Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Role of transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with extrahepatic metastases in the era of advancing systemic therapy
- Byeong Geun Song, Myung Ji Goh, Wonseok Kang, Dong Hyun Sinn, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Joon Hyeok Lee, Moon Seok Choi
- Received March 5, 2024 Accepted May 26, 2024 Published online June 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.05.26 [Accepted]

- 614 Views
- 33 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
Systemic therapy is the current standard treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with extrahepatic metastases (EHM). However, some patients with HCC and EHM undergo transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) to manage intrahepatic tumors. Herein, we aimed to explore the appropriateness of TACE in patients with HCC and EHM in an era of advanced systemic therapy.
Methods
This study analyzed 248 consecutive patients with HCC and EHM (median age 58.5 years, 83.5% male, and 88.7% Child-Pugh A) who received TACE or systemic therapy (83 sorafenib, 49 lenvatinib, 28 immunotherapy-based) between January 2018 and January 2021.
Results
Among the patients, 196 deaths were recorded during a median follow-up of 8.9 months. Patients who received systemic therapy had a higher albumin-bilirubin grade, elevated tumor markers, an increased number of intrahepatic tumors, larger-sized tumors, and more frequent portal vein invasion than those who underwent TACE. TACE was associated with longer median overall survival (OS) than sorafenib (15.1 vs. 4.7 months; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 11.1–22.2 vs. 3.7–7.3; hazard ratio [HR] 1.97, P<0.001). After adjustment for potential confounders, TACE was associated with statistically similar survival outcomes to those of lenvatinib (median OS: 8.0 months; 95% CI: 6.5–11.0; HR 1.21, P=0.411) and immunotherapies (median OS: 14.3 months; 95% CI: 9.5–27.0; HR 1.01, P=0.973), demonstrating survival benefits equivalent to these treatments.
Conclusion
In patients with HCC and EHM, TACE can provide a survival benefit comparable to that of newer systemic therapies. Accordingly, TACE remains a valuable option in this era of new systemic therapies.

Review Article
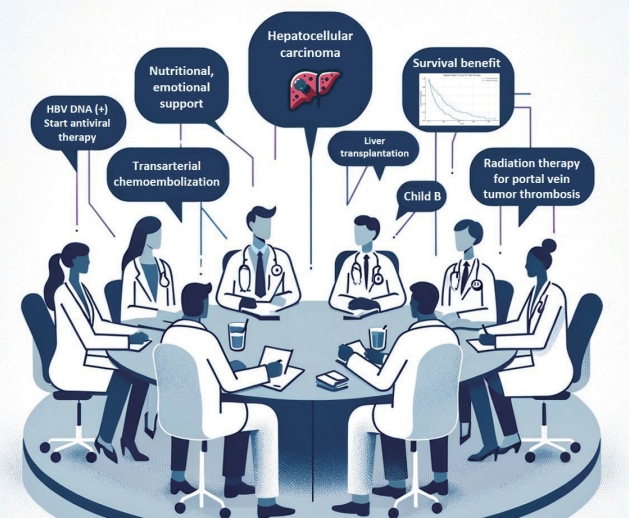
- Multidisciplinary approach for hepatocellular carcinoma patients: current evidence and future perspectives
- Joo Hyun Oh, Dong Hyun Sinn
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):47-56. Published online March 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.02.27

- 1,443 Views
- 89 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Management of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is challenging due to the complex relationship between underlying liver disease, tumor burden, and liver function. HCC is also notorious for its high recurrence rate even after curative treatment for early-stage tumor. Liver transplantation can substantially alter patient prognosis, but donor availability varies by each patient which further complicates treatment decision. Recent advancements in HCC treatments have introduced numerous potentially efficacious treatment modalities. However, high level evidence comparing the risks and benefits of these options is limited. In this complex situation, multidisciplinary approach or multidisciplinary team care has been suggested as a valuable strategy to help cope with escalating complexity in HCC management. Multidisciplinary approach involves collaboration among medical and health care professionals from various academic disciplines to provide comprehensive care. Although evidence suggests that multidisciplinary care can enhance outcomes of HCC patients, robust data from randomized controlled trials are currently lacking. Moreover, the implementation of a multidisciplinary approach necessitates increased medical resources compared to conventional cancer care. This review summarizes the current evidence on the role of multidisciplinary approach in HCC management and explores potential future directions.

Original Article
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
- Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Dong Ho Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Ju-Yeon Cho, Jonggi Choi, Young Chang, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):58-68. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.58
- 7,188 Views
- 277 Downloads
- 18 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aims
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related death in Korea. This study evaluated the characteristics of Korean patients newly diagnosed with HCC in 2015.
Methods
Data from the Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry (KPLCR), a representative sample of patients newly diagnosed with HCC in Korea, were analyzed. A total of 1,558 patients with HCC registered in the KPLCR in 2015 were investigated.
Results
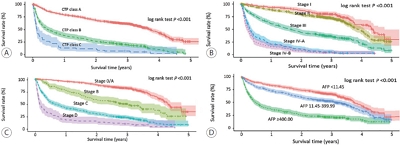
The median age was 61.0 years (interquartile range, 54.0-70.0 years), and men accounted for 79.7% of the subjects. Hepatitis B virus infection was the most common underlying liver disease (58.1%). According to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system, stage 0, A, B, C, and D HCCs accounted for 14.2%, 31.5%, 7.6%, 39.0%, and 7.8% of patients, respectively. Transarterial therapy (32.1%) was the most commonly performed initial treatment, followed by surgical resection (23.2%), best supportive care (20.2%), and local ablation therapy (10.7%). Overall, 34.5% of patients were treated in accordance with the BCLC guidelines: 59.2% in stage 0/A, 48.4% in stage B, 18.1% in stage C, and 71.6% in stage D. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 67.1%, 50.9%, and 27.0%, respectively.
Conclusions
In 2015, approximately 45% of Korean HCC cases were diagnosed at a very early or early stage, and 35% of patients underwent potentially curative initial treatment. BCLC guidance was followed in 34.5% of patients; in patients with stage B or C disease, there was relatively low adherence. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concurrent nivolumab and external beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A phase II study
Bo Hyun Kim, Hee Chul Park, Tae Hyun Kim, Young-Hwan Koh, Jung Yong Hong, Yuri Cho, Dong Hyun Sinn, Boram Park, Joong-Won Park
JHEP Reports.2024; 6(4): 100991. CrossRef - Identification of patients with favorable prognosis after resection in intermediate-stage-hepatocellular carcinoma
Han Ah Lee, Minjong Lee, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Ho Soo Chun, Yewan Park, Hwi Young Kim, Tae Hun Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Dong Hyun Sinn
International Journal of Surgery.2024; 110(2): 1008. CrossRef - Factors associated with the survival outcomes of patients with untreated hepatocellular carcinoma: An analysis of nationwide data
Min Jung Kwon, Soy Chang, Ji Hoon Kim, Ji Won Han, Jeong Won Jang, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Pil Soo Sung
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The imitator of immune-tolerant chronic hepatitis B: A killer in disguise
Moon Haeng Hur, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(2): 363. CrossRef - Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: a large-scale multicenter study
Sun Hong Yoo, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Han-Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim, Do Seon Song, Seong Hee Kang, Moon Young Kim, Young-Hwan Ahn, Jieun Han, Young Seok Kim, Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, J
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 189. CrossRef - A Case of Transverse Myelitis Following Treatment with Atezolizumab for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Kyung Han Kim, Yang-Hyun Baek, Yeo Wool Kang, Byeol-A Yoon, Sang Yi Moon
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 82(1): 35. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter, Propensity Score Study
Ji Kim, Hee-Chul Nam, Chang-Wook Kim, Hee Cho, Jae-Sung Yoo, Ji Han, Jeong Jang, Jong Choi, Seung Yoon, Hyun Yang, Si Bae, Suho Kim, Jung Oh, Ho Chun, Chang Jeon, Jaegyoon Ahn, Pil Sung
Cancers.2023; 15(17): 4233. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Modeling the Risk of Liver Cancer in Adults: A Machine Learning Investigation into the Role of Obesity and Overweight
Bah Karamo, Bah Adama Ns , Jallow Amadou Wurry
Archives of Pathology and Clinical Research.2023; 7(1): 034. CrossRef - Surgical resection versus ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma: The debate is still open
Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 174. CrossRef - Cause of death and cause-specific mortality for primary liver cancer in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study in hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Bo Hyun Kim, Dahhay Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Joo Won, Hyunsoon Cho
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 242. CrossRef - Impact of tumor size on hepatectomy outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma: a nationwide propensity score matching analysis
Suk Kyun Hong, Kwang-Woong Lee, Sola Lee, Su young Hong, Sanggyun Suh, Eui Soo Han, YoungRok Choi, Nam-Joon Yi, Kyung-Suk Suh
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2022; 102(4): 193. CrossRef - Efficacy and feasibility of surgery and external radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal invasion: A meta-analysis
Han Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, In-Soo Shin, Won Sup Yoon, Hye Yoon Lee, Chai Hong Rim
International Journal of Surgery.2022; 104: 106753. CrossRef - Yoon et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(2): 207. CrossRef - Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: It is time to move forward
Bo Hyun Kim, Yuri Cho, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 810. CrossRef - Treatment patterns for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with Child–Pugh class B and their impact on survival: A Korean nationwide registry study
Dongsub Jeon, Gi‐Won Song, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim
Liver International.2022; 42(12): 2830. CrossRef - Metastatic breast cancer from a hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report
Hyewon Bang, Nam-Hee Kim, Seung Hye Choi, Si Hyun Bae, Eun Sun Jung, Ki Ouk Min, Yong Hwa Eom
Korean Journal of Clinical Oncology.2022; 18(2): 93. CrossRef - Current Status and Future Directions of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance Test Based on Cost-effective Analysis
Jihyun An
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 78(5): 255. CrossRef
- Concurrent nivolumab and external beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A phase II study

Case Report
- Advanced Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Successfully Treated with Transarterial Radioembolization and Multi-tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy
- Myung Ji Goh, Wonseok Kang, Dong Hyun Sinn, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):160-166. Published online September 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.160

- 3,790 Views
- 136 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transarterial radioembolization (TARE) with yttrium-90 microspheres has become widely utilized in managing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The utility of TARE is expanding with new insights through experiences from real-world practice and clinical trials, and recently published data suggest that TARE in combination with sorafenib may improve the overall survival in selected patients. Here, we report a case of advanced stage HCC that was successfully treated with TARE and sorafenib. The patient achieved complete response (CR) at 12 months after the initial treatment with TARE and sorafenib, followed by additional transarterial chemoembolization and proton beam therapy for local tumor recurrence at 19-month post-TARE. The patient was followed up every 3 months thereafter and still achieved CR both biochemically and radiologically for the following 12 months. A combination strategy of TARE and systemic therapy may be a useful alternative treatment option for selected patients with advanced stage HCC.

Original Article
- A Survey of Liver Cancer Specialists’ Views on the National Liver Cancer Screening Program in Korea
- Won Sohn, Young-Sun Lee, Jae Geun Lee, Jihyun An, Eun Sun Jang, Dong Ho Lee, Dong Hyun Sinn
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):53-59. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.53

- 4,574 Views
- 137 Downloads
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aims
To reduce the cancer burden, the Korean government initiated the National Cancer Control Plan including the National Liver Cancer Screening Program (NLCSP). Ultrasonography examinations and α-fetoprotein tests at six-month intervals are currently offered for high-risk individuals. High-risk individuals are identified by reviewing the National Health Insurance Service claims data for medical use for the past two years using International Classification of Diseases Codes for specific liver disease. We surveyed the attitudes and opinions towards the NLCSP to understand the issues surrounding the NLCSP in Korea.
Methods
Altogether, 90 Korean Liver Cancer Association members participated in online and offline surveys between November and December 2019.
Results
Approximately one-quarter (27%) of the survey participants rated the NLCSP as very contributing and about two-thirds (68%) as contributing to some extent toward reducing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)-related deaths in Korea. Most (87.8%) responded that the current process of identifying high-risk individuals needs improvement. Many (78.9%) were concerned that the current process identifies individuals who use medical services and paradoxically misses those who do not. When asked for the foremost priority for improvement, solving ‘duplication issues between the NLCSP and private clinic HCC screening practices’ was the most commonly selected choice (23.3%).
Conclusions
The survey participants positively rated the role of the NLCSP in reducing liver cancer deaths. However, many participants rated the NCLSP as needing improvement in all areas. This survey can be a relevant resource for future health policy decisions regarding the NLCSP in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Potential role of Fibrosis‐4 score in hepatocellular carcinoma screening: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Sujeong Shin, Won Sohn, Yoosoo Chang, Yoosun Cho, Min‐Jung Kwon, Sarah H. Wild, Christopher D. Byrne, Seungho Ryu
Hepatology Research.2024; 54(6): 551. CrossRef - Recent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Managements in Korea: Focus on the Updated Guidelines in 2022
Yuri Cho, Bo Hyun Kim, Young-Suk Lim
Digestive Disease Interventions.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical practice guideline and real-life practice in hepatocellular carcinoma: A Korean perspective
Myung Ji Goh, Dong Hyun Sinn, Jong Man Kim, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ho Hyun, Jeong Il Yu, Jung Yong Hong, Moon Seok Choi
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(2): 197. CrossRef - Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: a large-scale multicenter study
Sun Hong Yoo, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Han-Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim, Do Seon Song, Seong Hee Kang, Moon Young Kim, Young-Hwan Ahn, Jieun Han, Young Seok Kim, Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, J
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 189. CrossRef - Selecting the Target Population for Screening of Hepatic Fibrosis in Primary Care Centers in Korea
Huiyul Park, Eileen L. Yoon, Mimi Kim, Seon Cho, Jung-Hwan Kim, Dae Won Jun, Eun-Hee Nah
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(6): 1474. CrossRef - Fibrosis Burden of Missed and Added Populations According to the New Definition of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver
Huiyul Park, Eileen L. Yoon, Mimi Kim, Jung-Hwan Kim, Seon Cho, Dae Won Jun, Eun-Hee Nah
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(19): 4625. CrossRef
- Potential role of Fibrosis‐4 score in hepatocellular carcinoma screening: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study

Case Reports
- Radiation-induced Myositis after Proton Beam Therapy to Huge Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jihye Kim, Gyu Sang Yoo, Dong Hyun Sinn, Hee Chul Park, Kwang Cheol Koh
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):136-142. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.136
- 6,540 Views
- 126 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Proton beam therapy (PBT) is one of the advances in radiotherapy techniques, which enables dose escalation with lower probability of radiation-induced liver or gastrointestinal injuries. However, the chest wall proximal to the tumor can be affected by high dose irradiation. Here, we report on a 58-year-old male patient who presented with huge hepatocellular carcinoma, received treatment with transarterial chemoembolization and PBT, and developed severe chest wall pain due to radiation-induced myositis. The patient’s symptoms were controlled by oral steroids.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pectoralis Major Radiation Myonecrosis After Lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
Jason Gurewitz, Anand Mahadevan, Benjamin T. Cooper
Practical Radiation Oncology.2024; 14(3): 189. CrossRef - Current role of proton beam therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Gyu Sang Yoo, Jeong Il Yu, Hee Chul Park
International Journal of Gastrointestinal Intervention.2021; 10(4): 175. CrossRef
- Pectoralis Major Radiation Myonecrosis After Lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy

- A Case of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Invasion that Showed Favorable Prognosis after Combined External Radiation Therapy and Sorafenib Therapy
- Namyoung Paik, Dong Hyun Sinn, Hee Chul Park, Woo Kyung Jeong, Min Sun Kim, Ji Hye Kim, Bumhee Yang
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(2):134-138. Published online September 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.2.134
- 1,092 Views
- 8 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) is dismal that the median survival is 2 to 4 months without treatment. Sorafenib, the standard regimen of advanced HCC, can prolong median survival only 1.5 months. A 50-year-old man with a history of chronic hepatitis B was diagnosed advanced HCC with PVTT. By a multidisciplinary medical team approach, the combination of 3-demensional conformal radiation therapy with sequential sorafenib was challenged. 4 months after initiation of treatment, he achieved partial response as modified response evaluation criteria in solid tumors criteria. Sorafenib was continued so far, and stable disease has been maintained up to now, without significant adverse effect.

Original Article
- Cause of Mortality for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients who were Diagnosed within the Milan Criteria
- Hyun-Woo Lee, Dong Hyun Sinn, Wonseok Kang, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(2):101-107. Published online September 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.2.101
- 1,668 Views
- 26 Downloads
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a unique condition where the cause of death might not only be due to progressive cancer, but also from liver failure. We evaluated specific causes of death for HCC patients who were initially diagnosed within the Milan criteria.
Methods
A retrospective cohort of 147 patients with mortality who were initially diagnosed with HCC within the Milan criteria between January 2008 and December 2012 at a single institution was reviewed.
Results
During follow-up, 104 patients (70.7%) experienced one or more cirrhotic complications, such as ascites, variceal bleeding, or hepatic encephalopathy. Near mortality, cancer progression (exceeding the Milan criteria) was recorded for 102 patients (69.3%), while cirrhosis progression (greater than two-point increase in Child-Pugh score) was noted in 110 (74.8%) patients. Alphafetoprotein, protein-induced by vitamin K antagonist-II levels and treatment modality were associated with cancer progression, while age and Child-Pugh class were associated with cirrhosis progression. There were 61 patients with in-hospital mortality; cancer progression plus liver failure was noted in 34 patients (55.7%), liver failure without cancer progression was seen in 20 patients (32.8%), and only four patients (6.6%) showed mortality from extrahepatic metastasis without liver failure.
Conclusions
Among HCC patients who were diagnosed within the Milan criteria, most of them had cirrhosis progression near mortality, and significant proportion died without uncontrolled cancer growth, mainly due to liver failure. These findings show the importance of liver function that should be considered in managing HCC patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes of Hepatitis B Virus–Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients with Undetectable Serum HBV DNA Levels
Jong-In Chang, Dong Hyun Sinn, Hyun Cho, Seonwoo Kim, Wonseok Kang, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2022; 67(9): 4565. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 583. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Korean Journal of Radiology.2022; 23(12): 1126. CrossRef - Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Oligometastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multi-Institutional Retrospective Study (KROG 20-04)
Tae Hyung Kim, Taek-Keun Nam, Sang Min Yoon, Tae Hyun Kim, Young Min Choi, Jinsil Seong
Cancers.2022; 14(23): 5848. CrossRef - Multidisciplinary approach is associated with improved survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients
Dong Hyun Sinn, Gyu-Seong Choi, Hee Chul Park, Jong Man Kim, Honsoul Kim, Kyoung Doo Song, Tae Wook Kang, Min Woo Lee, Hyunchul Rhim, Dongho Hyun, Sung Ki Cho, Sung Wook Shin, Woo Kyoung Jeong, Seong Hyun Kim, Jeong Il Yu, Sang Yun Ha, Su Jin Lee, Ho Yeon
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(1): e0210730. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma with extrahepatic metastasis: Are there still candidates for transarterial chemoembolization as an initial treatment?
Jihye Kim, Dong-Hyun Sinn, Moon Seok Choi, Wonseok Kang, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik, Enzo Tagliazucchi
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(3): e0213547. CrossRef
- 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma

Case Report
- Retraction: A Case of Rapid Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Radiofrequency Ablation
- Keol Lee, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik, Dong Hyun Sinn
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(1):67-67. Published online March 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.1.67
- 1,111 Views
- 15 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This paper (“A case of rapid progression of hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation” by Lee K, et al from Journal of Liver Cancer 2015;15(2):118-121) has been retracted because of the several figures (Fig. 1A, Fig. 3A, and Fig. 4) of the paper1 were identical to those of the previous published original article2 without agreement of the copyright holder. The authors informed that they will take full responsibility for this unintended duplicate publication of figures caused by lack of communication, and wish to apologize to readers of the journal for any convenience. To preserve scientific integrity, Journal of Liver Cancer agreed with the authors that this paper be retracted.

Original Article
- Cirrhosis in Surgically Resected Hepatitis C-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Hepatitis B Endemic Area
- Dong Hyun Sinn, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Jae-Won Joh, Seung Woon Paik, Byung Chul Yoo, Cheol Keun Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2014;14(2):108-114. Published online September 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.14.2.108
- 927 Views
- 3 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aims
Cirrhosis has generally been considered a prerequisite for hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected livers to develop hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but HCCs that arise in absence of cirrhosis has been reported. We assessed the prevalence and significance of cirrhosis in HCV-related HCC patients who underwent surgical resection.
Methods
A total of 78 HCC patients (65 male [83.3%]; mean age, 64.2 ± 8.6 years) were evaluated for the presence of cirrhosis. Cirrhosis was assessed based on histology, aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index (APRI) as well as clinical criteria, such as ascites, varices, thrombocytopenia, splenomegaly, and radiographic configuration of cirrhosis.
Results
Based on histology, cirrhosis, septal fibrosis, periportal fibrosis and no fibrosis was noticed in 33.3%, 60.3%, 5.1% and 1.3% of patients, respectively. The clinical criteria of cirrhosis were present in 76.9% of patients. APRI > 1.0 was seen in 47.4% of patients. There was no evidence of cirrhosis in 18 patients (23.1%), either by histology or clinically. Cirrhosis by histology was an independent factor for overall survival [hazard ratio: 3.87 (95% CI: 1.24 – 12.00), P=0.019].
Conclusions
Quite proportion of HCC patients had no evidence of cirrhosis, either by histology or clinically. Careful follow-up for HCC may be necessary even for non-cirrhotic HCVinfected Korean patients. (J Liver Cancer 2014;14:108-114)


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter