Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Previous issues
Review Articles
- Deciphering and Reversing Immunosuppressive Cells in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Su Jong Yu, Tim F. Greten
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):1-16. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.1
- 7,110 Views
- 197 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Use of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been partially successful. However, most HCC patients do not respond to immunotherapy. HCC has been shown to induce several immune suppressor mechanisms in patients. These suppressor mechanisms include involvement of myeloid-derived suppressor cells, regulatory T-cells, functionally impaired dendritic cells (DCs), neutrophils, monocytes, and tumor associated macrophages. The accumulation of immunosuppressive cells may lead to an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment as well as the dense fibrotic stroma which may contribute to immune tolerance. Our laboratory has been investigating different cellular mechanisms of immune suppression in HCC patients. In vitro as well as in vivo studies have demonstrated that abrogation of the suppressor cells enhances or unmasks tumor-specific antitumor immune responses. Two or three effective systemic therapies including ICIs and/or molecular targeted therapies and the addition of innovative combination therapies targeting immune suppressor cells may lead to increased immune recognition with a greater tumor response. We reviewed the literature for the latest research on immune suppressor cells in HCC, and here we provide a comprehensive summary of the recent studies in this field.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Higher Number of Tumor-Infiltrating PD-L1+ Cells Is Related to Better Response to Multikinase Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ji Won Han, Ji Hoon Kim, Dong Hyun Kim, Jeong Won Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Jaegyoon Ahn, Hyun Yang, Pil Soo Sung
Diagnostics.2023; 13(8): 1453. CrossRef - Immune checkpoint inhibitors in HCC: Cellular, molecular and systemic data
Uasim Harkus, Miriam Wankell, Pranavan Palamuthusingam, Craig McFarlane, Lionel Hebbard
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2022; 86: 799. CrossRef - Crosstalk between tumor-associated macrophages and neighboring cells in hepatocellular carcinoma
Pil Soo Sung
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(3): 333. CrossRef
- Higher Number of Tumor-Infiltrating PD-L1+ Cells Is Related to Better Response to Multikinase Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma

- Histopathological Variants of Hepatocellular Carcinomas: an Update According to the 5th Edition of the WHO Classification of Digestive System Tumors
- Haeryoung Kim, Mi Jang, Young Nyun Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):17-24. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.17

- 15,125 Views
- 1,044 Downloads
- 29 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is heterogeneous in pathogenesis, phenotype and biological behavior. Various histopathological features of HCC had been sporadically described, and with the identification of common molecular alterations of HCC and its genomic landscape over the last decade, morpho-molecular correlation of HCC has become possible. As a result, up to 35% of HCCs can now be classified into histopathological variants, many of which have unique molecular characteristics. This review will provide an introduction to the variously described histopathological variants of HCC in the updated WHO Classification of Digestive System Tumors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Computational Pathology: A Survey Review and The Way Forward
Mahdi S. Hosseini, Babak Ehteshami Bejnordi, Vincent Quoc-Huy Trinh, Lyndon Chan, Danial Hasan, Xingwen Li, Stephen Yang, Taehyo Kim, Haochen Zhang, Theodore Wu, Kajanan Chinniah, Sina Maghsoudlou, Ryan Zhang, Jiadai Zhu, Samir Khaki, Andrei Buin, Fatemeh
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2024; : 100357. CrossRef - Characterization of lymphocyte‐rich hepatocellular carcinoma and the prognostic role of tertiary lymphoid structures
Bokyung Ahn, Hee‐Sung Ahn, Jinho Shin, Eunsung Jun, Eun‐Young Koh, Yeon‐Mi Ryu, Sang‐Yeob Kim, Chang Ohk Sung, Ju Hyun Shim, JeongYeon Hong, Kyunggon Kim, Hyo Jeong Kang
Liver International.2024; 44(5): 1202. CrossRef - Clinical‐Radiologic Morphology‐Radiomics Model on Gadobenate Dimeglumine‐Enhanced MRI for Identification of Highly Aggressive Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Temporal Validation and Multiscanner Validation
Wanjing Zheng, Xiaodan Chen, Meilian Xiong, Yu Zhang, Yang Song, Dairong Cao
Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Model for Proliferative HCC Using LI‐RADS: Assessing Therapeutic Outcomes in Hepatectomy and TKI‐ICI Combination
Mengtian Lu, Zuyi Yan, Qi Qu, Guodong Zhu, Lei Xu, Maotong Liu, Jifeng Jiang, Chunyan Gu, Ying Chen, Tao Zhang, Xueqin Zhang
Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Post-International Gastrointestinal Cancers’ Conference (IGICC) Position Statements
Suayib Yalcin, Sahin Lacin, Ahmed Kaseb, Bora Peynircioğlu, Murat Cantasdemir, Barbaros Çil, Pervin Hurmuz, Ahmet Doğrul, Murat Bozkurt, Hüseyin Abali, Okan Akhan, Halis Şimşek, Berksoy Sahin, Faruk Aykan, İdris Yücel, Gürkan Tellioğlu, Fatih Selçukbirici
Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2024; Volume 11: 953. CrossRef - The impact of matrix stiffness on hepatic cell function, liver fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma—Based on quantitative data
Kiyoon Min, Sathish Kumar Karuppannan, Giyoong Tae
Biophysics Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Low-Baseline PD1+ Granulocytes Predict Responses to Atezolizumab–Bevacizumab in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Catia Giovannini, Fabrizia Suzzi, Francesco Tovoli, Mariangela Bruccoleri, Mariarosaria Marseglia, Eleonora Alimenti, Francesca Fornari, Massimo Iavarone, Fabio Piscaglia, Laura Gramantieri
Cancers.2023; 15(6): 1661. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the pathologist’s perspective
Wei-Qiang Leow, Anthony Wing-Hung Chan, Paulo Giovanni L. Mendoza, Regina Lo, Kihan Yap, Haeryoung Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(Suppl): S302. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Three-dimensional multifrequency magnetic resonance elastography improves preoperative assessment of proliferative hepatocellular carcinoma
Guixue Liu, Di Ma, Huafeng Wang, Jiahao Zhou, Zhehan Shen, Yuchen Yang, Yongjun Chen, Ingolf Sack, Jing Guo, Ruokun Li, Fuhua Yan
Insights into Imaging.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lymphocyte-Rich Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Multiple Lymphadenopathy and Positive Epstein–Barr Virus Encoding Region
Pin-Yi Wang, Yu-Hsuan Kuo, Ming-Jen Sheu, Hsing-Tao Kuo, Wen-Ying Lee, Yu-Ting Kuo, Su-Hung Wang, Zu-Yau Lin
Case Reports in Hepatology.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Genome-Wide Extrachromosomal Circular DNA Profiling of Paired Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Adjacent Liver Tissues
Jianyu Ye, Peixin Huang, Kewei Ma, Zixin Zhao, Ting Hua, Wenjing Zai, Jieliang Chen, Xiutao Fu
Cancers.2023; 15(22): 5309. CrossRef - Proliferative hepatocellular carcinomas in cirrhosis: patient outcomes of LI-RADS category 4/5 and category M
Subin Heo, Hyo Jeong Kang, Sang Hyun Choi, Sehee Kim, Youngeun Yoo, Won-Mook Choi, So Yeon Kim, Seung Soo Lee
European Radiology.2023; 34(5): 2974. CrossRef - Cellular heterogeneity and plasticity in liver cancer
Lo-Kong Chan, Yu-Man Tsui, Daniel Wai-Hung Ho, Irene Oi-Lin Ng
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2022; 82: 134. CrossRef - MRI features of histologic subtypes of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with histologic, genetic, and molecular biologic classification
Ja Kyung Yoon, Jin-Young Choi, Hyungjin Rhee, Young Nyun Park
European Radiology.2022; 32(8): 5119. CrossRef - Variant Hepatocellular Carcinoma Subtypes According to the 2019 WHO Classification: An Imaging-Focused Review
Liang Meng Loy, Hsien Min Low, Jin-Young Choi, Hyungjin Rhee, Chin Fong Wong, Cher Heng Tan
American Journal of Roentgenology.2022; 219(2): 212. CrossRef - Paraneoplastic syndromes in hepatocellular carcinoma: a review
Yuki Ong, Cheong Wei Terence Huey, Vishalkumar Girishchandra Shelat
Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2022; 16(5): 449. CrossRef - Morphomolecular Classification Update on Hepatocellular Adenoma, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
Venkata S. Katabathina, Lokesh Khanna, Venkateswar R. Surabhi, Marta Minervini, Krishna Shanbhogue, Anil K. Dasyam, Srinivasa R. Prasad
RadioGraphics.2022; 42(5): 1338. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 583. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Korean Journal of Radiology.2022; 23(12): 1126. CrossRef - Histomorphological Subtypes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Review and Update
Yoon Jung Hwang, Haeryoung Kim
AJSP: Reviews and Reports.2022; 27(6): 234. CrossRef - Pediatric Primary Hepatic Tumors: Diagnostic Considerations
Bryony Lucas, Sanjita Ravishankar, Irina Pateva
Diagnostics.2021; 11(2): 333. CrossRef - A Case of Lymphocyte-Rich Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Patient Who Was Treated for Colon Cancer
Jae Won Song, Ho Soo Chun, Jae Seung Lee, Hye Won Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Young Nyun Park, Dai Hoon Han, Do Young Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 69. CrossRef - HCC You Cannot See
Vaishnavi Boppana, Sakshi Sahni, Joseph Glass, Christopher Chang, Denis M McCarthy
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2021; 66(7): 2185. CrossRef - An update on subtypes of hepatocellular carcinoma: From morphology to molecular
Monika Vyas, Dhanpat Jain
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2021; 64(5): 112. CrossRef - HCC: role of pre- and post-treatment tumor biology in driving adverse outcomes and rare responses to therapy
Sandeep Arora, Roberta Catania, Amir Borhani, Natally Horvat, Kathryn Fowler, Carla Harmath
Abdominal Radiology.2021; 46(8): 3686. CrossRef - Gadoxetate-enhanced MRI Features of Proliferative Hepatocellular Carcinoma Are Prognostic after Surgery
Hyo-Jin Kang, Haeryoung Kim, Dong Ho Lee, Bo Yun Hur, Yoon Jung Hwang, Kyung-Suk Suh, Joon Koo Han
Radiology.2021; 300(3): 572. CrossRef - Radiologic Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Woo Kyoung Jeong
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 78(5): 261. CrossRef - Update on Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Brief Review from Pathologist Standpoint
Nese Karadag Soylu
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2020; 51(4): 1176. CrossRef
- Computational Pathology: A Survey Review and The Way Forward

- Liver Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance
- So Hyun Park, Bohyun Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):25-31. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.25
- 6,125 Views
- 252 Downloads
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) surveillance is recommended when the annual incidence of HCC exceeds 1.5%. In 2018, several international guidelines included alternative surveillance modalities, such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), as alternatives for patients with inadequate surveillance with an ultrasound. Currently, abbreviated MRI selectively includes several key sequences and is emerging as an effective tool for HCC surveillance with reduced cost and scan time and the required diagnostic performance. The incidence of HCC substantially impacts the benefits of surveillance in terms of cost-effectiveness. Therefore, we need to individualize imaging surveillance of HCC, tailor screening, and determine risk-stratified strategies. The purpose of this article was to present a brief overview of the diagnostic performance and cost-effectiveness of liver MRI as an HCC surveillance tool.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Post-International Gastrointestinal Cancers’ Conference (IGICC) Position Statements
Suayib Yalcin, Sahin Lacin, Ahmed Kaseb, Bora Peynircioğlu, Murat Cantasdemir, Barbaros Çil, Pervin Hurmuz, Ahmet Doğrul, Murat Bozkurt, Hüseyin Abali, Okan Akhan, Halis Şimşek, Berksoy Sahin, Faruk Aykan, İdris Yücel, Gürkan Tellioğlu, Fatih Selçukbirici
Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2024; Volume 11: 953. CrossRef - Adding MRI as a Surveillance Test for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis Can Improve Prognosis
Su Jong Yu, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Dong Ho Lee, Su Jin Kim, Eun Ju Cho, Se Hyung Kim, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Yoon Jun Kim, Jeong Min Lee, Jae Young Lee, Jung-Hwan Yoon
Biomedicines.2023; 11(2): 382. CrossRef - MRI features of histologic subtypes of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with histologic, genetic, and molecular biologic classification
Ja Kyung Yoon, Jin-Young Choi, Hyungjin Rhee, Young Nyun Park
European Radiology.2022; 32(8): 5119. CrossRef - Imaging features of hepatobiliary MRI and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma development
Jong-In Chang, Dong Hyun Sinn, Woo Kyoung Jeong, Jeong Ah Hwang, Ho Young Won, Kyunga Kim, Wonseok Kang, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung-Woon Paik
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology.2022; 57(12): 1470. CrossRef - Potential of a Non-Contrast-Enhanced Abbreviated MRI Screening Protocol (NC-AMRI) in High-Risk Patients under Surveillance for HCC
François Willemssen, Quido de Lussanet de la Sablonière, Daniel Bos, Jan IJzermans, Robert De Man, Roy Dwarkasing
Cancers.2022; 14(16): 3961. CrossRef - Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients diagnosed under regular surveillance: potential implications for surveillance goal
Joo Hye Song, Myung Ji Goh, Yewan Park, Joo Hyun Oh, Wonseok Kang, Dong Hyun Sinn, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 56(3): 274. CrossRef
- A Post-International Gastrointestinal Cancers’ Conference (IGICC) Position Statements

Original Articles
- Gut-microbiome Taxonomic Profiling as Non-invasive Biomarkers for the Early Detection of Alcoholic Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jun Seok, Ki Tae Suk
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):32-40. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.32
- 5,741 Views
- 238 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a prevalent form of primary liver cancer and the fifth leading cause of worldwide cancer mortality. Though early diagnosis of HCC is important, so far lack of effective biomarkers for early diagnosis of HCC has been a problem. In this study, we searched for potential functional biomarkers of alcoholic HCC by using metagenomics approach.
Methods
Between September 2017 and April 2019, normal control (n=44), alcoholic liver cirrhosis (n=44), and alcoholic HCC (n=13) groups were prospectively enrolled and analyzed. Gut microbiota was analyzed using the 16S-based microbiome taxonomic profiling platform of EzBioCloud Apps and analyzing system.
Results
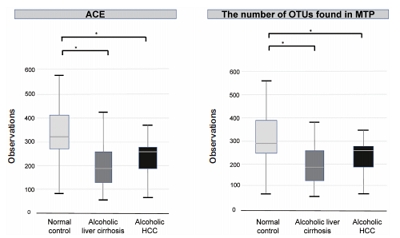
There was a statistically significant difference among groups in diversity (P<0.05). In the comparison of phylum between cirrhosis and HCC, Proteobacteria were increased and Bacteroidetes were decreased. Firmicutes were not significantly different among the three groups. In the taxonomic profiling, relative abundance of Lactobacillus in the cirrhosis and HCC groups showed richness (P<0.05). In the biomarker analysis between cirrhosis and HCC, obiquinome Fe-S protein 3, global nitrogen regulator, Vesicle-associated membrane protein 7, toxin YoeB, peroxisome-assembly ATPase, and nitrogen oxide reductase regulator were differently expressed (P<0.001).
Conclusions
Alcoholic HCC showed different expressions in the stool taxonomy and biomarker compared with that of cirrhosis and control. Therefore, new biomarkers using stool analysis for alcoholic HCC are necessary.

- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea Between 2008 and 2011: an Analysis of Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
- Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Young Eun Chon, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Young-Joo Won, Eunyang Kim, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):41-52. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.41

- 5,407 Views
- 198 Downloads
- 15 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Backgrounds/Aims
Backgrounds/Aims: In Korea, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cancer and results in the second-highest cancer death rate among all cancers. We aimed to describe the characteristics of patients who were newly diagnosed with HCC in Korea between 2008 and 2011.
Methods
The Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry (KPLCR) is a random sample consisting of approximately 15% of patients with newly diagnosed primary liver cancer registered in the Korean Central Cancer Registry. We investigated the baseline characteristics, treatment modalities, and overall survival (OS) of patients with HCC registered in the KPLCR between 2008 and 2011.
Results
A total of 6,083 patients were histologically or radiologically diagnosed with HCC. The hepatitis B virus was the predominant HCC etiology (72.0%). According to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system, stages 0, A, B, C, and D accounted for 8.6%, 39.7%, 11.5%, 33.8%, and 6.9%, respectively. Transarterial therapy (41.7%) was the most commonly performed initial treatment, followed by best supportive care (21.7%), surgical resection (16.7%), and local ablation therapies (10.6%). The overall rate of adherence to the BCLC treatment guideline was only 37.7%. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 65.6%, 46.2%, and 36.8%, respectively.
Conclusions
Between 2008 and 2011, approximately half of patients with HCC (48.3%) were candidates for curative treatment (BCLC stage 0 or A), but one-third of patients (33.8%) had advanced HCC (BCLC stage C). Transarterial therapy was the most commonly conducted initial treatment and the 5-year OS rate was 36.8% in this period. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adjuvant and neoadjuvant immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma
Josep M. Llovet, Roser Pinyol, Mark Yarchoan, Amit G. Singal, Thomas U. Marron, Myron Schwartz, Eli Pikarsky, Masatoshi Kudo, Richard S. Finn
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology.2024; 21(4): 294. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence is decreasing in Korea but increasing in the very elderly
Young Eun Chon, Seong Yong Park, Han Pyo Hong, Donghee Son, Jonghyun Lee, Eileen Yoon, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Bong Ahn, Soung Won Jeong, Dae Won Jun
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(1): 120. CrossRef - Implications of the first edition of the Korean expert consensus-based practice recommendations for transarterial chemoembolization in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Jin Wook Chung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 235. CrossRef - Surgical resection versus ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma: The debate is still open
Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 174. CrossRef - Cause of death and cause-specific mortality for primary liver cancer in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study in hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Bo Hyun Kim, Dahhay Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Joo Won, Hyunsoon Cho
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 242. CrossRef - Impact of expanding hepatitis B treatment guidelines: A modelling and economic impact analysis
Young‐Suk Lim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Jae‐Jun Shim, Homie Razavi, Devin Razavi‐Shearer, Dong Hyun Sinn
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2022; 56(3): 519. CrossRef - Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: It is time to move forward
Bo Hyun Kim, Yuri Cho, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 810. CrossRef - Therapeutic Decision Making in Hepatocellular Carcinoma According to Age and Child–Pugh Class: A Nationwide Cohort Analysis in South Korea
Sunmin Park, Chai Hong Rim, Young Kul Jung, Won Sup Yoon, Alessandro Granito
Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Outcome of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor and Molecular Target Agent Combination for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Beyond Sorafenib Era
Nae-Yun Heo
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 77(3): 145. CrossRef - Rare Case of Pyogenic Brain Abscess after Transarterial Chemoembolization in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Case Report and Literature Review
Jun-Ho Myeong, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 81. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Dong Ho Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Ju-Yeon Cho, Jonggi Choi, Young Chang, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 58. CrossRef - Glucose Variability and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Eun Ju Cho, Kyungdo Han, Soo Seong Heo, Bo-Yeon Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Su Jong Yu
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2021; 30(5): 974. CrossRef -
Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein improves diagnostic accuracy for hepatocellular carcinoma
Han Ah Lee, Yoo Ra Lee, Young-Sun Lee, Young Kul Jung, Ji Hoon Kim, Hyunggin An, Hyung Joon Yim, Yoon Tae Jeen, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun, Yeon Seok Seo
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(28): 4687. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Young Eun Chon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Sik Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(2): 135. CrossRef - Efficacy of Local Treatments for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Involving the Inferior Vena Cava and/or Right Atrium
Han Ah Lee, Chai Hong Rim
Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2020; Volume 7: 435. CrossRef
- Adjuvant and neoadjuvant immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma

- A Survey of Liver Cancer Specialists’ Views on the National Liver Cancer Screening Program in Korea
- Won Sohn, Young-Sun Lee, Jae Geun Lee, Jihyun An, Eun Sun Jang, Dong Ho Lee, Dong Hyun Sinn
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):53-59. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.53

- 4,574 Views
- 137 Downloads
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aims
To reduce the cancer burden, the Korean government initiated the National Cancer Control Plan including the National Liver Cancer Screening Program (NLCSP). Ultrasonography examinations and α-fetoprotein tests at six-month intervals are currently offered for high-risk individuals. High-risk individuals are identified by reviewing the National Health Insurance Service claims data for medical use for the past two years using International Classification of Diseases Codes for specific liver disease. We surveyed the attitudes and opinions towards the NLCSP to understand the issues surrounding the NLCSP in Korea.
Methods
Altogether, 90 Korean Liver Cancer Association members participated in online and offline surveys between November and December 2019.
Results
Approximately one-quarter (27%) of the survey participants rated the NLCSP as very contributing and about two-thirds (68%) as contributing to some extent toward reducing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)-related deaths in Korea. Most (87.8%) responded that the current process of identifying high-risk individuals needs improvement. Many (78.9%) were concerned that the current process identifies individuals who use medical services and paradoxically misses those who do not. When asked for the foremost priority for improvement, solving ‘duplication issues between the NLCSP and private clinic HCC screening practices’ was the most commonly selected choice (23.3%).
Conclusions
The survey participants positively rated the role of the NLCSP in reducing liver cancer deaths. However, many participants rated the NCLSP as needing improvement in all areas. This survey can be a relevant resource for future health policy decisions regarding the NLCSP in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Potential role of Fibrosis‐4 score in hepatocellular carcinoma screening: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Sujeong Shin, Won Sohn, Yoosoo Chang, Yoosun Cho, Min‐Jung Kwon, Sarah H. Wild, Christopher D. Byrne, Seungho Ryu
Hepatology Research.2024; 54(6): 551. CrossRef - Recent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Managements in Korea: Focus on the Updated Guidelines in 2022
Yuri Cho, Bo Hyun Kim, Young-Suk Lim
Digestive Disease Interventions.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical practice guideline and real-life practice in hepatocellular carcinoma: A Korean perspective
Myung Ji Goh, Dong Hyun Sinn, Jong Man Kim, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ho Hyun, Jeong Il Yu, Jung Yong Hong, Moon Seok Choi
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(2): 197. CrossRef - Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: a large-scale multicenter study
Sun Hong Yoo, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Han-Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim, Do Seon Song, Seong Hee Kang, Moon Young Kim, Young-Hwan Ahn, Jieun Han, Young Seok Kim, Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, J
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 189. CrossRef - Selecting the Target Population for Screening of Hepatic Fibrosis in Primary Care Centers in Korea
Huiyul Park, Eileen L. Yoon, Mimi Kim, Seon Cho, Jung-Hwan Kim, Dae Won Jun, Eun-Hee Nah
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(6): 1474. CrossRef - Fibrosis Burden of Missed and Added Populations According to the New Definition of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver
Huiyul Park, Eileen L. Yoon, Mimi Kim, Jung-Hwan Kim, Seon Cho, Dae Won Jun, Eun-Hee Nah
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(19): 4625. CrossRef
- Potential role of Fibrosis‐4 score in hepatocellular carcinoma screening: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study

Case Reports
- Lipiodol Pneumonitis Following Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Sungkeun Kim, Hee Yeon Kim, Su Lim Lee, Young Mi Ku, Yoo Dong Won, Chang Wook Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):60-66. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.60

- 5,631 Views
- 147 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a useful palliative therapeutic modality for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Postembolization syndromes, such as fever, abdominal pain, and elevated liver enzyme levels are commonly known complications of TACE. One post-TACE pulmonary complication, lipiodol pneumonitis, is rarely reported. Lipiodol pneumonitis after TACE appears to be associated with chemical injury due to accidental perfusion of lipiodol to the lung vasculature, promoted by arteriovenous shunts within the hypervascular HCC. Here, we report a 42-year-old man with unresectable HCC and hepatic vein thrombosis. The patient was initially treated with TACE. The following day after TACE, acute respiratory symptoms such as dyspnea and cough developed with decreased oxygen saturation. Chest X-ray and computed tomography showed multiple patches and diffuse ground-glass opacities in both lung fields, suggesting of lipiodol pneumonitis. The patient’s condition and radiologic abnormalities subsequently improved after 2 weeks of conservative treatment alone.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lipiodol-induced Pneumonitis Following Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Heechul Nam
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2022; 80(5): 233. CrossRef
- Lipiodol-induced Pneumonitis Following Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma

- Recurrent Coronary Artery Vasospasm in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sorafenib: a Case Report and Literature Review
- Dae Hyun Lim, Jai Hoon Yoon, Dae Won Jun, Oh Young Lee, Byung Chul Yoon, Hang Rak Lee, Kyung Soo Kim, Ho Soon Choi
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):67-71. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.67
- 4,675 Views
- 90 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Tyrosine kinase inhibitors are widely used as targeted treatments for various malignancies. Sorafenib is an orally active tyrosine kinase inhibitor that blocks the signaling pathways of several growth factors. Its use is approved for various malignancies such as unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, and gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Several adverse effects have been reported in the literature; however, cardiotoxicity is rare. We present a case of recurrent coronary vasospasm caused by short-term administration (5 days) of sorafenib. Since it caused refractory ischemia after re-administration, we had no choice but to stop the treatment.

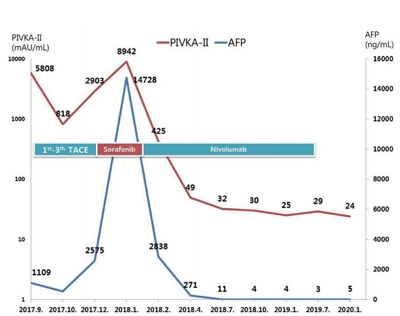
- Nivolumab for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Multiple Lung Metastases after Sorafenib Failure
- Jaewoong Kim, Jin Won Chang, Jun Yong Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):72-77. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.72
- 4,851 Views
- 143 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Over the past decade, standard first-line systemic treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been based on sorafenib, a multi-kinase inhibitor. Regorafenib, another tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is the only second-line therapy that has been globally approved after progression under sorafenib treatment. Recently, immunotherapeutic agents have emerged as promising treatment options in many different malignancies, including advanced HCC. Nivolumab is the first immunotherapy approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in HCC patients with advanced-stage second-line after sorafenib failure. In this report, a case of advanced HCC with multiple lung metastases in which a complete response and maintained progression-free status was achieved with nivolumab, following the failure of transarterial chemoembolization and sorafenib is presented. We hope this report may help expand the clinical application of second-line treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with multiple lung metastasis completely cured using nivolumab: a case report
Ji Eun Han, Hyo Jung Cho, Soon Sun Kim, Jae Youn Cheong
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(2): 169. CrossRef
- Infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with multiple lung metastasis completely cured using nivolumab: a case report

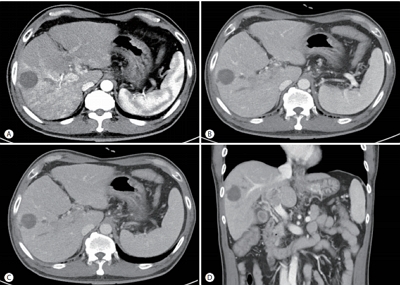
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis Treated by Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy
- Jin Yong Lee, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Seong Joon Chun, Sun Hyun Bae, Jae Myeong Lee, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):78-83. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.78
- 5,079 Views
- 99 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Sorafenib is the standard treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein thrombosis (PVT). Additionally, hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy has been used as a treatment option for advanced HCC. Here, we report a case of sustained partial response in a patient with advanced HCC with PVT after hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy and radiation therapy.

- Successful Sequential Therapy Involving Regorafenib after Failure of Sorafenib in a Patient with Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Liver Transplantation
- Soon Kyu Lee, Jeong Won Jang, Heechul Nam, Pil Soo Sung, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):84-89. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.84
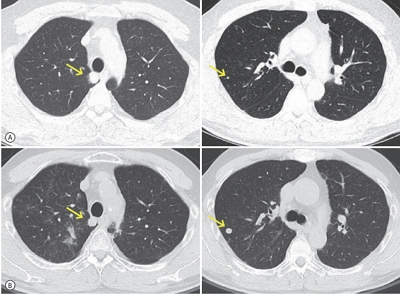
- 3,637 Views
- 92 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The efficacy and safety of sequential systemic therapy for the treatment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after liver transplantation (LT) are not well established. This study describes a successful experience where sequential therapy with sorafenib followed by regorafenib was used to treat recurrent HCC in a 54-year old male LT recipient. After HCC recurred in both lungs 10 months after LT, sorafenib was administered with radiation therapy to treat pulmonary metastases. However, after 4 months of sorafenib treatment showed progressive pulmonary metastases, sequential regorafenib treatment was started. After 3 months (cycles) of regorafenib treatment, tumor response was partial, and after 6 months (cycles), disease status remained stable without signs of progression or drug-related serious adverse events. This case suggests that sequential systemic therapy is feasible in patient with recurrent HCC after LT.

- Combined Transarterial Chemoembolization and External Beam Radiotherapy in a Patient with Recurrent Huge Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Hepatic Resection
- Jesang Yu, Jinhong Jung, Sang Min Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):90-97. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.90
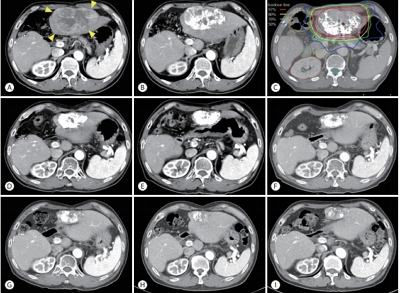
- 3,681 Views
- 82 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The optimal treatment strategy for unresectable huge hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is yet to be established. Non-surgical monotherapy demonstrated insufficient oncologic outcomes in previously reported studies. To improve the clinical outcomes of unresectable huge HCC, combined locoregional treatments can be considered in selected cases. Here, we report a case of 58-year-old male patient who was treated with combined transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and external beam radiotherapy for recurrent HCC after a previous hepatic resection. After combined TACE and radiotherapy for the intrahepatic lesion, two metastases were diagnosed in the pelvic bones and lung; each lesion was successfully treated with salvage radiotherapy. During the long-term follow-up period (around 8 years 7 months after combined TACE and radiotherapy for the recurrent huge HCC), no definite viable tumors were observed in any of the treated liver, bone, and lung lesions.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION



 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter