Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Advancing Korean nationwide registry for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic sampling approach utilizing the Korea Central Cancer Registry database
- Bo Hyun Kim, E Hwa Yun, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Geun Hong, Jun Yong Park, Ju Hyun Shim, Eunyang Kim, Hyun-Joo Kong, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Suk Lim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):57-61. Published online March 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.03
- 1,021 Views
- 38 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
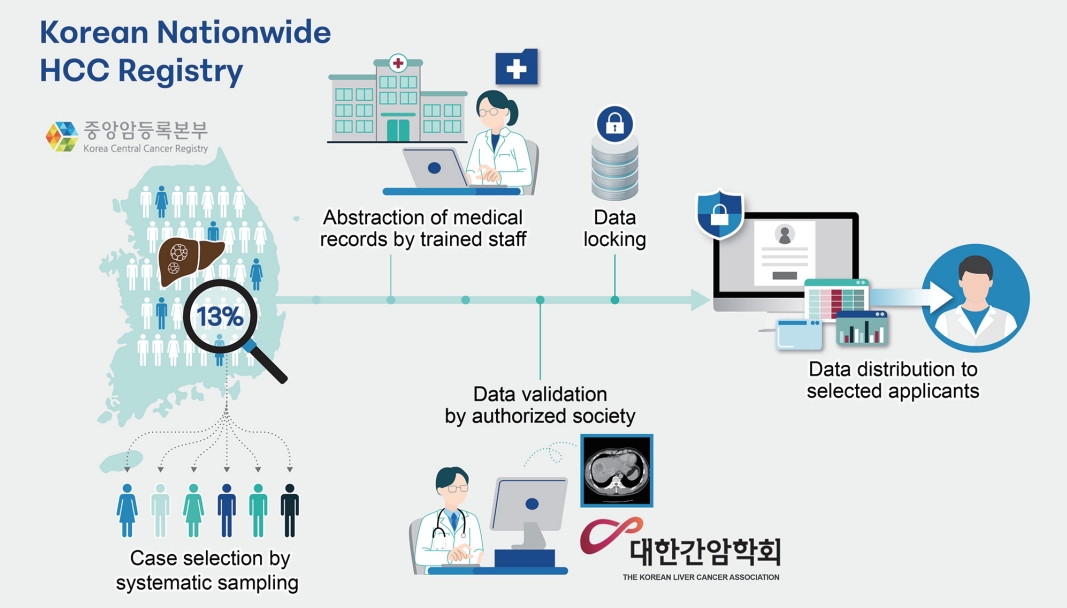
Supplementary Material - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presents a substantial public health challenge in South Korea as evidenced by 10,565 new cases annually (incidence rate of 30 per 100,000 individuals), in 2020. Cancer registries play a crucial role in gathering data on incidence, disease attributes, etiology, treatment modalities, outcomes, and informing health policies. The effectiveness of a registry depends on the completeness and accuracy of data. Established in 1999 by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, the Korea Central Cancer Registry (KCCR) is a comprehensive, legally mandated, nationwide registry that captures nearly all incidence and survival data for major cancers, including HCC, in Korea. However, detailed information on cancer staging, specific characteristics, and treatments is lacking. To address this gap, the KCCR, in partnership with the Korean Liver Cancer Association (KLCA), has implemented a systematic approach to collect detailed data on HCC since 2010. This involved random sampling of 10-15% of all new HCC cases diagnosed since 2003. The registry process encompassed four stages: random case selection, meticulous data extraction by trained personnel, expert validation, anonymization of personal data, and data dissemination for research purposes. This random sampling strategy mitigates the biases associated with voluntary reporting and aligns with stringent privacy regulations. This innovative approach positions the KCCR and KLCA as foundations for advancing cancer control and shaping health policies in South Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of modifiable metabolic risk factors and lifestyle with all-cause mortality in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Hwi Young Kim, Hye Ah Lee, Pompilia Radu, Jean-François Dufour
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of modifiable metabolic risk factors and lifestyle with all-cause mortality in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma

Original Articles
- The efficacy of treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly patients
- Han Ah Lee, Sangheun Lee, Hae Lim Lee, Jeong Eun Song, Dong Hyeon Lee, Sojung Han, Ju Hyun Shim, Bo Hyun Kim, Jong Young Choi, Hyunchul Rhim, Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):362-376. Published online September 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.08.03
- 1,733 Views
- 87 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
Despite the increasing proportion of elderly patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) over time, treatment efficacy in this population is not well established.
Methods
Data collected from the Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry, a representative cohort of patients newly diagnosed with HCC in Korea between 2008 and 2017, were analyzed. Overall survival (OS) according to tumor stage and treatment modality was compared between elderly and non-elderly patients with HCC.
Results
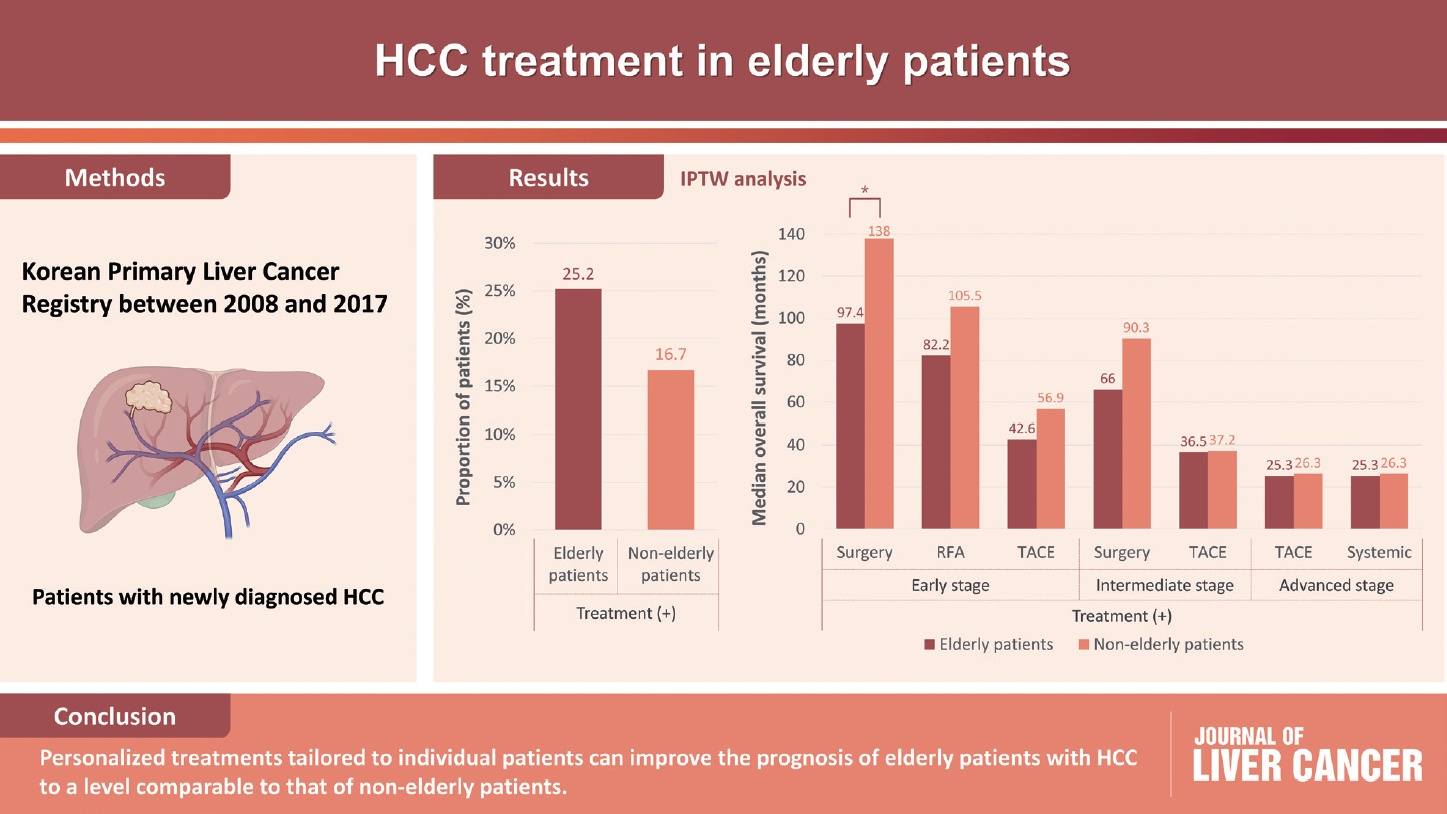
Among 15,186 study patients, 5,829 (38.4%) were elderly. A larger proportion of elderly patients did not receive any treatment for HCC than non-elderly patients (25.2% vs. 16.7%). However, OS was significantly better in elderly patients who received treatment compared to those who did not (median, 38.6 vs. 22.3 months; P<0.001). In early-stage HCC, surgery yielded significantly lower OS in elderly patients compared to non-elderly patients (median, 97.4 vs. 138.0 months; P<0.001), however, local ablation (median, 82.2 vs. 105.5 months) and transarterial therapy (median, 42.6 vs. 56.9 months) each provided comparable OS between the two groups after inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) analysis (all P>0.05). After IPTW, in intermediate-stage HCC, surgery (median, 66.0 vs. 90.3 months) and transarterial therapy (median, 36.5 vs. 37.2 months), and in advanced-stage HCC, transarterial (median, 25.3 vs. 26.3 months) and systemic therapy (median, 25.3 vs. 26.3 months) yielded comparable OS between the elderly and non-elderly HCC patients (all P>0.05).
Conclusions
Personalized treatments tailored to individual patients can improve the prognosis of elderly patients with HCC to a level comparable to that of non-elderly patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and Safety of Surgical Resection in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jin-Soo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Seungeun Ryoo, Jungeun Park, Gi Hong Choi, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Gut and Liver.2024; 18(4): 695. CrossRef - Achieving Sufficient Therapeutic Outcomes of Surgery in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients through Appropriate Selection
Han Ah Lee
Gut and Liver.2024; 18(4): 556. CrossRef
- Efficacy and Safety of Surgical Resection in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
- Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):330-340. Published online May 16, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.04.14
- 2,144 Views
- 124 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
Radiotherapy (RT) is an effective local treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, whether additional RT is safe and effective in patients with advanced HCC receiving atezolizumab plus bevacizumab remains unclear. This retrospective cohort study aimed to evaluate the feasibility of additional RT in these patients.
Methods
Between March and October 2021, we retrospectively analyzed seven patients with advanced HCC who received RT during treatment with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab. The median prescribed RT dose was 35 Gy (range, 33–66). Freedom from local progression (FFLP), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) after RT were analyzed.
Results
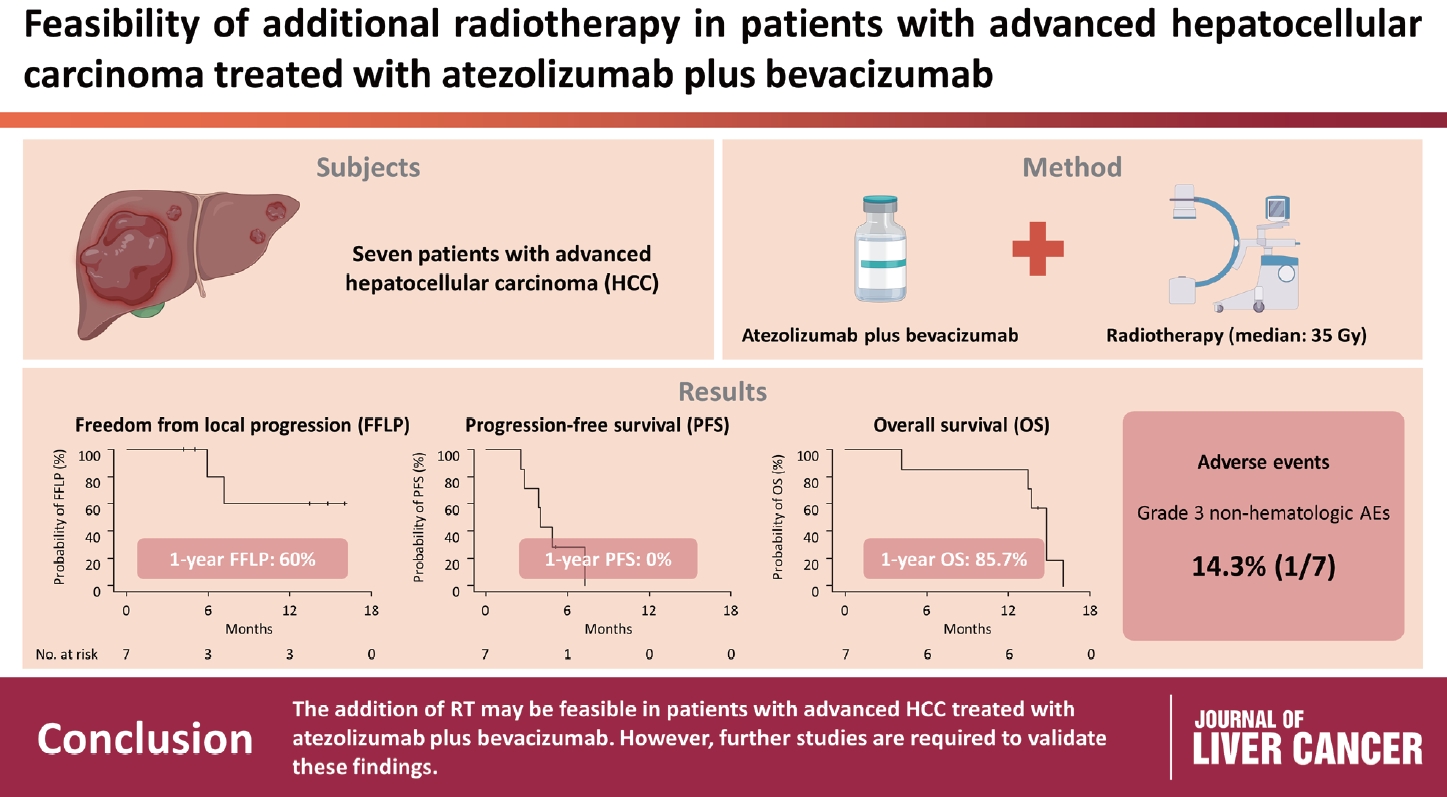
The median follow-up duration after RT was 14.2 months (range, 10.0–18.6). Of the seven patients, disease progression was noted in six (85.7%), the sites of disease progression were local in two (28.6%), intrahepatic in four (57.1%), and extrahepatic in four (57.1%). The median time of FFLP was not reached, and PFS and OS times were 4.0 (95% confidence interval [CI], 3.6–4.5) and 14.8% (95% CI, 12.5–17.2) months, respectively. The 1-year FFLP, PFS, and OS rates were 60% (95% CI, 43.8–76.2), 0%, and 85.7% (95% CI, 75.9–95.5), respectively. Grade 3 or higher hematologic adverse events (AEs) were not observed, but grade 3 nonhematologic AEs unrelated to RT were observed in one patient.
Conclusions
The addition of RT may be feasible in patients with advanced HCC treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab. However, further studies are required to validate these findings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Letter regarding “Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab”
Sun Hyun Bae, Hee Chul Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 402. CrossRef
- Letter regarding “Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab”

Case Reports
- A case of successful surgical treatment for peritoneal seeding of hepatocellular carcinoma after radiotherapy and atezolizumab plus bevacizumab combination treatment
- Yuri Cho, Bo Hyun Kim, Tae Hyun Kim, Young Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):206-212. Published online February 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.09
- 1,730 Views
- 63 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
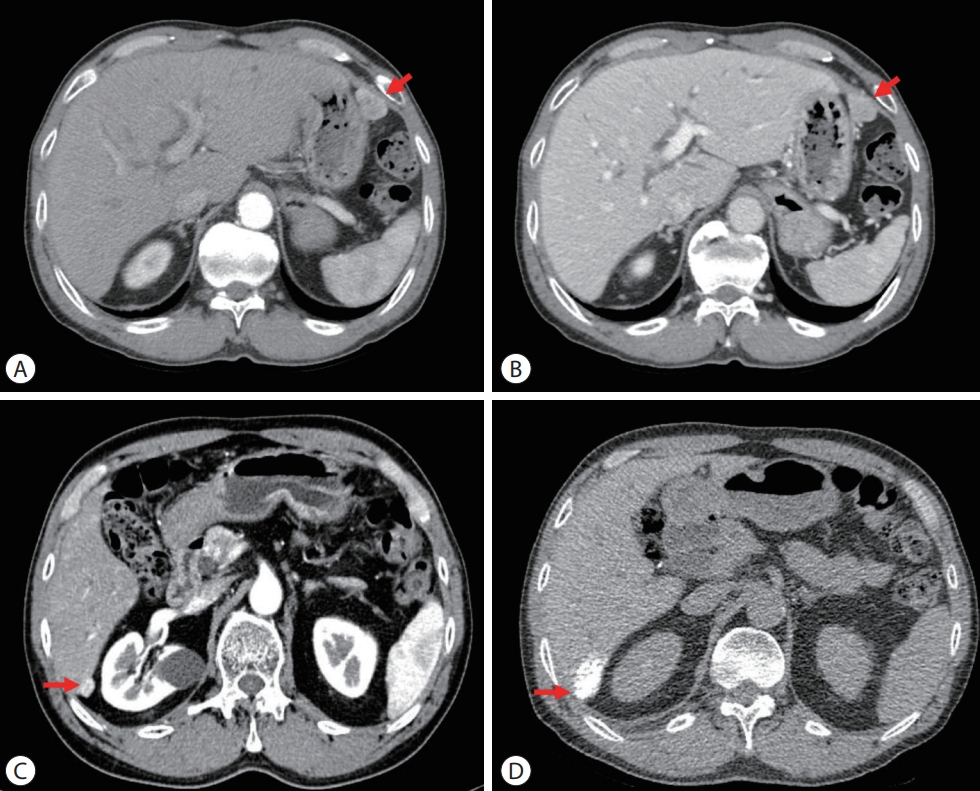
PDF - Peritoneal seeding of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is incurable and has poor prognosis. A 68-year-old man underwent surgical resection for a 3.5 cm single nodular HCC at the tip of segment 3 and transarterial chemoembolization for a 1.5 cm-sized recurrent HCC at the tip of segment 6. 3 months later, an increasing 1 cm pelvic nodule on the rectovesical pouch warranted radiotherapy. Although it stabilized, a new 2.7 cm-sized peritoneal nodule in the right upper quadrant (RUQ) omentum appeared 3.5 years after radiotherapy. Hence, omental mass and small bowel mesentery mass excision were performed. 3 years later, recurrent peritoneal metastases in the RUQ omentum and rectovesical pouch progressed. 33 cycles of atezolizumab and bevacizumab treatment elicited stable disease response. Finally, laparoscopic left pelvic peritonectomy was performed without tumor recurrence. Herein, we present a case of HCC with peritoneal seeding that was successfully treated with surgery after radiotherapy and systemic therapy, leading to complete remission.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 330. CrossRef
- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab

- Sorafenib combined with radiation therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal and hepatic vein invasion extending to the inferior vena cava: a complete response case according to modified RECIST criteria
- Yuri Cho, Bo Hyun Kim, Tae Hyun Kim, Young Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):63-68. Published online February 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.01.18

- 3,029 Views
- 93 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The prognosis of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with tumor thrombus extending to the inferior vena cava (IVC) is extremely poor. Herein, we present a rare case of advanced HCC that was treated with sorafenib and radiotherapy, leading to complete remission. This patient had a 9 cm infiltrative HCC occupying almost the entire left lobe with a tumor thrombus extending through the hepatic vein, IVC, and left portal vein. The patient received 400 mg sorafenib twice daily. One year after the start of sorafenib, intensity-modulated radiation therapy for viable HCC and tumor thrombus was performed with a dose of 5,500 cGy. Twenty-seven months after the starting date of sorafenib, there was no intratumoral arterial enhancement, which suggested a complete response according to the modified RECIST criteria. This case suggests that the combination of sorafenib and radiotherapy might provide clinical benefits in patients with advanced HCC with IVC tumor thrombus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Major Vascular Invasion
Tomoko Tadokoro, Joji Tani, Asahiro Morishita, Koji Fujita, Tsutomu Masaki, Hideki Kobara
Cancers.2024; 16(14): 2534. CrossRef - Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 330. CrossRef - Is multidisciplinary treatment effective for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus?
Won Hyeok Choe
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef
- The Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Major Vascular Invasion

Review Article
- Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: consideration for selecting second-line treatment
- Bo Hyun Kim, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):124-138. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.23
- 4,422 Views
- 120 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
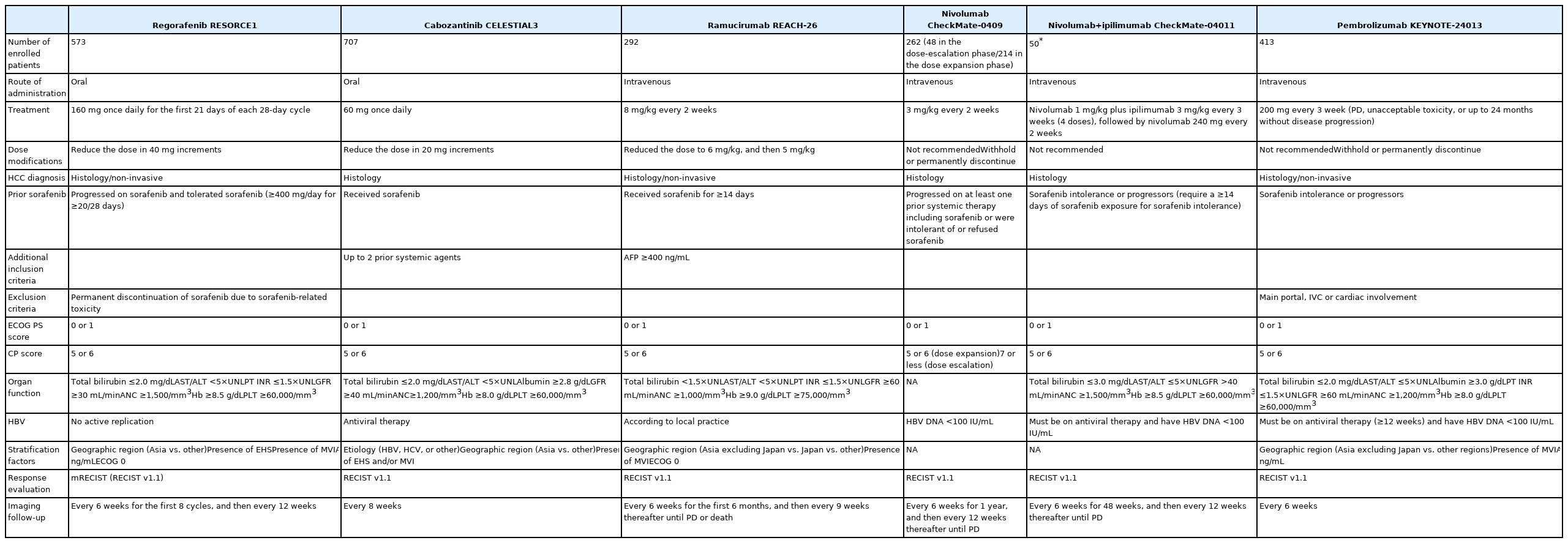
PDF - Several molecular-targeted agents have been tested as first- or second-line therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) but failed to improve clinical outcomes; sorafenib has been the only approved systemic agent for treating HCC for almost 10 years. Regorafenib resulted in a significant improvement in overall survival and thus was approved for HCC patients previously treated with sorafenib. Subsequently, cabozantinib and ramucirumab demonstrated superior overall survival compared with placebos in phase III clinical trials. Immune checkpoint inhibitors such as nivolumab with or without ipilimumab and pembrolizumab are also available in some countries for patients who are unresponsive to sorafenib. Some second-line agents are available for patients who are unresponsive to sorafenib; however, little is known about the considerations for selecting appropriate secondline systemic agents. Hence, this study aimed to review the current and future perspectives of second-line systemic agents.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expression of Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase 2 Is Closely Associated with Recurrence in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Sunho Uhm, Yoon Cho, Ji-Young Choe, Ji Park, Min-Jeong Kim, Won-Ho Han, Junyong Lee, Jung Lee, Dong Shin, Jae Soh, Hyun Lim, Ho Kang, Sung-Hoon Moon, Sung-Eun Kim
Diagnostics.2023; 13(4): 659. CrossRef - Expert consensus on the management of adverse events in patients receiving lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma
Bo Hyun Kim, Su Jong Yu, Wonseok Kang, Sung Bum Cho, Soo Young Park, Seung Up Kim, Do Young Kim
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 37(3): 428. CrossRef
- Expression of Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase 2 Is Closely Associated with Recurrence in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma

Case Report
- Ruptured Massive Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cured by Transarterial Chemoembolization
- Ji Eun Lee, Joong-Won Park, In Joon Lee, Bo Hyun Kim, Seoung Hoon Kim, Hyun Beom Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):154-159. Published online September 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.154
- 3,323 Views
- 66 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
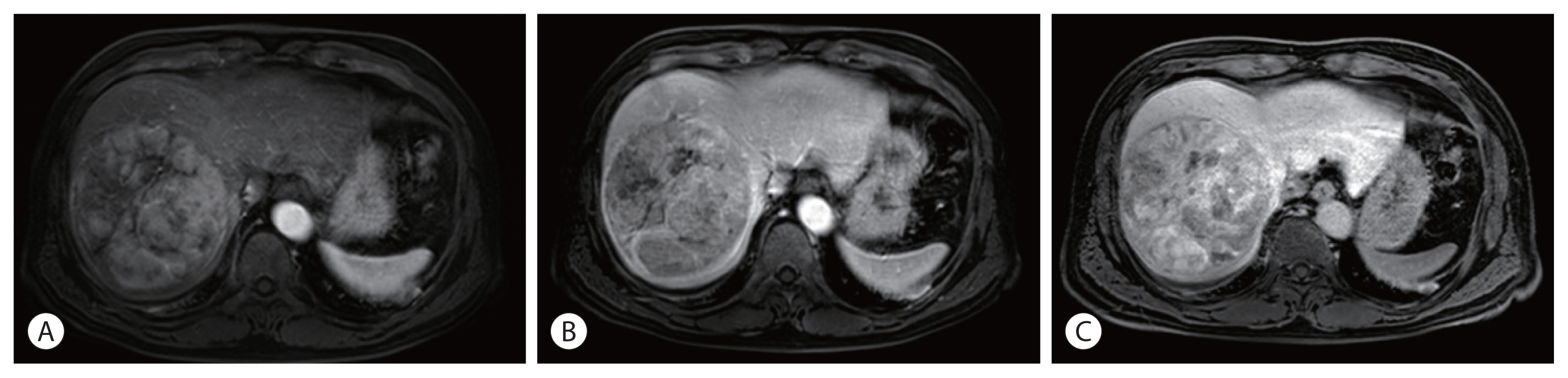
PDF - Spontaneous tumor rupture is a serious but rare complication of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and has a low survival rate. Here, we report a case of massive HCC that ruptured and was treated successfully with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). A 55-year-old man with abdominal pain was diagnosed with a 12-cm-wide ruptured HCC at segment 8. The overall liver function was scored as Child–Pugh A, but the single nodule tumor had ruptured; therefore, TACE treatment was initiated. After the first TACE treatment, residual tumors were found; thus, secondary TACE was performed 5 months later. No new lesions or extrahepatic metastases were found 16 months after the first TACE treatment, so hepatic resection was performed for curative treatment. The postoperative pathology results did not reveal any cancer cells; hence, TACE alone resulted in a cure. We report this case because the cure has been maintained for more than 3 years after resection.

Original Articles
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
- Young Eun Chon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Sik Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):135-147. Published online September 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.135
- 4,979 Views
- 164 Downloads
- 17 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aims
Considering the high prevalence and mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in Korea, accurate statistics for HCC are important. We evaluated the characteristics of Korean patients with newly diagnosed HCC.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated data from the Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry (KPLCR). The baseline characteristics, treatment modalities, and overall survival (OS) of 4,572 patients with HCC registered in the KPLCR between 2012 and 2014 were investigated.
Results
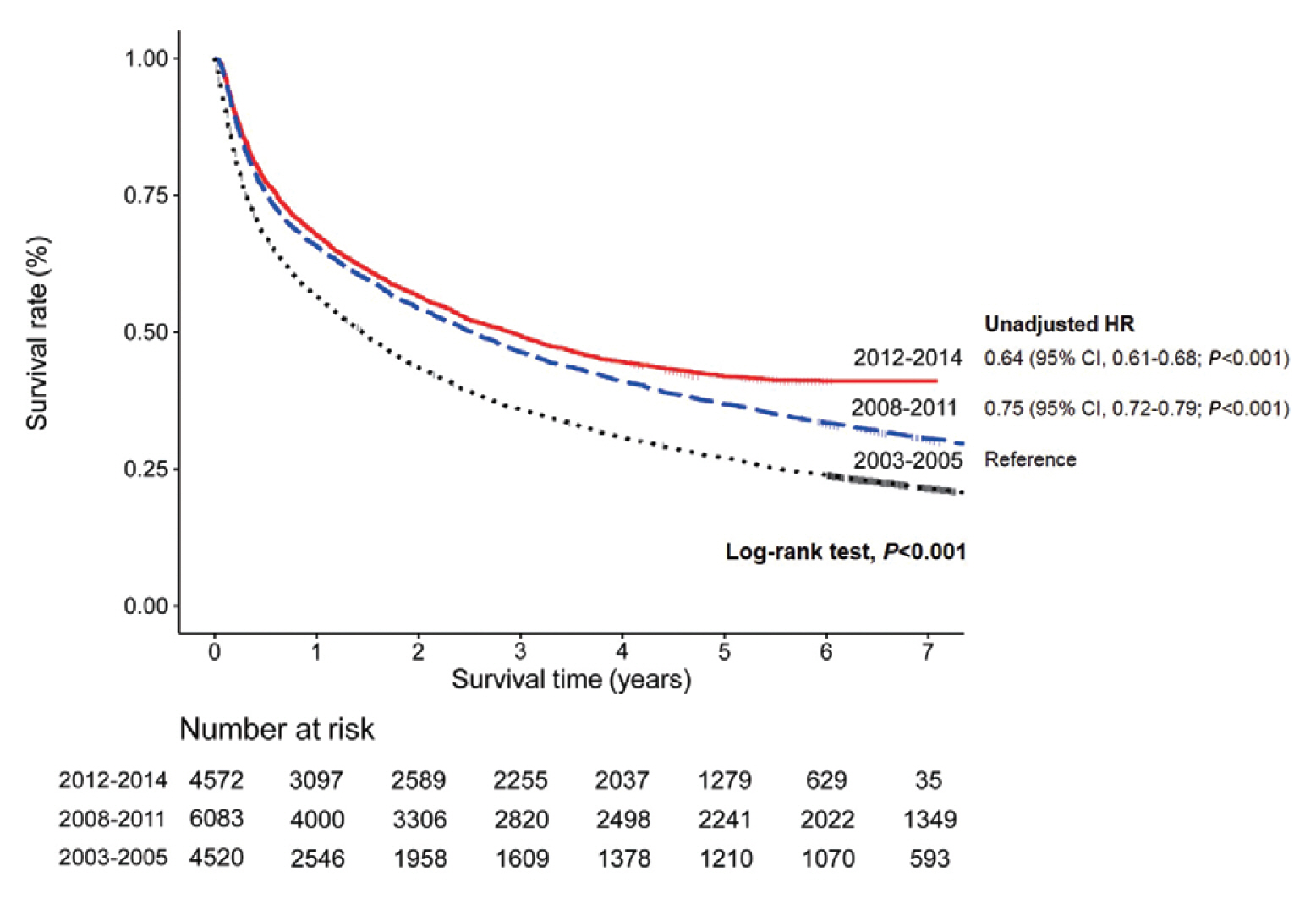
At the time of HCC diagnosis, the median age was 60.0 years, with male predominance (79.6%). Hepatitis B virus infection was the most common etiology (59.1%). The rates of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stages 0, A, B, C, and D at diagnosis were 3.9%, 36.9%, 12.5%, 39.4%, and 7.3%, respectively. The proportion of very early or early stage HCC at diagnosis (BCLC stage 0 or A) in the 2012-2014 cohort was significantly lower than that in the 2008-2011 cohort (40.8% vs. 48.3%, P<0.001). Transarterial therapy (37.5%) was the most commonly performed initial treatment, followed by surgical resection (19.8%), best supportive care (19.1%), and local ablation (10.6%). The median OS was 2.9 years, and the 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 67.7%, 49.3% and 41.9%, respectively. The OS rate of the 2012-2014 cohort was significantly higher than that of the 2008-2011 cohort (log-rank, P<0.001).
Conclusions
The OS of HCC patients registered in the KPLCR between 2012 and 2014 significantly improved. Nevertheless, as about half of the HCC patients were diagnosed at an advanced stage, vigorous and optimized HCC screening strategies should be implemented. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Managements in Korea: Focus on the Updated Guidelines in 2022
Yuri Cho, Bo Hyun Kim, Young-Suk Lim
Digestive Disease Interventions.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Limited Generalizability of Retrospective Single-Center Cohort Study in Comparison to Multicenter Cohort Study on Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ye Rim Kim, Sung Won Chung, Min-Ju Kim, Won-Mook Choi, Jonggi Choi, Danbi Lee, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim
Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2024; Volume 11: 1235. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence is decreasing in Korea but increasing in the very elderly
Young Eun Chon, Seong Yong Park, Han Pyo Hong, Donghee Son, Jonghyun Lee, Eileen Yoon, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Bong Ahn, Soung Won Jeong, Dae Won Jun
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(1): 120. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Factors associated with the survival outcomes of patients with untreated hepatocellular carcinoma: An analysis of nationwide data
Min Jung Kwon, Soy Chang, Ji Hoon Kim, Ji Won Han, Jeong Won Jang, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Pil Soo Sung
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical practice guideline and real-life practice in hepatocellular carcinoma: A Korean perspective
Myung Ji Goh, Dong Hyun Sinn, Jong Man Kim, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ho Hyun, Jeong Il Yu, Jung Yong Hong, Moon Seok Choi
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(2): 197. CrossRef - Implications of the first edition of the Korean expert consensus-based practice recommendations for transarterial chemoembolization in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Jin Wook Chung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 235. CrossRef - Nomogram for predicting overall survival in patients with large (>5 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma based on real-world practice
Nalee Kim, Jeong Il Yu, Hee Chul Park, Jung Yong Hong, Ho Yeong Lim, Myung Ji Goh, Yong-Han Paik
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 350. CrossRef - Surgical resection versus ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma: The debate is still open
Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 174. CrossRef - A case report of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy and sorafenib combination therapy followed by metastasectomy of lung and muscle metastases
Sang Yi Moon, Sang Young Han, Yang-Hyun Baek
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 57. CrossRef - Cause of death and cause-specific mortality for primary liver cancer in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study in hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Bo Hyun Kim, Dahhay Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Joo Won, Hyunsoon Cho
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 242. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 583. CrossRef - Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: It is time to move forward
Bo Hyun Kim, Yuri Cho, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 810. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Korean Journal of Radiology.2022; 23(12): 1126. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Dong Ho Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Ju-Yeon Cho, Jonggi Choi, Young Chang, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 58. CrossRef - Cost-Effectiveness of Adjuvant Immunotherapy With Cytokine-Induced Killer Cell for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on a Randomized Controlled Trial and Real-World Data
Jeong-Yeon Cho, Sun-Hong Kwon, Eui-Kyung Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Hye-Lin Kim
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Refractory to Transarterial Chemoembolization and Vascular Variation: A Case Study
Sang Yi Moon, Sang Young Han, Yang-Hyun Baek
Kosin Medical Journal.2021; 36(2): 161. CrossRef
- Recent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Managements in Korea: Focus on the Updated Guidelines in 2022

- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea Between 2008 and 2011: an Analysis of Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
- Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Young Eun Chon, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Young-Joo Won, Eunyang Kim, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):41-52. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.41

- 5,406 Views
- 198 Downloads
- 15 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Backgrounds/Aims
Backgrounds/Aims: In Korea, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cancer and results in the second-highest cancer death rate among all cancers. We aimed to describe the characteristics of patients who were newly diagnosed with HCC in Korea between 2008 and 2011.
Methods
The Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry (KPLCR) is a random sample consisting of approximately 15% of patients with newly diagnosed primary liver cancer registered in the Korean Central Cancer Registry. We investigated the baseline characteristics, treatment modalities, and overall survival (OS) of patients with HCC registered in the KPLCR between 2008 and 2011.
Results
A total of 6,083 patients were histologically or radiologically diagnosed with HCC. The hepatitis B virus was the predominant HCC etiology (72.0%). According to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system, stages 0, A, B, C, and D accounted for 8.6%, 39.7%, 11.5%, 33.8%, and 6.9%, respectively. Transarterial therapy (41.7%) was the most commonly performed initial treatment, followed by best supportive care (21.7%), surgical resection (16.7%), and local ablation therapies (10.6%). The overall rate of adherence to the BCLC treatment guideline was only 37.7%. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 65.6%, 46.2%, and 36.8%, respectively.
Conclusions
Between 2008 and 2011, approximately half of patients with HCC (48.3%) were candidates for curative treatment (BCLC stage 0 or A), but one-third of patients (33.8%) had advanced HCC (BCLC stage C). Transarterial therapy was the most commonly conducted initial treatment and the 5-year OS rate was 36.8% in this period. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adjuvant and neoadjuvant immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma
Josep M. Llovet, Roser Pinyol, Mark Yarchoan, Amit G. Singal, Thomas U. Marron, Myron Schwartz, Eli Pikarsky, Masatoshi Kudo, Richard S. Finn
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology.2024; 21(4): 294. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence is decreasing in Korea but increasing in the very elderly
Young Eun Chon, Seong Yong Park, Han Pyo Hong, Donghee Son, Jonghyun Lee, Eileen Yoon, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Bong Ahn, Soung Won Jeong, Dae Won Jun
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(1): 120. CrossRef - Implications of the first edition of the Korean expert consensus-based practice recommendations for transarterial chemoembolization in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Jin Wook Chung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 235. CrossRef - Surgical resection versus ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma: The debate is still open
Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 174. CrossRef - Cause of death and cause-specific mortality for primary liver cancer in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study in hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Bo Hyun Kim, Dahhay Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Joo Won, Hyunsoon Cho
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 242. CrossRef - Impact of expanding hepatitis B treatment guidelines: A modelling and economic impact analysis
Young‐Suk Lim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Jae‐Jun Shim, Homie Razavi, Devin Razavi‐Shearer, Dong Hyun Sinn
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2022; 56(3): 519. CrossRef - Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: It is time to move forward
Bo Hyun Kim, Yuri Cho, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 810. CrossRef - Therapeutic Decision Making in Hepatocellular Carcinoma According to Age and Child–Pugh Class: A Nationwide Cohort Analysis in South Korea
Sunmin Park, Chai Hong Rim, Young Kul Jung, Won Sup Yoon, Alessandro Granito
Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Outcome of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor and Molecular Target Agent Combination for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Beyond Sorafenib Era
Nae-Yun Heo
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 77(3): 145. CrossRef - Rare Case of Pyogenic Brain Abscess after Transarterial Chemoembolization in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Case Report and Literature Review
Jun-Ho Myeong, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 81. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Dong Ho Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Ju-Yeon Cho, Jonggi Choi, Young Chang, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 58. CrossRef - Glucose Variability and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Eun Ju Cho, Kyungdo Han, Soo Seong Heo, Bo-Yeon Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Su Jong Yu
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2021; 30(5): 974. CrossRef -
Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein improves diagnostic accuracy for hepatocellular carcinoma
Han Ah Lee, Yoo Ra Lee, Young-Sun Lee, Young Kul Jung, Ji Hoon Kim, Hyunggin An, Hyung Joon Yim, Yoon Tae Jeen, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun, Yeon Seok Seo
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(28): 4687. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Young Eun Chon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Sik Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(2): 135. CrossRef - Efficacy of Local Treatments for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Involving the Inferior Vena Cava and/or Right Atrium
Han Ah Lee, Chai Hong Rim
Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2020; Volume 7: 435. CrossRef
- Adjuvant and neoadjuvant immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma

Review Article
- The General Rules for the Study of Primary Liver Cancer
- Jae Young Jang, June Sung Lee, Hyung-Joon Kim, Jae-Jun Shim, Ji Hoon Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Choon Hyuck Kwon, Seung Duk Lee, Hae Won Lee, Jung Hoon Kim, Woo Kyoung Jeong, Jin-Young Choi, Heung Kyu Ko, Dong Ho Lee, Haeryoung Kim, Baek-hui Kim, Sang Min Yoon, Soon Ho Um
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):19-44. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.19
- 2,642 Views
- 202 Downloads
- 29 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The General Rules for the Study of Primary Liver Cancer was published in June 2001 as the first edition. Since then, the 5th edition of the General Rules for the Study of Primary Liver Cancer was published by the 17th Committee of the Korean Liver Cancer Association based on the most recent data. The 5th edition of the General Rules for the Study of Primary Liver Cancer ranged over numerous topics such as anatomy, medical assessment of the patients, staging of hepatocellular carcinoma, description of the image findings, summary of hepatic resection, description of the surgical specimens, liver transplantation, reporting the pathological findings, pathological examinations of liver specimen, non-surgical treatment, radiotherapy, and assessment of tumor response after non-surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. The 5th General Rules for the Study of Primary Liver Cancer will not only become the basis of academic development for liver cancer studies in Korea, but also serve as the primary form of national liver cancer data accumulation based on standardized rules.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preoperative Prediction of Microvascular Invasion with Gadoxetic Acid-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Implication of Surgical Decision on the Extent of Liver Resection
Na Reum Kim, Heejin Bae, Hyeo Seong Hwang, Dai Hoon Han, Kyung Sik Kim, Jin Sub Choi, Mi-Suk Park, Gi Hong Choi
Liver Cancer.2024; 13(2): 181. CrossRef - Radiologic Patterns Determine the Outcomes of Initial and Subsequent Transarterial Chemoembolization in Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ya-Wen Hung, I-Cheng Lee, Chen-Ta Chi, Rheun-Chuan Lee, Chien-An Liu, Nai-Chi Chiu, Hsuen-En Hwang, Yee Chao, Ming-Chih Hou, Yi-Hsiang Huang
Liver Cancer.2024; 13(1): 29. CrossRef - National guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma
Faisal Saud Dar, Zaigham Abbas, Irfan Ahmed, Muhammad Atique, Usman Iqbal Aujla, Muhammad Azeemuddin, Zeba Aziz, Abu Bakar Hafeez Bhatti, Tariq Ali Bangash, Amna Subhan Butt, Osama Tariq Butt, Abdul Wahab Dogar, Javed Iqbal Farooqi, Faisal Hanif, Jahanzai
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(9): 1018. CrossRef - Macroscopic Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Underexploited Source of Prognostic Factors
Stéphanie Gonvers, Sebastiao Martins-Filho, André Hirayama, Julien Calderaro, Rebecca Phillips, Emilie Uldry, Nicolas Demartines, Emmanuel Melloul, Young Nyun Park, Valérie Paradis, Swan Thung, Venancio Alves, Christine Sempoux, Ismail Labgaa
Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2024; Volume 11: 707. CrossRef - The impact of matrix stiffness on hepatic cell function, liver fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma—Based on quantitative data
Kiyoon Min, Sathish Kumar Karuppannan, Giyoong Tae
Biophysics Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-Invasive Imaging Biomarkers to Predict the Hepatopulmonary Shunt Fraction Before Transarterial Radioembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Charlie Alexander Hamm, Felix Busch, Anna Pöhlmann, Annabella Shewarega, Yubei He, Robin Schmidt, Han Xu, Gero Wieners, Bernhard Gebauer, Lynn Jeanette Savic
Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2023; Volume 10: 27. CrossRef - Histological subtypes of hepatocellular carcinoma: Their clinical and prognostic significance
So Hyun Shin, Joon Young Park, Chungsu Hwang, Hyun Jung Lee, Dong Hoon Shin, Jee Yeon Kim, Je Ho Ryu, Kwang Ho Yang, Tae Beom Lee, Jung Hee Lee
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2023; 64: 152134. CrossRef - Classification of microvascular invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with prognosis and magnetic resonance imaging
Yoon Jung Hwang, Jae Seok Bae, Youngeun Lee, Bo Yun Hur, Dong Ho Lee, Haeryoung Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(3): 733. CrossRef - Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review of Its Definition, Clinical Significance, and Comprehensive Management
Zehao Zheng, Renguo Guan, Wang Jianxi, Zhen Zhao, Tianyi Peng, Chunsheng Liu, Ye Lin, Zhixiang Jian, Yuan Seng Wu
Journal of Oncology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - A clinical and pathological update on hepatocellular carcinoma
Salvatore Lorenzo Renne, Luca Di Tommaso
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 14. CrossRef - Comparing efficacies of different treatment regimens in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma accompanied by portal vein tumor thrombus using network meta-analysis
Seungji Lee, Sung Kyu Song, Byungje Bae, Yongkeun Park
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2022; 103(5): 280. CrossRef - Post-TACE changes in ADC histogram predict overall and transplant-free survival in patients with well-defined HCC: a retrospective cohort with up to 10 years follow-up
Mohammadreza Shaghaghi, Mounes Aliyari Ghasabeh, Sanaz Ameli, Maryam Ghadimi, Bita Hazhirkarzar, Roya Rezvani Habibabadi, Pegah Khoshpouri, Ankur Pandey, Pallavi Pandey, Ihab R. Kamel
European Radiology.2021; 31(3): 1378. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Beyond Milan Recurrence After Hepatic Resection for Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma No Larger Than 5 Centimeters
Mina Kim, Taegyu Kim, Hyun Young Lee, Sung Yeon Hong, Hee‐Jung Wang, Bong‐Wan Kim
Liver Transplantation.2021; 27(8): 1116. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma: a clinical and pathological overview
Salvatore Lorenzo Renne, Samantha Sarcognato, Diana Sacchi, Maria Guido, Massimo Roncalli, Luigi Terracciano, Luca Di Tommaso
Pathologica.2021; 113(3): 203. CrossRef - Prognostic significance of viable tumor size measurement in hepatocellular carcinomas after preoperative locoregional treatment
Yoon Jung Hwang, Youngeun Lee, Hyunjin Park, Yangkyu Lee, Kyoungbun Lee, Haeryoung Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2021; 55(5): 338. CrossRef - Response to Comment on “Subclassification of Microscopic Vascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma”
Gi Hong Choi, Incheon Kang, Young Nyun Park
Annals of Surgery.2021; 274(6): e748. CrossRef - Subclassification of Microscopic Vascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Incheon Kang, Mi Jang, Jae Geun Lee, Dai Hoon Han, Dong Jin Joo, Kyung Sik Kim, Myoung Soo Kim, Jin Sub Choi, Soon Il Kim, Young Nyun Park, Gi Hong Choi
Annals of Surgery.2021; 274(6): e1170. CrossRef - Up-to-date Knowledge on the Pathological Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ji Hae Nahm, Young Nyun Park
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 78(5): 268. CrossRef - Survival according to recurrence patterns after resection for transplantable hepatocellular carcinoma in HBV endemic area: Appraisal of liver transplantation strategy
Chung Gyo Seo, Sun Young Yim, Soon Ho Um, Yoo Ra Lee, Yoo Jin Lee, Tae Hyung Kim, Hyun Gil Goh, Young Sun Lee, Sang Jun Suh, Na Yeon Han, Hyuk Soon Choi, Eun Sun Kim, Bora Keum, Yeon Seok Seo, Hyung Joon Yim, Ji Hoon Kim, Dong Sik Kim, Yoon Tae Jeen, Hoon
Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology.2020; 44(4): 532. CrossRef - Risk of Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Fontan Operation: A Need for Surveillance
Jun Sik Yoon, Dong Ho Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Mi Kyoung Song, Young Hun Choi, Gi Beom Kim, Yun Bin Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Su Jong Yu, Haeryoung Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon, Eun Jung Bae
Cancers.2020; 12(7): 1805. CrossRef - Update on Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Brief Review from Pathologist Standpoint
Nese Karadag Soylu
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2020; 51(4): 1176. CrossRef - How Should We Assign Large Infiltrative Hepatocellular Carcinomas for Staging?
Yoo Jin Lee, Yoo Ra Lee, Chung Gyo Seo, Hyun Gil Goh, Tae Hyung Kim, Sun Young Yim, Na Yeon Han, Jae Min Lee, Hyuk Soon Choi, Eun Sun Kim, Bora Keum, Hyonggin An, Beomjin Park, Yeon Seok Seo, Hyung Joon Yim, Ji Hoon Kim, Young Dong Yu, Dong Sik Kim, Yoon
Cancers.2020; 12(9): 2589. CrossRef - Substantial risk of recurrence even after 5 recurrence-free years in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients
Jihye Kim, Wonseok Kang, Dong Hyun Sinn, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2020; 26(4): 516. CrossRef - Role of tumor margin and ADC change in defining the need for additional treatments after the first TACE in patients with unresectable HCC
Mohammadreza Shaghaghi, Mounes AliyariG hasabeh, Sanaz Ameli, Maryam Ghadimi, Bita Hazhirkarzar, Roya Rezvani Habibabadi, Hao Tang, Pegah Khoshpouri, Qingxia Wu, Ankur Pandey, Pallavi Pandey, Azarakhsh Baghdadi, Ihab R. Kamel
European Journal of Radiology.2020; 133: 109389. CrossRef - The 7th/8th American Joint Committee on Cancer and the Modified Union for International Cancer Control Staging System for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
In-Gyu Kim, Xu-Guang Hu, Hee-Jung Wang, Bong-Wan Kim, Sung Yeon Hong, Xue-Yin Shen
Yonsei Medical Journal.2019; 60(2): 140. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma with extrahepatic metastasis: Are there still candidates for transarterial chemoembolization as an initial treatment?
Jihye Kim, Dong-Hyun Sinn, Moon Seok Choi, Wonseok Kang, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik, Enzo Tagliazucchi
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(3): e0213547. CrossRef - Evaluation of early treatment response to radiotherapy for HCC using pre- and post-treatment MRI
So Hee Song, Woo Kyoung Jeong, Dongil Choi, Young Kon Kim, Hee Chul Park, Jeong Il Yu
Acta Radiologica.2019; 60(7): 826. CrossRef - The Clinicopathological and Prognostic Significance of the Gross Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Yangkyu Lee, Hyunjin Park, Hyejung Lee, Jai Young Cho, Yoo-Seok Yoon, Young-Rok Choi, Ho-Seong Han, Eun Sun Jang, Jin-Wook Kim, Sook-Hyang Jeong, Soomin Ahn, Haeryoung Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2018; 52(2): 85. CrossRef - Hepatobiliary MRI as novel selection criteria in liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma
Ah Yeong Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Woo Kyoung Jeong, Young Kon Kim, Tae Wook Kang, Sang Yun Ha, Chul Keun Park, Gyu Seong Choi, Jong Man Kim, Choon Hyuck David Kwon, Jae-Won Joh, Min-Ji Kim, Insuk Sohn, Sin-Ho Jung, Seung Woon Paik, Won Jae Lee
Journal of Hepatology.2018; 68(6): 1144. CrossRef
- Preoperative Prediction of Microvascular Invasion with Gadoxetic Acid-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Implication of Surgical Decision on the Extent of Liver Resection


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter