Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Reports
- Advanced Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Successfully Treated with Transarterial Radioembolization and Multi-tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy
- Myung Ji Goh, Wonseok Kang, Dong Hyun Sinn, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):160-166. Published online September 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.160

- 3,561 Views
- 133 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transarterial radioembolization (TARE) with yttrium-90 microspheres has become widely utilized in managing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The utility of TARE is expanding with new insights through experiences from real-world practice and clinical trials, and recently published data suggest that TARE in combination with sorafenib may improve the overall survival in selected patients. Here, we report a case of advanced stage HCC that was successfully treated with TARE and sorafenib. The patient achieved complete response (CR) at 12 months after the initial treatment with TARE and sorafenib, followed by additional transarterial chemoembolization and proton beam therapy for local tumor recurrence at 19-month post-TARE. The patient was followed up every 3 months thereafter and still achieved CR both biochemically and radiologically for the following 12 months. A combination strategy of TARE and systemic therapy may be a useful alternative treatment option for selected patients with advanced stage HCC.

- Recurrent Coronary Artery Vasospasm in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sorafenib: a Case Report and Literature Review
- Dae Hyun Lim, Jai Hoon Yoon, Dae Won Jun, Oh Young Lee, Byung Chul Yoon, Hang Rak Lee, Kyung Soo Kim, Ho Soon Choi
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):67-71. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.67
- 4,361 Views
- 87 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
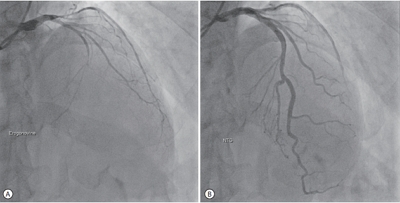
PDF - Tyrosine kinase inhibitors are widely used as targeted treatments for various malignancies. Sorafenib is an orally active tyrosine kinase inhibitor that blocks the signaling pathways of several growth factors. Its use is approved for various malignancies such as unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, and gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Several adverse effects have been reported in the literature; however, cardiotoxicity is rare. We present a case of recurrent coronary vasospasm caused by short-term administration (5 days) of sorafenib. Since it caused refractory ischemia after re-administration, we had no choice but to stop the treatment.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter