Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Assessment of Real-Time US-CT/MR-guided Percutaneous Gold Fiducial Marker Implementation in Malignant Hepatic Tumors for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
- Sungjun Hwang, Seok-Joo Chun, Eui Kyu Chie, Jeong Min Lee
- Received March 20, 2024 Accepted June 2, 2024 Published online June 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.06.03 [Accepted]

- 480 Views
- 13 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
This study explored the initial institutional experience of using gold fiducial markers for stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in treating malignant hepatic tumors using real-time ultrasound-computed tomography (CT)/magnetic resonance (MR) imaging fusion-guided percutaneous placement.
Methods
From May 2021 to August 2023, 19 patients with 25 liver tumors that were invisible on pre-contrast CT received fiducial markers following these guidelines. Postprocedural scans were used to confirm their placement. We assessed technical and clinical success rates and monitored complications. The implantation of fiducial markers facilitating adequate treatment prior to SBRT, which was achieved in 96% of the cases (24 of 25 tumors), was considered technical success. Clinical success was the successful completion of SBRT without evidence of marker displacement and was achieved in 88% of cases (22 of 25 tumors). Complications included one major subcapsular hematoma and marker migration into the right atrium in two cases, which prevented SBRT.
Results
Among the treated tumors, 83.3% (20 of 24) showed a complete response, 12.5% (3 of 24) remained stable, and 4.2% (1 of 24) progressed during an average 11.7-month follow-up (range, 2–32 months).
Conclusions
This study confirms that percutaneous gold fiducial marker placement using real-time CT/MR guidance is effective and safe for SBRT in hepatic tumors, but warns of marker migration risks, especially near the hepatic veins and in subcapsular locations. Using fewer markers than traditionally recommended—typically two per patient), the outcomes were still satisfactory, particularly given the increased risk of migration when markers were placed near major hepatic veins.

- Heavy Smoking Increases Early Mortality Risk in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Treatment
- Jaejun Lee, Jong Young Choi, Soon Kyu Lee
- Received April 24, 2024 Accepted June 2, 2024 Published online June 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.06.02 [Accepted]

- 582 Views
- 31 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Although cigarette smoking has been associated with an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), its association with HCC mortality remains underexplored. We aimed to evaluate the effect of smoking on early mortality in HCC patients following curative treatment.
Methods
Data from the Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry were examined for HCC patients who underwent liver resection or radiofrequency ablation between 2015 and 2018. Smoking cumulative dose was assessed in pack-years. The primary outcome was the 3-year overall survival (OS).
Results
Among 1924 patients, 161 were classified as heavy smokers (≥ 40 pack-years). Heavy smokers exhibited a lower 3-year survival rate (77.1 %) than nonsmokers (83.3%), with a significant difference observed in the 3-year OS (p = 0.016). The assessment of smoking packyears in relation to 3-year OS revealed a dose-dependent pattern, with the hazard ratio exceeding 1.0 at 20 pack-years and continuing to rise until 40 pack-years, reaching peak at 1.21 (95% confidence interval: 1.01, 1.45). Multivariate Cox-regression analysis revealed heavy smoking, age ≥ 60 y, underlying cirrhosis, tumor size > 3 cm, vascular invasion, and Child-Pugh class B/C as risk factors for 3-year OS. Subgroup analyses of patients with a tumor size < 3 cm, absence of vascular invasion, and meeting the Milan criteria also showed inferior outcomes for heavy smokers in all three subgroups.
Conclusion
Heavy smoking, defined as a history of > 40 pack-years, was linked to poorer 3-year survival outcomes in HCC patients undergoing curative treatments, underscoring the importance of smoking cessation in this population.

- Role of transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with extrahepatic metastases in the era of advancing systemic therapy
- Byeong Geun Song, Myung Ji Goh, Wonseok Kang, Dong Hyun Sinn, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Joon Hyeok Lee, Moon Seok Choi
- Received March 5, 2024 Accepted May 26, 2024 Published online June 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.05.26 [Accepted]

- 614 Views
- 33 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
Systemic therapy is the current standard treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with extrahepatic metastases (EHM). However, some patients with HCC and EHM undergo transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) to manage intrahepatic tumors. Herein, we aimed to explore the appropriateness of TACE in patients with HCC and EHM in an era of advanced systemic therapy.
Methods
This study analyzed 248 consecutive patients with HCC and EHM (median age 58.5 years, 83.5% male, and 88.7% Child-Pugh A) who received TACE or systemic therapy (83 sorafenib, 49 lenvatinib, 28 immunotherapy-based) between January 2018 and January 2021.
Results
Among the patients, 196 deaths were recorded during a median follow-up of 8.9 months. Patients who received systemic therapy had a higher albumin-bilirubin grade, elevated tumor markers, an increased number of intrahepatic tumors, larger-sized tumors, and more frequent portal vein invasion than those who underwent TACE. TACE was associated with longer median overall survival (OS) than sorafenib (15.1 vs. 4.7 months; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 11.1–22.2 vs. 3.7–7.3; hazard ratio [HR] 1.97, P<0.001). After adjustment for potential confounders, TACE was associated with statistically similar survival outcomes to those of lenvatinib (median OS: 8.0 months; 95% CI: 6.5–11.0; HR 1.21, P=0.411) and immunotherapies (median OS: 14.3 months; 95% CI: 9.5–27.0; HR 1.01, P=0.973), demonstrating survival benefits equivalent to these treatments.
Conclusion
In patients with HCC and EHM, TACE can provide a survival benefit comparable to that of newer systemic therapies. Accordingly, TACE remains a valuable option in this era of new systemic therapies.

- Downstaging with Atezolizumab-Bevacizumab: A Case Series
- Anand V. Kulkarni, Kumaraswamy P, Balachandran Menon, Anuradha Sekaran, Anuhya Rambhatl, Sowmya Iyengar, Manasa Alla, Shantan Venishetty, Sumana Kolar Ramachandra, Premkumar G V, Mithun Sharma, P. N Rao, Duvvur Nageshwar Reddy, Amit G. Singal
- Received April 3, 2024 Accepted May 12, 2024 Published online May 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.05.12 [Accepted]

- 1,047 Views
- 140 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/aims
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is generally diagnosed at an advanced stage, which limits curative treatment options for these patients. Locoregional therapy (LRT) is the standard approach to bridge and downstage unresectable HCC (uHCC) for liver transplantation (LT). Atezolizumab-bevacizumab (atezo-bev) can induce objective responses in nearly one-third of patients; however, the role and outcomes of downstaging using atezobev remains unknown.
Methods
In this retrospective single-center study, we included consecutive patients between November 2020 and August 2023, who received atezo-bev with or without LRT and were subsequently considered for resection/LT after downstaging.
Results
Of the 115 patients who received atezo-bev, 12 patients (10.4%) achieved complete or partial response and were willing to undergo LT; they (age: 58.5 years; women-17%; Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage System B/C:5/7) had received 3–12 cycles of atezo-bev, and 4 of them had received prior LRT. Three patients died before LT, while three were awaiting LT. Six patients underwent curative therapies: four underwent living donor LT after a median of 79.5 (54–114) days following the last atezo-bev dose, one underwent deceased donor LT 38 days after the last dose, and one underwent resection. All but one patient had complete pathologic response with no viable HCC. Three patients experienced wound healing complications, and one required re-exploration and succumbed to sepsis. After a median follow-up of 10 (4–30) months, none of the alive patients developed HCC recurrence or graft rejection.
Conclusions
Surgical therapy, including LT, is possible after atezo-bev therapy in wellselected patients after downstaging.

- Superselective Ablative Chemo-ethanol Embolization for Recurrent Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Six-Month Outcome Analysis
- Jae Hwan Lee, Kun Yung Kim, Chong-ho Lee, Minuk Kim, Chang Jin Yoon
- Received April 1, 2024 Accepted May 8, 2024 Published online May 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.05.08 [Accepted]

- 455 Views
- 29 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
To evaluate the safety and effectiveness of superselective ablative chemoethanol embolization (SACE) for the treatment of patients with recurrent single hepatocellular carcinoma (rHCC).
Materials and Methods
This retrospective study included 22 patients (19 men, median age 63 [range 38-86 y]) with Child-Pugh class of A/B/C (16/3/3) that underwent SACE between January and June 2023 for recurrent single HCCs measuring ≤ 5 cm in diameter using a mixture of 99% Ethanol and ethiodized oil/doxorubicin emulsion. The primary endpoint was the 6-month tumor response, and the secondary endpoints were the 1-month tumor response and treatment-related safety. This study was approved by our institutional review board, and the requirement for informed consent was waived.
Results
SACE was successfully performed in 22 (95.2%) patients. The complete response rates at 1-month and 6-month after treatment were 100% and 83.3%, respectively. At 6-month, local tumor progression occurred in one patient and intrahepatic distant metastasis was found in 6 (30%) patients. No 6-month mortalities were reported. No adverse events greater than grade 2 or laboratory deteriorations were observed. Biliary complications or liver abscesses were not observed.
Conclusion
SACE for a single rHCC was highly effective in achieving a favorable 6-month tumor response and showed acceptable adverse events. However, further prospective studies are required to verify these findings.

- Inter-reader Agreement for CT/MRI LI-RADS Category M Imaging Features: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Dong Hwan Kim, Sang Hyun Choi
- Received March 11, 2024 Accepted April 5, 2024 Published online April 15, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.04.05 [Accepted]

- 1,095 Views
- 36 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Backgrounds/Aims
To systematically evaluate inter-reader agreement in the assessment of individual Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) category M (LR-M) imaging features in computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging (CT/MRI) LI-RADS v2018, and to explore the causes of poor agreement in LR-M assignment.
Methods
Original studies reporting inter-reader agreement for LR-M features on multiphasic CT or MRI were identified using the MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases. The pooled kappa coefficient (κ) was calculated using the DerSimonian–Laird random-effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using Cochran’s Q test and I2 statistics. Subgroup meta-regression analyses were conducted to explore the study heterogeneity.
Results
In total, 24 eligible studies with 5,163 hepatic observations were included. The pooled κ values were 0.72 (95% confidence interval, 0.65–0.78) for rim arterial phase hyperenhancement, 0.52 (0.39–0.65) for peripheral washout, 0.60 (0.50–0.70) for delayed central enhancement, 0.68 (0.57–0.78) for targetoid restriction, 0.74 (0.65–0.83) for targetoid transitional phase/hepatobiliary phase appearance, 0.64 (0.49–0.78) for infiltrative appearance, 0.49 (0.30–0.68) for marked diffusion restriction, and 0.61 (0.48–0.73) for necrosis or severe ischemia. Substantial study heterogeneity was observed for all LR-M features (Cochran's Q test: p < 0.01; I2 ≥ 89.2%). Studies with a mean observation size of <3 cm, those performed using 1.5-T MRI, and those with multiple image readers, were significantly associated with poor agreement of LR-M features.
Conclusions
The agreement for peripheral washout and marked diffusion restriction was limited. The LI-RADS should focus on improving the agreement of LR-M features.

- Outcomes of Liver Resection and Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Multinodular BCLC-A Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jiwon Yang, Won-Mook Choi, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Deok-Bog Moon, Dong-Hwan Jung, Jonggi Choi
- Received March 3, 2024 Accepted March 25, 2024 Published online April 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.25 [Accepted]

- 760 Views
- 51 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to compare the outcomes of liver resection (LR) and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with multinodular hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) within the Milan criteria who were not eligible for liver transplantation.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 483 patients with multinodular HCC within the Milan criteria, who underwent either LR or TACE as an initial therapy between 2013 and 2022. The overall survival (OS) in the entire population and recurrence-free survival (RFS) in patients who underwent LR and TACE and achieved a complete response were analyzed. Propensity score (PS) matching analysis was also used for a fair comparison of outcomes between the two groups.
Results
Among the 483 patients, 107 (22.2%) and 376 (77.8%) underwent LR and TACE, respectively. The median size of the largest tumor was 2.0 cm, and 72.3% of the patients had two HCC lesions. The median OS and RFS were significantly longer in the LR group than in the TACE group (p <0.01 for both). In the multivariate analysis, TACE (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.81 and aHR, 2.41) and large tumor size (aHR, 1.43 and aHR, 1.44) were significantly associated with worse OS and RFS, respectively. The PS-matched analysis also demonstrated that the LR group had significantly longer OS and RFS than the TACE group (PS <0.05).
Conclusion
In this study, LR showed better OS and RFS than TACE in patients with multinodular Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A HCC. Therefore, LR can be considered an effective treatment option for these patients.

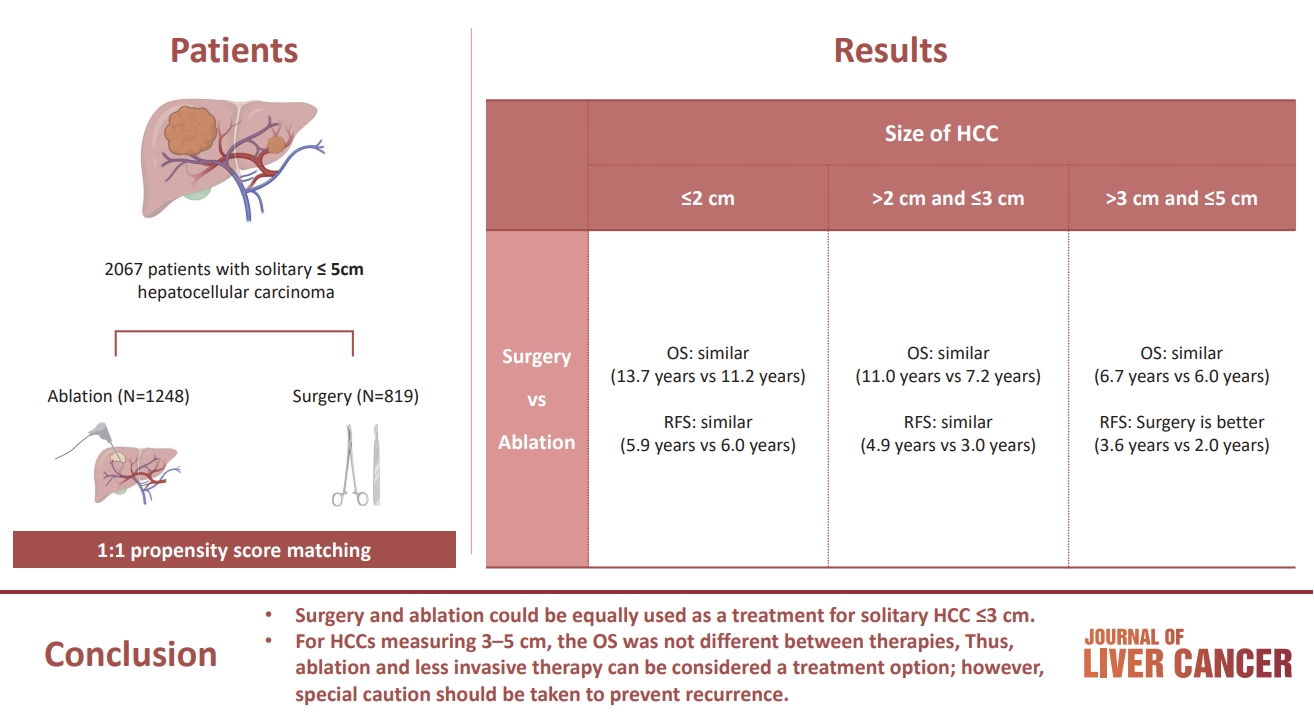
- Treatment options for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm: surgery vs. ablation: a multicenter retrospective study
- Kazuya Kariyama, Kazuhiro Nouso, Atsushi Hiraoka, Hidenori Toyoda, Toshifumi Tada, Kunihiko Tsuji, Toru Ishikawa, Takeshi Hatanaka, Ei Itobayashi, Koichi Takaguchi, Akemi Tsutsui, Atsushi Naganuma, Satoshi Yasuda, Satoru Kakizaki, Akiko Wakuta, Shohei Shiota, Masatoshi Kudo, Takashi Kumada
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):71-80. Published online November 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.09.11
- 1,892 Views
- 118 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
The aim of this study was to compare the therapeutic efficacy of ablation and surgery in solitary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) measuring ≤5 cm with a large HCC cohort database.
Methods
The study included consecutive 2,067 patients with solitary HCC who were treated with either ablation (n=1,248) or surgery (n=819). Th e patients were divided into three groups based on the tumor size and compared the outcomes of the two therapies using propensity score matching.
Results
No significant difference in recurrence-free survival (RFS) or overall survival (OS) was found between surgery and ablation groups for tumors measuring ≤2 cm or >2 cm but ≤3 cm. For tumors measuring >3 cm but ≤5 cm, RFS was significantly better with surgery than with ablation (3.6 and 2.0 years, respectively, P=0.0297). However, no significant difference in OS was found between surgery and ablation in this group (6.7 and 6.0 years, respectively, P=0.668).
Conclusion
The study suggests that surgery and ablation can be equally used as a treatment for solitary HCC no more than 3 cm in diameter. For HCCs measuring 3-5 cm, the OS was not different between therapies; thus, ablation and less invasive therapy can be considered a treatment option; however, special caution should be taken to prevent recurrence. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reply to the Letter regarding “Treatment options for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm: surgery vs. ablation: a multicenter retrospective study”
Kazuhiro Nouso, Kazuya Kariyama
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 5. CrossRef - Radiofrequency for hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 3 cm: potential for applications in daily practice
Ji Hoon Kim, Pil Soo Sung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Letter regarding “Treatment options for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm: surgery vs. ablation: a multicenter retrospective study”
Jongman Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 3. CrossRef
- Reply to the Letter regarding “Treatment options for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm: surgery vs. ablation: a multicenter retrospective study”

Case Reports
- Favorable response of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis after radiotherapy combined with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
- Yong Tae Kim, Jina Kim, Jinsil Seong
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):225-229. Published online March 16, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.27

- 1,389 Views
- 74 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Recently, the superiority of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (AteBeva) over sorafenib was proven in the IMbrave150 trial, and AteBeva became the first-line systemic treatment for untreated, unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). While the results are encouraging, more than half of patients with advanced HCC are still being treated in a palliative setting. Radiotherapy (RT) is known to induce immunogenic effects that may enhance the therapeutic efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Herein, we report the case of a patient with advanced HCC with massive portal vein tumor thrombosis treated with a combination of RT and AteBeva, who showed near complete response in tumor thrombosis and favorable response to HCC. Although this is a rare case, it shows the importance of reducing the tumor burden via RT to combination immunotherapy in patients with advanced HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 330. CrossRef - Carbon Ion Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hwa Kyung Byun, Changhwan Kim, Jinsil Seong
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 945. CrossRef
- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab

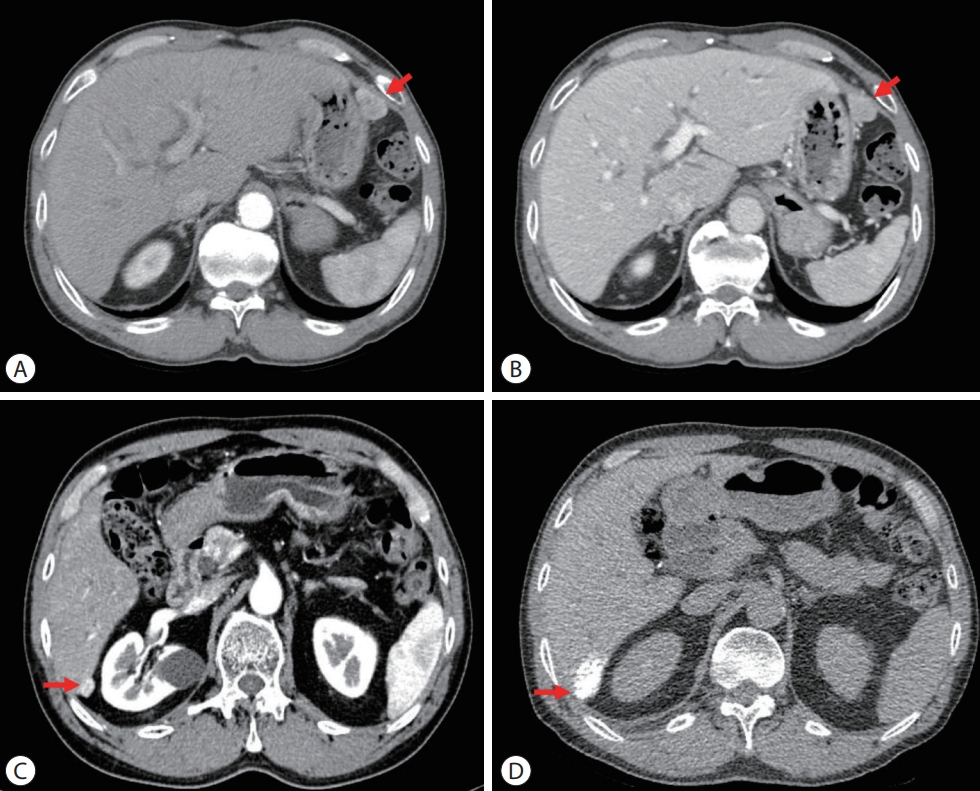
- A case of successful surgical treatment for peritoneal seeding of hepatocellular carcinoma after radiotherapy and atezolizumab plus bevacizumab combination treatment
- Yuri Cho, Bo Hyun Kim, Tae Hyun Kim, Young Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):206-212. Published online February 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.09
- 1,730 Views
- 63 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Peritoneal seeding of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is incurable and has poor prognosis. A 68-year-old man underwent surgical resection for a 3.5 cm single nodular HCC at the tip of segment 3 and transarterial chemoembolization for a 1.5 cm-sized recurrent HCC at the tip of segment 6. 3 months later, an increasing 1 cm pelvic nodule on the rectovesical pouch warranted radiotherapy. Although it stabilized, a new 2.7 cm-sized peritoneal nodule in the right upper quadrant (RUQ) omentum appeared 3.5 years after radiotherapy. Hence, omental mass and small bowel mesentery mass excision were performed. 3 years later, recurrent peritoneal metastases in the RUQ omentum and rectovesical pouch progressed. 33 cycles of atezolizumab and bevacizumab treatment elicited stable disease response. Finally, laparoscopic left pelvic peritonectomy was performed without tumor recurrence. Herein, we present a case of HCC with peritoneal seeding that was successfully treated with surgery after radiotherapy and systemic therapy, leading to complete remission.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 330. CrossRef
- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab

Original Article
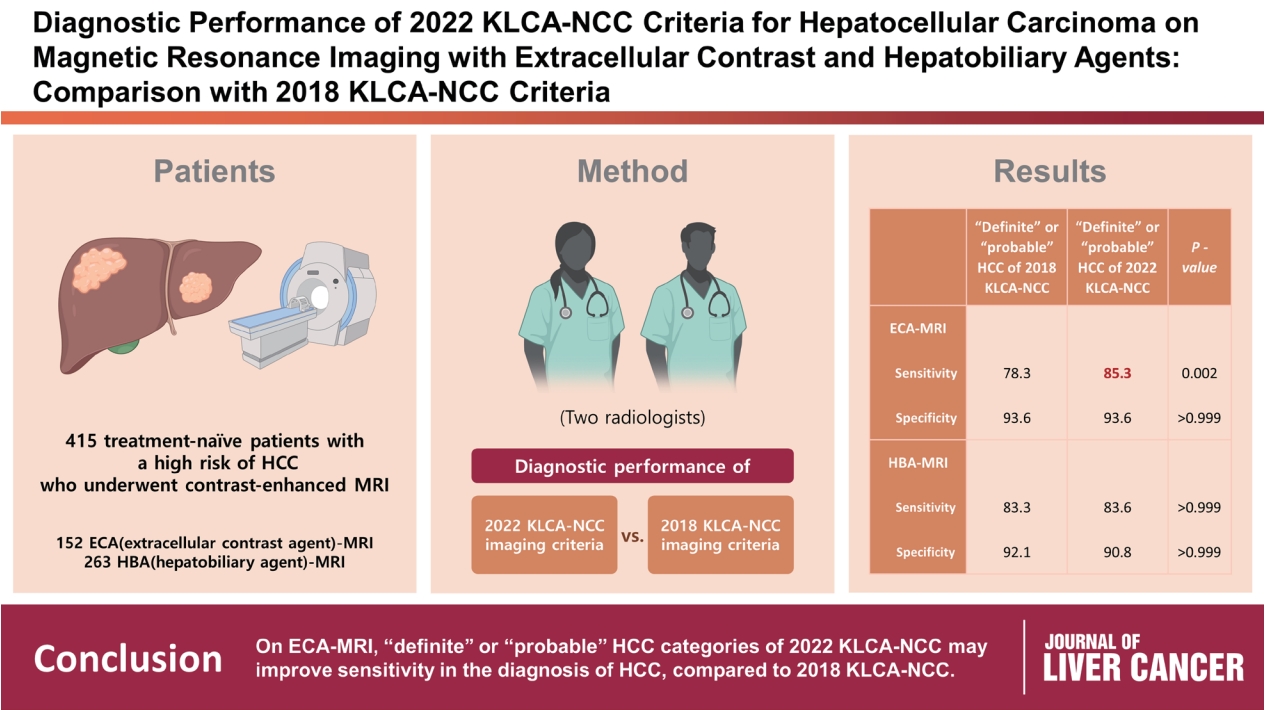
- Diagnostic performance of the 2022 KLCA-NCC criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma on magnetic resonance imaging with extracellular contrast and hepatobiliary agents: comparison with the 2018 KLCA-NCC criteria
- Ja Kyung Yoon, Sunyoung Lee, Jeong Ah Hwang, Ji Eun Lee, Seung-seob Kim, Myeong-Jin Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):157-165. Published online February 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.07
- 1,932 Views
- 101 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
This study aimed to determine the diagnostic performance of 2022 Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center (KLCA-NCC) imaging criteria compared with the 2018 KLCA-NCC for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in high-risk patients using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Methods
This retrospective study included 415 treatment-naïve patients (152 patients who underwent extracellular contrast agent [ECA]-MRI and 263 who underwent hepatobiliary agent [HBA]-MRI; 535 lesions, including 412 HCCs) with a high risk of HCC who underwent contrast-enhanced MRI. Two readers evaluated all lesions according to the 2018 and 2022 KLCA-NCC imaging diagnostic criteria, and the per-lesion diagnostic performances were compared.
Results
In “definite” HCC category of both 2018 and 2022 KLCA-NCC, HBA-MRI showed a significantly higher sensitivity for the diagnosis of HCC than ECA-MRI (77.0% vs. 64.3%, P=0.006) without a significant difference in specificity (94.7% vs. 95.7%, P=0.801). On ECAMRI, “definite” or “probable” HCC categories of the 2022 KLCA-NCC had significantly higher sensitivity than those of the 2018 KLCA-NCC (85.3% vs. 78.3%, P=0.002) with identical specificity (93.6%). On HBA-MRI, the sensitivity and specificity of “definite” or “probable” HCC categories of both 2018 and 2022 KLCA-NCC were not significantly different (83.3% vs. 83.6%, P>0.999 and 92.1% vs. 90.8%, P>0.999, respectively).
Conclusions
In “definite” HCC category of both 2018 and 2022 KLCA-NCC, HBA-MRI provides better sensitivity than ECA-MRI without compromising specificity. On ECA-MRI, “definite” or “probable” HCC categories of the 2022 KLCA-NCC may improve sensitivity in the diagnosis of HCC compared with the 2018 KLCA-NCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of the updated KLCA-NCC criteria for diagnosis of “probable HCC” in liver MRI: comparisons between KLCA v2022 and v2018
Jeong Hee Yoon
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 124. CrossRef
- Impact of the updated KLCA-NCC criteria for diagnosis of “probable HCC” in liver MRI: comparisons between KLCA v2022 and v2018

Guideline
- 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):1-120. Published online December 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.11.07
- 9,693 Views
- 333 Downloads
- 34 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common cancer worldwide and the fourth most common cancer among men in South Korea, where the prevalence of chronic hepatitis B infection is high in middle and old age. The current practice guidelines will provide useful and sensible advice for the clinical management of patients with HCC. A total of 49 experts in the fields of hepatology, oncology, surgery, radiology, and radiation oncology from the Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center Korea Practice Guideline Revision Committee revised the 2018 Korean guidelines and developed new recommendations that integrate the most up-to-date research findings and expert opinions. These guidelines provide useful information and direction for all clinicians, trainees, and researchers in the diagnosis and treatment of HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Contrast-enhanced US for HCC: Finally out from the waiting list?
Richard G. Barr, Luigi Bolondi
Hepatology.2024; 79(2): 267. CrossRef - The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis
Log Young Kim, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Young Chang, Hoongil Jo, Young Youn Cho, Sangheun Lee, Dong Hyeon Lee, Jae Young Jang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential role of Fibrosis‐4 score in hepatocellular carcinoma screening: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Sujeong Shin, Won Sohn, Yoosoo Chang, Yoosun Cho, Min‐Jung Kwon, Sarah H. Wild, Christopher D. Byrne, Seungho Ryu
Hepatology Research.2024; 54(6): 551. CrossRef - Research Progress of lncRNA-ATB/miR-141-3p/GP73 Ax-is-Mediated EMT Promoting TACE Refractoriness
棋 耿
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(01): 903. CrossRef - Response to atezolizumab plus bevacizumab specific for lung and lymph node metastases affects survival of patients with HCC
Jiwon Yang, Jonggi Choi, Won‐Mook Choi, Kang Mo Kim, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim
Liver International.2024; 44(4): 907. CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef - Management Consensus Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2023 Update on Surveillance, Diagnosis, Systemic Treatment, and Posttreatment Monitoring by the Taiwan Liver Cancer Association and the Gastroenterological Society of Taiwan
Wei Teng, Hung-Wei Wang, Shi-Ming Lin
Liver Cancer.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Complications of immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 9. CrossRef - Liver resection in selective hepatocellular carcinoma with Vp3 or Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis improves prognosis
Manuel Lim, Jongman Kim, Jinsoo Rhu, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 102. CrossRef - Comparison of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
Jeayeon Park, Yun Bin Lee, Yunmi Ko, Youngsu Park, Hyunjae Shin, Moon Haeng Hur, Min Kyung Park, Dae-Won Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Kyung-Hun Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Su Jong Yu, Tae-Yong Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Tae-You Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 81. CrossRef - Programmed Death 1 and Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Protein 4 Gene Expression in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Can Serve as Prognostic Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ji Ah Lee, Hei-Gwon Choi, Hyuk Soo Eun, Jiyoon Bu, Tae Min Jang, Jeongdong Lee, Chae Yeon Son, Min Seok Kim, Woo Sun Rou, Seok Hyun Kim, Byung Seok Lee, Ha Neul Kim, Tae Hee Lee, Hong Jae Jeon
Cancers.2024; 16(8): 1493. CrossRef - Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Steatotic Liver Disease and Its Newly Proposed Subclassification
Byeong Geun Song, Aryoung Kim, Myung Ji Goh, Wonseok Kang, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Dong Hyun Sinn
Liver Cancer.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Surgical Resection in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jin-Soo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Seungeun Ryoo, Jungeun Park, Gi Hong Choi, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Gut and Liver.2024; 18(4): 695. CrossRef - Consistent efficacy of hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy irrespective of PD‑L1 positivity in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
Ji Kim, Young Kim, Hee-Chul Nam, Chang-Wook Kim, Jae-Sung Yoo, Ji Han, Jeong Jang, Jong Choi, Seung Yoon, Ho Jong Chun, Jung Oh, Suho Kim, Sung Lee, Pil Sung
Oncology Letters.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Bleeding in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Young-Gi Song, Kyeong-Min Yeom, Eun Ae Jung, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Liver Cancer.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Trends in alcohol use and alcoholic liver disease in South Korea: a nationwide cohort study
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Dong Hyeon Lee, Young Chang, Hoongil Jo, Young Youn Cho, Sangheun Lee, Log Young Kim, Jae Young Jang
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Fatal intratumoral hemorrhage in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma following successful treatment with atezolizumab/bevacizumab: A case report
Kyeong-Hoon Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2024; 12(22): 5177. CrossRef - Diagnostic performance of the 2022 KLCA-NCC criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma on magnetic resonance imaging with extracellular contrast and hepatobiliary agents: comparison with the 2018 KLCA-NCC criteria
Ja Kyung Yoon, Sunyoung Lee, Jeong Ah Hwang, Ji Eun Lee, Seung-seob Kim, Myeong-Jin Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 157. CrossRef - Radiologic features of hepatocellular carcinoma related to prognosis
Shin Hye Hwang, Hyungjin Rhee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 143. CrossRef - Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: a large-scale multicenter study
Sun Hong Yoo, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Han-Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim, Do Seon Song, Seong Hee Kang, Moon Young Kim, Young-Hwan Ahn, Jieun Han, Young Seok Kim, Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, J
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 189. CrossRef - Smoking Increases the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Man Young Park, Eun Ju Cho, Su Jong Yu, Sang Gyune Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Young Seok Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3336. CrossRef - Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2023 Expert Consensus-Based Practical Recommendations of the Korean Liver Cancer Association
Yuri Cho, Jin Woo Choi, Hoon Kwon, Kun Yung Kim, Byung Chan Lee, Hee Ho Chu, Dong Hyeon Lee, Han Ah Lee, Gyoung Min Kim, Jung Suk Oh, Dongho Hyun, In Joon Lee, Hyunchul Rhim
Korean Journal of Radiology.2023; 24(7): 606. CrossRef - Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2023 expert consensus-based practical recommendations of the Korean Liver Cancer Association
Yuri Cho, Jin Woo Choi, Hoon Kwon, Kun Yung Kim, Byung Chan Lee, Hee Ho Chu, Dong Hyeon Lee, Han Ah Lee, Gyoung Min Kim, Jung Suk Oh, Dongho Hyun, In Joon Lee, Hyunchul Rhim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 241. CrossRef - Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2023 Expert consensus-based practical recommendations of the Korean Liver Cancer Association
Yuri Cho, Jin Woo Choi, Hoon Kwon, Kun Yung Kim, Byung Chan Lee, Hee Ho Chu, Dong Hyeon Lee, Han Ah Lee, Gyoung Min Kim, Jung Suk Oh, Dongho Hyun, In Joon Lee, Hyunchul Rhim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(3): 521. CrossRef - Classification of microvascular invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with prognosis and magnetic resonance imaging
Yoon Jung Hwang, Jae Seok Bae, Youngeun Lee, Bo Yun Hur, Dong Ho Lee, Haeryoung Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(3): 733. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma using Sonazoid: a comprehensive review
Woo Kyoung Jeong
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 272. CrossRef - The Current Evidence of Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Won Il Jang, Sunmi Jo, Ji Eun Moon, Sun Hyun Bae, Hee Chul Park
Cancers.2023; 15(20): 4914. CrossRef - Clinical outcome of surgical resection for multifocal T2-T3 hepatocellular carcinoma up to 3 nodules: a comparative analysis with a single nodule
Sehyeon Yu, Hye-Sung Jo, Young-Dong Yu, Yoo jin Choi, Dong-Sik Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 377. CrossRef - Sonazoid contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: strengths and shortcomings
Sung Won Lee, Min Kyu Kang, Xiang Zhang
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 238. CrossRef - Sequential regorafenib or nivolumab therapy in recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma with sorafenib failure in liver transplant patients does not improve prognosis
Jieun Kwon, Jongman Kim, Jinsoo Rhu, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
Annals of Liver Transplantation.2023; 3(2): 104. CrossRef - Concurrent nivolumab and external beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A phase 2 study
Bo Hyun Kim, Hee Chul Park, Tae Hyun Kim, Young-Hwan Koh, Jung Yong Hong, Yuri Cho, Dong Hyun Sinn, Boram Park, Joong-Won Park
JHEP Reports.2023; : 100991. CrossRef - Regular Alpha-Fetoprotein Tests Boost Curative Treatment and Survival for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients in an Endemic Area
Joo Hyun Oh, Jonghyun Lee, Eileen L. Yoon, Soung Won Jeong, Soon Sun Kim, Young Eun Chon, Sang Bong Ahn, Dae Won Jun
Cancers.2023; 16(1): 150. CrossRef - Adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma
Arndt Vogel, Robert C. Grant, Tim Meyer, Gonzalo Sapisochin, Grainne M. O’Kane, Anna Saborowski
Hepatology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Contrast-enhanced US for HCC: Finally out from the waiting list?

Review Article
- Liquid biopsy for early detection and therapeutic monitoring of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Eun-Ji Choi, Young-Joon Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):103-114. Published online September 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.09.08
- 4,252 Views
- 148 Downloads
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
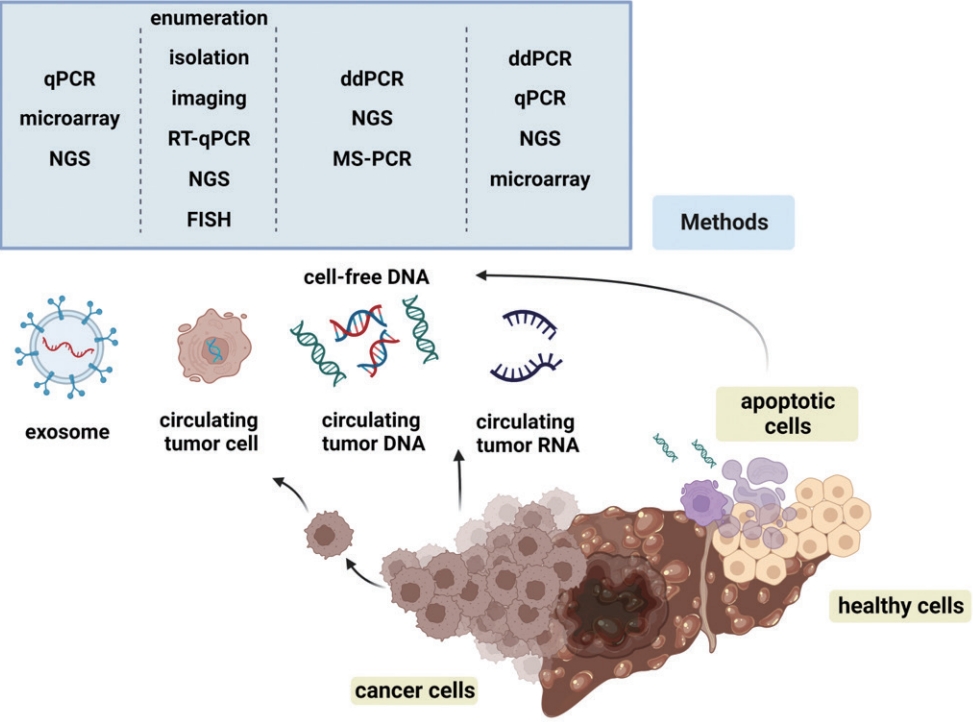
Supplementary Material - Advances in our knowledge of the molecular characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have enabled significant progress in the detection and therapeutic prediction of HCC. As a non-invasive alternative to tissue biopsy, liquid biopsy examines circulating cellular components such as exosomes, nucleic acids, and cell-free DNA found in body fluids (e.g., urine, saliva, ascites, and pleural effusions) and provides information about tumor characteristics. Technical advances in liquid biopsy have led to the increasing adoption of diagnostic and monitoring applications for HCC. This review summarizes the various analytes, ongoing clinical trials, and case studies of United States Food and Drug Administrationapproved in vitro diagnostic applications for liquid biopsy, and provides insight into its implementation in managing HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomarcatori tumorali: tra diagnostica clinica e medicina di precisione
Rossana FRANZIN
La Rivista Italiana della Medicina di Laboratorio.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - 16S rRNA Next-Generation Sequencing May Not Be Useful for Examining Suspected Cases of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
Chan Jin Yang, Ju Sun Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Keun Woo Park, Jina Yun, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(2): 289. CrossRef - Korean urobiome platform (KUROM) study for acute uncomplicated sporadic versus recurrent cystitis in women: Clinical significance
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Hee Bong Shin, Ji Eun Moon, Sul Hee Lee, Hyemin Jeong, Hee Jo Yang, Woong Bin Kim, Kwang Woo Lee, Jae Heon Kim, Young Ho Kim
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2024; 65(4): 378. CrossRef - Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: a large-scale multicenter study
Sun Hong Yoo, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Han-Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim, Do Seon Song, Seong Hee Kang, Moon Young Kim, Young-Hwan Ahn, Jieun Han, Young Seok Kim, Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, J
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 189. CrossRef - Correspondence on Letter regarding “Long-term prognosis and the need for histologic assessment of chronic hepatitis B in the serological immune tolerant phase”
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(2): 513. CrossRef - Exploring the Role of Circulating Cell-Free RNA in the Development of Colorectal Cancer
Chau-Ming Kan, Xiao Meng Pei, Martin Ho Yin Yeung, Nana Jin, Simon Siu Man Ng, Hin Fung Tsang, William Chi Shing Cho, Aldrin Kay-Yuen Yim, Allen Chi-Shing Yu, Sze Chuen Cesar Wong
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(13): 11026. CrossRef
- Biomarcatori tumorali: tra diagnostica clinica e medicina di precisione

Case Report
- Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma that was successfully treated with surgical resection: a case report
- Seong Kyun Na
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):178-182. Published online June 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.06.10
- 2,575 Views
- 72 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma (FLHCC) is a rare malignant hepatic cancer with characteristics that differ from those of typical hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Unlike conventional HCC, FLHCC is common in young patients without any underlying liver disease and is known to be associated with a unique gene mutation. This cancer type is rare in Asia, with only a few cases being reported in Korea. We report a case of FLHCC in a young woman that successfully underwent surgical resection. The efficacy of alternative treatments, such as transarterial chemoembolization or systemic chemotherapies, has not yet been established. To conclude, early diagnosis and appropriate surgical resection are important for the treatment of FLHCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fibrolamellar Hepatocellular Carcinoma (FLHCC) in a Young Patient Presenting With Nausea and Vomiting After a Greasy Meal
Mohamed Ismail , Sahiba Singh, Menna-Allah Elaskandrany , David s Kim, Yazan Abboud, Michael Bebawy, Abena Oduro, Ritik mahaveer Goyal, Omar Mohamed , Weizheng Wang
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Fibrolamellar Hepatocellular Carcinoma (FLHCC) in a Young Patient Presenting With Nausea and Vomiting After a Greasy Meal

Review Article
- Combination of interventional oncology local therapies and immunotherapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Dong-Hyun Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):93-102. Published online April 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.28
- 6,088 Views
- 181 Downloads
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
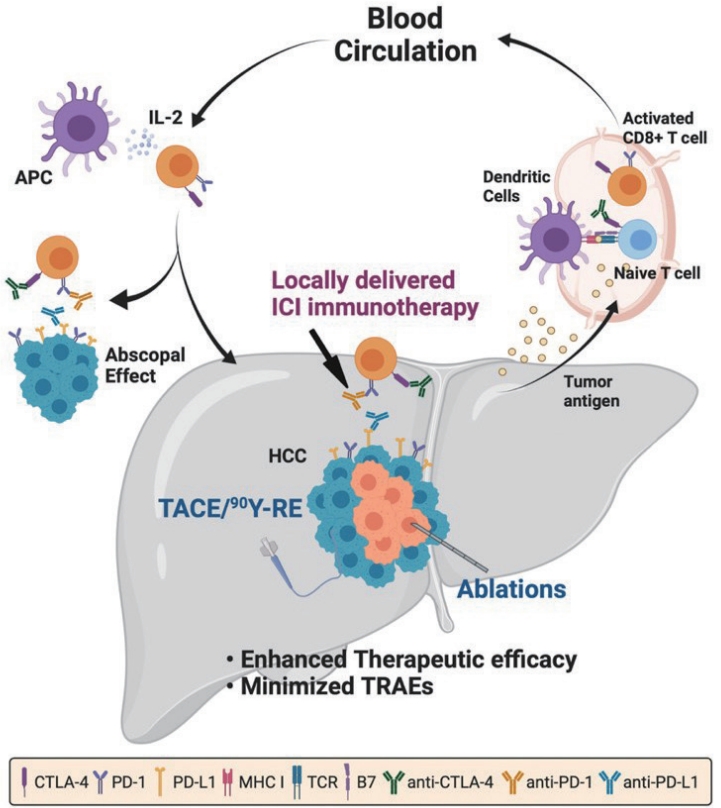
PDF - Interventional oncology (IO) local therapies of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can activate anti-cancer immunity and it is potentially leading to an anti-cancer immunity throughout the body. For the development of an effective HCC treatment regime, great emphasis has been dedicated to different IO local therapy mediated immune modulation and possible combinations with immune checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. In this review paper, we summarize the status of combination of IO local therapy and immunotherapy, as well as the prospective role of therapeutic carriers and locally administered immunotherapy in advanced HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reduced-Dose or Discontinuation of Bevacizumab Might Be Considered after Variceal Bleeding in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab: Case Reports
Kyeong-Min Yeom, Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(1): 157. CrossRef - CT-guided high dose rate brachytherapy can induce multiple systemic proteins of proliferation and angiogenesis predicting outcome in HCC
Lukas Salvermoser, Shraga Nahum Goldberg, Marianna Alunni-Fabbroni, Philipp Maximilian Kazmierczak, Moritz Nikolaus Gröper, Jan Niklas Schäfer, Elif Öcal, Tanja Burkard, Stefanie Corradini, Najib Ben Khaled, Agnese Petrera, Moritz Wildgruber, Jens Ricke,
Translational Oncology.2024; 43: 101919. CrossRef - Complications of immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 9. CrossRef - Syngeneic N1-S1 Orthotopic Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Sprague Dawley Rat for the Development of Interventional Oncology-Based Immunotherapy: Survival Assay and Tumor Immune Microenvironment
Bongseo Choi, Jason Pe, Bo Yu, Dong-Hyun Kim
Cancers.2023; 15(3): 913. CrossRef - Preclinical Development and Validation of Translational Temperature Sensitive Iodized Oil Emulsion Mediated Transcatheter Arterial Chemo‐Immuno‐Embolization for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Heegon Kim, Bongseo Choi, Samdeep K. Mouli, Hyunjun Choi, Kathleen R. Harris, Laura M. Kulik, Robert J. Lewandowski, Dong‐Hyun Kim
Advanced Healthcare Materials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Current Evidence of Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Won Il Jang, Sunmi Jo, Ji Eun Moon, Sun Hyun Bae, Hee Chul Park
Cancers.2023; 15(20): 4914. CrossRef - Inducing the Abscopal Effect in Liver Cancer Treatment: The Impact of Microwave Ablation Power Levels and PD-1 Antibody Therapy
Changli Liao, Guiyuan Zhang, Ruotong Huang, Linyuan Zeng, Bin Chen, Haitao Dai, Keyu Tang, Run Lin, Yonghui Huang
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(12): 1672. CrossRef
- Reduced-Dose or Discontinuation of Bevacizumab Might Be Considered after Variceal Bleeding in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab: Case Reports


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter