treated with combined TACE and RT (n=1,115) or systemic treatment (n=304) were analyzed. The primary outcome was overall survival (OS). Factors associated with OS were identified and assigned points by the Cox model. The patients were subclassified into three groups based on these points.
Results
The mean age was 55.4 years, and 87.8% were male. The median OS was 8.3 months. Multivariate analysis revealed a significant association of Child-Pugh B, infiltrative-type tumor or tumor size ≥10 cm, main or bilateral portal vein invasion, and extrahepatic metastasis with poor OS. The sub-classification was categorized into low (point ≤1), intermediate (point=2), and high (point ≥3) risks based on the sum of points (range, 0–4). The OS in the low, intermediate, and high-risk groups was 22.6, 8.2, and 3.8 months, respectively. In the low and intermediate-risk groups, patients treated with combined TACE and RT exhibited significantly longer OS (24.2 and 9.5 months, respectively) than those who received systemic treatment (6.4 and 5.1 months, respectively; P<0.0001).
Conclusions
Combined TACE and RT may be considered as a first-line treatment option for HCC patients with MVI when classified into low- and intermediate-risk groups. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Liver resection in selective hepatocellular carcinoma with Vp3 or Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis improves prognosis
Manuel Lim, Jongman Kim, Jinsoo Rhu, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 102. CrossRef - Comparison of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
Jeayeon Park, Yun Bin Lee, Yunmi Ko, Youngsu Park, Hyunjae Shin, Moon Haeng Hur, Min Kyung Park, Dae-Won Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Kyung-Hun Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Su Jong Yu, Tae-Yong Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Tae-You Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 81. CrossRef - How to optimize the treatment strategy for advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion
Beom Kyung Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 121. CrossRef
- Liver resection in selective hepatocellular carcinoma with Vp3 or Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis improves prognosis

- Stereotactic body radiation therapy for elderly patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective observational study
- Jeong Yun Jang, Jinhong Jung, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Jin-hong Park, Sang Min Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):136-145. Published online September 16, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.08.18
- 3,487 Views
- 79 Downloads
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
We aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in elderly patients with small hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC).
Methods
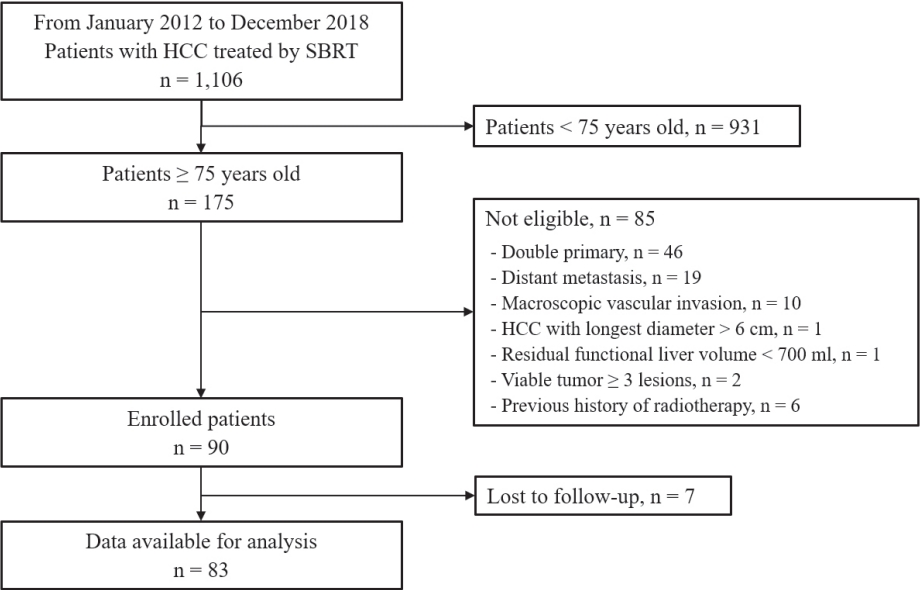
Eighty-three patients (89 lesions) with HCC who underwent SBRT between January 2012 and December 2018 were reviewed in this retrospective observational study. The key inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) age ≥75 years, 2) contraindications for hepatic resection or percutaneous ablative therapies, 3) no macroscopic vascular invasion, and 4) no extrahepatic metastasis.
Results
The patients were 75-90 years of age, and 49 (59.0%) of them were male. Most patients (94.0%) had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 or 1. Seventy-four patients (89.2%) had Child-Pugh class A hepatic function before SBRT. The median tumor size was 1.6 cm (range, 0.7-3.5). The overall median follow-up period was 34.8 months (range, 7.3-99.3). The 5-year local tumor control rate was 90.1%. The 3-year and 5-year overall survival rate was 57.1% and 40.7%, respectively. Acute toxicity grade ≥3 was observed in three patients (3.6%) with elevated serum hepatic enzymes; however, no patient experienced a worsening of the Child-Pugh score to ≥2 after SBRT. None of the patients developed late toxicity (grade ≥3).
Conclusions
SBRT is a safe treatment option with a high local control rate in elderly patients with small HCC who are not eligible for other curative treatments. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sujin Koo, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Seungeun Ryoo, Jungeun Park, Dong Ah Park
Current Oncology.2024; 31(1): 324. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Surgical Resection in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jin-Soo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Seungeun Ryoo, Jungeun Park, Gi Hong Choi, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Gut and Liver.2024; 18(4): 695. CrossRef - Radiotherapy trend in elderly hepatocellular carcinoma: retrospective analysis of patients diagnosed between 2005 and 2017
Bong Kyung Bae, Jeong Il Yu, Hee Chul Park, Myung Ji Goh, Yong-Han Paik
Radiation Oncology Journal.2023; 41(2): 98. CrossRef - Loco-regional therapies competing with radiofrequency ablation in potential indications for hepatocellular carcinoma: a network meta-analysis
Ha Il Kim, Jihyun An, Seungbong Han, Ju Hyun Shim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 1013. CrossRef - Has the growing evidence of radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma increased the use of radiotherapy in elderly patients?
Tae Hyun Kim
Radiation Oncology Journal.2023; 41(3): 141. CrossRef - Chronic Liver Disease in the Older Patient—Evaluation and Management
Daniel Anthony DiLeo, Tolga Gidener, Ayse Aytaman
Current Gastroenterology Reports.2023; 25(12): 390. CrossRef
- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

- The effects of immune checkpoint modulators on the clinical course of patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma
- Jihyun An, Hyo Jeong Kang, Eunsil Yu, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):40-50. Published online March 17, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.06

- 3,735 Views
- 121 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
Immune checkpoint proteins regulating T-cell mediated anti-tumor immunity have been reported to affect clinical outcomes in multiple malignancies. This study aimed to investigate the prognostic effect of histological expression of immune checkpoint proteins in patients with resected hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
A total of 221 patients with HCC who underwent curative resection were included. Expression of programmed-cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) in tumor cells (tPD-L1) and tumor infiltrating mononuclear cells (TIMCs) (iPD-L1), programmed-cell death-1 in TIMCs (iPD-1), and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 in TIMCs (iCTLA-4) were measured immunohistochemically.
Results
Histo-positivity for iCTLA-4, iPD-1, iPD-L1, and tPD-L1 was 32.1%, 42.5%, 35.3%, and 14.9%, respectively. Multivariate logistic analyses revealed that male sex and tumor >5 cm were variables related to iCTLA-4 positivity (odds ratio [OR], 0.46 and 1.94, respectively; P<0.05). Poor differentiation was related to PD-L1 expression in both tumor cells and TIMCs (OR, 2.88 and 3.46, respectively; P<0.05). Microvascular invasion was significantly associated only with iPD-L1 (OR, 2.24; P<0.05). In time-dependent outcome analyses, expression of immune checkpoint proteins in TIMCs (i.e., iCTLA-4, iPD-1, and iPD-L1) was significantly related to longer overall survival and non-cancer-related survival (all P<0.05), but not to time-to-recurrence or cancer-specific deaths. Concurrent activation of the PD-1:PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways predicted improved outcomes in terms of overall survival and non-cancer related survival (P=0.06 and P=0.03, respectively).
Conclusions
Immune checkpoint proteins upregulated in TIMCs in HCC tissues have individual and additive effects in prolonging the survival of patients, specifically in terms of survival not related to cancer recurrence. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role of PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway in cancer pathogenesis and treatment: a systematic review
Amirhosein Sabaghian, Shahnam Shamsabadi, Saghar Momeni, Mobina Mohammadikia, Kiarash Mohebbipour, Samira Sanami, Sajjad Ahmad, Nahid Akhtar, Neeta Raj Sharma, Raja Babu Singh Kushwah, Yash Gupta, Ajit Prakash, Hamidreza Pazoki-Toroudi
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The role of PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway in cancer pathogenesis and treatment: a systematic review

Case Reports
- A Case of the Effective Treatment of HCC with Bile Duct Invasion and Portal Vein Thrombosis
- Jihyun An, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Young-Hwa Chung, Yung Sang Lee
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2013;13(2):169-172. Published online September 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.13.2.169
- 1,340 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bile duct invasion of hepatocellular caricinoma (HCC) is rare, ranging from 1.2% to 9%. Moreover, the standard treatment of HCC with bile duct invasion is not yet established. We report a case of HCC with bile duct invasion and portal vein thrombosis which was successfully treated by trasarterial chemoembolization and radiotherapy. A 38-year-old female patient visited our hospital due to right upper quadrant pain. The level of total and direct bilirubin was 6.8 and 4.0 mg/dL, respectively. Her blood test showed HBs Ag positive and the level of alpha-fetoprotein was 43,000 ng/mL. Her CT scan revealed lobulating hypervascular mass involving right hepatic lobe, portal vein and both intrahepatic ducts. We performed endoscopic biliary drainage using biliary stent. She had been diagnosed as HCC on endobiliary biopsy. She was treated with radiotherapy (RT) to portal vein thrombosis, and seven transarterial chemoembolizations. After of all, we carried out radiotherapy to hepatic vein thrombosis and residual HCC near hepatic vein. After the RT, she has been taken care at outpatient clinic without evidence of recurrence during 8 months.

- A Case of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome after Cisplatin Based Transarterial Chemoembolization
- Chang Hyeon Seok, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Young-Hwa Chung, Yung Sang Lee
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(2):169-171. Published online September 30, 2012
- 667 Views
- 7 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a rare condition compromising the clinical triad of acute renal failure, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, and thrombocytopenia. HUS may be associated with a variety of etiologies, and chemotherapeutic agents have also been reported to be associated with HUS, including mitomycin, cisplatin, bleomycin, and most recently gemcitabine. HUS also has been observed in association with a number of disseminated malignancies in adults, most typically adenocarcinoma of the stomach and breast. But there was no case report of HUS after cisplatin based transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We experienced a case of HUS after cisplatin based TACE and reported this case with several literature reviews.

- A Case of Small HCC
- Chang Hyeon Seock, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Young-Hwa Chung, Yung Sang Lee
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(1):28-31. Published online February 28, 2012
- 528 Views
- 3 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - According to AASLD practice guideline, nodules that are smaller than 1 cm should be followed with ultrasound at intervals from 3-6 months and nodules larger than 1 cm found on ultrasound screening of a cirrhotic liver should be investigated further with either 4-phase multidetector CT scan or dynamic contrast enhanced MRI. If the appearances are typical of HCC, the lesion should be treated as HCC. We experienced a patient who has a hepatic nodule smaller than 1 cm and followed AASLD guideline and performed radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellularcarcinoma after 13 months later. MRI helped to diagnose hepatic nodule as a hepatocellularcarcinoma during surveillance.

- A Case of a Advanced Stage Hepatocelluar Carcinoma Patient with Relatively Good Response after Combination Therapy
- Chang Hyeon Seock, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Young-Hwa Chung, Yung Sang Lee
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(1):58-61. Published online February 28, 2012
- 544 Views
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - According to AASLD practice guideline, for patients who present with advanced hepatocelluar carcinoma, new data indicates the efficacy of sorafenib in prolonging life. But there are no data comparing combination transarterial chemoemboliation with sorafenib to sorafenib treatment alone. We experienced a case that treated a patient with combination therapy including transarterial chemoembolization for intrahepatic hepatocelluarcarcinoma, radiation therapy for portal vein thrombosis and sorafenib treatment. He was in stable disease state after 6 months later. Therefore, it seems to be need to study for comparing combination therapy to sorafenib, or to transarterial chemoembolization.

- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Bile Duct Invasion Surgically Resected after Transarterial Chemoembolization; Curative Resection after Tumor Downstaging
- Nae-Yun Heo, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young Suk Lim, Young-Hwa Chung, Yung Sang Lee, Dong Jin Suh
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2011;11(1):69-74. Published online February 28, 2011
- 580 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A surgical resection is a major curative treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in Korea. However, the respectability of HCC at the time of diagnosis is low (10-30%) because the cancer is often identified as advanced stage. Nevertheless, some of the patients were known to have a curative resection after successful downstaging therapy. We report a HCC with bile duct invasion which was successfully downstaged by the transarterial chemoembolization and treated by surgical resection.

- A Case of Pulmonary Metastasis from Hepatocellular Carcinoma Partially Responsive to Sorafenib
- Nae-Yun Heo, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Young-Suk Lim, Young-Hwa Chung, Yung Sang Lee, Dong Jin Suh
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2010;10(1):52-54. Published online June 30, 2010
- 549 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most important causes of cancer death in South Korea. Unfortunately, more than half of the patients are diagnosed in the advanced stage with multiple intra- or extrahepatic metastasis, so no more than 30% of patients are suitable to undergo curative resection. Lung is the most common organ of extrahepatic metastasis of HCC, and the pulmonary metastasis is known as poor prognosis factor, but no standard systemic therapy is established yet. Sorafenib is the only molecularly targeted agent which has been proven clinical benefit in the randomized clinical trials, but pulmonary metastasis is known as predictive factor of poor response. However, we experience a case of pulmonary metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma partially responsive to sorafenib, and report it.

- A Case of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Presenting as Skull Metastasis
- Nae-Yun Heo, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Young-Suk Lim, Young-Hwa Chung, Yung Sang Lee, Dong Jin Suh
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2010;10(1):73-75. Published online June 30, 2010
- 504 Views
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma is known to spread to distant organ via hematogenous or osseous route in about 15% of the patients during its clinical course. However, it is rare that the distant metastatic symptom and sign are the diagnostic clues to find the primary hepatocellular carcinoma, because most of the patients are likely to expire due to rapid disease progression before the presentation of the clinical findings of metastasis. Detection of early hepatocelluar carcinoma through surveillance of the high risk population will reduce the chance of initial presentation of metastatic symptom. In spite of this trend, we experienced a case of hepatocellular carcinoma presenting as skull metastasis at diagnosis, which suggests that some patients still complain of metastatic symptom as initial presentation of hepatocellular carcinoma.

- Extrahepatic Bile Duct Hepatocellular Carcinoma Presenting as Obstructive Jaundice
- Ju Hyun Shim, Joong-Won Park, Sung-Sik Han, Joon-Il Choi, Seong Hoon Kim, Sang Jae Park, Eun Kyung Hong, Chang-Min Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2008;8(1):51-54. Published online June 30, 2008
- 588 Views
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Obstructive jaundice is a rare initial symptom of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. We herein report a patient with extrahepatic bile duct HCC mimicking common bile duct (CBD) cancer. A 55-year-old woman with no risk factors developed jaundice of the obstructive type. On dynamic computed tomography, a low attenuated mass located in the lumen of CBD with the invasion of right posterior hepatic parenchyma was identified. After percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage, we performed hepatectomy. Pathologic examination of the lesion confirmed the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with biliary cell differentiation extended in the CBD.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter