Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Previous issues
Review Articles
- Liver Transplantation in Mixed Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cholangiocarcinoma
- Jong Man Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):85-90. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.85
- 4,049 Views
- 94 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
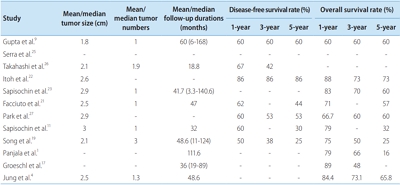
PDF - Mixed hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma (HCC-CC) are rare tumors, and the risk factors associated with them are not well understood yet. Moreover, the diagnosis of mixed HCC-CC can be complicated due to the difficulty in distinguishing mixed HCC-CC from HCC and intrahepatic CCC on radiological images. Serum tumor markers are useful when the radiological images are inconclusive. It remains unclear whether the prognosis of mixed HCC-CC differs from that of HCC. However, several studies have reported that the tumor recurrence and patient survival rates of mixed HCC-CC were similar to those of HCC after liver transplantation (LT) and liver resection. In this paper, we report that LT in patients with mixed HCC-CC achieves outcomes which are similar to those seen in LT for HCC. Therefore, the diagnosis of mixed HCC-CC should not be considered as a contraindication for LT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Liver transplantation for combined hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma: A multicenter study
Jongman Kim, Dong-Jin Joo, Shin Hwang, Jeong-Moo Lee, Je-Ho Ryu, Yang-Won Nah, Dong-Sik Kim, Doo-Jin Kim, Young-Kyoung You, Hee-Chul Yu
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2023; 15(7): 1340. CrossRef - The Role of Immunosuppression for Recurrent Cholangiocellular Carcinoma after Liver Transplantation
Safak Gül-Klein, Paulina Schmitz, Wenzel Schöning, Robert Öllinger, Georg Lurje, Sven Jonas, Deniz Uluk, Uwe Pelzer, Frank Tacke, Moritz Schmelzle, Johann Pratschke, Ramin Raul Ossami Saidy, Dennis Eurich
Cancers.2022; 14(12): 2890. CrossRef
- Liver transplantation for combined hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma: A multicenter study

- Contrast-enhanced Ultrasonography: The Third Modality for Differentiation of Liver Mass
- Min Kyu Kang, Moon Young Kim, Seong Hee Kang, Soon Koo Baik
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):91-96. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.91
- 4,995 Views
- 103 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
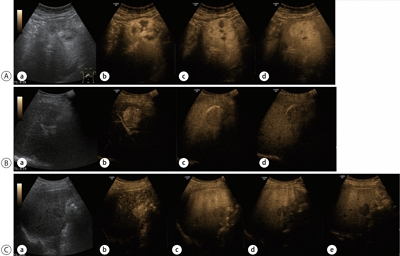
PDF - Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) using microbubble ultrasonography contrast agent can show the vascular structure and unique contrast enhancement patterns of focal liver lesions, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). CEUS shows three phases, similar to a vascular pattern on computer tomography (CT), and typical arterial enhancement and portal or late phase washout in HCC. CEUS can show real-time images without nephrotoxicity or radiation hazard and can be used as guidance for loco-regional treatment and estimation of treatment response of HCC. In addition, some data recently revealed the usefulness of CEUS in the early estimation of response to anti-cancer pharmacological (i.e., sorafenib) therapy in advanced HCC. Although CEUS has limitations in clinical practice and more investigation is needed for its validation, it is recommended as a main diagnostic modality in a few major clinical practice guidelines for HCC. Thus, greater understanding of CEUS is necessary to extend its application in real practice for diagnosis and management of diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perfluorobutane-Enhanced Ultrasound for Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma From Non-hepatocellular Malignancies or Benignancy: Comparison of Imaging Acquisition Methods
Seungchul Han, Se Woo Kim, Sungeun Park, Jeong Hee Yoon, Hyo-Jin Kang, Jeongin Yoo, Ijin Joo, Jae Seok Bae, Jeong Min Lee
Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology.2023; 49(10): 2256. CrossRef
- Perfluorobutane-Enhanced Ultrasound for Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma From Non-hepatocellular Malignancies or Benignancy: Comparison of Imaging Acquisition Methods

- The Genomic Landscape and Its Clinical Implications in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Sun Young Yim, Ju-Seog Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):97-107. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.97

- 6,861 Views
- 260 Downloads
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a complex process. During the last decade, advances in genomic technologies enabled delineation of the genomic landscape of HCC, resulting in the identification of the common underlying molecular alterations. The tumor microenvironment, regulated by inflammatory cells, including cancer cells, stromal tissues, and the surrounding extracellular matrix, has been extensively studied using molecular data. The integration of molecular, immunological, histopathological, and clinical findings has provided clues to uncover predictive biomarkers to enhance responses to novel therapies. Herein, we provide an overview of the current HCC genomic landscape, previously identified gene signatures that are used routinely to predict prognosis, and an immune-specific class of HCC. Since biomarker-driven treatment is still an unmet need in HCC management, translation of these discoveries into clinical practice will lead to personalized therapies and improve patient care, especially in the era of targeted and immunotherapies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comprehensive clinicopathologic study of alpha fetoprotein‐expression in a large cohort of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Dirk Andreas Ridder, Arndt Weinmann, Mario Schindeldecker, Lana Louisa Urbansky, Kristina Berndt, Tiemo Sven Gerber, Hauke Lang, Johannes Lotz, Karl J. Lackner, Wilfried Roth, Beate Katharina Straub
International Journal of Cancer.2022; 150(6): 1053. CrossRef - Two distinct stem cell‐like subtypes of hepatocellular carcinoma with clinical significance and their therapeutic potentials
Sung Hwan Lee, Yun Seong Jeong, Sunyoung Lee, Bo Hwa Sohn, Ho Kyoung Hwang, Gi Hong Choi, Chang Moo Kang, Jin Sub Choi, Woo Jung Lee, Jae‐Ho Cheong, Hee Jin Jang, Ahmed Kaseb, Lewis Roberts, Sun Young Yim, Yun Shin Chun, Ju‐Seog Lee
Cancer Communications.2022; 42(2): 179. CrossRef - Activated TAZ induces liver cancer in collaboration with EGFR/HER2 signaling pathways
Hyuk Moon, Hyunjung Park, Min Jee Chae, Hye Jin Choi, Do Young Kim, Simon Weonsang Ro
BMC Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Tumor aggressiveness is independent of radiation quality in murine hepatocellular carcinoma and mammary tumor models
Eshwar B. Udho, Shane M. Huebner, Dawn M. Albrecht, Kristina A. Matkowskyj, Linda Clipson, Catigan A. Hedican, Rachel Koth, Santina M. Snow, Emily L. Eberhardt, Devon Miller, Rachel Van Doorn, Genti Gjyzeli, Erin K. Spengler, Douglas R. Storts, Douglas H.
International Journal of Radiation Biology.2021; 97(8): 1140. CrossRef - Infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with multiple lung metastasis completely cured using nivolumab: a case report
Ji Eun Han, Hyo Jung Cho, Soon Sun Kim, Jae Youn Cheong
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(2): 169. CrossRef - Update on Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Brief Review from Pathologist Standpoint
Nese Karadag Soylu
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2020; 51(4): 1176. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma: new provisions of the WHO classification, 5th edition, 2019
E.M. Nepomnyashchaya, A.V. Shaposhnikov, E.A. Yurieva
Arkhiv patologii.2020; 82(6): 36. CrossRef
- Comprehensive clinicopathologic study of alpha fetoprotein‐expression in a large cohort of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma

Original Articles
- Serum PD-1 Levels Change with Immunotherapy Response but Do Not Predict Prognosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Hye Won Lee, Kyung Joo Cho, Soon Young Shin, Ha Yan Kim, Eun Ju Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):108-116. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.108
- 5,651 Views
- 154 Downloads
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aims
Programmed death receptor 1 (PD-1) is a promising new target for treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A high expression level of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a possible prognostic indicator for poor outcome in other malignancies. Here, we investigated the clinical significance of PD-1 and PD-L1 in patients with HCC.
Methods
We enrolled patients with HCC who underwent surgical resection at Severance Hospital between 2012 and 2017 and investigated the levels of PD-L1 in HCC tissues (tPD-L1) and PD-L1/PD-1 in serum (sPD-L1/sPD-1). We also aimed to determine whether expression levels correlated with clinical and histological features.
Results
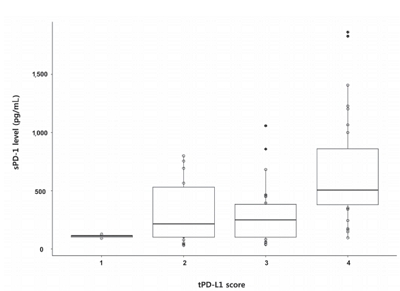
A total of 72 patient samples were analyzed. The median sPD-L1 and sPD-1 levels were 25.72 and 341.44 pg/mL, respectively. A positive correlation was detected between tPD-L1 and sPD-1 levels (R2=0.426, P<0.001). The median sPD-1 level increased linearly with tPD-L1 score (P=0.002). During the follow-up period, HCC recurred in eight (11.1%) patients and liverrelated mortality occurred in eight (11.1%) patients. Higher sPD-L1 levels (≥19.18 pg/mL) tended to be associated with liver-related mortality (hazard ratio 6.866; 95% confidence interval, 0.804-58.659, P=0.078). sPD-1 levels of patients treated with nivolumab as a second-line therapy changed serially, and a >50% reduction in sPD-1 levels was observed immediately after nivolumab administration. However, sPD-1 level was not associated directly with prognosis in patients with advanced HCC.
Conclusions
The results demonstrated that PD-L1 and PD-1 levels changed according to the immunotherapy. However, no significant association with clinical outcome in patients with HCC was detected. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Blood-based biomarkers for immune-based therapy in advanced HCC: Promising but a long way to go
Pil Soo Sung, Isaac Kise Lee, Pu Reun Roh, Min Woo Kang, Jaegyoon Ahn, Seung Kew Yoon
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum levels of soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1): A possible biomarker in predicting post-treatment outcomes in patients with early hepatocellular carcinoma
Tudor Mocan, Maria Ilies, Iuliana Nenu, Rares Craciun, Adelina Horhat, Ruxandra Susa, Iulia Minciuna, Ioana Rusu, Lavinia-Patricia Mocan, Andrada Seicean, Cristina Adela Iuga, Nadim Al Hajjar, Mihaela Sparchez, Daniel-Corneliu Leucuta, Zeno Sparchez
International Immunopharmacology.2021; 94: 107467. CrossRef - Interfacial interactions of SERS-active noble metal nanostructures with functional ligands for diagnostic analysis of protein cancer markers
Han-Jung Ryu, Won Kyu Lee, Yoon Hyuck Kim, Jae-Seung Lee
Microchimica Acta.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Status and Future Direction of Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What Do the Data Suggest?
Hye Won Lee, Kyung Joo Cho, Jun Yong Park
Immune Network.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Nivolumab for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Multiple Lung Metastases after Sorafenib Failure
Jaewoong Kim, Jin Won Chang, Jun Yong Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(1): 72. CrossRef
- Blood-based biomarkers for immune-based therapy in advanced HCC: Promising but a long way to go

- An Analysis for Survival Predictors for Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Who Failed to Sorafenib Treatment in Pre-regorafenib Era
- Chan Uk Lee, Young-Sun Lee, Ji Hoon Kim, Minjin Lee, Sehwa Kim, Young Kul Jung, Yeon Seok Seo, Hyung Joon Yim, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):117-127. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.117

- 4,433 Views
- 67 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
Sorafenib is the standard treatment for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We aimed to investigate the prognosis predictors and the role of second-line cytotoxic systemic chemotherapy (CSC) in patients with advanced HCC after sorafenib discontinuation in the pre-regorafenib era.
Methods
From 2007 to 2015 in the pre-regorafenib era, the medical records of 166 HCC patients, who had permanently discontinued sorafenib, were retrospectively reviewed. For further analysis of survival factors after sorafenib treatment failure, we compared the survival of patients who had maintained liver function after second-line treatment with the best supportive care (BSC) group and selective BSC (SBSC) group.
Results
After discontinuation of sorafenib, median overall survival (OS) was 2.8 (1.9-3.7) months. The OS in patients who discontinued sorafenib due to adverse effect, progression, and poor clinical condition were 5.5 (2.4-8.6), 5.5 (2.2-8.9), and 0.9 (0.5-1.3) months, respectively (P<0.001). The independent predictive factors of survival after sorafenib failure were serum level of bilirubin and albumin, α-fetoprotein, discontinuation cause, and second-line CSC. In comparison with survival between second-line CSC and BSC group, the CSC group showed better survival outcome compared to the BSC group (10.6 vs. 1.6 months, P<0.001) and SBSC group (10.6 vs. 4.2 months, P=0.023).
Conclusions
The survival after sorafenib failure in patients who discontinued sorafenib due to progression and adverse effects was significantly better than in those who discontinued treatment due to clinical deterioration. In the pre-regorafenib era, patients who received second-line CSC showed better survival than those who received only supportive care after sorafenib failure.

- Tenofovir and Entecavir Have Similar Renal Adverse Events on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Transarterial Chemoembolization
- Young Youn Cho, Young Hwan Choi, Su Jong Yu, Eun Ju Cho, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Yoon Jun Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):128-135. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.128
- 4,110 Views
- 50 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) is potentially nephrotoxic in chronic hepatitis B patients. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients treated using transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) are at an increased risk of renal injury. The aim of this study was to determine whether TDF is associated with more renal adverse events than entecavir (ETV) in HCC patients treated with TACE.
Methods
In this retrospective single-center study, we selected 53 HCC patients who were treated with TDF from January 2012 to July 2013 and had their first TACE procedure in the same period. These patients were matched by age and sex to patients treated with ETV.
Results
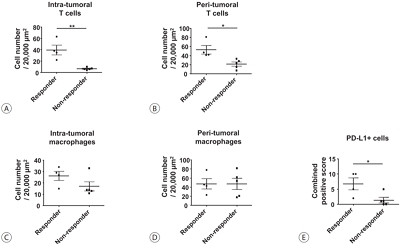
There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics, including HCC factors, and nephrotoxic drug use, between the two groups. The median follow-up period was 17.0 and 20.0 months for the TDF and ETV groups, respectively. There was no difference during the follow-up period between the TDF and ETV groups in the increase in creatinine over 0.5 mg/dL (17.0% and 17.0%, P=1.00, respectively) and the decrease in eGFR over 25% (43.4% and 41.5%, P=0.84, respectively). Multivariate analysis revealed that Child-Pugh class over B (hazard ratio [HR], 7.30; 95% confidence interval [CI] 2.79-19.10; P<0.01) was associated with increase in creatinine, and Child-Pugh class over B (HR, 82.74; 95% CI 12.31-555.83; P<0.01) and Barcelona-Clinic Liver Cancer stage over B (HR, 14.93; 95% CI 1.60-139.51; P=0.02) were associated with decrease in eGFR.
Conclusions
TDF has comparable safety to that of ETV for HCC patients undergoing TACE. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Big Data Information under Proportional Hazard Mathematical Model in Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus Infection Data of Patients with Interventional Liver Cancer through Antiviral Therapy of Entecavir
Yichi Zhang, Shuai Zhao, Han Ding, Xiaoling Song, Huijie Miao, Xuya Cui, Jian Wang, Bing Han, Enas Abdulhay
Journal of Healthcare Engineering.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Big Data Information under Proportional Hazard Mathematical Model in Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus Infection Data of Patients with Interventional Liver Cancer through Antiviral Therapy of Entecavir

Case Reports
- Radiation-induced Myositis after Proton Beam Therapy to Huge Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jihye Kim, Gyu Sang Yoo, Dong Hyun Sinn, Hee Chul Park, Kwang Cheol Koh
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):136-142. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.136
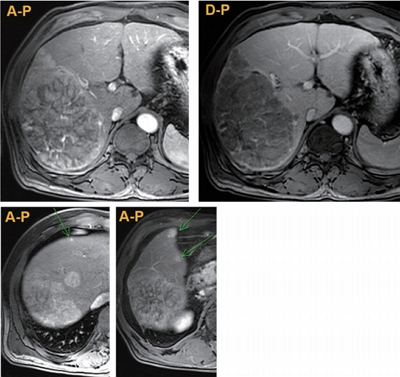
- 6,540 Views
- 126 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Proton beam therapy (PBT) is one of the advances in radiotherapy techniques, which enables dose escalation with lower probability of radiation-induced liver or gastrointestinal injuries. However, the chest wall proximal to the tumor can be affected by high dose irradiation. Here, we report on a 58-year-old male patient who presented with huge hepatocellular carcinoma, received treatment with transarterial chemoembolization and PBT, and developed severe chest wall pain due to radiation-induced myositis. The patient’s symptoms were controlled by oral steroids.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pectoralis Major Radiation Myonecrosis After Lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
Jason Gurewitz, Anand Mahadevan, Benjamin T. Cooper
Practical Radiation Oncology.2024; 14(3): 189. CrossRef - Current role of proton beam therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Gyu Sang Yoo, Jeong Il Yu, Hee Chul Park
International Journal of Gastrointestinal Intervention.2021; 10(4): 175. CrossRef
- Pectoralis Major Radiation Myonecrosis After Lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy

- Malignant Hepatic Solitary Fibrous Tumor
- Hong Il Kim, Seok Kyung In, Hyung Suk Yi, Min Jeong Lee, Hyo Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):143-148. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.143

- 3,879 Views
- 56 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatic solitary fibrous tumors (SFTs) are mostly benign and rare because of information regarding the clinical symptoms, treatment, and prognosis of their malignant forms is currently lacking. A literature review concerning malignant SFTs revealed that there were a few cases where patients experienced abdominal right upper quadrant (RUQ) pain as their first clinical symptom, and metastases were found after being diagnosed with hepatic SFT. Here, we report a patient who was previously healthy without any clinical symptoms such as RUQ pain or weight loss, but had the appearance of a metastatic mass as the first clinical presentation before a primary hepatic SFT was detected.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case of Hepatic Malignant Solitary Fibrous Tumor: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Zhiyan Fu, Evita B. Henderson-Jackson, Barbara A. Centeno, Gregory Y. Lauwers, Mihaela Druta, Daniel A. Anaya, Yukihiro Nakanishi, Samir Sami Amr
Case Reports in Pathology.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef
- A Case of Hepatic Malignant Solitary Fibrous Tumor: A Case Report and Review of the Literature

- Long-term Disease-free Survival after Trimodality Treatment of Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Involving the Inferior Vena Cava and Right Atrium
- Sunmin Park, Won Sup Yoon, Hyung Joon Yim, Chai Hong Rim
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):149-153. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.149
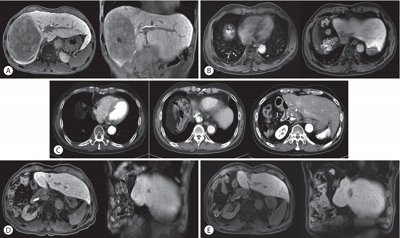
- 3,854 Views
- 76 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) involving the inferior vena cava (IVC) and/or right atrium (RA) is a rare and intractable disease. A standard treatment has not been established yet, owing to the rarity of disease and difficulties in the therapeutic treatment. Herein, we report the case of a patient who had recurrent HCC (after a prior lobectomy) involving both IVC and RA and underwent multimodality treatments including external beam radiotherapy and transarterial chemotherapy, followed by sorafenib treatment. The disease was well controlled with local treatments and sustained for 7 years until last follow-up after the systemic treatments. Our case shows a possibility of long-term survival for patients affected by HCC involving IVC and/or RA, after a rigorous multimodality treatment strategy.

- Sorafenib-induced Pancreatic Pseudocyst in a Patient with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Rare Adverse Event
- Dae-ha Kim, Minkoo Kim, Hyung Joon Yim, Sang Jun Suh, Young Kul Jung
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):154-158. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.154
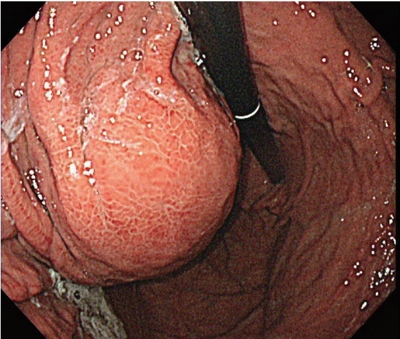
- 3,644 Views
- 52 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 54-year old man diagnosed with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma began treatment with sorafenib. After 3 weeks of treatment, he complained of abdominal pain and nausea. Abdominal sonography showed multiple hepatic lesions only. Serum amylase and lipase levels were 35 U/L and 191 U/L, respectively. The patient was diagnosed with sorafenib-induced acute pancreatitis. After 10 days of discontinuing sorafenib he still complained of nausea and loss of appetite. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed a large bulging lesion, which was suspected to cause extrinsic compression on the high body of the gastric anterior wall. Computed tomography scan revealed a cystic lesion, 8.3 cm in size, in the pancreatic tail, suggesting a pancreatic pseudocyst. After the withdrawal of sorafenib, systemic chemotherapy with Adriamycin and cisplatin was administered. Four months after the discontinuation of sorafenib, the size of the pancreatic pseudocyst decreased from 8.3 cm to 3 cm. The patient's symptoms were also relieved.

- Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Segmental Portal Vein Invasion Exhibiting a Complete Response after Transarterial Radioembolization
- Jun Sik Yoon, Su Jong Yu, Yun Bin Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Yoon Jun Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):159-164. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.159

- 5,506 Views
- 78 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The treatment options available for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein invasion (PVI) include sorafenib, transarterial radioembolization (TARE), radiation therapy (RT), transarterial chemoembolization with RT, and proton beam irradiation. Herein, we present a case of HCC with segmental PVI that was managed via TARE. The patient had a 4 cm HCC that invaded the segment VIII portal vein branch without extrahepatic spread. Liver function was Child-Pugh grade A, and performance status was good. TARE was performed without any adverse events, and a radiological complete response (CR) was achieved. Thereafter, the patient was followed-up every 3-6 months without any further treatment, and the CR was maintained for >3 years. Therefore, TARE may be a useful alternative therapeutic option for patients with HCC exhibiting segmental PVI.

- Early Onset Polymorphic Post-transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease Mimicking a Solitary Necrotizing Abscess in a Graft Liver
- Pil Soo Sung, Jaejun Lee, Joon Lee, Hee Chul Nam, Si Hyun Bae, Seung Kew Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):165-170. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.165

- 5,177 Views
- 78 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Although post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) after liver transplantation is very rare, its prognosis is worse than that of PTLD following other types of solid organ transplantation. Here, we report a rare case of early onset polymorphic PTLD in a graft liver occurring five months after deceased-donor liver transplantation due to hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis C virus infection. Initially, findings from contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging mistakenly suspected the lesion was a necrotizing abscess with central necrosis. However, 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and biopsy findings confirmed an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated, B cell type polymorphic PTLD with central necrosis. Our case suggests regular monitoring of EBV serologic status for liver transplant recipients who were initially in an EBV seronegative state. Although early-onset PTLD is very rare after liver transplantation, PTLD should be suspected when recipients show the seroconversion for EBV proteins and the development of new tumors with various clinical presentations.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION



 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter