Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Previous issues
Review Articles
- Ras Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling and Kinase Suppressor of Ras as Therapeutic Targets for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Hyuk Moon, Simon Weonsang Ro
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):1-11. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.1
- 6,965 Views
- 226 Downloads
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
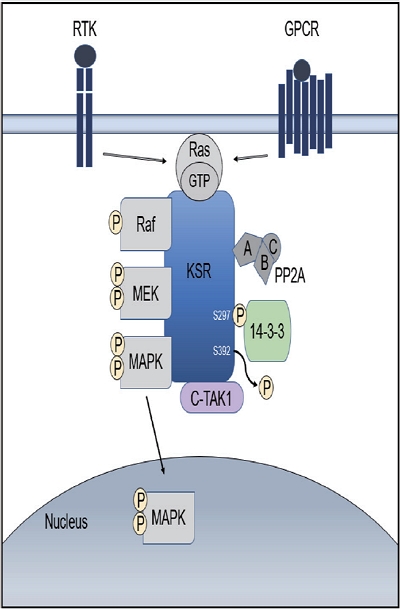
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a high incidence cancer and a major health concern worldwide. Among the many molecular signaling pathways that are dysregulated in HCC, the Ras mitogen-activated protein kinase (Ras/Raf/MAPK) signaling pathway has gained renewed attention from basic and clinical researchers. Mutations in Ras and Raf genes which are known to activate the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway have been infrequently detected in human HCC; however, the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway is activated in more than 50% of HCC cases, suggesting an alternative mechanism for the activation of the signaling pathway. Kinase suppressor of Ras acts as a molecular scaffold for facilitating the assembly of Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway components and has been implicated in the regulation of this signaling pathway. In this review, we provide important insights into the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the activation of the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway and discuss potential therapeutic strategies for HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lipid‐lowering activity and underlying mechanism of glycosylated peptide–calcium chelate prepared by transglutaminase pathway
Xiaoping Wu, Xu Chen, Xixi Cai, Shaoyun Wang
Food Frontiers.2024; 5(1): 160. CrossRef - CT-guided high dose rate brachytherapy can induce multiple systemic proteins of proliferation and angiogenesis predicting outcome in HCC
Lukas Salvermoser, Shraga Nahum Goldberg, Marianna Alunni-Fabbroni, Philipp Maximilian Kazmierczak, Moritz Nikolaus Gröper, Jan Niklas Schäfer, Elif Öcal, Tanja Burkard, Stefanie Corradini, Najib Ben Khaled, Agnese Petrera, Moritz Wildgruber, Jens Ricke,
Translational Oncology.2024; 43: 101919. CrossRef - Network-Pharmacology-Based Study on Active Phytochemicals and Molecular Mechanism of Cnidium monnieri in Treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Shakeel Ahmad Khan, Terence Kin Wah Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(10): 5400. CrossRef - Identification of potential target genes of honokiol in overcoming breast cancer resistance to tamoxifen
Adam Hermawan, Herwandhani Putri, Naufa Hanif, Nurul Fatimah, Heri Himawan Prasetio
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Lipid‐lowering activity and underlying mechanism of glycosylated peptide–calcium chelate prepared by transglutaminase pathway

- Update on Pathologic and Radiologic Diagnosis of Combined Hepatocellular-Cholangiocarcinoma
- Hyungjin Rhee, Jae Hyon Park, Young Nyun Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):12-24. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.12
- 6,411 Views
- 315 Downloads
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
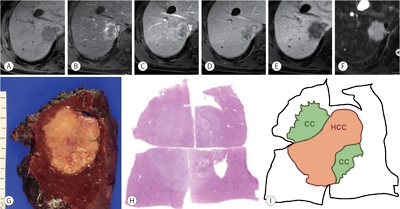
PDF - Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma (cHCC-CCA) is a malignant primary liver carcinoma characterized by the unequivocal presence of both hepatocytic and cholangiocytic differentiation within the same tumor. Recent research has highlighted that cHCC-CCAs are more heterogeneous than previously expected. In the updated consensus terminology and WHO 2019 classification, “classical type” and “subtypes with stem-cell features” of the WHO 2010 classification are no longer recommended. Instead, it is recommended that the presence and percentages of various histopathologic components and stem-cell features be mentioned in the pathologic report. The new terminology and classification enable the exchange of clearer and more objective information about cHCC-CCAs, facilitating multi-center and multinational research. However, there are limitations to the diagnosis of cHCC-CCA by imaging and biopsy. cHCC-CCAs showing typical imaging findings of HCC could be misdiagnosed as HCC and subjected to inappropriate treatment, if other clinical findings are not sufficiently considered. cHCC-CCAs showing at least one of the CCA-like imaging features or unusual clinical features should be subjected to biopsy. There may be a sampling error for the biopsy diagnosis of cHCC-CCA. An optimized diagnostic algorithm integrating clinical, radiological, and histopathologic information of biopsy is required to resolve these diagnostic pitfalls.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing liver cirrhosis varices and CSPH risk prediction with spleen stiffness measurement using 100-Hz probe
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sun Ah Maeng, Young Chang, Sae Hwan Lee, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, Gab Jin Cheon, Young Seok Kim, Hong Soo Kim, Sang Gyune Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - MRI features of combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma
Noor Fatima Majeed, Mathew Macey, Marta Braschi Amirfarzan, Sheida Sharifi, Jeremy R Wortman
Abdominal Radiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Differentiation between hepatic angiomyolipoma and hepatocellular carcinoma in individuals who are not at-risk for hepatocellular carcinoma
Sungtae Park, Myeong-Jin Kim, Kyunghwa Han, Jae Hyon Park, Dai Hoon Han, Young Nyun Park, Jaehyo Kim, Hyungjin Rhee
European Journal of Radiology.2023; 166: 110957. CrossRef - The Human TOR Signaling Regulator Is the Key Indicator of Liver Cancer Patients’ Overall Survival: TIPRL/LC3/CD133/CD44 as Potential Biomarkers for Early Liver Cancers
Soo Young Jun, Hyang Ran Yoon, Ji-Yong Yoon, Su-Jin Jeon, Jeong-Ju Lee, Debasish Halder, Jin-Man Kim, Nam-Soon Kim
Cancers.2021; 13(12): 2925. CrossRef
- Enhancing liver cirrhosis varices and CSPH risk prediction with spleen stiffness measurement using 100-Hz probe

- External Beam Radiotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Review of the Current Guidelines in the East and the West
- Sang Min Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):25-33. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.25
- 4,595 Views
- 168 Downloads
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
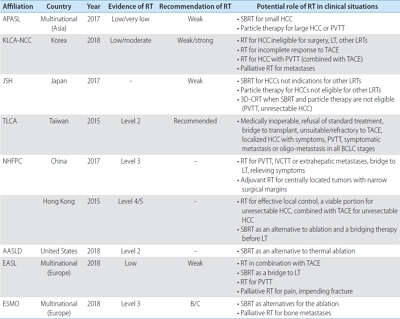
PDF - The incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is geographically heterogeneous depending on the underlying liver disease. Moreover, the decisions and recommendations about standard treatments differ between countries, especially between the East and the West. Because of the complexity of treatment decisions for the management of HCC, a multidisciplinary approach is recommended to maximize the therapeutic efficacy. External beam radiotherapy (RT) has been increasingly used to manage HCC when recommended treatments cannot be applied in real-world clinical practice. However, Western guidelines for the management of HCC do not recommend RT as a treatment option due to the lack of clinical evidence. RT has often been used more in Eastern countries than in Western countries; hence, it is necessary to review both Eastern and Western guidelines for HCC treatment regarding the recommendations about RT. In this study, the comments and potential roles of external beam RT are summarized from several treatment guidelines for the management of HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concurrent nivolumab and external beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A phase II study
Bo Hyun Kim, Hee Chul Park, Tae Hyun Kim, Young-Hwan Koh, Jung Yong Hong, Yuri Cho, Dong Hyun Sinn, Boram Park, Joong-Won Park
JHEP Reports.2024; 6(4): 100991. CrossRef - Novel paradigm in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Anticipating breakthroughs with particle therapy
Sang Min Yoon
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 977. CrossRef - Loco-regional therapies competing with radiofrequency ablation in potential indications for hepatocellular carcinoma: a network meta-analysis
Ha Il Kim, Jihyun An, Seungbong Han, Ju Hyun Shim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 1013. CrossRef - Differences in radiotherapy application according to regional disease characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma
Chai Hong Rim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(2): 113. CrossRef
- Concurrent nivolumab and external beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A phase II study

Original Articles
- Incidence and Clinical Features of Hepatitis C Virus-associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients without Liver Cirrhosis in Hepatitis B Virus-endemic Area
- Jongbeom Shin, Jung Hwan Yu, Young-Joo Jin, Jin-Woo Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):34-44. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.34

- 4,674 Views
- 98 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
/objective: Hepatitis C virus (HCV)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is rarely observed in patients without liver cirrhosis (LC). We evaluated the incidence and clinical feature of HCV-associated HCC patients with or without LC.
Methods
The medical records of 1,516 patients diagnosed as having primary HCC at our hospital between January 2005 and December 2017 were retrospectively reviewed. Of these, 154 (10.2%) HCV-associated HCC patients were analyzed. LC was diagnosed histologically or clinically.
Results
Seventeen (11.0%) of the 154 patients had non-cirrhotic HCC, and all were of Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) class A, Among the 17 patients, 88.2% were male, all had nodular type HCC, and only 2 (11.8%) were under HCC surveillance. Median overall survival (OS) of HCV-associated HCC patients with and without LC was 15 months and 37 months, respectively. Cumulative OS rates were not different between non-cirrhotic patients and cirrhotic patients with CTP class A (P=0.229). Cumulative OS rates were significantly higher in non-cirrhotic patients than in cirrhotic patients of CTP class B (P<0.001) or C (P<0.001). Multivariate analyses showed serum AST (hazard ratio [HR] 1.01, P=0.003) and AFP levels (HR 1.01, P=0.016), antiviral therapy (HR 0.25, P=0.022), and LC of CTP class B (HR, 5.24, P=0.006) or C (HR 21.79, P<0.001) were significantly associated with prognosis in HCV-associated HCC patients.
Conclusions
HCC in a non-cirrhotic liver was found in 11% of HCV-associated HCC patients. OSs of HCV-associated HCC patients were better in those of CTP A, regardless of LC than in those with LC of CTP class B or C. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef
- Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma

- Prediction of Post-resection Prognosis Using the ADV Score for Huge Hepatocellular Carcinomas ≥13 cm
- Shin Hwang, Ki-Hun Kim, Deok-Bog Moon, Chul-Soo Ahn, Tae-Yong Ha, Gi-Won Song, Dong-Hwan Jung, Gil-Chun Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):45-57. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.45
- 4,568 Views
- 79 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
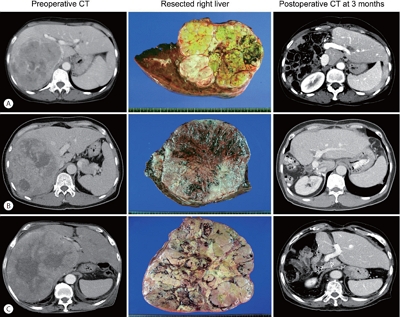
PDF - Background/Aims
Multiplication of α-fetoprotein, des-γ-carboxy prothrombin, and tumor volume (ADV score) is a surrogate marker for post-resection prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study aimed to validate the predictive power of the ADV score-based prognostic prediction model for patients with solitary huge HCC.
Methods
Of 3,018 patients, 100 patients who underwent hepatic resection for solitary HCC ≥13 cm between 2008 and 2012 were selected.
Results
The median tumor diameter and tumor volume were 15.0 cm and 886 mL, respectively. Tumor recurrence and overall survival (OS) rates were 70.7% and 66.0% at one year and 84.9% and 34.0% at five years, respectively. Microvascular invasion (MVI) was the only independent risk factor for disease-free survival (DFS) and OS. DFS and OS, stratified by ADV score with 1-log intervals, showed significant prognostic contrasts (P=0.007 and P=0.017, respectively). DFS and OS, stratified by ADV score with a cut-off of 8-log, showed significant prognostic contrasts (P=0.014 and P=0.042, respectively). The combination of MVI and ADV score with a cut-off of 8-log also showed significant prognostic contrasts in DFS (P<0.001) and OS (P=0.001) considering the number of risk factors. Prognostic contrast was enhanced after combining the MVI and ADV score.
Conclusions
The prognostic prediction model with the ADV score could reliably predict the risk of tumor recurrence and long-term patient survival outcomes in patients with solitary huge HCCs ≥13 cm. The results of this study suggest that our prognostic prediction models can be used to guide surgical treatment and post-resection follow-up for patients with huge HCCs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ADV score is a reliable surrogate biomarker of hepatocellular carcinoma in liver resection and transplantation
Shin Hwang, Dong-Hwan Jung, Gi-Won Song
Annals of Liver Transplantation.2023; 3(2): 86. CrossRef
- ADV score is a reliable surrogate biomarker of hepatocellular carcinoma in liver resection and transplantation

- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
- Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Dong Ho Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Ju-Yeon Cho, Jonggi Choi, Young Chang, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):58-68. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.58
- 7,186 Views
- 277 Downloads
- 18 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aims
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related death in Korea. This study evaluated the characteristics of Korean patients newly diagnosed with HCC in 2015.
Methods
Data from the Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry (KPLCR), a representative sample of patients newly diagnosed with HCC in Korea, were analyzed. A total of 1,558 patients with HCC registered in the KPLCR in 2015 were investigated.
Results
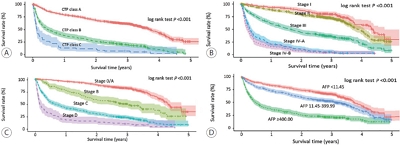
The median age was 61.0 years (interquartile range, 54.0-70.0 years), and men accounted for 79.7% of the subjects. Hepatitis B virus infection was the most common underlying liver disease (58.1%). According to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system, stage 0, A, B, C, and D HCCs accounted for 14.2%, 31.5%, 7.6%, 39.0%, and 7.8% of patients, respectively. Transarterial therapy (32.1%) was the most commonly performed initial treatment, followed by surgical resection (23.2%), best supportive care (20.2%), and local ablation therapy (10.7%). Overall, 34.5% of patients were treated in accordance with the BCLC guidelines: 59.2% in stage 0/A, 48.4% in stage B, 18.1% in stage C, and 71.6% in stage D. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 67.1%, 50.9%, and 27.0%, respectively.
Conclusions
In 2015, approximately 45% of Korean HCC cases were diagnosed at a very early or early stage, and 35% of patients underwent potentially curative initial treatment. BCLC guidance was followed in 34.5% of patients; in patients with stage B or C disease, there was relatively low adherence. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concurrent nivolumab and external beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A phase II study
Bo Hyun Kim, Hee Chul Park, Tae Hyun Kim, Young-Hwan Koh, Jung Yong Hong, Yuri Cho, Dong Hyun Sinn, Boram Park, Joong-Won Park
JHEP Reports.2024; 6(4): 100991. CrossRef - Identification of patients with favorable prognosis after resection in intermediate-stage-hepatocellular carcinoma
Han Ah Lee, Minjong Lee, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Ho Soo Chun, Yewan Park, Hwi Young Kim, Tae Hun Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Dong Hyun Sinn
International Journal of Surgery.2024; 110(2): 1008. CrossRef - Factors associated with the survival outcomes of patients with untreated hepatocellular carcinoma: An analysis of nationwide data
Min Jung Kwon, Soy Chang, Ji Hoon Kim, Ji Won Han, Jeong Won Jang, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Pil Soo Sung
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The imitator of immune-tolerant chronic hepatitis B: A killer in disguise
Moon Haeng Hur, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(2): 363. CrossRef - Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: a large-scale multicenter study
Sun Hong Yoo, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Han-Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim, Do Seon Song, Seong Hee Kang, Moon Young Kim, Young-Hwan Ahn, Jieun Han, Young Seok Kim, Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, J
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 189. CrossRef - A Case of Transverse Myelitis Following Treatment with Atezolizumab for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Kyung Han Kim, Yang-Hyun Baek, Yeo Wool Kang, Byeol-A Yoon, Sang Yi Moon
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 82(1): 35. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter, Propensity Score Study
Ji Kim, Hee-Chul Nam, Chang-Wook Kim, Hee Cho, Jae-Sung Yoo, Ji Han, Jeong Jang, Jong Choi, Seung Yoon, Hyun Yang, Si Bae, Suho Kim, Jung Oh, Ho Chun, Chang Jeon, Jaegyoon Ahn, Pil Sung
Cancers.2023; 15(17): 4233. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Modeling the Risk of Liver Cancer in Adults: A Machine Learning Investigation into the Role of Obesity and Overweight
Bah Karamo, Bah Adama Ns , Jallow Amadou Wurry
Archives of Pathology and Clinical Research.2023; 7(1): 034. CrossRef - Surgical resection versus ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma: The debate is still open
Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 174. CrossRef - Cause of death and cause-specific mortality for primary liver cancer in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study in hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Bo Hyun Kim, Dahhay Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Joo Won, Hyunsoon Cho
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 242. CrossRef - Impact of tumor size on hepatectomy outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma: a nationwide propensity score matching analysis
Suk Kyun Hong, Kwang-Woong Lee, Sola Lee, Su young Hong, Sanggyun Suh, Eui Soo Han, YoungRok Choi, Nam-Joon Yi, Kyung-Suk Suh
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2022; 102(4): 193. CrossRef - Efficacy and feasibility of surgery and external radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal invasion: A meta-analysis
Han Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, In-Soo Shin, Won Sup Yoon, Hye Yoon Lee, Chai Hong Rim
International Journal of Surgery.2022; 104: 106753. CrossRef - Yoon et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(2): 207. CrossRef - Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: It is time to move forward
Bo Hyun Kim, Yuri Cho, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 810. CrossRef - Treatment patterns for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with Child–Pugh class B and their impact on survival: A Korean nationwide registry study
Dongsub Jeon, Gi‐Won Song, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim
Liver International.2022; 42(12): 2830. CrossRef - Metastatic breast cancer from a hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report
Hyewon Bang, Nam-Hee Kim, Seung Hye Choi, Si Hyun Bae, Eun Sun Jung, Ki Ouk Min, Yong Hwa Eom
Korean Journal of Clinical Oncology.2022; 18(2): 93. CrossRef - Current Status and Future Directions of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance Test Based on Cost-effective Analysis
Jihyun An
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 78(5): 255. CrossRef
- Concurrent nivolumab and external beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A phase II study

Case Reports
- A Case of Lymphocyte-Rich Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Patient Who Was Treated for Colon Cancer
- Jae Won Song, Ho Soo Chun, Jae Seung Lee, Hye Won Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Young Nyun Park, Dai Hoon Han, Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):69-75. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.69
- 3,942 Views
- 88 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
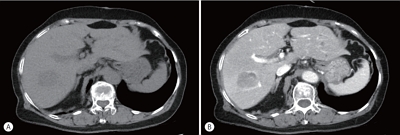
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) primarily originates in the liver with hepatic differentiation. However, HCCs are not homogenous, and approximately 35% of HCC cases are classified as histopathological variants that present distinct pathologic characteristics. In particular, the lymphocyte-rich variant is the rarest subtype accounting for less than 1% of HCCs, which is not well known to date about molecular features and pathophysiology. Herein, we present a case of a patient who was suspected of metastatic liver cancer and confirmed as lymphocyte-rich HCC pathologically. A 78-year-old woman who underwent a right hemicolectomy for colon cancer was referred to our hospital for a newly detected liver mass. We could not make a decision because of insufficient evidence for diagnosis from imaging studies. After resection, we found that it was a lymphocyte-rich HCC. The pathologic features and prognostic trends of this subtype are also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterization of lymphocyte‐rich hepatocellular carcinoma and the prognostic role of tertiary lymphoid structures
Bokyung Ahn, Hee‐Sung Ahn, Jinho Shin, Eunsung Jun, Eun‐Young Koh, Yeon‐Mi Ryu, Sang‐Yeob Kim, Chang Ohk Sung, Ju Hyun Shim, JeongYeon Hong, Kyunggon Kim, Hyo Jeong Kang
Liver International.2024; 44(5): 1202. CrossRef - Uncommon variants of hepatocellular carcinoma: Not one size fits all
Reetu Kundu, Nalini Gupta, Debajyoti Chatterjee, Ajay Duseja
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2022; 50(1): 28. CrossRef
- Characterization of lymphocyte‐rich hepatocellular carcinoma and the prognostic role of tertiary lymphoid structures

- Huge Hepatic Angiomyolipoma Mimicking Low Grade Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Hyeo Seong Hwang, Dae Hoon Han
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):76-80. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.76

- 3,896 Views
- 68 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 41-year-old man was diagnosed with a huge symptomatic liver mass and was referred to our hospital for liver biopsy and further evaluation. He presented with right upper quadrant tenderness. Enhanced abdominal computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging revealed a 12.5-cm relatively well-defined heterogeneous enhancing mass in the right inferior liver with a large exophytic component containing a fat component and progressive delayed enhancement. The patient underwent right inferior sectionectomy. The pathological diagnosis was confirmed as angiomyolipoma, 12.3×9.2×5.0 cm in size, with tumor necrosis in 20% of the tissue. Hepatic angiomyolipoma is known as a benign tumor, but in our case, because of the large tumor size and coagulative necrosis, this tumor had malignant potential; surgical resection was deemed to be appropriate, and close follow-up monitoring was essential postoperatively.

- Rare Case of Pyogenic Brain Abscess after Transarterial Chemoembolization in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Case Report and Literature Review
- Jun-Ho Myeong, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):81-86. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.81

- 3,045 Views
- 70 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a useful treatment option for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). TACE can particularly be used as a treatment for localized HCC, where surgical resection is impossible due to decreased liver function. However, TACE is associated with several complications, including vascular complications, liver failure, non-target embolization, infection, and death. The main risk factor for complications after TACE is decreased liver function. There have been only few reports of brain abscesses after TACE that are difficult to be distinguished from hepatic encephalopathy. Here, we report a rare case of brain abscess caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae that occurred after TACE.

- Hepatocellular Carcinoma Arising from Hepatocellular Adenoma in an Elderly Male Patient
- Manuel Lim, Jong Man Kim, Ji Eun Kwon, Eun Sung Jeong, Jaehun Yang, Okjoo Lee, Kyeong Deok Kim, Sang Jin Kim, Jinsoo Rhu, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):87-91. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.87
- 4,668 Views
- 106 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
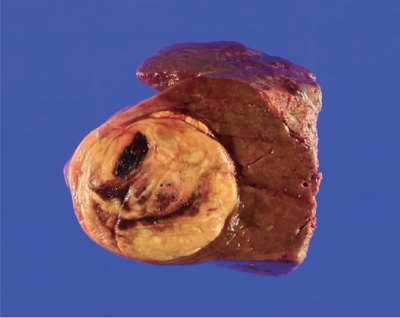
PDF - Hepatocellular adenoma is a benign tumor of the liver occurring predominantly in young women taking oral contraceptives. The malignant transformation of hepatocellular adenoma into hepatocellular carcinoma has rarely been reported. Herein, we report the case of an elderly male patient with hepatocellular carcinoma that developed from hepatocellular adenoma. The patient’s high risk for surgery and conflicting biopsy and imaging results made it difficult to determine the treatment direction. Eventually, the mass was completely removed by laparoscopic left hemi-hepatectomy without complications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sujin Koo, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Seungeun Ryoo, Jungeun Park, Dong Ah Park
Current Oncology.2024; 31(1): 324. CrossRef
- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

- A Case of Metastatic Melanoma in the Liver Mimicking Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jae-Kyoung So, Ji-Yun Hong, Min-Woo Chung, Sung-Bum Cho
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):92-96. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.92

- 7,471 Views
- 273 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The liver is one of the most common sites of metastasis. Although most metastatic liver cancers are hypovascular, some hypervascular metastases, such as those from melanoma, need to be differentiated from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) because they may show similar radiologic findings due to their hypervascularity. We encountered a case of multinodular liver masses with hyperenhancement during the arterial phase and washout during the portal venous and delayed phases, which were consistent with imaging hallmarks of HCC. The patient had a history of malignant melanoma and had undergone curative resection 11 years earlier. We performed a liver biopsy for pathologic confirmation, which revealed a metastatic melanoma of the liver. Metastatic liver cancer should be considered if a patient without chronic liver disease has a history of other primary malignancies, and caution should be exercised with hypervascular cancers that may mimic HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A case of metastatic melanoma in the liver mimicking colorectal cancer with synchronous liver metastasis
E.A. Warshowsky, M. McCarthy, K. Wells, A. Arcidiacono, L. Csury, J.R. Nitzkorski
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2024; 119: 109686. CrossRef - The importance of ultrasound-guided biopsy: lesson from a case of liver metastasis from uveal melanoma
Maria Boe, Susanna Vicari, Andrea Boccatonda, Fabio Piscaglia
Journal of Ultrasound.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- A case of metastatic melanoma in the liver mimicking colorectal cancer with synchronous liver metastasis

- Advanced Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Successfully Treated with Liver-directed Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy and Sequential Transarterial Radio-embolization
- Minho Noh, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):97-103. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.97

- 3,377 Views
- 79 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Optimal treatment strategies for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is yet to be determined. Herein, we present a case of advanced HCC with tumor invasion into the right anterior portal vein and right hepatic vein where complete response (CR) was achieved via a multidisciplinary approach. This patient had a 10.5 cm-sized HCC invading segment VI, without extrahepatic spread. Liver function was classified as Child-Pugh class A, and the performance status was good. Transarterial radio-embolization (TARE) was performed 6 weeks after the completion of liver-directed concurrent chemoradiotherapy, and CR was confirmed 3 months post-TARE. Adoptive cell therapies were performed as adjuvant therapy and CR was maintained for over 15 months, until the local recurrence of a 2 cm-sized HCC was found. Therefore, in selected cases with preserved liver function, combination therapies, including LRTs and systemic therapy, can be a useful therapeutic option for advanced HCC.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION



 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter