Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Liver Cancer > Volume 21(1); 2021 > Article
-
Review Article
Ras Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling and Kinase Suppressor of Ras as Therapeutic Targets for Hepatocellular Carcinoma - Hyuk Moon, Simon Weonsang Ro
-
Journal of Liver Cancer 2021;21(1):1-11.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.1
Published online: March 31, 2021
Department of Genetic Engineering, Kyung Hee University College of Life Sciences, Yongin, Korea
-
Corresponding author: Simon Weonsang Ro, Department of Genetic Engineering, Kyung Hee University College of Life Sciences, 1732 Deogyeong-daero, Giheung-gu, Yongin 17104, Korea,
Tel. +82-31-201-5640, Fax. +82-31-204-8116, E-mail; simonro@khu.ac.kr, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2187-3698
Copyright © 2021 by The Korean Liver Cancer Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 6,293 Views
- 218 Downloads
- 4 Citations
Abstract
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a high incidence cancer and a major health concern worldwide. Among the many molecular signaling pathways that are dysregulated in HCC, the Ras mitogen-activated protein kinase (Ras/Raf/MAPK) signaling pathway has gained renewed attention from basic and clinical researchers. Mutations in Ras and Raf genes which are known to activate the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway have been infrequently detected in human HCC; however, the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway is activated in more than 50% of HCC cases, suggesting an alternative mechanism for the activation of the signaling pathway. Kinase suppressor of Ras acts as a molecular scaffold for facilitating the assembly of Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway components and has been implicated in the regulation of this signaling pathway. In this review, we provide important insights into the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the activation of the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway and discuss potential therapeutic strategies for HCC.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide and accounts for about 80% of all primary liver cancers. HCC is thus a major global health problem, and its incidence continues to rise.1
- The diagnosis of HCC has improved significantly over the past few years; however, less than 30% of patients are diagnosed with HCC in the early stages, despite the availability of resection, liver transplantation, and local ablation.2,3 Systemic therapy is recommended as the standard treatment option for advanced HCC; however, prognosis has been unsatisfactory in general.4,5
- Common risk factors for HCC include hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, alcohol consumption, aflatoxin B1 exposure, and metabolic syndrome. 1 Chronic inflammation caused by these risk factors promotes hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis, eventually causing HCC.6,7 HCC involves multiple genetic and epigenetic alterations in proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes and the dysregulation of multiple molecular signaling pathways.8,9
- Identification of molecular signaling pathways associated with tumorigenesis can aid the discovery of novel therapeutic targets. Targeted therapies can act on specific proteins and minimize cytotoxicity, unlike conventional cytotoxic agents.9 Sorafenib is a representative targeted therapeutic agent for HCC; it was approved in 2006 for unresectable HCC and partially targets multiple kinases involved in the progression of advanced HCC.10,11
- 1. The Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway
- Multiple signaling pathways, such as Ras mitogen-activated protein kinase (Ras/Raf/MAPK), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), Wnt/beta-catenin, Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducer activator of transcription factor (STAT) (JAK-STAT), Hedgehog (HH), and Hippo-Yes-associated protein (YAP)/Transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) signaling pathways, are dysregulated in HCC. As knowledge regarding oncogenic molecular pathways in HCC is accumulating, there is growing interest in investigating novel therapeutic targets for HCC associated with these pathways.9 Among the molecular signaling pathways related to HCC, the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway contributes significantly to HCC development.12,13
- The Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway is activated through signal transduction from cell surface receptors, such as receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs).14,15 Dysregulation of the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway leads to abnormal cellular behaviors, like increased proliferation, de-differentiation, and survival, promoting carcinogenesis.15
- The receptors that can activate the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway include, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), fibroblast growth factor receptor, platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), insulin-like growth factor receptor, hepatocyte growth factor receptor (also known as C-Met), and the stem cell growth factor receptor/c-KIT.9,16
- Ligand binding to these receptors leads to the activation of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases (TKs), which phosphorylate tyrosine residues at the cytoplasmic tails of the receptors. This event recruits the Grb2/Shc/SOS adapter molecular complexes to the plasma membrane, subsequently converting guanosine diphosphate (GDP)-bound Ras to active guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-bound Ras. After Ras activation, serine/threonine kinase Raf proteins (A-Raf, B-Raf, and C-Raf) are recruited to the cell membrane and activated in a complex series of processes that include phosphorylation and dimerization with scaffolding complexes.17 Raf proteins directly regulate mitogen/extracellular protein kinases (MEK1 and MEK2), ultimately leading to the phosphorylation of the downstream signaling molecules extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1 and ERK2; also known as MAPK3 and MAPK1, respectively).9 Interestingly, MEKs are tyrosine and serine/threonine dual-specificity kinases.9 Phosphorylated ERK1 and ERK2 translocate to the nucleus, activating two key transcription factors of the AP-1 family, namely, c-Jun and c-Fos.18 The genes activated by these transcription factors are involved in cell cycle progression.14,15
- 2. Kinase suppressor of Ras
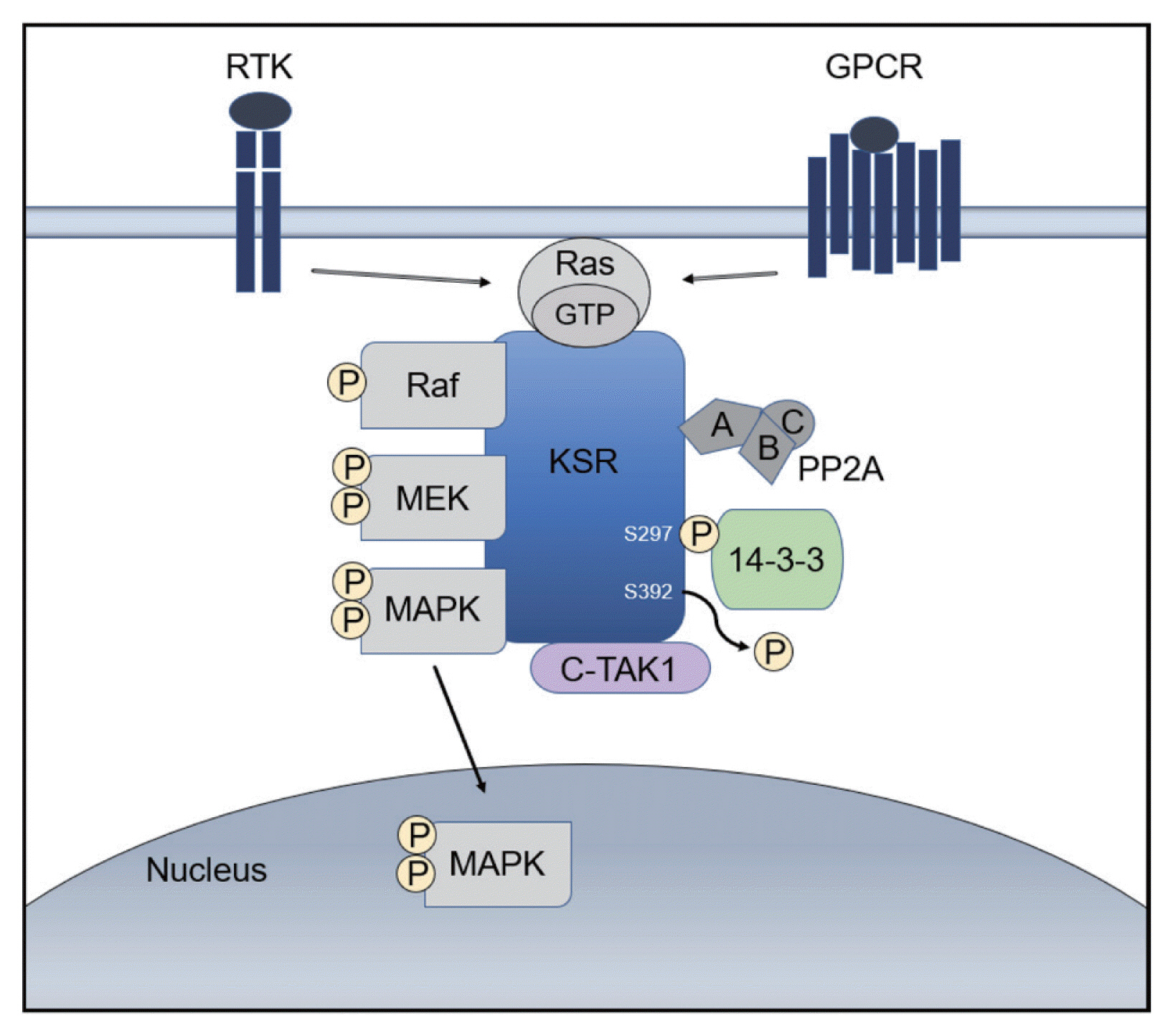
- A kinase suppressor of Ras (KSR) acts as a molecular scaffold that assembles Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling components for the effective transfer of a signal.19 KSR was identified as a regulator of Ras-mediated signal transduction more than 20 years ago by genetic screenings in Drosophila (KSR1) and Caenorhabditis elegans (KSR2).20,21 In quiescent cells, KSR1 is phosphorylated at S297 and S392 by C-TAK1 and binds to the 14-3-3 protein, remaining in an inactive state in the cytosol. 22 Activation of growth factor and Ras stimulates the dephosphorylation of KSR1 at S392 by the protein phosphatase-2A (PP2A) and its localization to the plasma membrane, where it facilitates the phosphorylation of MEK by Raf and, further, the activation of ERK by MEK (Fig. 1).22
- The structures of the KSR proteins are highly homologous, containing five conserved areas (CA1-CA5) that are related to the Raf protein (Fig. 2).23–27 The first conserved area is CA1, which is present at the N-terminus28 and contains 40 amino acids that encode a coiled-coil and sterile-α-motif (CC-SAM) structure, which contributes to the membrane localization of KSR and promotes its binding to B-Raf.29,30 CA2 is a proline-rich region, and its function has not yet been well reported.31 The region between CA2 and CA3 in the KSR2 protein is required for the interaction of KSR with AMPK.32 CA3 contains an atypical C1 motif homologous to the cysteine-rich CR1 region in Raf, which mediates membrane localization of KSR via the recruitment of phospholipids. 24,33 CA4 is a serine/threonine-rich region containing an FXFP motif that mediates the interaction of KSR proteins with ERK.23,24 CA5 encodes a kinase (or pseudokinase) domain that is highly homologous to the CR3 kinase domains in Raf family proteins.24 The CA5 region binds to MEK1/2, and the protein interaction leads to the activation of cell growth.34 Substitution of amino acids in the CA5 region diminishes its interaction with MEK and reduces MAPK signaling. 24
- Various studies have demonstrated that the KSR protein acts as a molecular scaffold for the Raf/MEK/ERK kinase cascade. 35–37 The disorganized hair follicle phenotype manifested in EGFR knockout mice is recapitulated in KSR1 knockout mice, supporting the concept that EGFR, Ras, and KSR1 belong to the same signaling pathway.38 KSR promotes MEK phosphorylation by Raf and is required for the maximal activation of Ras-mediated ERK.23 Increase in the expression levels of KSR1 reinforce its interactions with Raf, MEK, and ERK and lead to the activation of ERK signaling.39 The scaffold activity of KSR is temporally and spatially regulated by the state of Ras signaling.23 McKay et al.40 reported that B-Raf: KSR2 heterodimerization causes conformational changes in the KSR2:MEK complex, promoting the phosphorylation and activation of MEK by additional B-Raf proteins.
- 3. The role of the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway in HCC
- The Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in tumorigenesis, and mutations in its components are highly prevalent in human cancers.41 About 20–30% of all human tumors are reported to have mutations in Ras-associated genes.15,42 B-Raf mutations occur in −50% of melanoma patients, and agents targeting B-Raf (vemurafenib and dabrafenib) demonstrate improved clinical outcomes in these patients.43,44 Additionally, inhibitors of the B-Raf downstream molecule, MEK, also have a significant effect on melanoma patients.45
- The importance of the Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway in human HCC has been neglected for a long time, mainly because Ras and Raf mutations are not frequently detected in HCC, being present in less than 10% of HCCs.46 Nevertheless, the oncogenic role of the Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway in liver cancer has been proven in experimental mouse models.15 Harada et al.47 reported rapid development of HCC in transgenic mice with activated H-Ras mutations. It is noteworthy that, despite the low frequency of mutations in the components of the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway, frequent activation of the signaling pathway has been found in HCC patients.48 Elevated expression levels of Ras effectors highly correlate with poor survival rates in HCC patients.49 Raf1 overexpression is considered to be an independent marker of early tumor recurrence and poor prognosis in HCC.15,49 Based on MEK/ERK expression and phosphorylation, Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling is considered to be activated in over 50% of HCC patients.41,50
- The activity of the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway in HCC is also aberrantly increased by hepatitis viral proteins, dysregulated upstream signals of RTKs, inactivation of Raf kinase inhibitor proteins, and activation of scaffold proteins of the Raf/MEK/ERK kinase cascade (Fig. 3).13 Infections with HBV and HCV play an important role in the activation of the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway in HCC.5,51,52 The Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway plays a fundamental role in the control of key cellular processes, including cell survival and proliferation, and its aberrant activation induced by HBV or HCV infection is associated with the malignant transformation and progression of HCC.15,53 Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling can affect cell cycle progression by regulating senescence markers, such as p16, p15, and p21.50,54,55 In addition, the ETS transcription factor is phosphorylated by ERK and restores telomeres through the transcriptional activation of the telomerase gene (hTERT), contributing to senescence evasion50,56 Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling promotes survival by inhibiting pro-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins and inducing the expression of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members, such as BCL-2, BCL-XL, and MCL-1.50,57 The Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway also upregulates the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related genes, such as those encoding mesenchymal proteins, and those encoding transcription repressors of epithelial genes. Activation of EMT can contribute to the maintenance of the undifferentiated state of tumor cells.50,58 The Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway also induces the mobility and invasiveness of cancer cells by activating the Rho/Rac-actin pathway and matrix metalloproteinase.59,60 Furthermore, B-Raf induces angiogenesis through the involvement of hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and VEGF, while C-Raf promotes endothelial cell survival. 50,61
- It is noteworthy that KSR is extensively implicated in Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling-mediated cancers.19,62 Neilsen et al.23 compared KSR1 expression between colon cancer cell lines and non-transformed human colon epithelial cell lines; their findings suggested that upregulation of KSR1 expression can lead to colorectal cancer via enhanced Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling. 63 In line with this, depleting KSR1 using multiple shRNA sequences repressed the growth of colon cancer cells expressing mutant K-Ras in an in vitro soft agar assay and an in vivo xenograft mouse model.23,63 In addition, immortalized KSR1−/− mouse embryonic fibroblasts show resistance to carcinogenic transformation by H-RasV12 and can be rescued by ectopic expression of KSR1.39,64 Koral et al.65 reported that leukocyte-specific protein 1 interacts with KSR and suppresses the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway by downregulating the function of KSR in HCC cell lines. Skin tumors caused by H-Ras are suppressed in KSR1 knockout mice,38 and the mammary tumor burden was significantly reduced by KSR1 deficiency in mice expressing the transgenic polyomavirus middle T-Antigen.24,36 KSR1 knockout mice also have an impaired immunological response, particularly regarding T-cell activation, due to reduced ERK signaling.23,36 Overall, these results demonstrate that KSR1 is necessary for Ras-driven tumorigenesis. Although studies on the role of KSR in HCC have not yet been reported in vivo, it is hypothesized that KSR plays a pivotal role in hepatic carcinogenesis through the activation of the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway.
- 4. The Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway as a therapeutic target
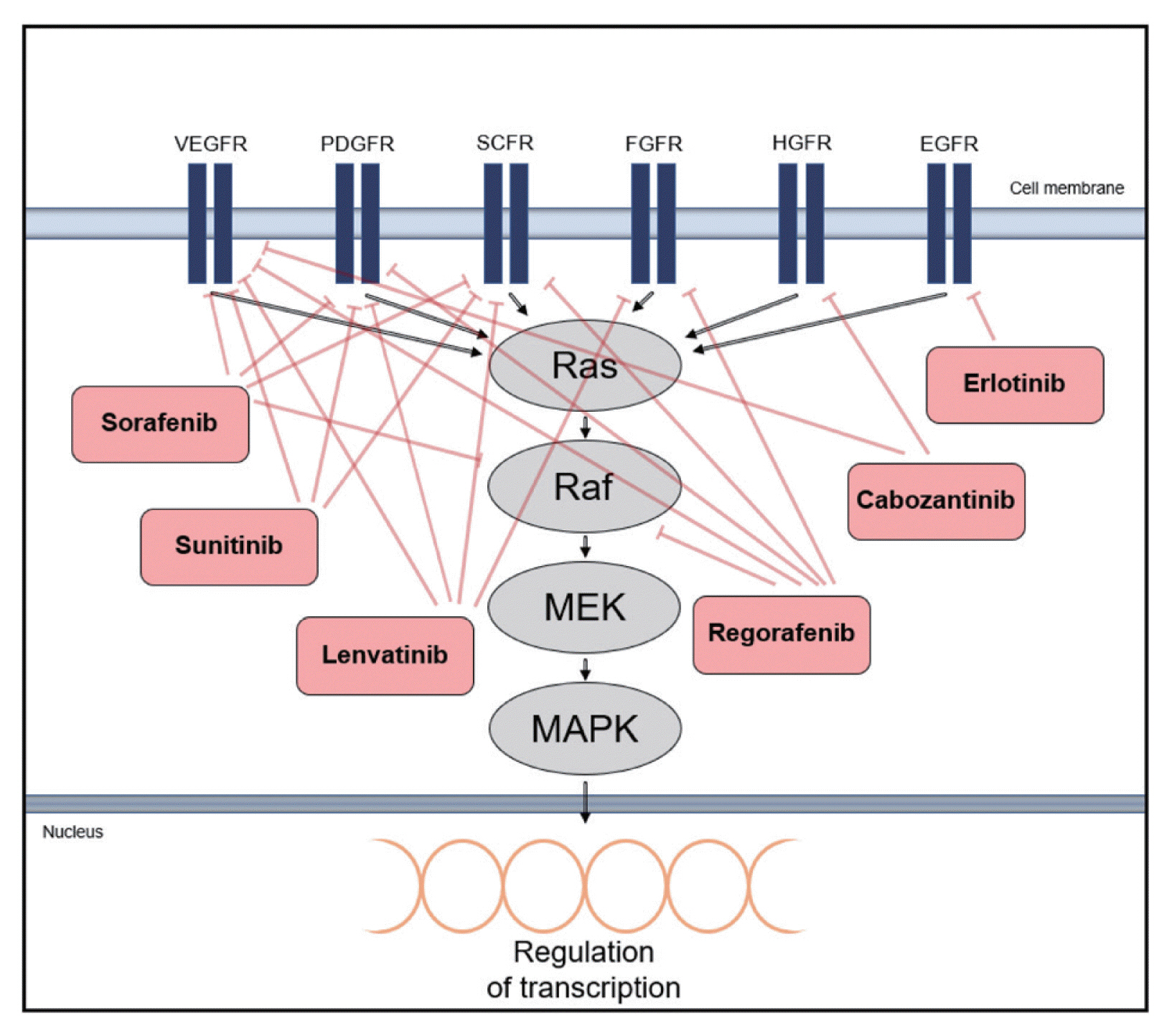
- There has been an increasing interest in targeting oncogenic signaling pathways, and recent successes in anti-cancer treatment via molecular targeted therapies has gained attention from basic researchers as well as clinicians.5 In particular, TKs play a crucial role in cell growth and metabolism and are thus considered therapeutic targets for HCC.66 Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) competitively inhibit ATP binding to the catalytic domains of diverse oncogenic TKs (Type I kinase inhibitor).67 There are also non-ATP competitor TKIs, which cause conformational shifts via structural changes in the receptor TKs and interfere with tyrosine phosphorylation by binding to non-catalytic sites within the TK domain, leading to reduced kinase activity (Type II kinase inhibitor).66,68 The mechanisms of action and phase III clinical investigations of drugs targeting TKs in HCC are summarized in Fig. 4 and Table 1.
- Sorafenib is the first approved drug for HCC that targets the Raf kinase and interferes with RTKs, such as VEGF-2, VEGF-3, PDGFR-β, and c-KIT.13,69,70 Several preclinical trials have evaluated the effects of simultaneous blocking of molecules associated with Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling through drug combinations with sorafenib.7 Refametinib, a MEK1/2 inhibitor, exhibits anti-tumor activities in preclinical murine and rat HCC models in combination with sorafenib.71
- The activation of EGFR downstream signal transduction was blocked by Erlotinib, a potent EGFR inhibitor, in vitro 72 and showed anti-tumor activity in a phase II study involving 38 patients with unresectable or metastatic HCC.9,73
- Sunitinib, a multi-kinase inhibitor targeting PDGFR, VEGFR, c-KIT, and FMS-like TK3 (FLT-3) demonstrated unsatisfactory results compared with sorafenib in patients with advanced-stage HCC. The median overall survival (OS) of patients in the sorafenib group was 10.2 months and that of patients in the sunitinib group was 7.9 months.74,75
- Regorafenib was approved as a second-line oral drug for unresectable HCC in 2017 and has similar targets and structure as sorafenib; however, it more effectively represses the STAT3 signaling pathway through the activation of the Src homology 2 domain-containing phosphatase 1 (SHP1).76,77 It also hampers the activation of various oncogenic factors associated with the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway, such as V600-mutated B-Raf and Tie2.76 Regorafenib showed a more effective suppression of TKs and revealed a better drug tolerance profile than sorafenib in HCC patients. The median survival in patients receiving regorafenib treatment was 10.6 months, as compared to the median survival of 7.8 months in the placebo group; a second-line therapy with regorafenib provided a survival benefit in sorafenib-refractory patients.78
- Lenvatinib has proven non-inferior to sorafenib and is considered as a promising candidate for HCC treatment. It was highly effective in targeting angiogenesis in HCC cell lines and increased the OS in HCC patients not eligible for surgical tumor removal.79 Lenvatinib targets VEGF, PDGF, FGF, and stem cell factor, reducing angiogenesis and lymphoangiogenesis. 79 To overcome acquired resistance to lenvatinib by cancer cells, the drug is currently being tested in combination with golvatinib.66,80
- Cabozantinib, an inhibitor targeting VEGFR, HGFR, rearranged during transfection (RET), and AXL, was approved for patients with HCC who previously underwent sorafenib treatment.81 The fact that cabozantinib provides a dual VEGFR/MET blockade is remarkable, since the upregulation of proangiogenic pathways by MET is considered to occur through the activation of VEGFR.81 The median OS of patients treated with cabozantinib was 10.2 months compared to the median OS of 8.0 months achieved with placebo, and the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 5.2 months compared to the median PFS of 1.9 months achieved with placebo.66,82
- 5. KSR as a therapeutic target
- Considering the significance of KSR in regulating Raf/MEK/ERK kinase cascades in tumor cells,24 inhibition of KSR1 is suggested to target Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling in cancers. In a functional signature ontology study using a high-throughput gene expression screening, KSR1-dependent signals enhanced the viability of human colon tumor cells but did not affect non-transformed human colon epithelial cells.63,83 Moreover, in vitro and in vivo studies using RNA interference (RNAi) exhibited reduced growth of cancer cells with KSR1 deficiency.24,84 Further, targeting KSR1 mRNA by continuous infusion of a phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotide into established tumors led to the suppression of metastasis without overt toxicity.84
- KSR undergoes allosteric regulation through dimerization with Raf.85,86 In a recent study, it was reported that a small molecule APS-2-79 inhibited KSR:Raf heterodimerization and oncogenic Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling,62 and Neilsen et al.23 demonstrated the efficacy of APS-2-79 in a simplified cell-based reconstruction system.62 KSR facilitates Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling by promoting the phosphorylation of MEK at Ser218/Ser222 by Raf in a dose-dependent manner; this increased phosphorylation was suppressed by APS-2-79. Additionally, APS-2-79 reduced cell viability in Ras-mutated HCT116 and A549 cancer cell lines.62 Transient siRNA-mediated depletion of KSR1 in HCT116 cell lines reduced the viability of cancer cells in vitro, and stable shRNA-mediated depletion of KSR1 suppressed tumor growth in vivo.23,63 suppressed tumor growth in vivo.23,63
HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA
- Understanding the molecular pathways of tumorigenesis can help predict patient responses to targeted therapies. Cancer cells show oncogenic addiction to cancer driver genes.41,87 In general, the abnormal growth of tumors depends on a driver oncogene, and the inhibition of this oncogene significantly affects tumor growth. Melanoma patients with B-Raf mutation respond remarkably to vemurafenib, and non-small-cell lung cancer patients with Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) fusion rearrangements are particularly responsive to crizotinib, an ALK-targeting agent.41,44
- Genetic heterogeneity is a notable feature of HCC. A study conducted on HCC patients with multiple tumor nodules reported tumors with different clonalities in 36% patients.7,88 In addition, a study analyzing a patient with recurrent HCC after surgical resection revealed multiple distinct cell populations in the recurrent tumors.89 The development of HCC is a complex, multi-step process, and genetically heterogeneous tumor populations can develop during carcinogenesis due to alterations in various cancer-related genes.90 Among the various oncogenic signaling pathways, the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway is activated in approximately 50% of all early stage HCC patients and in almost all patients with advanced-stage HCC.41,50 Numerous studies indicate the central role of Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling in HCC development.5,14 Specifically, MEK and MAPK mRNAs were overexpressed in 40% and 50% of HCC patients, respectively.5,91 Overexpression of Raf1 was also found in tumor lesions of all HCC patients compared to Raf1 expression levels in pre-tumoral lesions, such as cirrhosis lesions.92 Further, enhanced activity of phosphorylated ERK is observed in human HCC tissues and in vivo murine HCC models.9,14,93
- Upregulation of the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway is significantly found in HCC patients; however, mutations in the intracellular effectors of this signaling pathway are infrequent. 94 Mutations in Ras genes occur in 2% of HCC patients, and those in B-Raf occur in as low as 0.3% patients.5 Thus, activation of Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling is induced in the presence of wild-type Ras and Raf in most human HCCs.15,95 Considering this, current cancer therapeutic agents targeting Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling have intrinsic limitations for the treatment of HCC, as many Raf kinase inhibitors act specifically on an activated mutant Raf and increase dimer formation of endogenous Raf. Thus, these inhibitors can lead to increased Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling by reinforcing the dimerization of wild-type Raf proteins.23,96
- KSR can be an effective alternative target molecule to selectively block the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway. For example, the KSR inhibitor APS-2-79 not only antagonizes the heterodimerization of KSR and Raf but also suppresses the phosphorylation of KSR-bound MEK.62 In addition, APS-2-79 enhances the efficacy of several MEK inhibitors in Ras-mutated cancer cell lines.62 These results suggest that targeting the scaffolding activity of KSR is a promising therapeutic strategy for HCC with activated Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling. KSR1−/− mice are normal and fertile without major developmental defects,36 suggesting that inhibition of KSR can specifically affect cancer with an activated Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway while inducing minimal toxicity to normal cells.
PERSPECTIVES AND CONCLUSION
Acknowledgments
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
-
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Article information


Data accessed in August 2020 on the ClinicalTrials.gov online database: A keyword search for ‘hepatocellular carcinoma’ was used to identify relevant trials investigating targeted molecular therapies.
HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; c-KIT, c-Kit proto-oncogene; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; RET, rearranged during transfection; FGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptor; SCFR, stem cell growth factor receptor; HGFR, hepatocyte growth factor receptor.
- 1. Mittal S, El-Serag HB. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: consider the population. J Clin Gastroenterol 2013;47(Suppl): S2−S6.PubMedPMC
- 2. Yang JD, Roberts LR. Hepatocellular carcinoma: a global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;7:448−458.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018;391:1301−1314.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Knudsen ES, Gopal P, Singal AG. The changing landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma: etiology, genetics, and therapy. Am J Pathol 2014;184:574−583.PubMedPMC
- 5. Gnoni A, Licchetta A, Memeo R, Argentiero A, Solimando AG, Longo V, et al. Role of BRAF in hepatocellular carcinoma: a rationale for future targeted cancer therapies. Medicina (Kaunas) 2019;55:754. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2003;362:1907−1917.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Quetglas IM, Moeini A, Pinyol R, Llovet JM. Integration of genomic information in the clinical management of HCC. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2014;28:831−842.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Liu M, Jiang L, Guan XY. The genetic and epigenetic alterations in human hepatocellular carcinoma: a recent update. Protein Cell 2014;5:673−691.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Dimri M, Satyanarayana A. Molecular signaling pathways and therapeutic targets in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:491. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2008;359:378−390.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Caruso S, Calatayud AL, Pilet J, La Bella T, Rekik S, Imbeaud S, et al. Analysis of liver cancer cell lines identifies agents with likely efficacy against hepatocellular carcinoma and markers of response. Gastroenterology 2019;157:760−776.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Galuppo R, Ramaiah D, Ponte OM, Gedaly R. Molecular therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma: what can we target? Dig Dis Sci 2014;59:1688−1697.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Chen C, Wang G. Mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma and challenges and opportunities for molecular targeted therapy. World J Hepatol 2015;7:1964−1970.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Ito Y, Sasaki Y, Horimoto M, Wada S, Tanaka Y, Kasahara A, et al. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases/extracellular signal-regulated kinases in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 1998;27:951−958.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Delire B, Stärkel P. The Ras/MAPK pathway and hepatocarcinoma: pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Eur J Clin Invest 2015;45:609−623.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Chang F, Steelman LS, Lee JT, Shelton JG, Navolanic PM, Blalock WL, et al. Signal transduction mediated by the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway from cytokine receptors to transcription factors: potential targeting for therapeutic intervention. Leukemia 2003;17:1263−1293.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Rajalingam K, Schreck R, Rapp UR, Albert S. Ras oncogenes and their downstream targets. Biochim Biophys Acta 2007;1773:1177−1195.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 2007;26:3279−3290.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Razidlo GL, Kortum RL, Haferbier JL, Lewis RE. Phosphorylation regulates KSR1 stability, ERK activation, and cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 2004;279:47808−47814.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Kornfeld K, Hom DB, Horvitz HR. The ksr-1 gene encodes a novel protein kinase involved in Ras-mediated signaling in C. elegans. Cell 1995;83:903−913.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Sundaram M, Han M. The C. elegans ksr-1 gene encodes a novel Raf-related kinase involved in Ras-mediated signal transduction. Cell 1995;83:889−901.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Ory S, Zhou M, Conrads TP, Veenstra TD, Morrison DK. Protein phosphatase 2A positively regulates Ras signaling by dephosphorylating KSR1 and Raf-1 on critical 14-3-3 binding sites. Curr Biol 2003;13:1356−1364.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Neilsen BK, Frodyma DE, Lewis RE, Fisher KW. KSR as a therapeutic target for Ras-dependent cancers. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2017;21:499−509.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Frodyma D, Neilsen B, Costanzo-Garvey D, Fisher K, Lewis R. Coordinating ERK signaling via the molecular scaffold kinase suppressor of Ras. F1000Res 2017;6:1621. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Therrien M, Chang HC, Solomon NM, Karim FD, Wassarman DA, Rubin GM. KSR, a novel protein kinase required for RAS signal transduction. Cell 1995;83:879−888.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Roy F, Laberge G, Douziech M, Ferland-McCollough D, Therrien M. KSR is a scaffold required for activation of the ERK/MAPK module. Genes Dev 2002;16:427−438.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 27. Clapéron A, Therrien M. KSR and CNK: two scaffolds regulating RAS-mediated RAF activation. Oncogene 2007;26:3143−3158.ArticlePubMed
- 28. McKay MM, Ritt DA, Morrison DK. Signaling dynamics of the KSR1 scaffold complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009;106:11022−11027.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Koveal D, Schuh-Nuhfer N, Ritt D, Page R, Morrison DK, Peti W. A CC-SAM, for coiled coil-sterile α motif, domain targets the scaffold KSR-1 to specific sites in the plasma membrane. Sci Signal 2012;5:ra94. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Kolch W. Coordinating ERK/MAPK signalling through scaffolds and inhibitors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005;6:827−837.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Michaud NR, Therrien M, Cacace A, Edsall LC, Spiegel S, Rubin GM, et al. KSR stimulates Raf-1 activity in a kinase-independent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1997;94:12792−12796.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Costanzo-Garvey DL, Pfluger PT, Dougherty MK, Stock JL, Boehm M, Chaika O, et al. KSR2 is an essential regulator of AMP kinase, energy expenditure, and insulin sensitivity. Cell Metab 2009;10:366−378.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 33. Zhou M, Horita DA, Waugh DS, Byrd RA, Morrison DK. Solution structure and functional analysis of the cysteine-rich C1 domain of kinase suppressor of Ras (KSR). J Mol Biol 2002;315:435−446.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Cacace AM, Michaud NR, Therrien M, Mathes K, Copeland T, Rubin GM, et al. Identification of constitutive and ras-inducible phosphorylation sites of KSR: implications for 14-3-3 binding, mitogen-activated protein kinase binding, and KSR overexpression. Mol Cell Biol 1999;19:229−240.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Morrison DK. KSR: a MAPK scaffold of the Ras pathway? J Cell Sci 2001;114(Pt 9): 1609−1612.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 36. Nguyen A, Burack WR, Stock JL, Kortum R, Chaika OV, Afkarian M, et al. Kinase suppressor of Ras (KSR) is a scaffold which facilitates mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 2002;22:3035−3045.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 37. Ritt DA, Daar IO, Morrison DK. KSR regulation of the Raf-MEK-ERK cascade. Methods Enzymol 2006;407:224−237.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Lozano J, Xing R, Cai Z, Jensen HL, Trempus C, Mark W, et al. Deficiency of kinase suppressor of Ras1 prevents oncogenic ras signaling in mice. Cancer Res 2003;63:4232−4238.PubMed
- 39. Kortum RL, Lewis RE. The molecular scaffold KSR1 regulates the proliferative and oncogenic potential of cells. Mol Cell Biol 2004;24:4407−4416.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 40. McKay MM, Freeman AK, Morrison DK. Complexity in KSR function revealed by Raf inhibitor and KSR structure studies. Small GTPases 2011;2:276−281.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 41. Llovet JM, Villanueva A, Lachenmayer A, Finn RS. Advances in targeted therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma in the genomic era. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2015;12:408−424.ArticlePubMed
- 42. Fernández-Medarde A, Santos E. Ras in cancer and developmental diseases. Genes Cancer 2011;2:344−358.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 43. Hauschild A, Grob JJ, Demidov LV, Jouary T, Gutzmer R, Millward M, et al. Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012;380:358−365.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med 2011;364:2507−2516.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 45. Flaherty KT, Infante JR, Daud A, Gonzalez R, Kefford RF, Sosman J, et al. Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition in melanoma with BRAF V600 mutations. N Engl J Med 2012;367:1694−1703.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 46. Taketomi A, Shirabe K, Muto J, Yoshiya S, Motomura T, Mano Y, et al. A rare point mutation in the Ras oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg Today 2013;43:289−292.ArticlePubMed
- 47. Harada N, Oshima H, Katoh M, Tamai Y, Oshima M, Taketo MM. Hepatocarcinogenesis in mice with beta-catenin and Ha-ras gene mutations. Cancer Res 2004;64:48−54.ArticlePubMed
- 48. Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Gorden A, Farina M, Conner EA, Lee JS, et al. Ubiquitous activation of Ras and Jak/Stat pathways in human HCC. Gastroenterology 2006;130:1117−1128.ArticlePubMed
- 49. Chen L, Shi Y, Jiang CY, Wei LX, Wang YL, Dai GH. Expression and prognostic role of pan-Ras, Raf-1, pMEK1 and pERK1/2 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol 2011;37:513−520.ArticlePubMed
- 50. Neuzillet C, Tijeras-Raballand A, de Mestier L, Cros J, Faivre S, Raymond E. MEK in cancer and cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther 2014;141:160−171.ArticlePubMed
- 51. Hayashi J, Aoki H, Kajino K, Moriyama M, Arakawa Y, Hino O. Hepatitis C virus core protein activates the MAPK/ERK cascade synergistically with tumor promoter TPA, but not with epidermal growth factor or transforming growth factor alpha. Hepatology 2000;32:958−961.ArticlePubMed
- 52. Chen Y, Chen J, Wang H, Shi J, Wu K, Liu S, et al. HCV-induced miR-21 contributes to evasion of host immune system by targeting MyD88 and IRAK1. PLoS Pathog 2013;9:e1003248. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 53. Min L, He B, Hui L. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in hepatocellular carcinoma development. Semin Cancer Biol 2011;21:10−20.ArticlePubMed
- 54. Roovers K, Assoian RK. Integrating the MAP kinase signal into the G1 phase cell cycle machinery. Bioessays 2000;22:818−826.ArticlePubMed
- 55. Gysin S, Lee SH, Dean NM, McMahon M. Pharmacologic inhibition of RAF-->MEK-->ERK signaling elicits pancreatic cancer cell cycle arrest through induced expression of p27Kip1. Cancer Res 2005;65:4870−4880.ArticlePubMed
- 56. Maurer G, Tarkowski B, Baccarini M. Raf kinases in cancer-roles and therapeutic opportunities. Oncogene 2011;30:3477−3488.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Ballif BA, Blenis J. Molecular mechanisms mediating mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MEK)-MAPK cell survival signals. Cell Growth Differ 2001;12:397−408.PubMed
- 58. Tan X, Tamori Y, Egami H, Ishikawa S, Kurizaki T, Takai E, et al. Analysis of invasion-metastasis mechanism in pancreatic cancer: involvement of tight junction transmembrane protein occludin and MEK/ERK signal transduction pathway in cancer cell dissociation. Oncol Rep 2004;11:993−998.ArticlePubMed
- 59. Tan X, Egami H, Abe M, Nozawa F, Hirota M, Ogawa M. Involvement of MMP-7 in invasion of pancreatic cancer cells through activation of the EGFR mediated MEK-ERK signal transduction pathway. J Clin Pathol 2005;58:1242−1248.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 60. Kim EK, Choi EJ. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010;1802:396−405.ArticlePubMed
- 61. Zhang M, Ma Q, Hu H, Zhang D, Li J, Ma G, et al. Stem cell factor/c-kit signaling enhances invasion of pancreatic cancer cells via HIF-1α under normoxic condition. Cancer Lett 2011;303:108−117.ArticlePubMed
- 62. Dhawan NS, Scopton AP, Dar AC. Small molecule stabilization of the KSR inactive state antagonizes oncogenic Ras signalling. Nature 2016;537:112−116.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 63. Fisher KW, Das B, Kim HS, Clymer BK, Gehring D, Smith DR, et al. AMPK promotes aberrant PGC1β expression to support human colon tumor cell survival. Mol Cell Biol 2015;35:3866−3879.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 64. Kortum RL, Fernandez MR, Costanzo-Garvey DL, Johnson HJ, Fisher KW, Volle DJ, et al. Caveolin-1 is required for kinase suppressor of Ras 1 (KSR1)-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation, H-RasV12-induced senescence, and transformation. Mol Cell Biol 2014;34:3461−3472.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 65. Koral K, Paranjpe S, Bowen WC, Mars W, Luo J, Michalopoulos GK. Leukocyte-specific protein 1: a novel regulator of hepatocellular proliferation and migration deleted in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2015;61:537−547.ArticlePubMed
- 66. Jindal A, Thadi A, Shailubhai K. Hepatocellular carcinoma: etiology and current and future drugs. J Clin Exp Hepatol 2019;9:221−232.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 67. Hojjat-Farsangi M. Small-molecule inhibitors of the receptor tyrosine kinases: promising tools for targeted cancer therapies. Int J Mol Sci 2014;15:13768−13801.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 68. Garuti L, Roberti M, Bottegoni G. Non-ATP competitive protein kinase inhibitors. Curr Med Chem 2010;17:2804−2821.ArticlePubMed
- 69. Coriat R, Nicco C, Chéreau C, Mir O, Alexandre J, Ropert S, et al. Sorafenib-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell death depends on reactive oxygen species production in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 2012;11:2284−2293.ArticlePubMed
- 70. Zhang HL, Zhu Y, Qin XJ, Wang CF, Yao XD, Zhang SL, et al. c-KIT: potential predictive factor for the efficacy of sorafenib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid feature. Clin Genitourin Cancer 2013;11:134−140.ArticlePubMed
- 71. Schmieder R, Puehler F, Neuhaus R, Kissel M, Adjei AA, Miner JN, et al. Allosteric MEK1/2 inhibitor refametinib (BAY 86-9766) in combination with sorafenib exhibits antitumor activity in preclinical murine and rat models of hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasia 2013;15:1161−1171.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 72. Huether A, Hopfner M, Sutter AP, Baradari V, Schuppan D, Scherubl H. Signaling pathways involved in the inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor by erlotinib in hepatocellular cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2006;12:5160−5167.PubMedPMC
- 73. Philip PA, Mahoney MR, Allmer C, Thomas J, Pitot HC, Kim G, et al. Phase II study of Erlotinib (OSI-774) in patients with advanced hepatocellular cancer. J Clin Oncol 2005;23:6657−6663.ArticlePubMed
- 74. Cheng AL, Kang YK, Lin DY, Park JW, Kudo M, Qin S, et al. Sunitinib versus sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular cancer: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 2013;31:4067−4075.ArticlePubMed
- 75. Couri T, Pillai A. Goals and targets for personalized therapy for HCC. Hepatol Int 2019;13:125−137.ArticlePubMed
- 76. Bruix J, Tak WY, Gasbarrini A, Santoro A, Colombo M, Lim HY, et al. Regorafenib as second-line therapy for intermediate or advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: multicentre, open-label, phase II safety study. Eur J Cancer 2013;49:3412−3419.ArticlePubMed
- 77. Tai WT, Chu PY, Shiau CW, Chen YL, Li YS, Hung MH, et al. STAT3 mediates regorafenib-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2014;20:5768−5776.ArticlePubMed
- 78. Bruix J, Qin S, Merle P, Granito A, Huang YH, Bodoky G, et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017;389:56−66.ArticlePubMed
- 79. Yamamoto Y, Matsui J, Matsushima T, Obaishi H, Miyazaki K, Nakamura K, et al. Lenvatinib, an angiogenesis inhibitor targeting VEGFR/FGFR, shows broad antitumor activity in human tumor xenograft models associated with microvessel density and pericyte coverage. Vasc Cell 2014;6:18. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 80. Nakazawa Y, Kawano S, Matsui J, Funahashi Y, Tohyama O, Muto H, et al. Multitargeting strategy using lenvatinib and golvatinib: maximizing anti-angiogenesis activity in a preclinical cancer model. Cancer Sci 2015;106:201−207.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 81. Cochin V, Gross-Goupil M, Ravaud A, Godbert Y, Le Moulec S. Cabozantinib: Mechanism of action, efficacy and indications. Bull Cancer 2017;104:393−401.PubMed
- 82. Schöffski P, Gordon M, Smith DC, Kurzrock R, Daud A, Vogelzang NJ, et al. Phase II randomised discontinuation trial of cabozantinib in patients with advanced solid tumours. Eur J Cancer 2017;86:296−304.ArticlePubMed
- 83. McCall JL, Gehring D, Clymer BK, Fisher KW, Das B, Kelly DL, et al. KSR1 and EPHB4 regulate Myc and PGC1β to promote survival of human colon tumors. Mol Cell Biol 2016;36:2246−2261.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 84. Zhang J, Zafrullah M, Yang X, Yin X, Zhang Z, Fuks Z, et al. Down-regulation of KSR1 in pancreatic cancer xenografts by antisense oligonucleotide correlates with tumor drug uptake. Cancer Biol Ther 2008;7:1490−1495.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 85. Rajakulendran T, Sahmi M, Lefrançois M, Sicheri F, Therrien M. A dimerization-dependent mechanism drives RAF catalytic activation. Nature 2009;461:542−545.ArticlePubMed
- 86. Brennan DF, Dar AC, Hertz NT, Chao WC, Burlingame AL, Shokat KM, et al. A Raf-induced allosteric transition of KSR stimulates phosphorylation of MEK. Nature 2011;472:366−369.ArticlePubMed
- 87. Weinstein IB. Cancer. Addiction to oncogenes--the Achilles heal of cancer. Science 2002;297:63−64.ArticlePubMed
- 88. Ng IO, Guan XY, Poon RT, Fan ST, Lee JM. Determination of the molecular relationship between multiple tumour nodules in hepatocellular carcinoma differentiates multicentric origin from intrahepatic metastasis. J Pathol 2003;199:345−353.ArticlePubMed
- 89. Tao Y, Ruan J, Yeh SH, Lu X, Wang Y, Zhai W, et al. Rapid growth of a hepatocellular carcinoma and the driving mutations revealed by cell-population genetic analysis of whole-genome data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011;108:12042−12047.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 90. Farazi PA, DePinho RA. Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer 2006;6:674−687.ArticlePubMed
- 91. Hoffmann K, Shibo L, Xiao Z, Longerich T, Büchler MW, Schemmer P. Correlation of gene expression of ATP-binding cassette protein and tyrosine kinase signaling pathway in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res 2011;31:3883−3890.PubMed
- 92. Gollob JA, Wilhelm S, Carter C, Kelley SL. Role of Raf kinase in cancer: therapeutic potential of targeting the Raf/MEK/ERK signal transduction pathway. Semin Oncol 2006;33:392−406.ArticlePubMed
- 93. Feng DY, Zheng H, Tan Y, Cheng RX. Effect of phosphorylation of MAPK and Stat3 and expression of c-fos and c-jun proteins on hepatocarcinogenesis and their clinical significance. World J Gastroenterol 2001;7:33−36.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 94. Totoki Y, Tatsuno K, Covington KR, Ueda H, Creighton CJ, Kato M, et al. Trans-ancestry mutational landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma genomes. Nat Genet 2014;46:1267−1273.ArticlePubMed
- 95. Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Conner EA, Seo D, Hsieh JT, Factor VM, et al. Inactivation of Ras GTPase-activating proteins promotes unrestrained activity of wild-type Ras in human liver cancer. J Hepatol 2011;54:311−319.ArticlePubMed
- 96. Freeman AK, Ritt DA, Morrison DK. Effects of Raf dimerization and its inhibition on normal and disease-associated Raf signaling. Mol Cell 2013;49:751−758.ArticlePubMedPMC
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Lipid‐lowering activity and underlying mechanism of glycosylated peptide–calcium chelate prepared by transglutaminase pathway
Xiaoping Wu, Xu Chen, Xixi Cai, Shaoyun Wang
Food Frontiers.2024; 5(1): 160. CrossRef - CT-guided high dose rate brachytherapy can induce multiple systemic proteins of proliferation and angiogenesis predicting outcome in HCC
Lukas Salvermoser, Shraga Nahum Goldberg, Marianna Alunni-Fabbroni, Philipp Maximilian Kazmierczak, Moritz Nikolaus Gröper, Jan Niklas Schäfer, Elif Öcal, Tanja Burkard, Stefanie Corradini, Najib Ben Khaled, Agnese Petrera, Moritz Wildgruber, Jens Ricke,
Translational Oncology.2024; 43: 101919. CrossRef - Network-Pharmacology-Based Study on Active Phytochemicals and Molecular Mechanism of Cnidium monnieri in Treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Shakeel Ahmad Khan, Terence Kin Wah Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(10): 5400. CrossRef - Identification of potential target genes of honokiol in overcoming breast cancer resistance to tamoxifen
Adam Hermawan, Herwandhani Putri, Naufa Hanif, Nurul Fatimah, Heri Himawan Prasetio
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef

 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Download Citation
Download Citation

 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter