Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Report
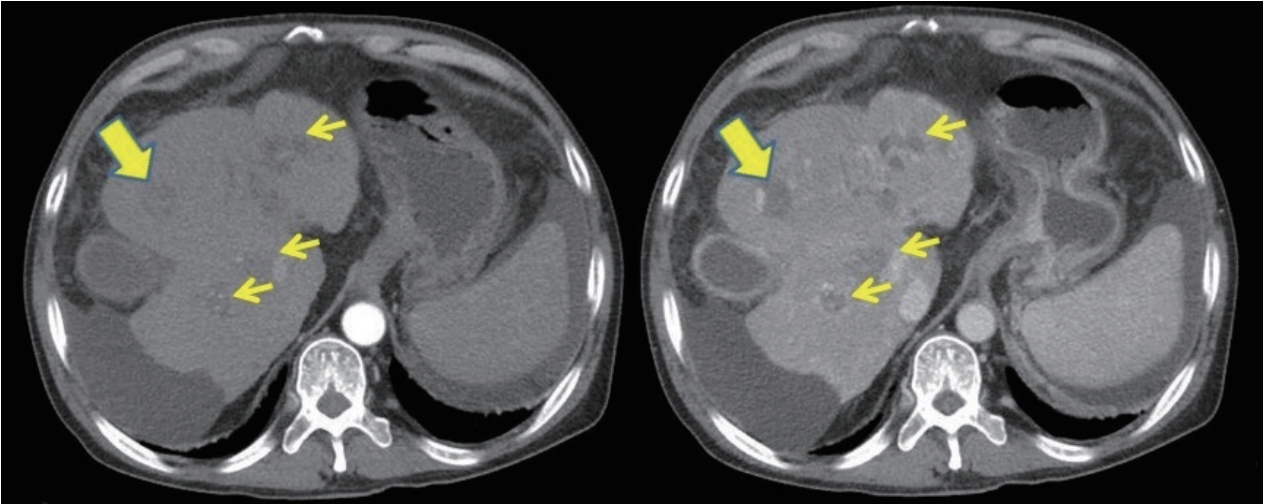
- Hepatic Failure Due to Hepatitis E Virus Infection in a Patient with Necrotic Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Ji Hye Kim, Young Seok Doh, Ji Woong Jang, Min Seok Kang, Nak Min Kim, Sae Hee Kim, Il Hyun Baek, Sung Hee Jung
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(1):55-58. Published online March 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.1.55
- 3,415 Views
- 47 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) or liver cirrhosis (LC) accompanied by hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection, hepatic failure often leads to debility. Here, we report about a 63-year-old man with alcoholic LC who was referred to our hospital with jaundice and abdominal distension 10 days earlier. Abdominal computed tomography showed necrotic HCC accompanied by left lobe shrinkage without tumor progression. Laboratory and imaging findings revealed no acute infection focus. The patient reported no herbal medicine or alcohol consumption, and there was no evidence of acute viral hepatitis. One month later, HEV immunoglobulin M positivity was confirmed, and deterioration of liver function due to HEV infection was suspected. The patient often ate raw oysters and sashimi, as well as boar meat, which is a well-known risk food for HEV infection. His umbilical hernia deteriorated due to tense ascites and infection by skin abrasion. The patient progressed to hepatorenal syndrome and eventually died. Liver function preservation is important when treating HCC patients. Therefore, clinicians should pay more attention to the prevention of HEV and others causes of direct liver injury.

Original Article
- Cause of Mortality for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients who were Diagnosed within the Milan Criteria
- Hyun-Woo Lee, Dong Hyun Sinn, Wonseok Kang, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(2):101-107. Published online September 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.2.101
- 1,474 Views
- 23 Downloads
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a unique condition where the cause of death might not only be due to progressive cancer, but also from liver failure. We evaluated specific causes of death for HCC patients who were initially diagnosed within the Milan criteria.
Methods
A retrospective cohort of 147 patients with mortality who were initially diagnosed with HCC within the Milan criteria between January 2008 and December 2012 at a single institution was reviewed.
Results
During follow-up, 104 patients (70.7%) experienced one or more cirrhotic complications, such as ascites, variceal bleeding, or hepatic encephalopathy. Near mortality, cancer progression (exceeding the Milan criteria) was recorded for 102 patients (69.3%), while cirrhosis progression (greater than two-point increase in Child-Pugh score) was noted in 110 (74.8%) patients. Alphafetoprotein, protein-induced by vitamin K antagonist-II levels and treatment modality were associated with cancer progression, while age and Child-Pugh class were associated with cirrhosis progression. There were 61 patients with in-hospital mortality; cancer progression plus liver failure was noted in 34 patients (55.7%), liver failure without cancer progression was seen in 20 patients (32.8%), and only four patients (6.6%) showed mortality from extrahepatic metastasis without liver failure.
Conclusions
Among HCC patients who were diagnosed within the Milan criteria, most of them had cirrhosis progression near mortality, and significant proportion died without uncontrolled cancer growth, mainly due to liver failure. These findings show the importance of liver function that should be considered in managing HCC patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes of Hepatitis B Virus–Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients with Undetectable Serum HBV DNA Levels
Jong-In Chang, Dong Hyun Sinn, Hyun Cho, Seonwoo Kim, Wonseok Kang, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2022; 67(9): 4565. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 583. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Korean Journal of Radiology.2022; 23(12): 1126. CrossRef - Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Oligometastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multi-Institutional Retrospective Study (KROG 20-04)
Tae Hyung Kim, Taek-Keun Nam, Sang Min Yoon, Tae Hyun Kim, Young Min Choi, Jinsil Seong
Cancers.2022; 14(23): 5848. CrossRef - Multidisciplinary approach is associated with improved survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients
Dong Hyun Sinn, Gyu-Seong Choi, Hee Chul Park, Jong Man Kim, Honsoul Kim, Kyoung Doo Song, Tae Wook Kang, Min Woo Lee, Hyunchul Rhim, Dongho Hyun, Sung Ki Cho, Sung Wook Shin, Woo Kyoung Jeong, Seong Hyun Kim, Jeong Il Yu, Sang Yun Ha, Su Jin Lee, Ho Yeon
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(1): e0210730. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma with extrahepatic metastasis: Are there still candidates for transarterial chemoembolization as an initial treatment?
Jihye Kim, Dong-Hyun Sinn, Moon Seok Choi, Wonseok Kang, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik, Enzo Tagliazucchi
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(3): e0213547. CrossRef
- 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma

Review Article
- How to Prevent Post Operative Hepatic Failure after Hepatic Resection
- Jinsub Choi
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2005;5(1):7-11. Published online June 30, 2005
- 493 Views
- 1 Download

Case Report
- A Case of Liver Failure after Liver Resection for Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Kyung Woo Park, Sang Jae Park, Young Il Kim, Seong Hoon Kim, Hong Suk Park, Woo Jin Lee, Dae Young Kim, Eun Kyoung Hong, Joong-Won Park, Chang-Min Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2005;5(1):49-51. Published online June 30, 2005
- 475 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Liver resection is an important curable treatment modality for patient with early hepatocelluar carcinoma (HCC)
with good underlying liver function. Recently, mortality after liver resection for HCC became low, however
morbidity is still significantly high. Liver failure is the most serious complication of liver resection. We report a
case
of liver failure following liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma who recovered spontaneously.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter