Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Previous issues
Review Articles
- Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
- Sang Jin Kim, Jong Man Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):105-112. Published online September 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.03.17

- 5,428 Views
- 234 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traditionally, liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis is not recommended. However, with recent developments in locoregional therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma, more aggressive treatments have been attempted for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Recently, various studies on locoregional therapies for downstaging followed by living donor liver transplantation reported inspiring overall survival and recurrence-free survival of patients. These downstaging procedures included three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy, trans-arterial chemoembolization, stereotactic body radiation therapy, trans-arterial radioembolization, hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy and combinations of these therapies. Selection of the optimal downstaging protocol should depend on tumor location, biology and background liver status. The risk factors affecting outcome include pre-downstaging alpha-fetoprotein values, delta alpha-fetoprotein values, disappearance of portal vein tumor thrombosis on imaging and meeting the Milan criteria or not after downstaging. For hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis, downstaging procedure with liver transplantation in mind would be helpful. If the reaction of the downstaged tumor is good, liver transplantation may be performed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis confirmed on blind liver biopsy
Hun Kim, Tae Hoon Roh, Jun Seop Lee, Min Seong Kim, Beom Kyung Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 113. CrossRef - Refining MRI-based criteria for portal vein invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: improving sensitivity beyond portal vein tumor thrombosis
Jeongju Kim, Woo Kyoung Jeong, Jong Man Kim, Sang Yun Ha, Kyunga Kim
Abdominal Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction models of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver transplantation: A comprehensive review
Sang Jin Kim, Jong Man Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 739. CrossRef
- Metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis confirmed on blind liver biopsy

- Differences in radiotherapy application according to regional disease characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Chai Hong Rim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):113-123. Published online August 11, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.05.26
- 5,882 Views
- 107 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There are differences in opinion regarding the application of external beam radiotherapy in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Some major guidelines state that external beam radiotherapy is yet to attain a sufficient level of evidence. However, caution should be exercised when attempting to understand the clinical need for external beam radiotherapy solely based on the level of evidence. Previously, external beam radiotherapy had low applicability in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma before computed tomography-based planning was popularized. Modern external beam radiotherapy can selectively target tumor cells while sparing normal liver tissues. Recent technologies such as stereotactic body radiotherapy have enabled more precise treatment. The characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma differ significantly according to the regional etiology. The main cause of hepatocellular carcinoma is the hepatitis B virus. It is commonly diagnosed as a locally advanced tumor but with relatively preserved hepatic function. The majority of these hepatocellular carcinoma cases are found in the East Asian population. Hepatocellular carcinoma caused by hepatitis C virus or other benign hepatitis tends to be diagnosed as a less locally aggressive tumor but with deteriorated liver function. The Western world and Japan tend to have patients with such causes. External beam radiotherapy has been more commonly performed for the former, although the use of external beam radiotherapy in the latter might have more concerns with regard to hepatic toxicity. This review discusses the above subjects along with perspectives regarding external beam radiotherapy in recent guidelines.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Meta-Analysis and International Stereotactic Radiosurgery Society Practice Guidelines
Sun Hyun Bae, Seok-Joo Chun, Joo-Hyun Chung, Eunji Kim, Jin-Kyu Kang, Won Il Jang, Ji Eun Moon, Isaure Roquette, Xavier Mirabel, Tomoki Kimura, Masayuki Ueno, Ting-Shi Su, Alison C. Tree, Matthias Guckenberger, Simon S. Lo, Marta Scorsetti, Ben J. Slotman
International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics.2024; 118(2): 337. CrossRef - Will the collaboration of surgery and external radiotherapy open new avenues for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis?
Jung Wan Choe, Hye Yoon Lee, Chai Hong Rim
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2022; 28(7): 704. CrossRef
- Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Meta-Analysis and International Stereotactic Radiosurgery Society Practice Guidelines

- Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: consideration for selecting second-line treatment
- Bo Hyun Kim, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):124-138. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.23
- 4,422 Views
- 120 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
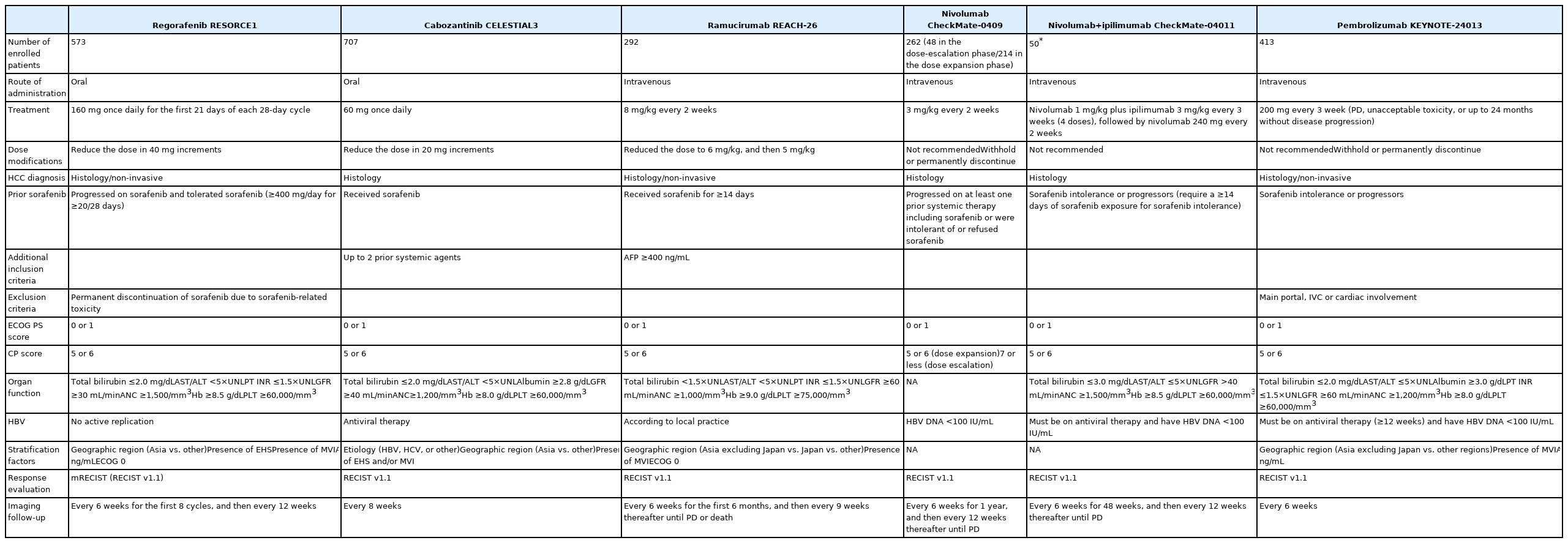
PDF - Several molecular-targeted agents have been tested as first- or second-line therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) but failed to improve clinical outcomes; sorafenib has been the only approved systemic agent for treating HCC for almost 10 years. Regorafenib resulted in a significant improvement in overall survival and thus was approved for HCC patients previously treated with sorafenib. Subsequently, cabozantinib and ramucirumab demonstrated superior overall survival compared with placebos in phase III clinical trials. Immune checkpoint inhibitors such as nivolumab with or without ipilimumab and pembrolizumab are also available in some countries for patients who are unresponsive to sorafenib. Some second-line agents are available for patients who are unresponsive to sorafenib; however, little is known about the considerations for selecting appropriate secondline systemic agents. Hence, this study aimed to review the current and future perspectives of second-line systemic agents.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expression of Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase 2 Is Closely Associated with Recurrence in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Sunho Uhm, Yoon Cho, Ji-Young Choe, Ji Park, Min-Jeong Kim, Won-Ho Han, Junyong Lee, Jung Lee, Dong Shin, Jae Soh, Hyun Lim, Ho Kang, Sung-Hoon Moon, Sung-Eun Kim
Diagnostics.2023; 13(4): 659. CrossRef - Expert consensus on the management of adverse events in patients receiving lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma
Bo Hyun Kim, Su Jong Yu, Wonseok Kang, Sung Bum Cho, Soo Young Park, Seung Up Kim, Do Young Kim
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 37(3): 428. CrossRef
- Expression of Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase 2 Is Closely Associated with Recurrence in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma

- Advances in immune checkpoint inhibitors for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Ji Won Han, Su-Hyung Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):139-145. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.24
- 3,972 Views
- 105 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
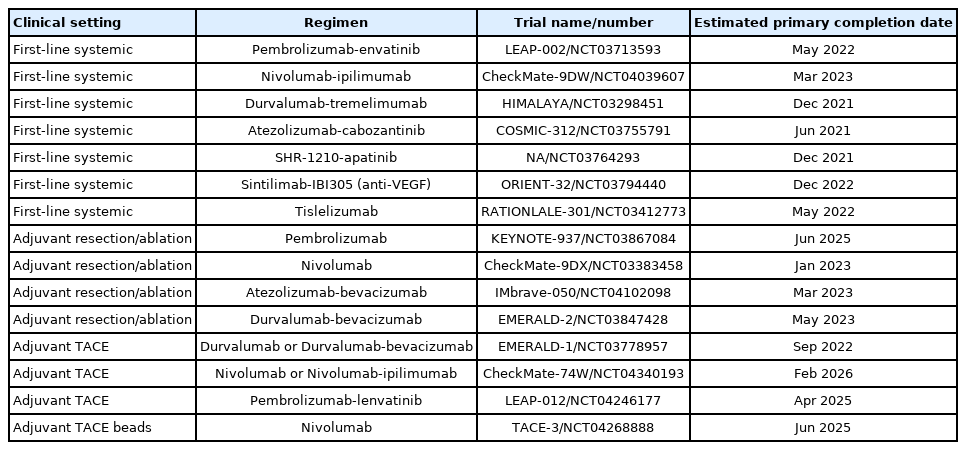
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common cancer, and the second leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Although recent advances in immune checkpoint inhibitor-based immunotherapy have initiated a new era for advanced HCC treatment, the majority of HCC patients receiving immune checkpoint blockades do not derive clinical benefit. Thus, there remains an urgent need for novel immunotherapeutic strategies with improved therapeutic efficacy. Here we review recent studies of immune checkpoint blockade in HCC, providing the necessary basis for the rational design of immunotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Systematic Review of Molecular Targeted Therapies for Adult-Type Diffuse Glioma: An Analysis of Clinical and Laboratory Studies
Logan Muzyka, Nicolas K. Goff, Nikita Choudhary, Michael T. Koltz
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(13): 10456. CrossRef - Integrative analysis of lactylation-related genes and establishment of a novel prognostic signature for hepatocellular carcinoma
Diankui Cai, Xiaoqing Yuan, D. Q. Cai, Ang Li, Sijia Yang, Weibang Yang, Jinxin Duan, Wenfeng Zhuo, Jun Min, Li Peng, Jinxing Wei
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2023; 149(13): 11517. CrossRef - Editorial on Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Samantha M Ruff, Timothy M Pawlik
Immunotherapy.2023; 15(16): 1323. CrossRef
- Systematic Review of Molecular Targeted Therapies for Adult-Type Diffuse Glioma: An Analysis of Clinical and Laboratory Studies

Original Articles
- Transarterial chemoembolization using drug-eluting bead compared with radiofrequency ablation for treatment of single small hepatocellular carcinoma: a pilot non-randomized trial
- Tae Hoon Kim, Na Hye Kim, Jin Dong Kim, Young Nam Kim, Yu Jin Kim, Eun Jung Kim, Ki Deok Yoo, Choong Heon Ryu, Ha Hun Song, Hyun Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):146-154. Published online August 11, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.05.20
- 4,925 Views
- 141 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
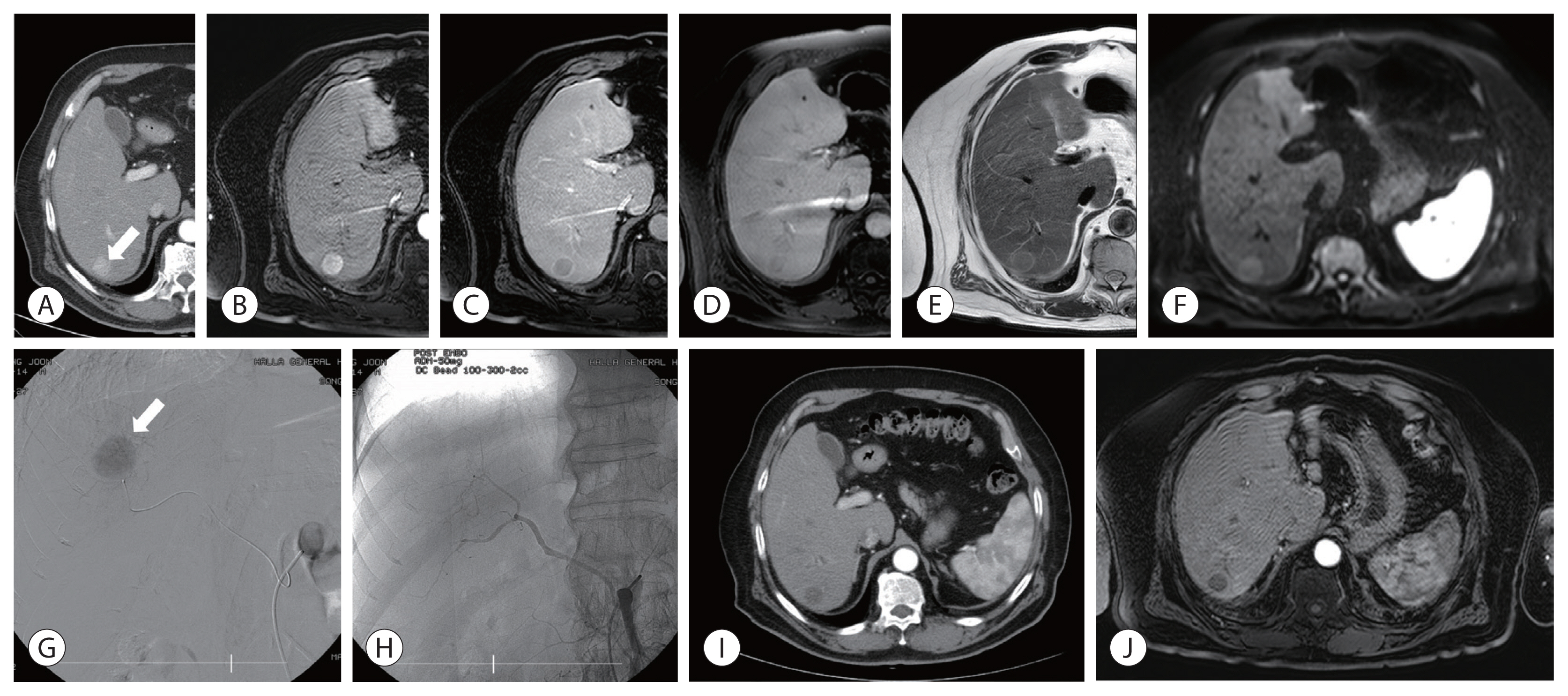
Supplementary Material - Background/Aims
Surgical resection, transplantation, and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) are generally accepted as amenable treatments for small hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recently drug-eluting beads (DEB) which had several treatment advantages were introduced for transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). The aim of this study was to evaluate feasibility and safety of DEB-TACE compared with RFA for the treatment of single small HCC.
Methods
In this pilot non-randomized trial, we assessed retrospective data of 40 patients who underwent DEB-TACE (n=21) or RFA (n=19) for single small (≤3 centimeter in greatest dimension) HCC. The primary outcomes were tumor response and time to recurrence. The secondary outcome was treatment-related complications.
Results
Complete response rate to DEB-TACE and RFA after first follow-up assessment was 90.5% and 94.7%, respectively (P=1.000). During mean follow-up of 87.6 months (95% confidence interval: 74.4-102), 7 patients experienced local recurrence. The 6- and 12-month cumulative local recurrence rate was 5.0% and 21.8% in DEB-TACE vs. 11.1% and 17.0% in RFA group (P=0.877). A total 14 distant intrahepatic recurrences were developed and 12- and 24-month cumulative distant intrahepatic recurrence rate was 20.6% and 42.7% in DEBTACE vs. 17.2% and 36.3% in RFA group (P=0.844). Two patients experienced gangrenous cholecystitis after DEB-TACE requiring cholecystectomy as treatment-related adverse event.
Conclusions
Tumor response and recurrence rate after single session of DEB-TACE or RFA were similar. DEB-TACE could be applied selectively in patients with a single small HCC if the other therapeutic modality is unfeasible. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incidence and Risk Factors of Acute Ischemic Cholecystitis after Transarterial Chemoembolization: Correlation with Cone Beam CT Findings
Jong Yeong Kim, Jung Suk Oh, Ho Jong Chun, Su Ho Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2024; 85(2): 363. CrossRef - Drug-Eluting Bead Transarterial Chemoembolization Versus Radiofrequency Ablation as an Initial Treatment of Single Small (≤ 3 cm) Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Somin Lee, Yong Yeon Jeong, Byung Chan Lee, Sang Soo Shin, Suk Hee Heo, Hyoung Ook Kim, Chan Park, Won Gi Jeong
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparable Outcomes in Early Hepatocellular Carcinomas Treated with Trans-Arterial Chemoembolization and Radiofrequency Ablation
Benjamin Wei Rong Tay, Daniel Q. Huang, Muthiah Mark, Neo Wee Thong, Lee Guan Huei, Lim Seng Gee, Low How Cheng, Lee Yin Mei, Prem Thurairajah, Lim Jia Chen, Cheng Han Ng, Wen Hui Lim, Darren Jun Hao Tan, Da Costa Maureen, Kow Wei Chieh Alfred, Iyer Shrid
Biomedicines.2022; 10(10): 2361. CrossRef
- Incidence and Risk Factors of Acute Ischemic Cholecystitis after Transarterial Chemoembolization: Correlation with Cone Beam CT Findings

- The effect of nucleos(t)ide analogues on clinical outcomes of patients treated with transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation for hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
- Jae Min Park, Won Hyeok Choe, Jeong Han Kim, So Young Kwon, Byung Chul Yoo
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):155-162. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.22

- 3,736 Views
- 96 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aims
Because hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication has been known to play an important role in cancer recurrence after curative treatment of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), we examined whether treatment based on nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs) might decrease the recurrence rate and improve patient survival.
Methods
The retrospective cohort study enrolled 73 patients with chronic hepatitis B who were treated with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) with curative intent for HCC. Among those, 30 and 43 patients were treated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) and entecavir (ETV), respectively.
Results
Of the 73 patients, 51 experienced HCC recurrence, and 14 patients were dead during a follow-up of 73±34 months. Multivariate analyses showed that tumor size (hazard ratio [HR], 1.590; 95% confidence-interval [CI], 1.106-2.285; P=0.012) and Child-Pugh class B (vs. class A/non cirrhosis; HR, 5.794; 95% CI, 2.311-14.523; P=0.001) was significantly associated with HCC recurrence, and Child-Pugh class B (HR, 7.357; 95% CI, 2.100-25.777; P=0.002) was an independent unfavorable prognostic factor for survival. During NAs therapy, TDF was superior to ETV for complete viral response at 1 year after the date of combination of TACE and RFA (P=0.016). However, the risks of HCC recurrence and survival were not significantly different between those treated with TDF versus ETV.
Conclusions
TDF was superior to ETV for achieving complete viral response. However, the recurrence and mortality after TACE and RFA for HBV-related HCC were not significantly different between patients treated with TDF versus ETV. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced prognosis of HCC patients undergoing radical treatments with tenofovir versus entecavir: A meta-analysis based on propensity score matching studies
Qingyan Kong, Mengshi Yi, Fei Teng, Zheyu Chen
Asian Journal of Surgery.2024; 47(1): 55. CrossRef - Tenofovir versus entecavir on the prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Hui Liu, Cheng-Long Han, Bao-Wen Tian, Zi-Niu Ding, Ya-Fei Yang, Yun-Long Ma, Chun-Cheng Yang, Guang-Xiao Meng, Jun-Shuai Xue, Dong-Xu Wang, Zhao-Ru Dong, Zhi-Qiang Chen, Jian-Guo Hong, Tao Li
Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2023; 17(6): 623. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Enhanced prognosis of HCC patients undergoing radical treatments with tenofovir versus entecavir: A meta-analysis based on propensity score matching studies

Case Reports
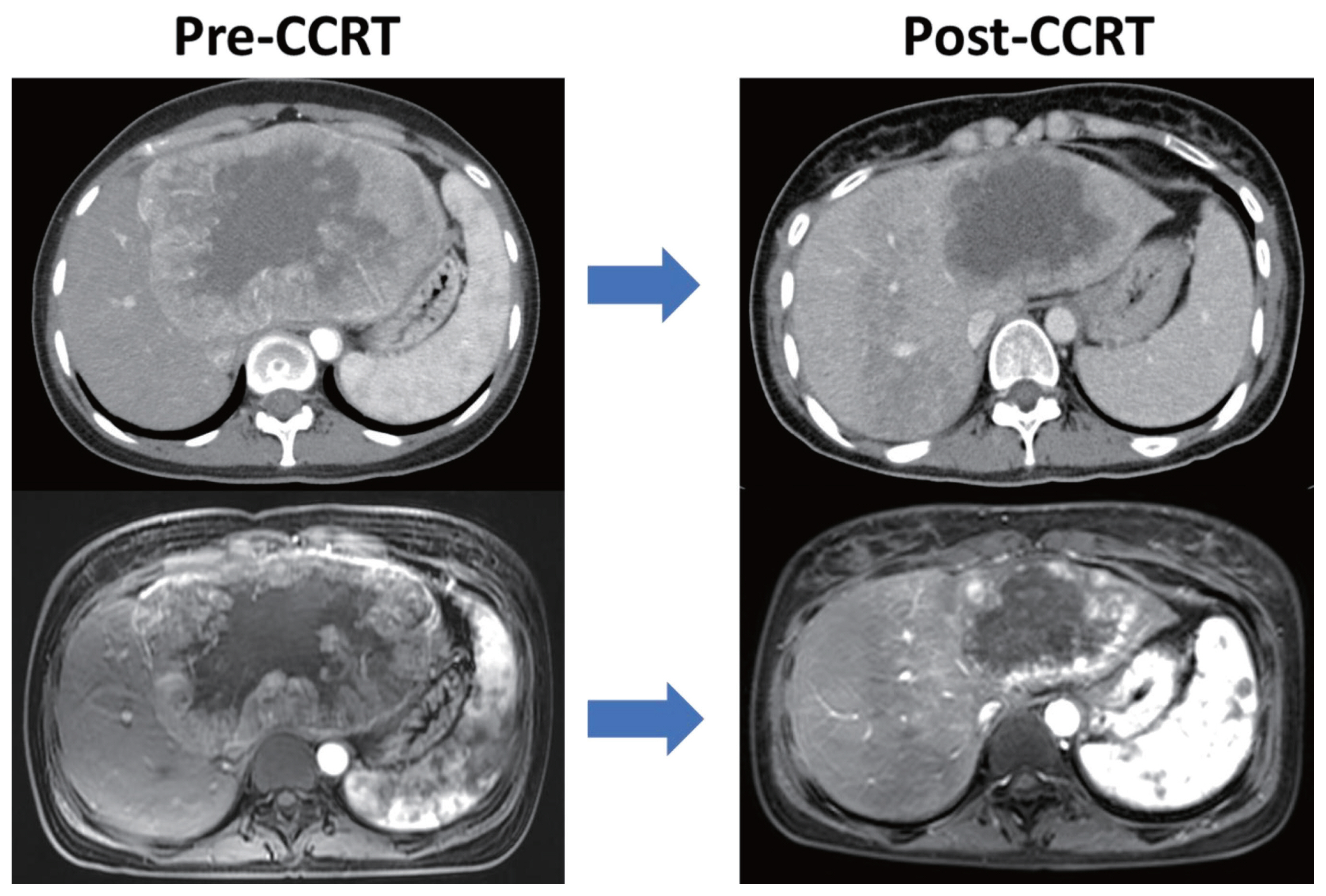
- Long-term survival after multimodal treatment involving radiotherapy for huge hepatocellular carcinoma with oligometastasis: a case report
- Byung Min Lee, Jinsil Seong
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):163-168. Published online September 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.08.06
- 2,826 Views
- 79 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The clinical efficacy of local ablative treatment for oligometastasis is widely accepted in most cancers. However, due to limited data, this has not been the case for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, we report a case of pulmonary oligometastasis of a huge HCC that was treated by multimodality with liver-directed concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) plus subsequent resection of the primary lesion and local ablative radiotherapy (RT) for subsequent lung oligometastatic lesions. In this patient, liver-directed CCRT induced significant tumor shrinkage with compensatory hypertrophy of the non-tumor liver, followed by curative resection. Surgical resection of the first and second pulmonary metastatic lesions as well as local ablative RT of the third lesion achieved complete tumor regression, which led to long-term survival of 6 years. Therefore, the active use of local ablative RT requires full consideration in cases of oligometastatic HCC.

- Infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with multiple lung metastasis completely cured using nivolumab: a case report
- Ji Eun Han, Hyo Jung Cho, Soon Sun Kim, Jae Youn Cheong
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):169-176. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.08.26

- 3,714 Views
- 83 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The current Food and Drug Administration-approved systemic treatments for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) include multikinase inhibitors (tyrosine kinase inhibitor [TKI]) and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Among ICIs, nivolumab is used as secondline therapy for advanced HCC after sorafenib failure or patient intolerance. In this case, a patient with infiltrative HCC and portal vein tumor thrombosis was treated with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) and radiation therapy. New lung metastasis developed after HAICs; thus, lenvatinib treatment was initiated. However, the disease progressed. Thereafter, sorafenib treatment was initiated but he developed intolerance, with grade 3 sorafenib-related diarrhea. Subsequently, nivolumab was administered as rescue therapy. He demonstrated a partial response to nivolumab after the third treatment and viable HCCs in the lungs and liver completely disappeared after the 24th treatment. These findings suggest that nivolumab could be used as an effective rescue therapy for advanced HCC progression after TKI treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intermediate-stage (BCLC stage B) infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma: safety and efficacy of chemoembolization
Seong Ho Kim, Jin Hyoung Kim, Gun Ha Kim, Ji Hoon Kim, Heung-Kyu Ko, Hee Ho Chu, Ji Hoon Shin, Dong Il Gwon, Gi-Young Ko, Hyun-Ki Yoon, Shakir Aljerdah, Nayoung Kim
European Radiology.2023; 33(12): 8736. CrossRef
- Intermediate-stage (BCLC stage B) infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma: safety and efficacy of chemoembolization

- Complete response in hepatocellular carcinoma with lymph node metastasis by combination therapy of atezolizumab and bevacizumab: a case report
- Sang Youn Hwang, Sun Mi Lee, Jeong Woo Lim, Gi Jung Jeon, Hye Won Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):177-180. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.10
- 3,389 Views
- 85 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Sorafenib is the oldest first line systemic treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and has been used exclusively for nearly 10 years. The superiority of administering a combination of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (AteBeva) compared to sorafenib as first line systemic treatment for unresectable HCC was recently proven during the IMbrave150 Phase III randomized trial. While clinicians can expect improved responses and treatment outcomes due to the good results of the IMbrave 150 trial, they must also consider that atezolizumab can cause various immune-related adverse events (IrAEs). Based on the above suggestions, we herein present a case of HCC with lymph node metastasis who achieved complete remission following treatment with AteBeva and developed an IrAE (adrenal insufficiency). Further study of real-life data regarding combination therapy with AteBeva is needed to manage patients with advanced HCC.

- Curative liver transplantation after lung resection for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with lung metastasis and inferior vena cava tumor thrombosis: a case report
- Dong Jin Joo, Do Young Kim, Jinsil Seong, Hyun Jeong Kim, Jae Geun Lee, Dai Hoon Han, Gi Hong Choi, Myoung Soo Kim, Jin Sub Choi, Soon Il Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):181-186. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.08

- 4,136 Views
- 98 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with distant metastasis is an absolute contraindication for liver transplantation (LT). However, it is still unclear whether LT is feasible or acceptable in such patients, albeit after being treated with a multidisciplinary approach and after any metastatic lesion is ruled out. We report one such successful treatment with living donor LT (LDLT) after completely controlling far-advanced HCC with inferior vena cava tumor thrombosis and multiple lung metastases. The patient has been doing well without HCC recurrence for eight years since LDLT. The current patient could be an anecdotal case, but provides a case for expanding LDLT indications in the context of advanced HCC and suchlike.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inferior Vena Cava Thrombectomy and Stenting as Bridge to Liver Transplantation After Radiotherapy-Induced Thrombosis
Raphael PH Meier, Shani Kamberi, Josue Alvarez-Casas, Barton F. Lane, Chandra S. Bhati, Saad Malik, William Twaddell, Kirti Shetty, Adam Fang, Hyun S. Kim, Daniel G. Maluf
Progress in Transplantation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inferior Vena Cava Thrombectomy and Stenting as Bridge to Liver Transplantation After Radiotherapy-Induced Thrombosis

- Primary multifocal cystic signet ring neuroendocrine tumor of liver: a case report
- Nalini Bansal, Brahmananda Satapathy
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):187-193. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.17

- 3,455 Views
- 78 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary signet ring neuroendocrine tumors of the liver are extremely rare tumors. Morphologically, they mimic signet ring cell adenocarcinomas; however, the absence of mucin by special stains and the expression of neuroendocrine markers help to diagnose these tumors. We herein report a case of a 47-year-old female who presented with multiple solid and cystic lesions in both liver lobes, which were initially suggested to be biliary cystadenocarcinoma on imaging. Liver biopsy of the lesion revealed the presence of a signet ring neoplasm with diffuse expression of synaptophysin and pan-cytokeratin. The case was subsequently diagnosed as a primary hepatic signet ring neuroendocrine tumor. The patient was offered 3 cycles of chemotherapy and is well preserved after 14 months of diagnosis. Although this is an extremely rare entity, its possibility should be considered in the differential diagnosis of neoplasms characterized by signet ring cell morphology.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumor With Cystic Hepatic Metastases Mimicking Hepatic Echinococcosis: A Case Report
Rahul Gupta, Deepak Gusain, Nalini Bansal, Rahul Varshney, Arvind Singh
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - HER-2-positive primary neuroendocrine neoplasms of the breast with signet ring feature: A case report and review of literature
Yunjin Li, Yi Cao, Xiaoying Wu, Ruijie Liu, Kuansong Wang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumor With Cystic Hepatic Metastases Mimicking Hepatic Echinococcosis: A Case Report

- A case report of a patient presented with skin ulcer after treatment of lenvatinib
- Serin Cha, Dong Woo Kim, Jung Wan Choe, Tae Hyung Kim, Seung Young Kim, Jong Jin Hyun, Sung Woo Jung, Ja Seol Koo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):194-198. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.20
- 3,635 Views
- 86 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 60-year-old man diagnosed with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presented to the hospital with pain in the perineal region. He had been taking lenvatinib every day for 2 months after he was diagnosed with HCC with metastases to the lymph node, small bowel mesentery, and retroperitoneal space. Enhanced abdominal computed tomography revealed mild elevation in intensity in the perineal subcutaneous tissue with subcutaneous emphysema. The patient was diagnosed with Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events grade 3, skin ulceration of stage IV with full-thickness skin loss and tissue necrosis in the muscular layer. The patient was taken off the medication with prescription of antibiotics, and after 3 weeks, the skin has fully recovered. This is the first report of an HCC patient who presented with a skin ulceration of stage IV after lenvatinib treatment. We recommend stopping the medication immediately and changing to alternative treatments with appropriate supportive care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multiple lenvatinib‐associated skin ulcers: A case report and literature review
Soo Hyun Jeon, Woo Jin Lee, Chong Hyun Won, Sung Eun Chang, Mi Woo Lee, Joon Min Jung
Australasian Journal of Dermatology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Tyrosine kinase inhibitors induced scrotal ulcerations: Report of 2 cases
Abhipsa Samal, Nibedita Dixit, BikashR Kar, Liza Mohapatra
Indian Journal of Dermatology.2023; 68(2): 235. CrossRef
- Multiple lenvatinib‐associated skin ulcers: A case report and literature review


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION



 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter