Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Multidisciplinary approach for hepatocellular carcinoma patients: current evidence and future perspectives
- Joo Hyun Oh, Dong Hyun Sinn
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):47-56. Published online March 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.02.27

- 556 Views
- 46 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Management of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is challenging due to the complex relationship between underlying liver disease, tumor burden, and liver function. HCC is also notorious for its high recurrence rate even after curative treatment for early-stage tumor. Liver transplantation can substantially alter patient prognosis, but donor availability varies by each patient which further complicates treatment decision. Recent advancements in HCC treatments have introduced numerous potentially efficacious treatment modalities. However, high level evidence comparing the risks and benefits of these options is limited. In this complex situation, multidisciplinary approach or multidisciplinary team care has been suggested as a valuable strategy to help cope with escalating complexity in HCC management. Multidisciplinary approach involves collaboration among medical and health care professionals from various academic disciplines to provide comprehensive care. Although evidence suggests that multidisciplinary care can enhance outcomes of HCC patients, robust data from randomized controlled trials are currently lacking. Moreover, the implementation of a multidisciplinary approach necessitates increased medical resources compared to conventional cancer care. This review summarizes the current evidence on the role of multidisciplinary approach in HCC management and explores potential future directions.

Original Article
- Comparison of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
- Jeayeon Park, Yun Bin Lee, Yunmi Ko, Youngsu Park, Hyunjae Shin, Moon Haeng Hur, Min Kyung Park, Dae-Won Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Kyung-Hun Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Su Jong Yu, Tae-Yong Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Tae-You Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):81-91. Published online January 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.12.25
- 1,032 Views
- 134 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
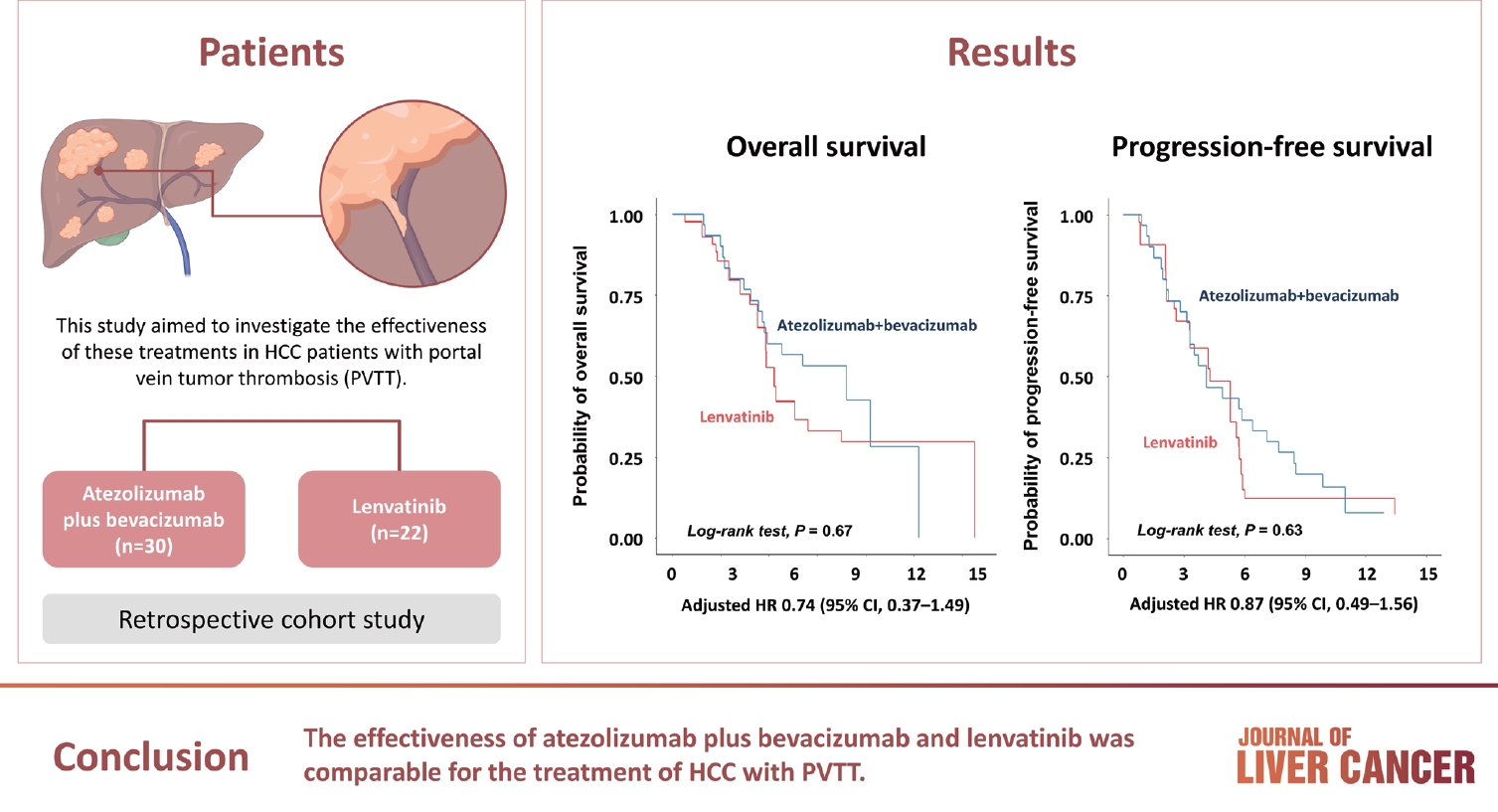
Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib are currently available as first-line therapy for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, comparative efficacy studies are still limited. This study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of these treatments in HCC patients with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT).
Methods
We retrospectively included patients who received either atezolizumab plus bevacizumab or lenvatinib as first-line systemic therapy for HCC with PVTT. Primary endpoint was overall survival (OS), and secondary endpoints included progressionfree survival (PFS) and disease control rate (DCR) determined by response evaluation criteria in solid tumors, version 1.1.
Results
A total of 52 patients were included: 30 received atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and 22 received lenvatinib. The median follow-up duration was 6.4 months (interquartile range, 3.9-9.8). The median OS was 10.8 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 5.7 to not estimated) with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and 5.8 months (95% CI, 4.8 to not estimated) with lenvatinib (P=0.26 by log-rank test). There was no statistically significant difference in OS (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.71; 95% CI, 0.34-1.49; P=0.37). The median PFS was similar (P=0.63 by log-rank test), with 4.1 months (95% CI, 3.3-7.7) for atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and 4.3 months (95% CI, 2.6-5.8) for lenvatinib (aHR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.51-1.69; P=0.80). HRs were similar after inverse probability treatment weighting. The DCRs were 23.3% and 18.2% in patients receiving atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib, respectively (P=0.74).
Conclusion
The effectiveness of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib was comparable for the treatment of HCC with PVTT.

Review Article
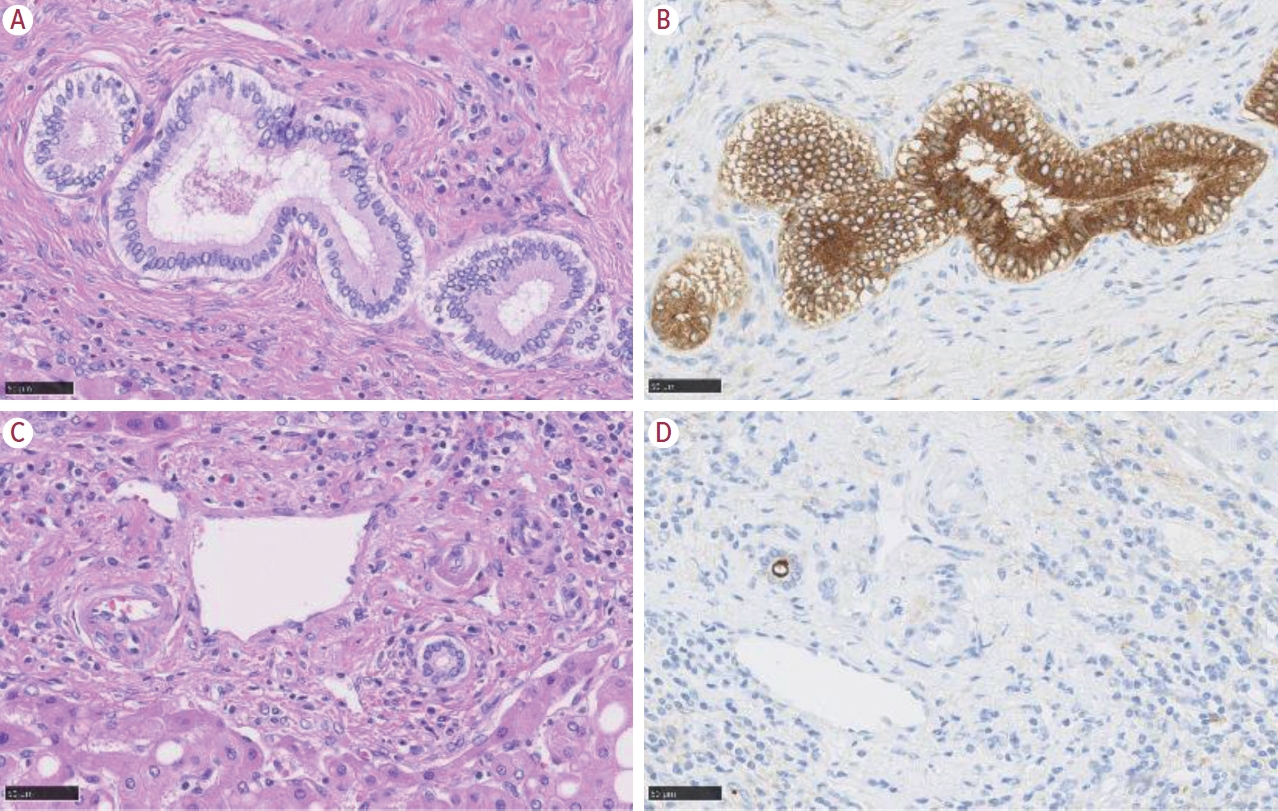
- Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: histological diversity and the role of the pathologist
- Mina Komuta
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):17-22. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.12.11
- 817 Views
- 95 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) is one of the primary liver cancers and presents with tumor heterogeneity. About 50% of iCCAs comprise actionable mutations, which completely change patient management. In addition, the precise diagnosis of iCCA, including subtype, has become crucial, and pathologists play an important role in this regard. This review focuses on iCCA heterogeneity; looking at different perspectives to guide diagnosis and optimal treatment choice.

Case Report
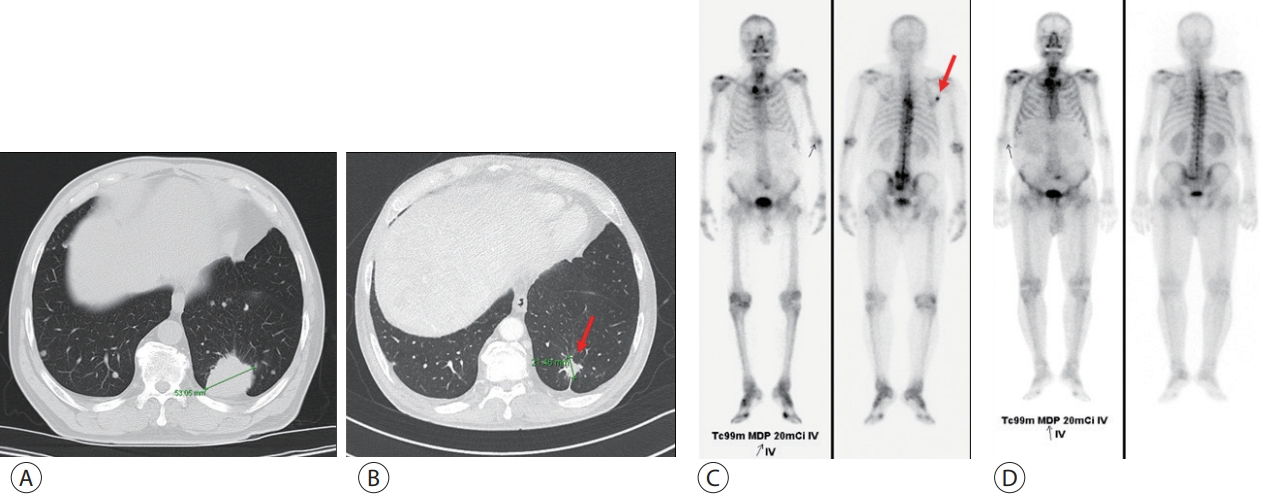
- The development of hepatocellular carcinoma during long-term treatment for recurrent non-small cell lung cancer: a case report
- Seong Kyun Na, Seong Hee Kang
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):230-234. Published online March 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.03.03
- 748 Views
- 56 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Multiple primary malignancies (MPMs) are defined as the presence of two or more malignancies in different organs, without a subordinate relationship. Although rarely reported, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) occasionally presents with simultaneous or metachronous primary malignancies in other organs. In this report, we describe a patient with lung adenocarcinoma and lymph node and bone metastases, treated with five chemotherapeutic regimens for 24 months. Changing the chemotherapy regimen based on the suspicion of metastasis of a new liver mass did not lead to improvements. This prompted a liver biopsy and a revised diagnosis of HCC. Sixth-line treatment with the concurrent use of cisplatin-paclitaxel for lung cancer and sorafenib for HCC, stabilized the disease. The concurrent treatment was not tolerated and was discontinued owing to adverse events. Considering our findings, treatment with increased efficacy and lower toxicity for MPMs is warranted.

Original Article
- The effects of immune checkpoint modulators on the clinical course of patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma
- Jihyun An, Hyo Jeong Kang, Eunsil Yu, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):40-50. Published online March 17, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.06

- 3,353 Views
- 112 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
Immune checkpoint proteins regulating T-cell mediated anti-tumor immunity have been reported to affect clinical outcomes in multiple malignancies. This study aimed to investigate the prognostic effect of histological expression of immune checkpoint proteins in patients with resected hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
A total of 221 patients with HCC who underwent curative resection were included. Expression of programmed-cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) in tumor cells (tPD-L1) and tumor infiltrating mononuclear cells (TIMCs) (iPD-L1), programmed-cell death-1 in TIMCs (iPD-1), and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 in TIMCs (iCTLA-4) were measured immunohistochemically.
Results
Histo-positivity for iCTLA-4, iPD-1, iPD-L1, and tPD-L1 was 32.1%, 42.5%, 35.3%, and 14.9%, respectively. Multivariate logistic analyses revealed that male sex and tumor >5 cm were variables related to iCTLA-4 positivity (odds ratio [OR], 0.46 and 1.94, respectively; P<0.05). Poor differentiation was related to PD-L1 expression in both tumor cells and TIMCs (OR, 2.88 and 3.46, respectively; P<0.05). Microvascular invasion was significantly associated only with iPD-L1 (OR, 2.24; P<0.05). In time-dependent outcome analyses, expression of immune checkpoint proteins in TIMCs (i.e., iCTLA-4, iPD-1, and iPD-L1) was significantly related to longer overall survival and non-cancer-related survival (all P<0.05), but not to time-to-recurrence or cancer-specific deaths. Concurrent activation of the PD-1:PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways predicted improved outcomes in terms of overall survival and non-cancer related survival (P=0.06 and P=0.03, respectively).
Conclusions
Immune checkpoint proteins upregulated in TIMCs in HCC tissues have individual and additive effects in prolonging the survival of patients, specifically in terms of survival not related to cancer recurrence.

Case Reports
- A Case of Metastatic Melanoma in the Liver Mimicking Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jae-Kyoung So, Ji-Yun Hong, Min-Woo Chung, Sung-Bum Cho
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):92-96. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.92

- 6,940 Views
- 267 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The liver is one of the most common sites of metastasis. Although most metastatic liver cancers are hypovascular, some hypervascular metastases, such as those from melanoma, need to be differentiated from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) because they may show similar radiologic findings due to their hypervascularity. We encountered a case of multinodular liver masses with hyperenhancement during the arterial phase and washout during the portal venous and delayed phases, which were consistent with imaging hallmarks of HCC. The patient had a history of malignant melanoma and had undergone curative resection 11 years earlier. We performed a liver biopsy for pathologic confirmation, which revealed a metastatic melanoma of the liver. Metastatic liver cancer should be considered if a patient without chronic liver disease has a history of other primary malignancies, and caution should be exercised with hypervascular cancers that may mimic HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A case of metastatic melanoma in the liver mimicking colorectal cancer with synchronous liver metastasis
E.A. Warshowsky, M. McCarthy, K. Wells, A. Arcidiacono, L. Csury, J.R. Nitzkorski
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2024; 119: 109686. CrossRef
- A case of metastatic melanoma in the liver mimicking colorectal cancer with synchronous liver metastasis

- Malignant Hepatic Solitary Fibrous Tumor
- Hong Il Kim, Seok Kyung In, Hyung Suk Yi, Min Jeong Lee, Hyo Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):143-148. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.143

- 3,578 Views
- 51 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatic solitary fibrous tumors (SFTs) are mostly benign and rare because of information regarding the clinical symptoms, treatment, and prognosis of their malignant forms is currently lacking. A literature review concerning malignant SFTs revealed that there were a few cases where patients experienced abdominal right upper quadrant (RUQ) pain as their first clinical symptom, and metastases were found after being diagnosed with hepatic SFT. Here, we report a patient who was previously healthy without any clinical symptoms such as RUQ pain or weight loss, but had the appearance of a metastatic mass as the first clinical presentation before a primary hepatic SFT was detected.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case of Hepatic Malignant Solitary Fibrous Tumor: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Zhiyan Fu, Evita B. Henderson-Jackson, Barbara A. Centeno, Gregory Y. Lauwers, Mihaela Druta, Daniel A. Anaya, Yukihiro Nakanishi, Samir Sami Amr
Case Reports in Pathology.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef
- A Case of Hepatic Malignant Solitary Fibrous Tumor: A Case Report and Review of the Literature

- A Case of Successful Living Donor Liver Transplantation after Downstaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with the Beyond Milan Criteria by Radioembolization, Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy, and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
- Yeong Jin Kim, Yeon Seung Chung, Beom Kyung Kim, Jin Sil Sung, Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(2):182-185. Published online September 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.2.182
- 1,911 Views
- 16 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Liver transplantation for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) within the Milan criteria
generally yields a 4-year overall survival rate of 75% and 4-year recurrence free survival rate of 83%.
But, many HCC patients present with the disease beyond the Milan criteria. On the other hands, the
overall survival of patients with advanced HCC with portal vein invasion is very poor. We report a
case
of successful living donor liver transplantation for advanced HCC with portal vein invasion by down-staging through radioembolization, hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy, and stereotactic body radiation therapy.

Original Article
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Recurrent Peritoneal Metastasis after Hepatectomy Who Showed Complete Response by Surgical Resection
- Hyo Young Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Joon Yeul Nam, Young Chang, Hyeki Cho, Young Youn Cho, Eung Ju Cho, Su Jong Yu, Yoon Jun Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(2):153-157. Published online September 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.2.153
- 1,729 Views
- 15 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after hepatic resection is quite common. Peritoneal
recurrence has been considered incurable status and related to poor prognosis. Although
peritoneal metastasectomy is a therapeutic option for some selected patients with a few
peritoneal metastasis, the indication and therapeutic effect has not been clear. We report a
case
of a 61-year-old man achieving complete remission of recurrent peritoneal metastasis after repeated surgical resection by a multidisciplinary approach. Peritoneal metastasectomy might be a therapeutic option for selected patients with localized oligonodular peritoneal metastasis.

Review Article
- Current Status of Research on Liver Cancer in Korea
- Jae-Jun Shim
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(2):105-110. Published online September 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.2.105
- 1,922 Views
- 26 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Liver cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related death in Korea. Liver cancer imposes a considerable societal burden due to its high incidence and high mortality rate in younger patients, as compared to other cancers. However, interest in liver cancer among researchers and health-policy makers is low. In this review, recent trends in the number of published articles on liver cancer in Korea and internationally were analyzed. The key finding is that the rate of growth in the number of published articles on liver cancer is slowly decreasing and financial investment for research into liver cancer is very limited, despite the increasing research and development investment budget in Korea. Meanwhile, the rate of growth of research into liver cancer in China has recently increased markedly. Therefore, the scale and rate of growth of research into liver cancer in Korea should be enhanced.

Original Article
- Academic Trend and Clinical Status of Radiotherapy for Hepatobiliary Cancer Over the Past 20 Years in Korea
- Won IL Jang, Yong-Seok Seo, Mi-Sook Kim, Heejin Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2015;15(2):100-105. Published online September 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.15.2.100
- 1,142 Views
- 18 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: To analyze the future trends through the status of radiotherapy in the hepatobiliary cancer in Korea and related articles published in the world.
Methods
Science citation index (SCI) and science citation index expanded (SCIE) articles, published in the 20 years from 1995 until 2014, were searched that contain the keywords related hepatobiliary cancer and radiotherapy using the Scopus. The incidence of hepatobiliary cancer was analyzed using annual reports from the Korea Central Cancer Registry. The status of radiotherapy was analyzed using data obtained form the Korean Society for Radiation Oncology and the National Health Insurance Service.
Results
Total 2,302 papers related radiotherapy for hepatobiliary cancer were searched in the world. By 2014, the cumulative number of papers published by domestic authors was a total 221 pieces. In 1999, total 16,305 hepatobiliary cancer patients were developed, of which 729 patients have been treated with radiotherapy. In 2013, it was expected that total 22,482 hepatobiliary cancer patients would be developed, of which 3,075 patients have been treated with radiotherapy.
Conclusions
Over the past 20 years, South Korea has made clinically and academically remarkable advances in the area of radiotherapy for hepatobiliary cancer. The researchers will continue to announce the results such as an objective status data and published papers in the future. (J Liver Cancer 2015;15:100-105)

Case Report
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Bile Duct Invasion Treated with Transarterial Chemoembolization
- Hee Yeon Kim, Chang Wook Kim, Chang Don Lee, Soo Lim Lee, Yoo Dong Won, Ye Il Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2013;13(2):158-163. Published online September 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.13.2.158
- 1,031 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 53-year-old female patient visited our hospital complaining of intermittent right upper quadrant pain for 6 months. Computed tomography (CT) scan revealed an irregular shaped tumor at segment 4 of the liver with biliary tumor thrombi extending into the common bile duct. Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage was done for decompression of bile duct dilatation. The patient underwent 6 sessions of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Partial response was obtained shortly after TACE. However, regrowth of intraductal tumor resulted in an obstructive jaundice. After a slight decompression of the obstructive jaundice, the patient underwent TACE. Jaundice temporarily worsened following the TACE, but improved, and follow-up CT demonstrated some shrinkage of the intraductal mass. This case indicates that obstructive-type jaundice may not be a contraindication for TACE, and aggressive TACE may improve prognoses of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and biliary tumor thrombi.

Review Articles
- Clinical Safety and Efficacy of JX-594, a Targeted Multi-Mechanistic Oncolytic Pox Virus in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jeong Heo
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2011;11(2):149-154. Published online September 30, 2011
- 610 Views
- 4 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - JX-594 is a targeted oncolytic vaccinia virus designed to selectively replicate in and destroy cancer cells with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/ras pathway activation. Direct oncolysis plus granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) expression is accompanied by tumor vascular shutdown and anti-tumoral immunity. In a Phase 1 trial, JX-594 injection into hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was well-tolerated and associated with viral replication, anti-cancer immunity, decreased tumor perfusion and tumor necrosis. JX-594 has been shown to be well-tolerated by intravenous (IV) infusion and intratumoral (IT) injection and JX-594 is being developed as a novel therapy for patients with refractory or advanced HCC. Synergistic anti-tumor effects are predicted with JX-594 and sorafenib due to acute vascular shut down effect and tumor-specific antibody formation of JX-594 and chronic anti-angiogenic effects of sorafenib. JX-594 shows promise as a novel agent for the treatment of advanced HCC.

- Multistep Carcinogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Ja-June Jang
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2008;8(1):39-46. Published online June 30, 2008
- 560 Views
- 17 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Epidemiological and experimental data have demonstrated that the process of carcinogenesis is progressive and multistage in nature. Model systems in animals exhibit this property of cancer development for several organ systems. The rat liver is one of the most extensively studied models of carcinogenesis. Multiple formats have been described for the analysis of cancer development in this organ, including the resistant hepatocyte selection regimens, the neonatal rat model and the partial hepatectomy model. The evolution of hepatic neoplasia is a slow process leading from the normal state via preneoplasia to benign and malignant neoplasia. On the histological level, hepatic preneoplasia usually emerges as foci of altered hepatocytes (FAH) which are perfectly integrated in the normal liver parenchyma and have no obvious neoplastic nature. The early emergence of FAH seems to be a general phenomenon of hepatocarcinogenesis in all species, no matter how this process has been elicited. The hallmark for the definition and detection of hepatic preneoplasia are biochemical and morphological changes in the hepatocellular phenotypes, which are neither uniform nor stable. In rodent liver treated with various chemical carcinogens, most of phenotypes have been shown to represent successive stages in an ordered sequence of cellular changes, progressing from glycogenic, clear and eosinophilic cell foci, through intermediate, mixed and basophilic cell populations, to hepatocellular adenomas and carcinomas, the fast growing variants of which consist of glycogen-poor, basophilic (ribosome-rich) cells. The identification of the placental isozyme of glutathione S-transferase (GST-P) as a highly expressed cytoplasmic protein during early carcinogenesis has led to its use as a marker of hepatic tumor development in early focal lesions, nodules and carcinomas. Different lesions have been suggested to represent preneoplastic conditions in human liver. They include large-cell change, small-cell change, foci of altered hepatocytes and dysplastic nodules. Experimental results suggest that multiple progressive factors are also involved in human hepatocarcinogenesis.

Case Report
- Hepatoid Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach with Liver Metastasis Mimicking Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Se Hyung Kim, Byung Ihn Choi
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2003;3(1):65-68. Published online July 31, 2003
- 495 Views
- 5 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We describe a case of hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach with liver metastasis mimicking hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Ultrasonography demonstrated an ill-defined heterogeneous hyperechoic mass at right lobe of the liver and high echoic thrombi that filled both portal veins. Contrast enhanced CT scan revealed an ill-defined low attenuated lesion in right lobe of the liver and left portal vein and posterior branch of right portal vein that were filled with low attenuated tumor thrombi. Diffuse and irregular wall thickening with enhancement was also visualized on the posterior wall of the stomach from cardia to angle. Endoscopic biopsy for gastric lesion and US-guided percutaneous core biopsy for hepatic mass were performed. Microscopic examination and immunohistochemical staining revealed aFP-producing hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach and metastatic tumor of the liver.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter