Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Report
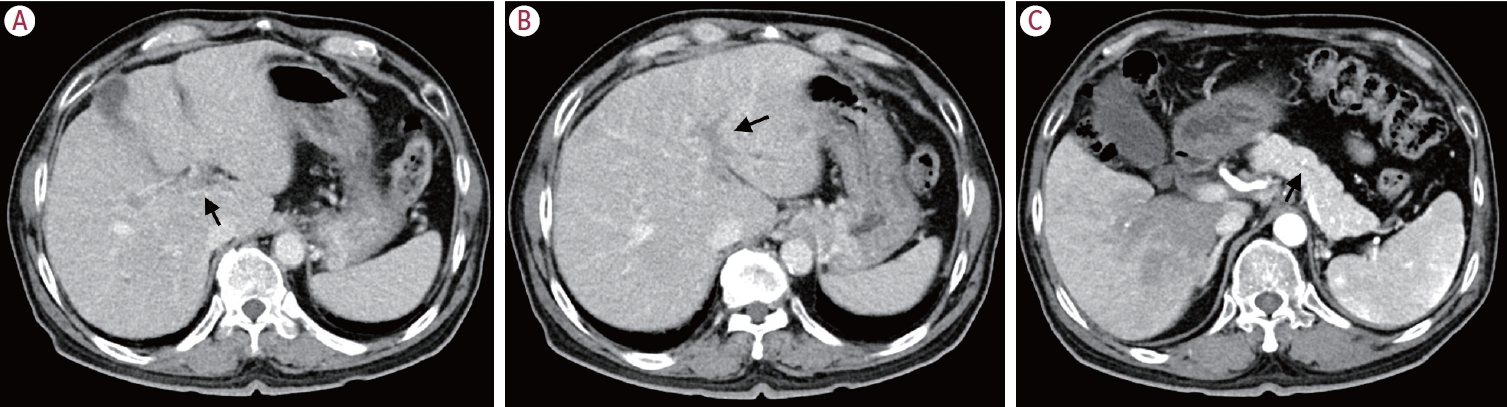
- Metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis confirmed on blind liver biopsy
- Hun Kim, Tae Hoon Roh, Jun Seop Lee, Min Seong Kim, Beom Kyung Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):113-117. Published online November 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.11.05
- 897 Views
- 82 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) is an uncommon condition in which tumor cells expand into the vessels, causing blood clot formation in the portal vein. PVTT is mainly associated with hepatocellular carcinoma, leading to an unfavorable prognosis; however, it can also develop in patients with other cancer types. Herein, we report a case of metastatic renal cell carcinoma diagnosed by a blind liver biopsy in a patient with dynamic computed tomography-confirmed portal vein thrombosis and cholangiopathy. This case illustrates the importance of systematic surveillance with routine laboratory tests and contrast-enhanced imaging studies on patients with cancer to detect potential liver infiltration of metastatic cancer.

Review Article
- Locoregional Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis
- Sang Youn Hwang, Ryoung-Go Kim, Cheol-Won Choi, Sang Bu Ahn
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(2):69-81. Published online September 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.2.69
- 1,012 Views
- 10 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) have a extremely poor prognosis. According to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer guideline, sorafenib is a standard therapy in this situation, but many clinicians still select locoregional therapy (LRT) such as transarterial therapy, external beam radiation therapy (EBRT), even surgical resection (SR) or combination of LRTs because the survival improvement by sorafenib is unsatisfactory. Based on recent meta-analysis and prospective study, transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and transarterial radioembolization seem to be effective and safe therapeutic option that have comparable outcome to sorafenib. Recently large nationwide studies demonstrated that SR can be a potentially curative treatment in selected patients. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) can be also good option, especially in Child class B patients based on small volume prospective studies. Moreover, multidisciplinary strategies based on the combination of LRTs (SR plus TACE, TACE + EBRT, TACE + Sorafenib, HAIC + EBRT etc.) may improve survival of HCC patients with PVTT. Finally we discuss individualized and tailored treatment strategies for different clinical situations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Progress in Non-Surgical Treatment of Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Combined Portal Vein Carcinoma Thrombosis
文豪 寇
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(07): 11779. CrossRef
- Progress in Non-Surgical Treatment of Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Combined Portal Vein Carcinoma Thrombosis

Case Report
- A Case of Cyberknife Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis
- Chan Ran You, Si Hyun Bae, Hyun Young Woo, Soung Won Jeong, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Hong Seok Jang, Dong Hoon Lee, Byung Gil Choi
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2007;7(1):82-86. Published online June 30, 2007
- 778 Views
- 14 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 64 year-old-male patient was transferred to our hospital for infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) without treatment response because of treatment failure and disease progression. He had been diagnosed infiltrating HCC 9 months ago and then treated with three times of transarterial chemolipiodolization (TACL) in other hospital. But, HCC was progressed. Abdominal CT showed infiltrating HCC in S7 and a small daughter nodule in S8 with right and main portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT). We performed stereotatic radiosurgery (Cyberknife) for the treatment of PVTT and four times of TACL for the treatment of intrahepatic HCC every 4weeks. The total radiation doses using with Cyberknife were 36Gy with a prescription isodose 80% in 3 fractions over the three consecutive days. After treatment, infiltrating HCC was decreased in size and PVTT was markedly regressed. Response rate of serum AFP was 57.2%. In conclusion, we report the case of good treatment response in the patient with HCC with PVTT after combination treatment of Cyberknife and TACL.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter