Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Use of doxorubicin-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion: a prospective study
- Su Jong Yu, Yun Bin Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Hyo-Cheol Kim, Jin Wook Chung, Jung-Hwan Yoon, Yoon Jun Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):166-176. Published online March 3, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.08
- 2,077 Views
- 95 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
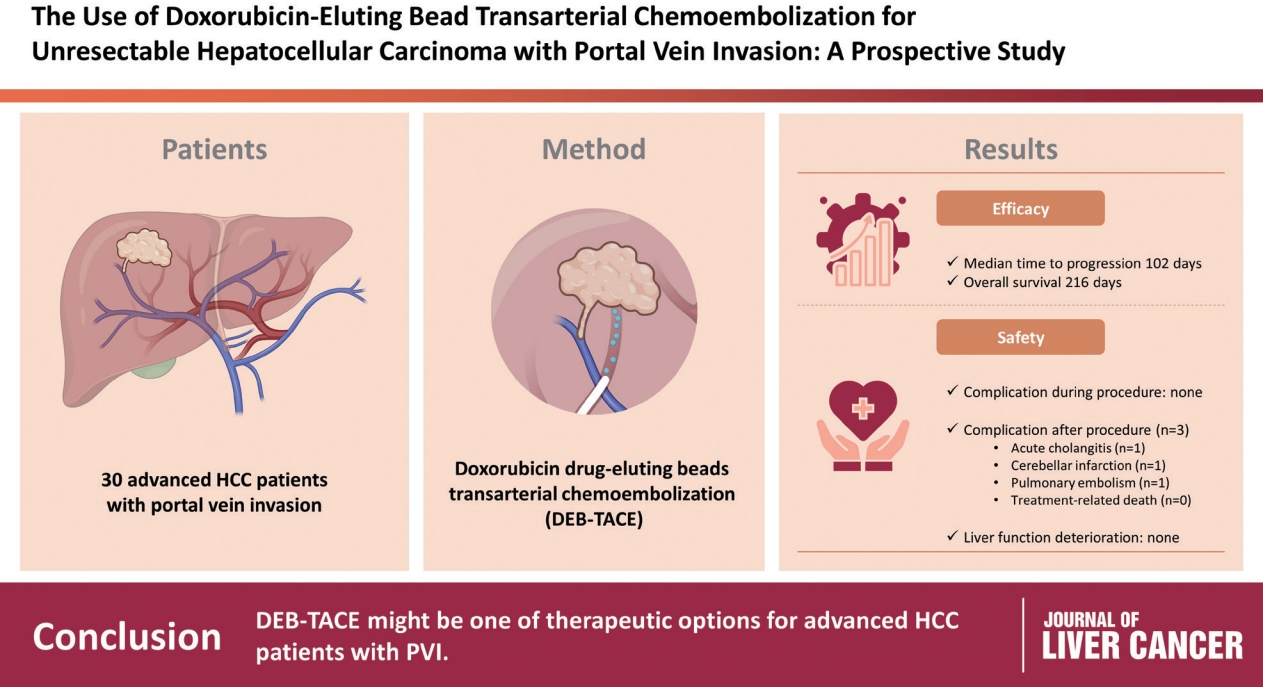
To evaluate the applicability of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) treatment with doxorubicin drug-eluting beads (DEBs) in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with portal vein invasion (PVI).
Methods
This prospective study was approved by the institutional review board and informed consent was obtained from all participants. A total of 30 HCC patients with PVI received DEB-TACE between 2015 and 2018. The following parameters were evaluated: complications during DEB-TACE, abdominal pain, fever, and laboratory outcomes, including liver function change. Overall survival (OS), time to progression (TTP), and adverse events were also analyzed and assessed.
Results
DEBs measuring 100–300 μm in diameter were loaded with doxorubicin (150 mg per procedure). There were no complications during DEB-TACE and no significant differences in the levels of prothrombin time, serum albumin, or total bilirubin at follow-up compared to baseline. The median TTP was 102 days (95% confidence interval [CI], 42–207 days) and the median OS was 216 days (95% CI, 160–336 days). Three patients (10%) had severe adverse reactions, including transient acute cholangitis (n=1), cerebellar infarction (n=1), and pulmonary embolism (n=1), but no treatment-related death occurred.
Conclusions
DEB-TACE may be a therapeutic option for advanced HCC patients with PVI.

Case Reports
- Hepatocellular carcinoma with Budd-Chiari syndrome due to membranous obstruction of the inferior vena cava with long-term follow-up: a case report
- Choong Hee Kim, Gwang Hyeon Choi, Hee Young Na, Chang Jin Yoon, Jai Young Cho, Sangmi Jang, Ji Hye Kim, Eun Sun Jang, Jin-Wook Kim, Sook-Hyang Jeong
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):194-201. Published online September 15, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.08.24
- 2,336 Views
- 55 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Membranous obstruction of the inferior vena cava (MOVC) is a rare subset of Budd-Chiari syndrome (BCS) with a subacute onset that is often complicated by cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here we report a case of recurrent HCC in a patient with cirrhosis and BCS that was treated with several episodes of transarterial chemoembolization followed by surgical tumorectomy, whereas the MOVC was successfully treated with balloon angioplasty followed by endovascular stenting. The patient was followed up for 9.9 years without anticoagulation and experienced no stent thrombosis. After the tumorectomy, the patient was HCC-free for 4.4 years of follow-up.

- Lipiodol Pneumonitis Following Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Sungkeun Kim, Hee Yeon Kim, Su Lim Lee, Young Mi Ku, Yoo Dong Won, Chang Wook Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):60-66. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.60

- 5,102 Views
- 140 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a useful palliative therapeutic modality for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Postembolization syndromes, such as fever, abdominal pain, and elevated liver enzyme levels are commonly known complications of TACE. One post-TACE pulmonary complication, lipiodol pneumonitis, is rarely reported. Lipiodol pneumonitis after TACE appears to be associated with chemical injury due to accidental perfusion of lipiodol to the lung vasculature, promoted by arteriovenous shunts within the hypervascular HCC. Here, we report a 42-year-old man with unresectable HCC and hepatic vein thrombosis. The patient was initially treated with TACE. The following day after TACE, acute respiratory symptoms such as dyspnea and cough developed with decreased oxygen saturation. Chest X-ray and computed tomography showed multiple patches and diffuse ground-glass opacities in both lung fields, suggesting of lipiodol pneumonitis. The patient’s condition and radiologic abnormalities subsequently improved after 2 weeks of conservative treatment alone.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lipiodol-induced Pneumonitis Following Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Heechul Nam
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2022; 80(5): 233. CrossRef
- Lipiodol-induced Pneumonitis Following Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma

Original Article
- Transarterial Chemolipiodolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Central Bile Duct Invasion Causing Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia: Safety and Prognostic Factors for Survival
- Yang, Keungmo , Sung, Pil Soo , Oh, Jung Suk , Chun, Ho Jong , Jang, Jeong Won , Bae, Si Hyun , Choi, Jong Young , Yoon, Seung Kew
- J Liver Cancer. 2018;18(2):121-129. Published online September 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.18.2.121
- 2,359 Views
- 39 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: The treatments and outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with bile duct invasion are not well known. We aimed to confirm the safety of transarterial chemolipiodolization (TACL) and identify prognostic factors for patients with bile duct invasion treated with TACL.
Methods
Fifty patients with central bile duct invasion treated with TACL between 2005 and 2017 were enrolled. Patients were divided into three groups: hyperbilirubinemia (total bilirubin ≥2.5 mg/dL) with pre-TACL biliary drainage, hyperbilirubinemia without biliary drainage, and without hyperbilirubinemia. Tumor response to TACL, survival outcomes, length of hospitalization, adverse events using Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), and factors affecting overall survival were compared.
Results
TACL-induced changes of mean CTCAE grades for albumin, alanine aminotransferase, creatinine, prothrombin time, and platelet were not significantly different among patients with or without initial hyperbilirubinemia. Serum bilirubin level was not significantly changed after TACL in all the three groups. Overall survival was not significantly different among the three groups (P=0.097). On multivariate analysis, alpha-fetoprotein <400 ng/dL (hazard ratio [HR]=0.477, P=0.048) and highest total bilirubin level of <2.5 mg/dL within one month after TACL (HR=0.335, P=0.004) were significantly associated with longer survival.
Conclusions
TACL was a safe treatment for HCC patients with central bile duct invasion, irrespective of the presence of initial hyperbilirubinemia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Proton Beam Therapy in Managing Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Bile Duct Invasion
Ching-Hsin Lee, An-Hsin Chen, Sheng-Ping Hung, Cheng-En Hsieh, Jeng-Hwei Tseng, Po-Jui Chen, Jen-Yu Cheng, Joseph Tung-Chieh Chang, Kun-Ming Chan, Shi-Ming Lin, Chen-Chun Lin, Wei-Ting Chen, Wan-Yu Chen, Bing-Shen Huang
Cancers.2022; 14(7): 1616. CrossRef - An Analysis for Survival Predictors for Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Who Failed to Sorafenib Treatment in Pre-regorafenib Era
Chan Uk Lee, Young-Sun Lee, Ji Hoon Kim, Minjin Lee, Sehwa Kim, Young Kul Jung, Yeon Seok Seo, Hyung Joon Yim, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun
Journal of Liver Cancer.2019; 19(2): 117. CrossRef
- Proton Beam Therapy in Managing Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Bile Duct Invasion

Case Report
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Presenting Early Intrahepatic Recurrence Following Hepatic Resection
- Jaejun Shim, Byung-Ho Kim, Young Hwangbo, Sang Wook Lee, Young Ju Lee, Seung Hyung Ha, Jae Young Jang, Seok Ho Dong, Hyo Jong Kim, Young Woon Chang, Rin Chang, Sang Mok Lee
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):33-36. Published online June 30, 2009
- 505 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Long term results of hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are not satisfactory due to a high incidence of postoperative recurrence. To improve the prognosis in patients who underwent hepatic resection, identification of risk factors for recurrence and development of effective preventive strategies are required. A single nodular mass was found in the right hepatic lobe of 53-year old male with B viral cirrhosis by surveillance ultrasonography. Dynamic abdominal CT showed a 3 cm-sized hypervascular mass in the right posteroinferior segment (S6). AFP was 359 ng/mL. Child-Pugh classification was A, and ICG R15 was 18.8%. After preoperative transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), right hepatic wedge resection was performed. Resection margin was free of tumor. Microinvasions in the surrounding vessels, lymphatics, bile ducts were not found and microsatellite nodules were absent in the resected specimen. Although there were no risk factors that associated with high postoperative recurrence, multifocal intrahepatic recurrence in the right lobe and left medial lobe occurred at 7 months after hepatic resection. He underwent two sessions of TACE.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter