Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Liver Cancer > Volume 22(2); 2022 > Article
-
Review Article
Combination of interventional oncology local therapies and immunotherapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma -
Dong-Hyun Kim1,2,3,4

-
Journal of Liver Cancer 2022;22(2):93-102.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.28
Published online: April 22, 2022
1Department of Radiology, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL, USA
2Department of Biomedical Engineering, McCormick School of Engineering, Evanston, IL, USA
3Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center, Chicago, IL, USA
4Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA
-
Corresponding author: Dong-Hyun Kim Department of Radiology, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, 633 Clark St, Evanston, IL 60208, USA
Tel. +1-312-926-3279, Fax. +1-312-926-5991 E-mail: dhkim@northwestern.edu
Copyright © 2022 The Korean Liver Cancer Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 6,085 Views
- 181 Downloads
- 7 Citations
Abstract
- Interventional oncology (IO) local therapies of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can activate anti-cancer immunity and it is potentially leading to an anti-cancer immunity throughout the body. For the development of an effective HCC treatment regime, great emphasis has been dedicated to different IO local therapy mediated immune modulation and possible combinations with immune checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. In this review paper, we summarize the status of combination of IO local therapy and immunotherapy, as well as the prospective role of therapeutic carriers and locally administered immunotherapy in advanced HCC.
- Most systemic and regional therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) offer palliation rather than cure. Systemic chemotherapy offers limited survival benefit 1,2. The first line systemic sorafenib therapy has shown less than 1 year median survival time and the tumor response rate of less than 5%. Local ablation therapies, including thermal and chemical ablation, have limited efficacy with significant recurrence 3,4. Representatively, the 5-year overall survival (OS) of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) has been reported as 40.1-86.0% 5,6, but recurrence after ablation of early-stage HCC occurs in up to 60-85% of patients by 5 years 7. Other treatment options include catheter-directed therapies, such as transcatheter arterial embolization, transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), and 90Y (yttrium)-radioembolization (90Y-RE) 8. Catheter directed therapies improve liver cancer patient survival but the overall prognosis of these patients remains poor with potential metastasis 9,10. The overall median survival of the catheter directed therapies is about 8.0-30.0 months 11. As demonstrated promising immuno-therapeutic outcomes in various types of tumors such as melanoma, lung cancer and renal cell carcinoma and so on 12, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) immunotherapy have emerged as an effective and promising treatment for HCC 13,14. Currently, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved ICIs have been being evaluated for the treatment of HCC in clinical trials (Table 1). Nivolumab (programmed cell death protein-1, PD-1) ICI was approved for the treatment of advanced HCC patients after sorafenib treatment by FDA with an accelerated process. FDA also granted the use of pembrolizumab for the HCC with a clinical result of 20% objective tumor remission rate and prolonged survival. However, following this FDA approvals, phase III studies of single-agent nivolumab (CheckMate 459) and pembrolizumab (KEYNOTE-240) in the first line and second-line settings, respectively, did not meet their primary overall survival end points 14,15. Nivolumab monotherapy was voluntarily withdrawn from the US market. Unique immune suppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) of HCC might be a significant challenge to achieve satisfactory therapeutic efficacy level of ICI monotherapies. Indeed, TME of HCC is dominated by various immunosuppressive cells including macrophages (Kupffer cells), monocyte-derived macrophages, regulatory T (Treg) cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and signals that foster immunosuppressive roles implicated in HCC immune evasion 16.
- Additional therapeutics which can convert immune suppressive TME in HCC are required. Recent studies revealed that the response to PD-1/programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) ICI immunotherapy significantly relies on a pre-existing immune status. Various immunogenic interventional oncology (IO) local therapies such as RFA, cryoablation, percutaneous ethanol ablation, irreversible electroporation, TACE, 90Y-RE and so on that can overturn the immune suppressive TME of HCC have been actively investigated in clinical trials. However, finding optimal synergistic combination and managing the treatment-related adverse effects (TRAEs) or immune-related adverse effects (irAEs) are the main challenges. More understanding on immune response of IO local therapies and subsequent evaluation for the synergistic combination with ICI immunotherapies are required. Development of new therapeutic regimens with advanced image guide technique and therapeutic delivery technologies will be imperative tasks for advancing immunotherapy for the treatment of HCC. Recent development of various multifunctional carriers and locally administered immunotherapy will allow enhanced immunotherapy of HCC. Here we are summarizing recent progress of combination of IO local therapies and ICI immunotherapy. Future direction and potential role of therapeutic carriers and local combination immunotherapy for an advanced immuno-therapeutic of HCC will be discussed.
INTRODUCTION
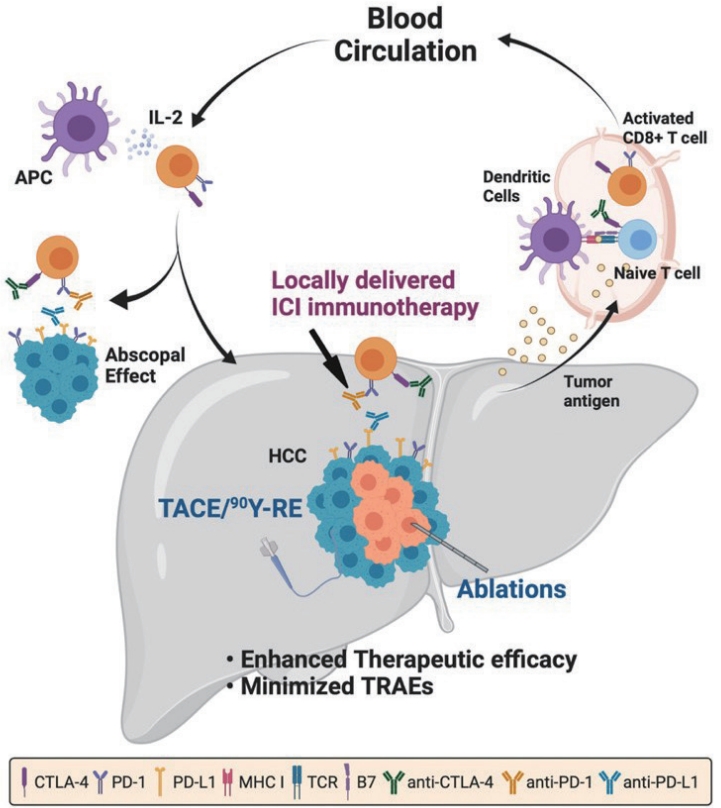
- IO local therapies treating the primary tumor induces the shrinkage of untreated distant tumors as known as abscopal effect. The immunogenicity of IO local therapies can activate antigen presenting cells (APCs) being recognized by the dendritic cells and it is potentially activating an anti-cancer immunity throughout the body. Indeed, the investigation of various IO local therapy mediated immune modulation and anti-cancer immunity are now in great interest for the potential combination with ICI immunotherapy. Such local tumoral accessibility of clinical IO therapies makes HCC ideal for the local interventions that can cause immunogenic cell death (ICD) or local immune conversion in immune suppressive TME of HCC.
- ICD induced by IO local therapies commonly can convert the immune suppressive TME in HCC. ICD releases the tumor-associated antigens, high mobility group box 1, and adenosine triphosphate to recruit the various immune cells to TME and expresses the surface calreticulin as a “eat-me” signal. Circulating phagocytic APCs accumulate to immunogenic TME by ICD and subsequently synergize with ICI cancer immunotherapy (Fig. 1) 17. Therefore, various kinds of clinical trials in a different combinations of immunogenic IO local therapy and ICI immunotherapy are on-going to improve the overall therapeutic outcomes and survival benefit versus monotherapy 18-20. Recently, Duffy et al. showed enhanced cytotoxic lymphocytes (CTLs) accumulation in the tumor after a synergistic combination of anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (aCTLA-4) immunotherapy and various ablation techniques such as TACE, RFA, and cryoablation 21,22. Partial tumor ablation with RFA or TACE in advanced HCC patients receiving systemic tremelimumab resulted in a response rate of 26% and a disease control rate of 89%, with 45% of the stabilizations lasting longer than 6 months, and an overall survival of 12.3 months 23. These encouraging data have triggered many different combinational clinical trials in which systemically administered ICIs are given in combination with IO local therapies of ablations, TACE or TARE. Percutaneous ablation (KEYNOTE-937 [NCT03867084], EMRALD-2 [NCT03847428], CHECKMATE-9DX [NCT03383458], IMBRAVE-050 [NCT04102098], and so on), TACE (EMRALD-1 [NCT03778957], CHECKMATE-74W [NCT04340193], TACE3 [NCT04268888], and so on), and ROWAN [NCT05063565], and so on) are primarily ongoing to evaluate the various forms of combination IO local therapies and ICI immunotherapy. Additional information is added in Table 2 and more details can be found in other review papers 11,24,25. Indeed, combination of IO local therapy and ICI immunotherapy is an emerging strategy to overcome current challenges of both IO local therapies and immunotherapies. More effort to develop the image guided combination IO local therapy and ICI immunotherapy are urgently required to establish optimal benefit of combination IO local therapy and immunotherapy in overall therapeutic outcomes and safety.
COMBINATION OF IMMUNOGENIC IO LOCAL THERAPY AND SYSTEMIC ICI IMMUNOTHERAPY
- Combination of IO local therapy and ICI immunotherapy is promising for enhancing the therapeutic efficacy. However, current standard approaches to combine IO local therapies with systemically administered ICI immunotherapy are initiated based on minimum data with a shortage of clinical information. Most recent data showed that systemically administered ICI immunotherapy can induce therapeutic resistance/ignorance and severe side effects involved with autoimmunity. When it combined with IO local therapies, additional TRAEs can be occurred and ended up being moderate therapeutic outcomes. Severe side effect (Grade 3 or 4) incidence has been reported as high as 90% in the combination of systemic ICIs immunotherapies following an IO local therapy 26.
- 1. Pharmacokinetics of ICIs
- Current ICI immunotherapies are performed with systemic administration of anti-CTLA4, anti-PD-1 (aPD-1) or anti-PD-L1 (aPD-L1) immunoglobulin G (IgG) based monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). Those ICI mAbs may not be effective to achieve an anti-cancer immune response with IO local therapies in immune-suppressive HCC 27-29. Upon systemic administration of mAb, non-specific binding and short circulation time of ICI mAbs can affect the therapeutic efficacy 30. Current ICI mAbs are mostly humanized or human IgG antibodies. The pharmacokinetics of ICI mAbs are similar with other therapeutic mAbs in the systemic administration. Systemically administrated ICI mAbs circulate in the central vasculature and are distributed to peripheral tissues and tumors. During the circulation, off-target binding with IC molecules of normal tissues and proteolytic clearance limits the tumor specific ICI mAb dose 30-32.
- 2. TRAEs
- The limited pharmacokinetics of ICI mAbs can induce an excessive immune response after combination of ICI immunotherapy and IO local therapy 33. These symptoms are mostly accompanied with the pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, myocarditis, as a category of irAEs 34. Steroid-based treatments are commonly given to suppress the immune responses. Those irAEs and concurrent immunosuppressive treatment subsequently reduces the efficacy of immunotherapy by increasing incident rate and mortality 35. In the clinical data, 85% patients treated with ipilimumab (aCTLA-4) ICI immunotherapy in monotherapy experienced irAEs 36. 26% patient treated with PD-1 ICIs (nivolumab, pembrolizumab, and cemiplimab), and 14% patient treated with PD-L1 ICIs (atezolizumab, avelumab, and durvalumab) showed irAEs 37. The combination of ICIs with IO local therapy for better therapeutic response led to more severe incidence of irAEs (93%) 38-41. The combination ICI immunotherapies and IO local therapy might need additional consideration of additive side effect of IO local therapies. Unfortunately, once irAEs is occurred with autoimmunity, discontinued ICI immunotherapies might not be resumed with immunological memory effect 42. Intensive investigation of minimizing TRAEs including irAEs is required to find the synergistic combination of IO local therapy and ICI immunotherapy.
CURRENT CHALLENGES ON COMBINATION IO LOCAL THERAPY AND ICI IMMUNOTHERAPY
- Development of new strategy to enhance targeting and controlled release of ICI molecules at desired immune activation sites is the key to increase the response rates and control the TRAEs of combination IO local therapy and ICI immunotherapy. Multifunctional carriers including injectable therapeutic carriers, nanocarriers, and local administration routes may overcome physical TME barriers and enhance the controlled immune modulation for the treatment of HCC.
- 1. ICI delivery carriers
- Drug delivery carriers have shown excellence in improving the pharmacokinetics of anti-cancer agents. Currently, 45 different nano-drug carrier-formulations have been approved for the clinical uses by the FDA, and over 80 clinical trials are on-going to evaluate the potential clinical translation of nanocarriers 43. Nanocarriers basically provides high surface area where can load various therapeutic molecules and the size scale is compatible with cellular component allowing easy penetration. An enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect using the characteristic high permeability of tumor vessels and the retention effect in tumors by poor lymphatic clearance demonstrated the potential of nanocarriers for delivering ICI mAbs 44. Active targeting utilizing tumor specific molecules can further increase targeting efficiency of nanocarriers. In preclinical studies, nanocarriers have been suggested for the delivery of various immunotherapies, as a form of nano-immunotherapy. For ICI cancer immunotherapy, nanocarriers incorporating ICI molecules have suggested to improve the therapeutic efficacy of ICI immunotherapy. Many preclinical studies have demonstrated the enhanced targeted delivery of ICI and sustained ICI release of ICI loaded nanocarriers 45-48. Various ICI mAb conjugated nanocarriers have shown enormous potential to improve the efficacy of ICI immunotherapy and combinational ICI immunotherapy 49-51. However, ICI mAb-nanocarriers often lose the available Fab which can bind with immune checkpoints and at the same time, FcγR of ICI mAb are exposed outside that causes rapid clearance with the FcγR mediated endocytosis 52-55. More efforts to improve the ICI mAbs loading protocol is necessary for the high affinity and specificity of ICI mAb-nanocarrier 56. Beyond the nanocarriers, injectable carriers are a promising approach to deliver and release ICI locally and combine additional IO local therapy together. Lipiodol, iodinated ethyl esters of fatty acids from poppy seed oil, exhibits transient and plastic embolic effects and facilitates localized delivery of doxorubicin to HCC during cTACE of HCC 57,58. The development of lipiodol-based formulations or various injectable gels that can enhance targeted ICI delivery may allow an opportunity for safe incorporation of potent ICI immunomodulatory agents with IO local therapies.
- 2. Hepatic intra-arterial delivery of ICIs
- Current limitations relying on systemic administration of ICI immunotherapy and ICI loaded carriers might be overcome with image guided local ICI administration route 59. Image guided local delivery including intra-tumoral injection and tumor associated vascular injection may result in high doses of ICI combination therapy in local tumor and TME without systemic exposure of toxic therapeutics. HCC receives most of their blood supply from hepatic arteries unlike the normal liver. Even hepatic metastases >3 mm derive 80-100% of their blood supply from the hepatic arterial rather than the portal venous circulation 60. Moreover, the density of arterial vessels around a metastatic lesion is estimated to be 3 times more than in normal liver tissue 61. Thus, if ICI molecules or ICI loaded carriers are infused into the hepatic artery, the infused dose preferentially reaches the tumor as opposed to the normal liver. Currently, ICI agents, lipiodol, gel-form, microspheres, nanocarriers and so on have been tested for the hepatic intra-arterial infusion for high local delivery of therapeutics in HCC 46,62-68. During the IA infusion, MRI, CT and X-ray angiography are used to practice tumor specific hepatic arterial infusion, monitor the procedure, and confirm the distribution of infused therapeutics. A phase III clinical trial (NCT03949231) is ongoing to compare the effects of IA infusion and IV administration of PD-1/PD-L1 ICIs on the survival benefit of patients with advanced liver cancer, including ORR, DCR, median survival time, and safety. Clinical trials (NCT04945720 and NCT04191889) also are testing IA infused chemotherapy and aPD-1/aPD-L1 (durvaluamab or camrelizumab) mixture for the efficacy and safety in advanced HCC. A clinical trial (NCT02850536) also testing hepatic arterials infusion of CAR-T for CEA-Expressing Liver Metastases. Another clinical trial (NCT04823403) is investigating the optimized dosage of hepatic IA administration of Ipilimumab in combination with IV administered nivolumab for advanced HCC (HIPANIV).
- 3. Percutaneous intra-tumoral delivery of ICIs
- Percutaneous intra-tumoral therapeutic delivery also plays a key role in the management of HCC. Percutaneous intratumoral ethanol injection is a well-established technique for the treatment of HCC 69. Ultrasound real-time guidance of intratumoral ethanol injection allows faster procedure, precise centering of the needle in the tumor target, and continuous monitoring of the injection. This local injection is conveniently performed under local anesthesia on an out-patient basis and the treatment sessions and schedule can be flexible according to the distribution of the injected ethanol within the tumor and the prognosis. Several clinical trials of local intratumoral administration of immunotherapy are on-going. Intratumorally injected aPD-1 and aCTLA-4 ICIs (NCT03058289) are being tested in HCC. A phase 1 clinical trials are testing tumor targeted injected TLR9 agonist CpG oligonucleotides and OX40 agonist (NCT03831295). Phase I-II study (NCT03792724) evaluates the safety and activity of intratumoral urelumab combined with systemic nivolumab in patients with advanced solid tumors. Additionally, intracavitary infusions 70,71 and the direct lymph node infusion could be available for the local delivery of toxic immune adjuvants.
LOCAL TUMOR TARGETED COMBINATION IO LOCAL THERAPY AND ICI IMMUNOTHERAPY
- Various clinical trials evaluating the combination of IO local therapies and ICI immunotherapy has been tested and promising interim data has been released 11. When the IO local therapies are combined with ICI immunotherapy, the median survival, ORR, PFS are surpassing those indications of IO local therapy alone. It is implicating the rationale for the combination of IO local therapy and ICI immunotherapy can be synergistic (Fig. 1). Although additional robust clinical evidence is further required, the development of various synergistic combination strategies should be investigated in a consideration of TRAEs. Since each IO local therapy and ICI monotherapy itself showed high percentage of complications, new approaches that can minimize side effect of the combination IO local therapy and ICI immunotherapy are urgently required. Specially, those side effect can easily impair liver functions during the HCC treatment, lowered side effect during the combination will be an important consideration. Developed multifunctional therapeutic carriers and effective local delivery routes can critically contribute to the safe and effective combination of IO local therapy and ICI immunotherapy. Carriers mediated ICI delivery, controlled ICI release, and immune modulation have demonstrated the effectiveness to overcome the ICI therapeutic tumor resistance, ignorance, and off-target side effect (irAEs). Additionally, the multifunctionality of carriers in imaging and therapeutic delivery have shown excellent potential for improving the interventional procedures. Development of delivery route for ICI immunotherapy or ICI loaded carriers is another essential component to further enhance the therapeutic efficacy of combination IO local therapy and ICI immunotherapy. Most of ICI immunotherapy has been tested with systemic administration. The efficacy evaluation of local administration of ICI immunotherapy comparing to systemic administration of ICI has been initiated recently. Established hepatic artery local administration and percutaneous intra-tumoral administration routes in HCC will allow rapid development and optimization of local ICI immunotherapy and the combination of IO local therapy and ICI immunotherapy. During the process, current ICI dosage regime should be revised for each administration routes and in-depth biodistribution studies are further needed. Additionally, ICI residence time and following time-dependent immunity changes after the locally administered combination immunotherapy should be investigated and compared with systemic administration of ICI immunotherapy. Optimal sequencing and interval of IO local therapies and ICI immunotherapy in the combination also need to be investigated. Lastly, it is critical to develop key biomarkers that can identify immune response and therapeutic response to the combination of IO local therapy and ICI immunotherapy. Considering the complexity of the immune suppressive TME and anti-cancer immunity in HCC, substantial effort is required to integrate multifunctional carriers and image guided local delivery technique into the novel combination of IO local therapy and ICI immunotherapy strategies for treating various stages of HCC safely and effectively.
PERSPECTIVES
Acknowledgments
-
Conflicts of Interest
D.H.K, a contributing editor of the Journal of Liver Cancer, was not involved in the editorial evaluation or decision to publish this article.
-
Ethics Statement
This review was exempted from the IACUC or IRB.
-
Funding Statement
This work was mainly supported by grants R01CA218659 and R01EB026207 from the National Cancer Institute and National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering.
-
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during this study.
-
Author Contribution
Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Writing-original draft, Writing-review & editing, Approval of final manuscript: DHK.
Article information
- 1. Chow PK, Tai BC, Tan CK, Machin D, Win KM, Johnson PJ, et al. High-dose tamoxifen in the treatment of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Hepatology 2002;36:1221−1226.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Lai CL, Wu PC, Chan GC, Lok AS, Lin HJ. Doxorubicin versus no antitumor therapy in inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. A prospective randomized trial. Cancer 1988;62:479−483.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Ahmed M, Goldberg SN. Thermal ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2002;13:S231−S244.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Clark TW, Soulen MC. Chemical ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2002;13:S245−S252.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Vitale A, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Giannini EG, Vibert E, Sieghart W, Van Poucke S, et al. Personalized treatment of patients with very early hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2017;66:412−423.ArticlePubMed
- 6. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2018;69:182−236.ArticlePubMed
- 7. N'Kontchou G, Mahamoudi A, Aout M, Ganne-Carrié N, Grando V, Coderc E, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results and prognostic factors in 235 Western patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2009;50:1475−1483.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Ackerman NB. Experimental studies on the circulation dynamics of intrahepatic tumor blood supply. Cancer 1972;29:435−439.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Marelli L, Stigliano R, Triantos C, Senzolo M, Cholongitas E, Davies N, et al. Transarterial therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: which technique is more effective? A systematic review of cohort and randomized studies. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2007;30:6−25.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Biolato M, Marrone G, Racco S, Di Stasi C, Miele L, Gasbarrini G, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for unresectable HCC: a new life begins? Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2010;14:356−362.PubMed
- 11. Llovet JM, De Baere T, Kulik L, Haber PK, Greten TF, Meyer T, et al. Locoregional therapies in the era of molecular and immune treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;18:293−313.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Yarchoan M, Albacker LA, Hopkins AC, Montesion M, Murugesan K, Vithayathil TT, et al. PD-L1 expression and tumor mutational burden are independent biomarkers in most cancers. JCI Insight 2019;4:e126908.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Kudo M. Immune checkpoint blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2015;4:201−207.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. El-Khoueiry AB, Melero I, Crocenzi TS, Welling TH, Yau TC, Yeo WN, et al. Phase I/II safety and antitumor activity of nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): CA209-040. J Clin Oncol 2015;33 Suppl 15:LBA101. Article
- 15. Rizvi NA, Mazières J, Planchard D, Stinchcombe TE, Dy GK, Antonia SJ, et al. Activity and safety of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, for patients with advanced, refractory squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 063): a phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol 2015;16:257−265.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Ringelhan M, Pfister D, O'Connor T, Pikarsky E, Heikenwalder M. The immunology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Immunol 2018;19:222−232.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Krysko DV, Garg AD, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O, Agostinis P, Vandenabeele P. Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2012;12:860−875.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Lu J, Liu X, Liao YP, Salazar F, Sun B, Jiang W, et al. Nano-enabled pancreas cancer immunotherapy using immunogenic cell death and reversing immunosuppression. Nat Commun 2017;8:1811. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 19. Emens LA, Middleton G. The interplay of immunotherapy and chemotherapy: harnessing potential synergies. Cancer Immunol Res 2015;3:436−443.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, Crocenzi TS, Kudo M, Hsu C, et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017;389:2492−2502.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Xie C, Duffy AG, Mabry-Hrones D, Wood B, Levy E, Krishnasamy V, et al. Tremelimumab in combination with microwave ablation in patients with refractory biliary tract cancer. Hepatology 2019;69:2048−2060.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Duffy AG, Ulahannan SV, Makorova-Rusher O, Rahma O, Wedemeyer H, Pratt D, et al. Tremelimumab in combination with ablation in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2017;66:545−551.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Kudo M. Immuno-oncology therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: current status and ongoing trials. Liver Cancer 2019;8:221−238.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Sangro B, Sarobe P, Hervás-Stubbs S, Melero I. Advances in immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;18:525−543.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Liu Z, Liu X, Liang J, Liu Y, Hou X, Zhang M, et al. Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: current status and future prospects. Front Immunol 2021;12:765101. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Zhan C, Ruohoniemi D, Shanbhogue KP, Wei J, Welling TH, Gu P, et al. Safety of combined yttrium-90 radioembolization and immune checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2020;31:25−34.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Prieto J, Melero I, Sangro B. Immunological landscape and immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;12:681−700.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Greten TF, Wang XW, Korangy F. Current concepts of immune based treatments for patients with HCC: from basic science to novel treatment approaches. Gut 2015;64:842−848.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Tsuchiya N, Sawada Y, Endo I, Uemura Y, Nakatsura T. Potentiality of immunotherapy against hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:10314−10326.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Centanni M, Moes DJAR, Trocóniz IF, Ciccolini J, van Hasselt JGC. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Clin Pharmacokinet 2019;58:835−857.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Keizer RJ, Huitema AD, Schellens JH, Beijnen JH. Clinical pharmacokinetics of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Clin Pharmacokinet 2010;49:493−507.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Riley RS, June CH, Langer R, Mitchell MJ. Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2019;18:175−196.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 33. Friedman CF, Proverbs-Singh TA, Postow MA. Treatment of the immune-related adverse effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors: a review. JAMA Oncol 2016;2:1346−1353.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, Bingham CO 3rd, Brogdon C, Dadu R, et al. Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer 2017;5:95. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Wang DY, Salem JE, Cohen JV, Chandra S, Menzer C, Ye F, et al. Fatal toxic effects associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol 2018;4:1721−1728.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Horvat TZ, Adel NG, Dang TO, Momtaz P, Postow MA, Callahan MK, et al. Immune-related adverse events, need for systemic immunosuppression, and effects on survival and time to treatment failure in patients with melanoma treated with ipilimumab at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. J Clin Oncol 2015;33:3193−3198.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 37. Weber JS, Hodi FS, Wolchok JD, Topalian SL, Schadendorf D, Larkin J, et al. Safety profile of nivolumab monotherapy: a pooled analysis of patients with advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol 2017;35:785−792.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Wolchok JD, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Rutkowski P, Grob JJ, Cowey CL, et al. Overall survival with combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med 2017;377:1345−1356.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 39. Hodi FS, Chesney J, Pavlick AC, Robert C, Grossmann KF, McDermott DF, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab versus ipilimumab alone in patients with advanced melanoma: 2-year overall survival outcomes in a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 2016;17:1558−1568.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 40. Hellmann MD, Paz-Ares L, Bernabe Caro R, Zurawski B, Kim SW, Carcereny Costa E, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2019;381:2020−2031.ArticlePubMed
- 41. Larkin J, Hodi FS, Wolchok JD. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med 2015;373:1270−1271.Article
- 42. Nakajima EC, Lipson EJ, Brahmer JR. Challenge of rechallenge: when to resume immunotherapy following an immune-related adverse event. J Clin Oncol 2019;37:2714−2718.ArticlePubMed
- 43. Choi YH, Han HK. Nanomedicines: current status and future perspectives in aspect of drug delivery and pharmacokinetics. J Pharm Investig 2018;48:43−60.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 44. Kim DH. Image-Guided Cancer Nanomedicine. J Imaging 2018;4:18. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 45. Yu B, Zhang W, Kwak K, Choi H, Kim DH. Electric pulse responsive magnetic nanoclusters loaded with indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor for synergistic immuno-ablation cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020;12:54415−54425.ArticlePubMed
- 46. Choi B, Choi H, Yu B, Kim DH. Synergistic local combination of radiation and anti-programmed death ligand 1 immunotherapy using radiation-responsive splintery metallic nanocarriers. ACS Nano 2020;14:13115−13126.ArticlePubMed
- 47. Yu B, Choi B, Li W, Kim DH. Magnetic field boosted ferroptosis-like cell death and responsive MRI using hybrid vesicles for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun 2020;11:3637. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 48. Choi B, Jung H, Yu B, Choi H, Lee J, Kim DH. Sequential MR imageguided local immune checkpoint blockade cancer immunotherapy using ferumoxytol capped ultralarge pore mesoporous silica carriers after standard chemotherapy. Small 2019;15:e1904378.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 49. Wang D, Wang T, Yu H, Feng B, Zhou L, Zhou F, et al. Engineering nanoparticles to locally activate T cells in the tumor microenvironment. Sci Immunol 2019;4:e. aau6584.Article
- 50. Bu J, Nair A, Iida M, Jeong WJ, Poellmann MJ, Mudd K, et al. An avidity-based PD-L1 antagonist using nanoparticle-antibody conjugates for enhanced immunotherapy. Nano Lett 2020;20:4901−4909.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 51. Jiang CT, Chen KG, Liu A, Huang H, Fan YN, Zhao DK, et al. Immunomodulating nano-adaptors potentiate antibody-based cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun 2021;12:1359. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 52. Wilhelm S, Tavares AJ, Dai Q, Ohta S, Audet J, Dvorak HF, et al. Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours. Nat Rev Mater 2016;1:16014. Article
- 53. Blanco E, Shen H, Ferrari M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat Biotechnol 2015;33:941−951.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 54. Bertrand N, Grenier P, Mahmoudi M, Lima EM, Appel EA, Dormont F, et al. Mechanistic understanding of in vivo protein corona formation on polymeric nanoparticles and impact on pharmacokinetics. Nat Commun 2017;8:777. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 55. Desnoyer A, Broutin S, Delahousse J, Maritaz C, Blondel L, Mir O, et al. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies used in oncology: part 2, immune checkpoint inhibitor antibodies. Eur J Cancer 2020;128:119−128.ArticlePubMed
- 56. Yong KW, Yuen D, Chen MZ, Porter CJH, Johnston APR. Pointing in the right direction: controlling the orientation of proteins on nanoparticles improves targeting efficiency. Nano Lett 2019;19:1827−1831.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Kwak K, Yu B, Mouli SK, Larson AC, Kim DH. Sodium cholate bile acid-stabilized ferumoxytol-doxorubicin-lipiodol emulsion for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2020;31:1697−1705. e3.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 58. Park W, Cho S, Kang D, Han JH, Park JH, Lee B, et al. Tumor microenvironment targeting nano-bio emulsion for synergistic combinational X-Ray PDT with oncolytic bacteria therapy. Adv Healthc Mater 2020;9:e1901812.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 59. Choi B, Kim DH. Multifunctional nanocarriers-mediated synergistic combination of immune checkpoint inhibitor cancer immunotherapy and interventional oncology therapy. Adv NanoBiomed Res 2021;1:100010. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 60. Lien WM, Ackerman NB. The blood supply of experimental liver metastases. II. A microcirculatory study of the normal and tumor vessels of the liver with the use of perfused silicone rubber. Surgery 1970;68:334−340.PubMed
- 61. Kennedy AS, Nutting C, Coldwell D, Gaiser J, Drachenberg C. Pathologic response and microdosimetry of (90)Y microspheres in man: review of four explanted whole livers. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2004;60:1552−1563.ArticlePubMed
- 62. Choi H, Choi B, Yu B, Li W, Matsumoto MM, Harris KR, et al. Ondemand degradable embolic microspheres for immediate restoration of blood flow during image-guided embolization procedures. Biomaterials 2021;265:120408. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 63. Ji J, Park WR, Cho S, Yang Y, Li W, Harris K, et al. Iron-oxide nanocluster labeling of clostridium novyi-NT spores for MR imaging-monitored locoregional delivery to liver tumors in rat and rabbit models. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2019;30:1106−1115. e1.ArticlePubMed
- 64. Cho S, Min NG, Park W, Kim SH, Kim DH. Janus microcarriers for magnetic field-controlled combination chemotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv Funct Mater 2019;29:1901384. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 65. Matsumoto MM, Kim DH, Larson AC, Mouli SK. Interventional nanotheranostics: advancing nanotechnology applications with IR. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2019;30:1824−1829. e1.ArticlePubMed
- 66. Gournaris E, Park W, Cho S, Bentrem DJ, Larson AC, Kim DH. Nearinfrared fluorescent endoscopic image-guided photothermal ablation therapy of colorectal cancer using dual-modal gold nanorods targeting tumor-infiltrating innate immune cells in a transgenic TS4 CRE/APC loxΔ468 mouse model. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019;11:21353−21359.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 67. Park W, Cho S, Ji J, Lewandowski RJ, Larson AC, Kim DH. Development and validation of sorafenib-eluting microspheres to enhance therapeutic efficacy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in a rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiol Imaging Cancer 2021;3:e200006.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 68. Park W, Kim SJ, Cheresh P, Yun J, Lee B, Kamp DW, et al. Magneto mitochondrial dysfunction mediated cancer cell death using intracellular magnetic nano-transducers. Biomater Sci 2021;9:5497−5507.ArticlePubMed
- 69. Lencioni R, Cioni D, Crocetti L, Bartolozzi C. Percutaneous ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: state-of-the-art. Liver Transpl 2004;10(2 Suppl 1):S91−S97.Article
- 70. Adusumilli PS, Zauderer MG, Rusch VW, O'Cearbhaill RE, Zhu A, Ngai DA, et al. A phase I clinical trial of malignant pleural disease treated with regionally delivered autologous mesothelin-targeted CAR T cells: Safety and efficacy. Cancer Res 2019;79(Suppl 13): CT036.
- 71. Ishikawa W, Kikuchi S, Ogawa T, Tabuchi M, Tazawa H, Kuroda S, et al. boosting replication and penetration of oncolytic adenovirus by paclitaxel eradicate peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics 2020;18:262−271.ArticlePubMedPMC
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Reduced-Dose or Discontinuation of Bevacizumab Might Be Considered after Variceal Bleeding in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab: Case Reports
Kyeong-Min Yeom, Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(1): 157. CrossRef - CT-guided high dose rate brachytherapy can induce multiple systemic proteins of proliferation and angiogenesis predicting outcome in HCC
Lukas Salvermoser, Shraga Nahum Goldberg, Marianna Alunni-Fabbroni, Philipp Maximilian Kazmierczak, Moritz Nikolaus Gröper, Jan Niklas Schäfer, Elif Öcal, Tanja Burkard, Stefanie Corradini, Najib Ben Khaled, Agnese Petrera, Moritz Wildgruber, Jens Ricke,
Translational Oncology.2024; 43: 101919. CrossRef - Complications of immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 9. CrossRef - Syngeneic N1-S1 Orthotopic Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Sprague Dawley Rat for the Development of Interventional Oncology-Based Immunotherapy: Survival Assay and Tumor Immune Microenvironment
Bongseo Choi, Jason Pe, Bo Yu, Dong-Hyun Kim
Cancers.2023; 15(3): 913. CrossRef - Preclinical Development and Validation of Translational Temperature Sensitive Iodized Oil Emulsion Mediated Transcatheter Arterial Chemo‐Immuno‐Embolization for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Heegon Kim, Bongseo Choi, Samdeep K. Mouli, Hyunjun Choi, Kathleen R. Harris, Laura M. Kulik, Robert J. Lewandowski, Dong‐Hyun Kim
Advanced Healthcare Materials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Current Evidence of Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Won Il Jang, Sunmi Jo, Ji Eun Moon, Sun Hyun Bae, Hee Chul Park
Cancers.2023; 15(20): 4914. CrossRef - Inducing the Abscopal Effect in Liver Cancer Treatment: The Impact of Microwave Ablation Power Levels and PD-1 Antibody Therapy
Changli Liao, Guiyuan Zhang, Ruotong Huang, Linyuan Zeng, Bin Chen, Haitao Dai, Keyu Tang, Run Lin, Yonghui Huang
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(12): 1672. CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Download Citation
Download Citation
- Download Citation
- Close
- Related articles
-
- Complications of immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
- A multidisciplinary approach with immunotherapies for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
- The role of lenvatinib in the era of immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Liquid biopsy for early detection and therapeutic monitoring of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Deciphering and Reversing Immunosuppressive Cells in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma

 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION


 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter