Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Liver Cancer > Volume 23(2); 2023 > Article
-
Original Article
Isolation and characterization of cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma -
Kyoungdo Mun1
 , Jiwon Han1,2
, Jiwon Han1,2 , Pureun Roh1
, Pureun Roh1 , Jonggeun Park1
, Jonggeun Park1 , Gahee Kim3
, Gahee Kim3 , Wonhee Hur3
, Wonhee Hur3 , Jeongwon Jang1,2
, Jeongwon Jang1,2 , Jongyoung Choi1,2
, Jongyoung Choi1,2 , Seungkew Yoon1,2
, Seungkew Yoon1,2 , Youngkyoung You4
, Youngkyoung You4 , Hojoong Choi4
, Hojoong Choi4 , Pilsoo Sung1,2
, Pilsoo Sung1,2
-
Journal of Liver Cancer 2023;23(2):341-349.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.04.30
Published online: June 12, 2023
1The Catholic University Liver Research Center and POSTECH-Catholic Biomedical Engineering Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University Korea, Seoul, Korea
2Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
3Division of Chronic Viral Disease Research, Center for Emerging Virus Research, National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Cheongju, Korea
4Department of Surgery, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
-
Corresponding author: Pilsoo Sung, Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, 222 Banpo-daero, Seocho-gu, Seoul 06591, Korea
Tel. +82-2-2258-2073, Fax. +82-2-3481-4025 E-mail: pssung@catholic.ac.kr
© 2023 The Korean Liver Cancer Association.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 3,209 Views
- 202 Downloads
- 2 Citations
Abstract
-
Background/Aim
- Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) play an immunosuppressive role in the tumor microenvironment (TME) of human cancers; however, their characteristics and role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain to be elucidated.
-
Methods
- Nine tumor and surrounding liver tissue samples from patients with HCC who underwent surgery were used to isolate patient-derived CAFs. Cell morphology was observed using an optical microscope after culture, and cell phenotypes were evaluated using flow cytometry and immunoblotting. Cytokines secreted by CAFs into culture medium were quantified using a multiplex cytokine assay.
-
Results
- CAFs were abundant in the TME of HCC and were adjacent to immune cells. After culture, the CAFs and non-tumor fibroblasts exhibited spindle shapes. We observed a robust expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin and fibroblast activation protein in CAFs, whereas alpha-fetoprotein, epithelial cell adhesion molecule, platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1, and E-cadherin were not expressed in CAFs. Furthermore, CAFs showed high secretion of various cytokines, namely C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, and C-C motif chemokine ligand 2.
-
Conclusions
- CAFs are abundant in the TME of HCC and play a crucial role in tumor progression. These fibroblasts secrete cytokines that promote tumor growth and metastasis.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common type of malignant tumor and is ranked third in cancer-related mortality worldwide.1,2 When used as a monotherapy for HCC, immune checkpoint inhibitors have a treatment response rate of only approximately 15-20%.3 To perform immunotherapy, T cells in the body must be activated to kill tumor cells; however, regulatory T cells, tumor-associated macrophages, and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) can interfere with this process.4 Moreover, HCC is very heterogeneous.5 Some parts of a large HCC respond well to immunotherapy, while other parts do not, eventually causing treatment resistance.6
- In the tumor microenvironment (TME), HCC cells and CAFs interact with various cells in their vicinity, including several immune and stromal cells.7,8 The growth factors secreted by HCC cells, which include the transforming growth factor-β and platelet-derived growth factor, as well as chemokines and cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, and C-C motif chemokine ligand (CCL) 5, exert a significant effect on hepatocytes and adjacent immune cells.9,10 CAFs are activated by these cytokines and then interact with nearby immune cells.9 Cells with anti-tumor functions, such as M1 macrophages and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, are inhibited by immune checkpoint molecules, such as programmed death-ligand 1, T-cell immunoglobulin, and mucin-domain containing-3, which are expressed in CAFs.11,12 CAFs have a direct immunosuppressive effect on anti-tumor immune cells by activating immunosuppressive cells, such as regulatory T cells, M2 macrophages, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells.13,14
- In this study, we identified CAFs using histopathological analysis and measured the levels of cytokines secreted by CAFs isolated from tissues of patients with HCC.
INTRODUCTION
- 1. Patient samples and clinical data
- In this study, samples from nine patients with HCC who underwent hepatectomy or liver transplantation between June 2022 and January 2023 were collected. Table 1 summarizes patient and tumor characteristics. Paraffin blocks and snap-frozen tissues were stored for subsequent histopathological analysis. Some of the HCC tumor and non-tumor tissues obtained after surgical resection or liver transplantation were used to isolate CAFs through dissociation, and the remaining tissues were stored at -70℃.
- 2. Isolation of CAFs
- The tumor and surrounding liver tissues of patients with HCC were dissociated using a tumor dissociation kit (Miltenyi Biotech, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) and gentleMACS™ dissociator (Miltenyi Biotech). A finely cut cross section of the surgically removed tissue was placed in Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 (Welgene, Gyeongsan, Korea) without fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and tumor dissociation was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After dissociation, the sample was transferred to a fresh 50 mL tube with a 70 µm strainer for centrifugation at 50×g and 25℃ for 2 minutes. The supernatant was then removed and the cell pellet was cultured in a culture dish measuring 60×15 mm containing Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium/Nutrient Mixture F-12 (DMEM/F-12) (Welgene) in a 1:1 ratio.
- 3. Flow cytometry
- Single-stain flow cytometry was performed on Huh7, Hep3B, HepG2, SK-hep-1, CAFs and non-tumor fibroblasts. The following antibodies were used: allophycocyanin-conjugated anti-human alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) (R&D system, Minneapolis, MN, USA), anti-human fibroblast activation protein (FAP) (R&D system), phycoerythrinconjugated anti-human alpha-fetoprotein (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), and anti-human epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) (BD Biosciences). The FlowJo software (TreeStar, Ashland, OR, USA) was used for data analysis.
- 4. Immunoblotting
- Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), Huh7, CAFs and non-tumor fibroblasts were lysed in radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer supplemented with a protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). The lysates were separated using 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and the proteins were transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes (Schleicher and Schuell, Keene, NH, USA). For immunoblotting, rabbit polyclonal anti-α-SMA antibody (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), rabbit monoclonal anti-vimentin (D21H3) antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), rabbit monoclonal anti-E-cadherin (24E10) antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), mouse monoclonal anti-CD31 (PECAM-1) antibody (Cell Signaling Technology), and rabbit monoclonal anti-GAPDH (14C10) antibody (Cell Signaling Technology) were used.
- 5. Multiplex analysis
- To measure the cytokines secreted by the cultured CAFs into the medium, we performed multiplex analysis using the ProcartaPlex Hu Cytokine/Chemokine Panel 1A 34plex (Thermo Fisher Scientific). This panel measured the levels of CCL3, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12), IL-27, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, CXCL10, IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-10, CCL11, CCL5, TNF-α, CCL4, CCL2, CXCL1, and IL-21. Data analysis was conducted using xPonent v3.1 software (Luminex, Austin, TX, USA), and graphs were generated using GraphPad Prism 7 (GraphPad, Boston, MA. USA).
- 6. Statistical analysis
- All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 7. Numerical variables were evaluated using independent t-tests. Statistical significance was set at P<0.05.
METHODS
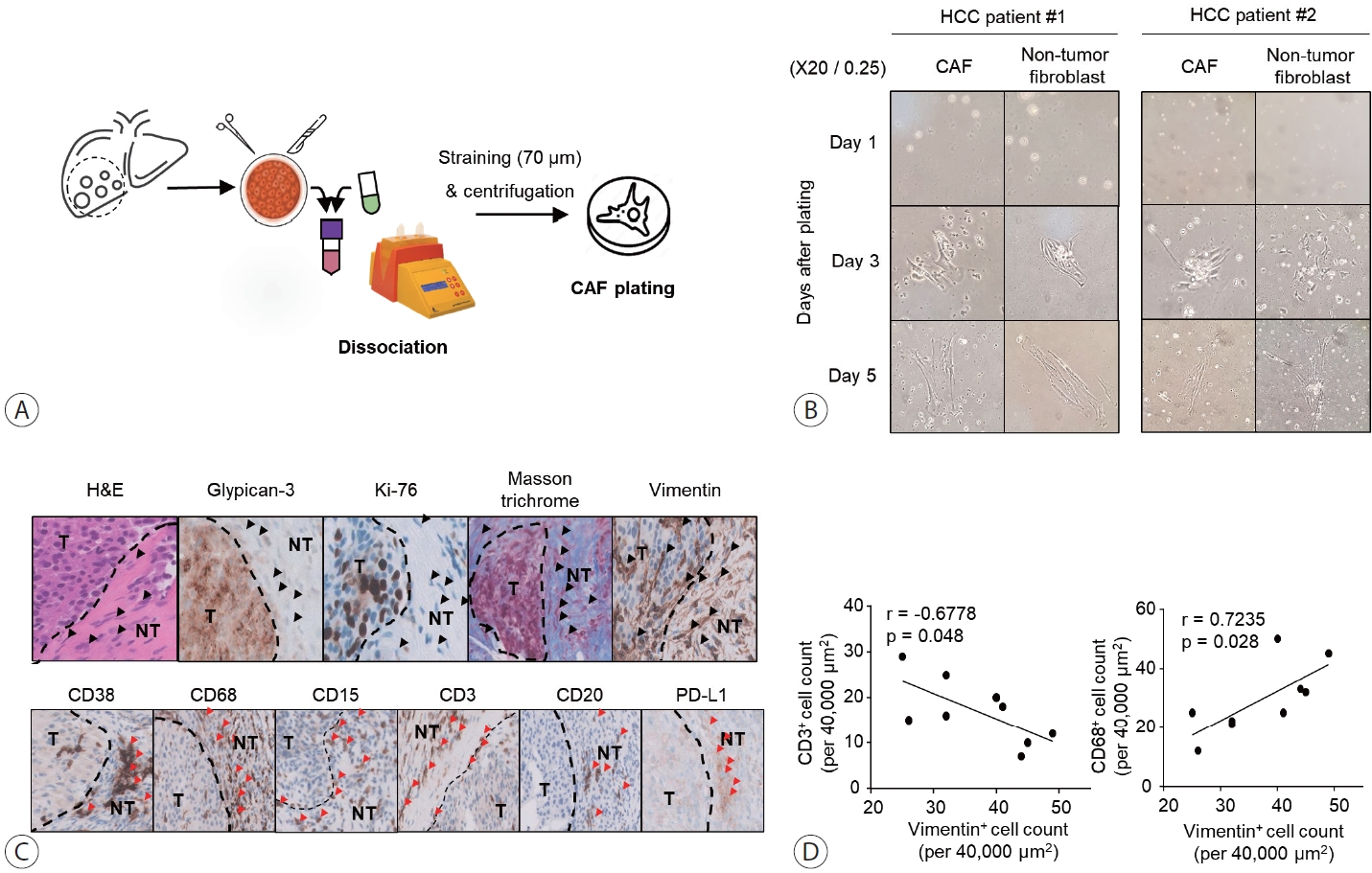
- 1. Morphology of isolated CAFs and non-tumor fibroblasts from tumor and non-tumor liver tissues of patients with HCC
- We cultured CAFs and non-tumor fibroblasts isolated from tumor and non-tumor liver tissues (Fig. 1A) in a 60×15 mm culture dish with 10% FBS DMEM/F-12. We examined the morphology of the cultured CAFs and non-tumor fibroblasts on days 1, 3, and 5 (Fig. 1B). Isolated CAFs and non-tumor fibroblasts showed spindle shapes on days 3 and 5, respectively. Over time, they formed a single cluster, as previously observed in patient tissue analyses. These findings suggest that CAFs and non-tumor fibroblasts cannot be distinguished morphologically.
- 2. CAFs are abundant in the TME of HCC and adjacent to immune cells
- Tumor tissues were collected from nine patients diagnosed with HCC after surgical resection (Table 1). Immunohistochemical analysis for vimentin showed that CAFs formed a thick layer of fiber around HCC cells in tissues that were confirmed to have advanced HCC (Fig. 1). Vimentin staining also revealed that fibroblasts exhibited characteristics similar to those of fibroblasts clustered around HCC cells in the vicinity (black arrowheads) (Fig. 1C). Vimentin+ fibroblast clusters were more abundant in the intra-tumoral periphery than inside the tumor. Immune cells were detected near fibroblast clusters (red arrowheads) (Fig. 1C). Furthermore, vimentin-expressing CAFs were more strongly correlated with CD68+ macrophages than with CD3+ T cells in the peri-tumor sections (Fig. 1D).
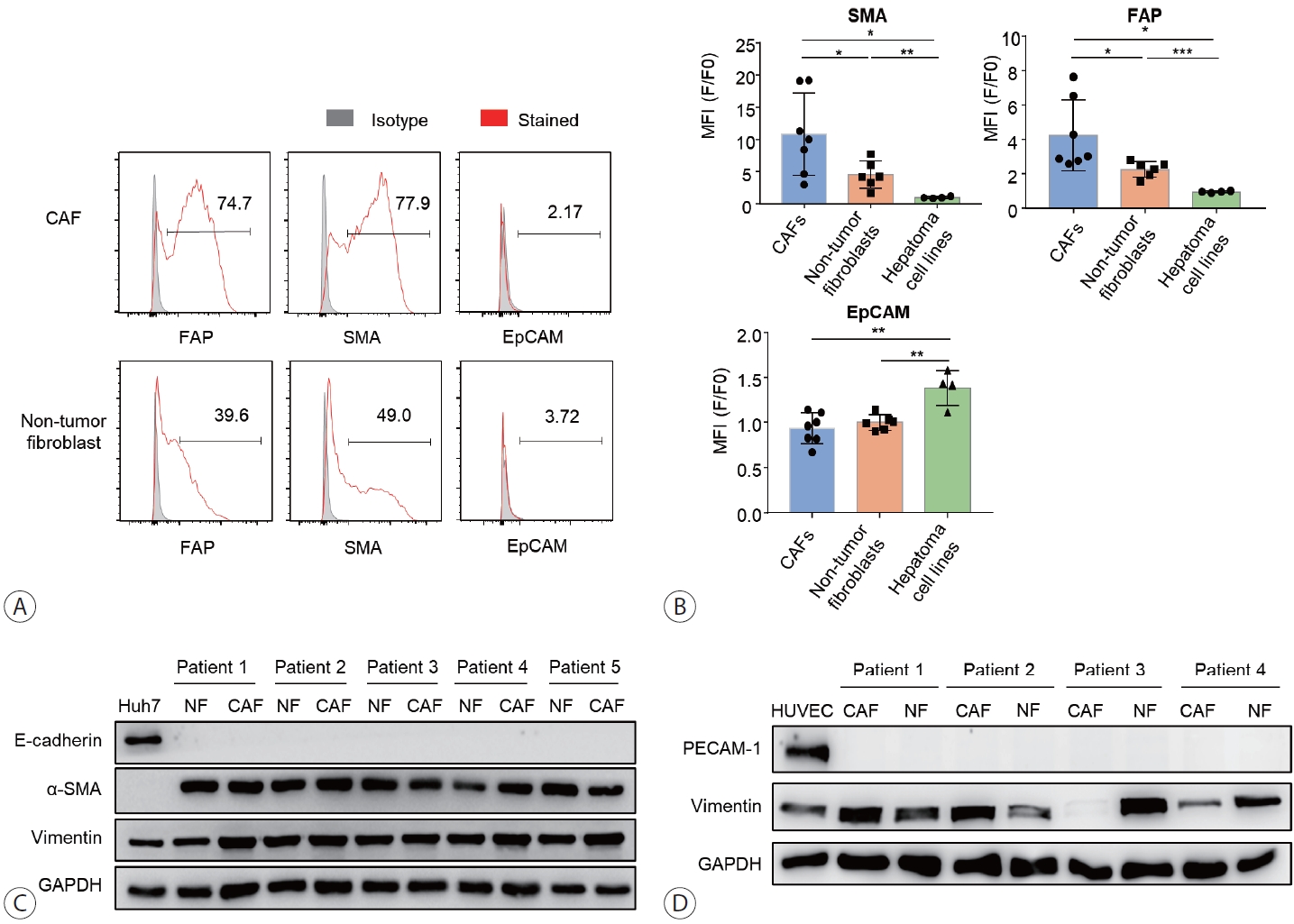
- 3. CAFs robustly express FAP and α-SMA
- Single-stain flow cytometry was used to characterize isolated CAFs, non-tumor fibroblasts, and hepatoma cells, namely Huh7, Hep3B, HepG2, SK-hep-1, based on the expression of α-SMA, FAP, and EpCAM (Fig. 2A, B). The results showed that α-SMA and FAP, but not EpCAM and E-cadherin, were expressed in both CAFs and non-tumor fibroblasts (Fig. 2B, C). The expression of α-SMA and FAP was higher in CAFs compared to non-tumor fibroblasts. Compared to HCC cells, CAFs and non-tumor fibroblasts showed lower expression of EpCAM and E-cadherin, whereas FAP expression was only detected in CAFs and non-tumor fibroblasts. PECAM-1, a well-known marker of endothelial cells, was expressed in HUVECs, but not in CAFs isolated from the patients (Fig. 2D).
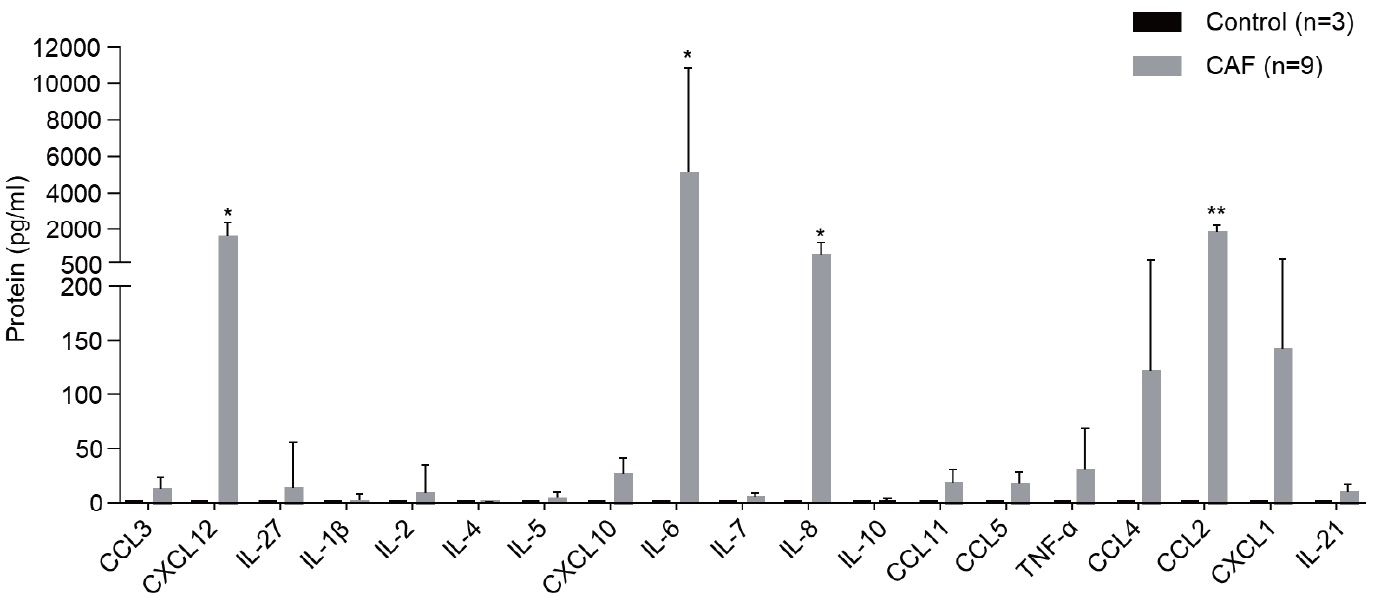
- 4. CAFs secrete various cytokines
- Multiplex analysis was performed to detect the cytokines secreted by CAFs into the medium (Fig. 3). CCL3, CXCL12, IL-27, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-5, CXCL10, IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-10, CCL11, CCL5, TNF-α, CCL4, CCL2, CXCL1, and IL-21 were detected in the CAF-cultured medium. However, the levels of CXCL12, IL-6, IL-8, and CCL2, which are involved in immune responses, were considerably high.
RESULTS
- Compared to research on CAFs in other tumor types, studies on CAFs in HCC have only recently been actively conducted. Thus, most studies on CAFs in HCC are based on experiments with CAFs isolated from tumors of other organs, such as pancreatic, lung, and breast cancers.15,16 Notably, studies have shown a close association between CAFs in pancreatic cancer and CAFs in HCC, leading to frequent comparisons between the two fibroblast environments.17 However, further studies are required to characterize CAFs in HCC.
- CAFs in HCC, identified by the expression of α-SMA and FAP, were observed throughout the TME, including the tumor septum, fibrous capsule, and hepatic blood sinusoids. A recent study showed that CAFs in HCC may originate from multiple cell types, such as hepatic stellate cells, tumor cells that have undergone epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells that have undergone endothelial-mesenchymal transition.18 CAFs play an important role in TME.19 CAFs in the TME of HCC promote EMT in tumor cells by upregulating FAP and vimentin.18 This leads to a more aggressive phenotype and poorer prognosis for HCC. CAFs induce fibrosis and inflammation and affect immune responses around tumor cells. CAFs exist in various subsets, such as inflammatory, myofibroblastic, and antigen-presenting cells, each playing a different role.20,21 These diverse subsets create a complex TME that regulates tumor growth, metastasis, and resistance to cancer treatment. Understanding how these active factors, such as FAP and vimentin, regulate the subsets of CAFs in liver cancer is important to improve TME and develop cancer treatments.22 Furthermore, CAFs can be important targets for HCC treatment because of their crosstalk with HCC cells and other surrounding cells in the TME.
- In this study, we found that fibroblasts clustering in the peri-tumor of the liver in patients with HCC inhibited the activity of immune cells attempting to infiltrate HCC cells, thereby impeding the immune response. CD68+ macrophages showed the strongest correlation with immune cells in HCC tissues. Macrophages are typically divided into M1 phenotypes, which have anti-tumor functions and promote inflammation, and M2 phenotypes, which suppress inflammation and immune activity for the tumor progression in the TME of HCC.12 The correlation between macrophages and CAFs may play a role in the immune function of macrophages.
- Cultured CAFs were found to secrete immune-related cytokines. In particular, IL-8, CCL2, and IL-6 are involved in the differentiation and inhibition of T cells and macrophages and suppress CD8+ T cells, activate regulatory T cells, and promote M2 differentiation of macrophages and neutrophils.23,24 Based on the immunosuppressive function of CAFs, we predict that controlling CAFs will be critical in future immunotherapies for HCC.11
- The results of this study demonstrated that CAFs are abundant around HCC cells, where they inhibit nearby immune cells. Furthermore, through the identification and characterization of CAFs in tissues and the assessment of their interactions with immune cells, this study confirmed that CAFs exert an inhibitory effect on immune cells.
DISCUSSION
-
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
-
Ethics Statement
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Boards of Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital (KC20TISI0669). The study conformed to the ethical guidelines of the Helsinki Declaration. Written informed consent was obtained from each patient prior to enrollment. Informed consents were obtained from all included patients.
-
Funding Statement
This work was partly supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (2021R1C1C1005844 to PSS) and the Research Fund of Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital of the Catholic University of Korea. This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (grant number 2022R1I1A1A01063636 to JWH). This study was supported by the Korean Liver Cancer Association Research Award (2021).
-
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
-
Author Contribution
Conceptualization: PSS
Data curation: PSS
Formal analysis: KM, PSS
Investigation: KM, PR, JP, GK, WH
Methodology: KM, PSS
Project administration: KM, PSS
Resources: JH, JJ, JC, SY, YY, HC
Software: GK, WH
Supervision: PSS
Validation: KM, PSS
Visualization: KM, PR, PSS
Writing–original draft: KM, JP, PSS
Writing–review & editing: KM, JH, PSS
Article information
- 1. Sung PS, Choi MH, Yang H, Lee SK, Chun HJ, Jang JW, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in hepatocellular carcinoma as a predictor of a response to cisplatin-based hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. Front Oncol 2020;10:600233. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Park SH, Heo S, Kim B, Lee J, Choi HJ, Sung PS, et al. Targetoid primary liver malignancy in chronic liver disease: prediction of postoperative survival using preoperative MRI findings and clinical factors. Korean J Radiol 2023;24:190−203.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 3. Feng MY, Chan LL, Chan SL. Drug treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: first-line and beyond. Curr Oncol 2022;29:5489−5507.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Mizukoshi E, Kaneko S. Immune cell therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol Oncol 2019;12:52. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 5. Zhang Q, Lou Y, Bai XL, Liang TB. Intratumoral heterogeneity of hepatocellular carcinoma: from single-cell to population-based studies. World J Gastroenterol 2020;26:3720−3736.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Sung PS, Jang JW, Lee J, Lee SK, Lee HL, Yang H, et al. Real-world outcomes of nivolumab in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in an endemic area of hepatitis B virus infection. Front Oncol 2020;10:1043. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Sas Z, Cendrowicz E, Weinhäuser I, Rygiel TP. Tumor microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma: challenges and opportunities for new treatment options. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23:3778. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Park DJ, Sung PS, Lee GW, Cho S, Kim SM, Kang BY, et al. Preferential expression of programmed death ligand 1 protein in tumorassociated macrophages and its potential role in immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:4710. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Sung PS. Crosstalk between tumor-associated macrophages and neighboring cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol 2022;28:333−350.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 10. Zampaglione L, Ferrari J, Pedica F, Goossens N. HCC in metabolic syndrome: current concepts and future directions. Hepatoma Res 2021;7:55. Article
- 11. Eskandari-Malayeri F, Rezaei M. Immune checkpoint inhibitors as mediators for immunosuppression by cancer-associated fibroblasts: a comprehensive review. Front Immunol 2022;13:996145. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Sung PS, Lee IK, Roh PR, Kang MW, Ahn J, Yoon SK. Blood-based biomarkers for immune-based therapy in advanced HCC: promising but a long way to go. Front Oncol 2022;12:1028728. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Loh JJ, Ma S. The role of cancer-associated fibroblast as a dynamic player in mediating cancer stemness in the tumor microenvironment. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021;9:727640. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Liu T, Han C, Wang S, Fang P, Ma Z, Xu L, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: an emerging target of anti-cancer immunotherapy. J Hematol Oncol 2019;12:86. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 15. Zhang T, Ren Y, Yang P, Wang J, Zhou H. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis 2022;13:897. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Foster DS, Januszyk M, Delitto D, Yost KE, Griffin M, Guo J, et al. Multiomic analysis reveals conservation of cancer-associated fibroblast phenotypes across species and tissue of origin. Cancer Cell 2022;40:1392−1406.e7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Norton J, Foster D, Chinta M, Titan A, Longaker M. Pancreatic cancer associated fibroblasts (CAF): under-explored target for pancreatic cancer treatment. Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:1347. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18. Eun JW, Yoon JH, Ahn HR, Kim S, Kim YB, Lim SB, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived secreted phosphoprotein 1 contributes to resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib and lenvatinib. Cancer Commun (Lond) 2023;43:455−479.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 19. Simon T, Salhia B. Cancer-associated fibroblast subpopulations with diverse and dynamic roles in the tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer Res 2022;20:183−192.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 20. Toledo B, Picon-Ruiz M, Marchal JA, Perán M. Dual role of fibroblasts educated by tumour in cancer behavior and therapeutic perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23:15576. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Desbois M, Wang Y. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: key players in shaping the tumor immune microenvironment. Immunol Rev 2021;302:241−258.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Feng B, Wu J, Shen B, Jiang F, Feng J. Cancer-associated fibroblasts and resistance to anticancer therapies: status, mechanisms, and countermeasures. Cancer Cell Int 2022;22:166. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. Sullivan KM, Jiang X, Guha P, Lausted C, Carter JA, Hsu C, et al. Blockade of interleukin 10 potentiates antitumour immune function in human colorectal cancer liver metastases. Gut 2023;72:325−337.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Raskov H, Orhan A, Gaggar S, Gögenur I. Cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumor-associated macrophages in cancer and cancer immunotherapy. Front Oncol 2021;11:668731. ArticlePubMedPMC
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Rebuilding the microenvironment of primary tumors in humans: a focus on stroma
Siwon Mun, Hyun Jin Lee, Pilnam Kim
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2024; 56(3): 527. CrossRef - Intrahepatic IgA complex induces polarization of cancer-associated fibroblasts to matrix phenotypes in the tumor microenvironment of HCC
Jong Geun Park, Pu Reun Roh, Min Woo Kang, Sung Woo Cho, Suhyun Hwangbo, Hae Deok Jung, Hyun Uk Kim, Ji Hoon Kim, Jae-Sung Yoo, Ji Won Han, Jeong Won Jang, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Young Kyoung You, Ho Joong Choi, Jae Yong Ryu, Pil Soo Sung
Hepatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Download Citation
Download Citation
- Download Citation
- Close
- Related articles
-
- The role of lenvatinib in the era of immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma
- 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Combination of interventional oncology local therapies and immunotherapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Deciphering and Reversing Immunosuppressive Cells in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma

 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION


 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter