Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Articles
- Advancing Korean nationwide registry for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic sampling approach utilizing the Korea Central Cancer Registry database
- Bo Hyun Kim, E Hwa Yun, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Geun Hong, Jun Yong Park, Ju Hyun Shim, Eunyang Kim, Hyun-Joo Kong, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Suk Lim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):57-61. Published online March 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.03
- 349 Views
- 20 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
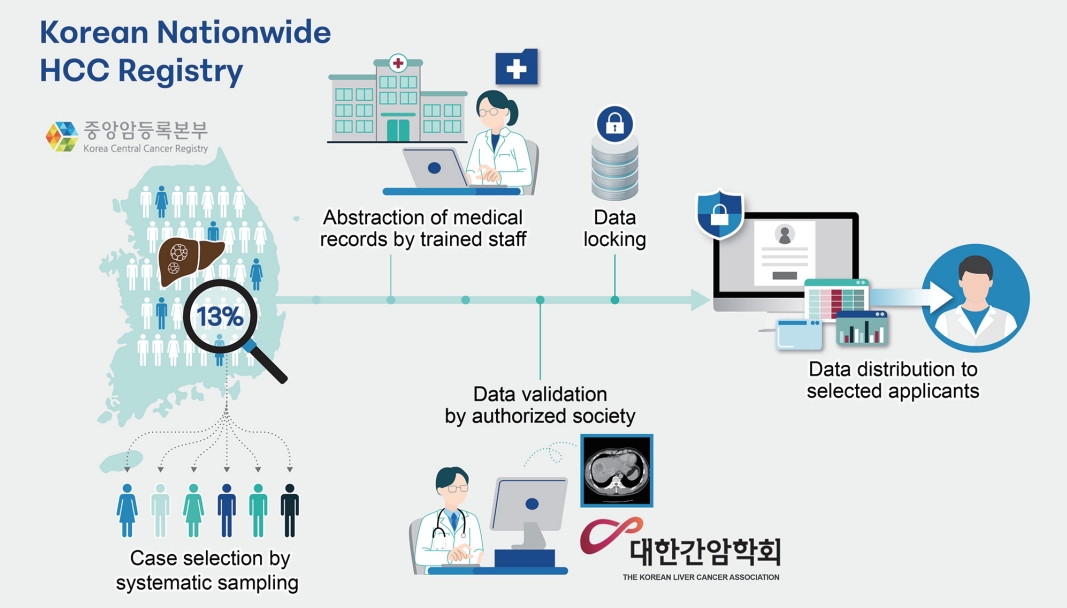
Supplementary Material - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presents a substantial public health challenge in South Korea as evidenced by 10,565 new cases annually (incidence rate of 30 per 100,000 individuals), in 2020. Cancer registries play a crucial role in gathering data on incidence, disease attributes, etiology, treatment modalities, outcomes, and informing health policies. The effectiveness of a registry depends on the completeness and accuracy of data. Established in 1999 by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, the Korea Central Cancer Registry (KCCR) is a comprehensive, legally mandated, nationwide registry that captures nearly all incidence and survival data for major cancers, including HCC, in Korea. However, detailed information on cancer staging, specific characteristics, and treatments is lacking. To address this gap, the KCCR, in partnership with the Korean Liver Cancer Association (KLCA), has implemented a systematic approach to collect detailed data on HCC since 2010. This involved random sampling of 10-15% of all new HCC cases diagnosed since 2003. The registry process encompassed four stages: random case selection, meticulous data extraction by trained personnel, expert validation, anonymization of personal data, and data dissemination for research purposes. This random sampling strategy mitigates the biases associated with voluntary reporting and aligns with stringent privacy regulations. This innovative approach positions the KCCR and KLCA as foundations for advancing cancer control and shaping health policies in South Korea.

- Changing etiology and epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: Asia and worldwide
- Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):62-70. Published online March 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.13
- 736 Views
- 59 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
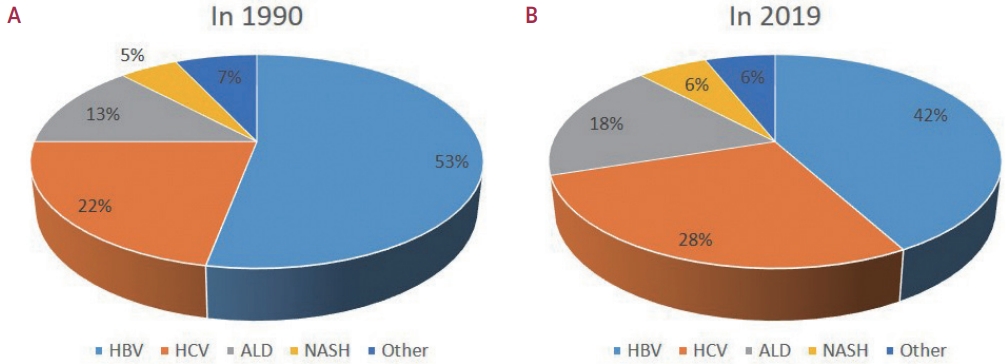
PDF - Approximately 80% of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cases arise in sub-Saharan Africa and Eastern Asia, following a similarly high prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) carriers in these regions. The etiology and epidemiology of HCC have recently changed worldwide. Although HBV infection is the main contributor to HCC development, a slow but continuous decline in HBV infection rates has been reported since 1990. Owing to the widespread use of direct-acting antivirals, the incidence of hepatitis C virus-related HCC has remarkably decreased in Japan and European countries. In Korea, Taiwan, and Singapore, the incidence of HBV-related HCC has significantly decreased owing to vaccination against HBV. Globally, while HBV accounted for more than half of HCCs in 1990, this had decreased to 42% in 2019. In contrast, the proportion of patients with alcoholic- and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) increased from 13% to 18% and from 5% to 6%, respectively. NASH-related HCC has characteristics that differ from those of virus-associated HCC. Compared with other etiologies, patients with NASHassociated HCC are older, have a higher body mass index, and have higher rates of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and cardiovascular disease. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)-associated HCC is also known to develop in the absence of cirrhosis, unlike alcohol-related and autoimmune liver diseases. Because patients with NAFLD usually have diabetes or obesity, surveying this population is challenging. Optimal selection of the target population and surveillance tools among patients with NAFLD needs to be determined.

Original Articles
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
- Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Dong Ho Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Ju-Yeon Cho, Jonggi Choi, Young Chang, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):58-68. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.58
- 6,586 Views
- 265 Downloads
- 18 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
s: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related death in Korea. This study evaluated the characteristics of Korean patients newly diagnosed with HCC in 2015.
Methods
Data from the Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry (KPLCR), a representative sample of patients newly diagnosed with HCC in Korea, were analyzed. A total of 1,558 patients with HCC registered in the KPLCR in 2015 were investigated.
Results
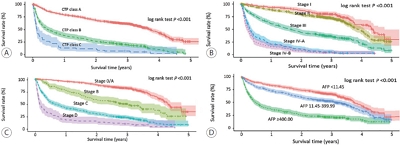
The median age was 61.0 years (interquartile range, 54.0-70.0 years), and men accounted for 79.7% of the subjects. Hepatitis B virus infection was the most common underlying liver disease (58.1%). According to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system, stage 0, A, B, C, and D HCCs accounted for 14.2%, 31.5%, 7.6%, 39.0%, and 7.8% of patients, respectively. Transarterial therapy (32.1%) was the most commonly performed initial treatment, followed by surgical resection (23.2%), best supportive care (20.2%), and local ablation therapy (10.7%). Overall, 34.5% of patients were treated in accordance with the BCLC guidelines: 59.2% in stage 0/A, 48.4% in stage B, 18.1% in stage C, and 71.6% in stage D. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 67.1%, 50.9%, and 27.0%, respectively.
Conclusions
In 2015, approximately 45% of Korean HCC cases were diagnosed at a very early or early stage, and 35% of patients underwent potentially curative initial treatment. BCLC guidance was followed in 34.5% of patients; in patients with stage B or C disease, there was relatively low adherence. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concurrent nivolumab and external beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A phase II study
Bo Hyun Kim, Hee Chul Park, Tae Hyun Kim, Young-Hwan Koh, Jung Yong Hong, Yuri Cho, Dong Hyun Sinn, Boram Park, Joong-Won Park
JHEP Reports.2024; 6(4): 100991. CrossRef - Identification of patients with favorable prognosis after resection in intermediate-stage-hepatocellular carcinoma
Han Ah Lee, Minjong Lee, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Ho Soo Chun, Yewan Park, Hwi Young Kim, Tae Hun Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Dong Hyun Sinn
International Journal of Surgery.2024; 110(2): 1008. CrossRef - Factors associated with the survival outcomes of patients with untreated hepatocellular carcinoma: An analysis of nationwide data
Min Jung Kwon, Soy Chang, Ji Hoon Kim, Ji Won Han, Jeong Won Jang, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Pil Soo Sung
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The imitator of immune-tolerant chronic hepatitis B: A killer in disguise
Moon Haeng Hur, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(2): 363. CrossRef - Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: a large-scale multicenter study
Sun Hong Yoo, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Han-Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim, Do Seon Song, Seong Hee Kang, Moon Young Kim, Young-Hwan Ahn, Jieun Han, Young Seok Kim, Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, J
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 189. CrossRef - A Case of Transverse Myelitis Following Treatment with Atezolizumab for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Kyung Han Kim, Yang-Hyun Baek, Yeo Wool Kang, Byeol-A Yoon, Sang Yi Moon
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 82(1): 35. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter, Propensity Score Study
Ji Kim, Hee-Chul Nam, Chang-Wook Kim, Hee Cho, Jae-Sung Yoo, Ji Han, Jeong Jang, Jong Choi, Seung Yoon, Hyun Yang, Si Bae, Suho Kim, Jung Oh, Ho Chun, Chang Jeon, Jaegyoon Ahn, Pil Sung
Cancers.2023; 15(17): 4233. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Modeling the Risk of Liver Cancer in Adults: A Machine Learning Investigation into the Role of Obesity and Overweight
Bah Karamo, Bah Adama Ns , Jallow Amadou Wurry
Archives of Pathology and Clinical Research.2023; 7(1): 034. CrossRef - Surgical resection versus ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma: The debate is still open
Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 174. CrossRef - Cause of death and cause-specific mortality for primary liver cancer in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study in hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Bo Hyun Kim, Dahhay Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Joo Won, Hyunsoon Cho
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 242. CrossRef - Impact of tumor size on hepatectomy outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma: a nationwide propensity score matching analysis
Suk Kyun Hong, Kwang-Woong Lee, Sola Lee, Su young Hong, Sanggyun Suh, Eui Soo Han, YoungRok Choi, Nam-Joon Yi, Kyung-Suk Suh
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2022; 102(4): 193. CrossRef - Efficacy and feasibility of surgery and external radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal invasion: A meta-analysis
Han Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, In-Soo Shin, Won Sup Yoon, Hye Yoon Lee, Chai Hong Rim
International Journal of Surgery.2022; 104: 106753. CrossRef - Yoon et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(2): 207. CrossRef - Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: It is time to move forward
Bo Hyun Kim, Yuri Cho, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 810. CrossRef - Treatment patterns for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with Child–Pugh class B and their impact on survival: A Korean nationwide registry study
Dongsub Jeon, Gi‐Won Song, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim
Liver International.2022; 42(12): 2830. CrossRef - Metastatic breast cancer from a hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report
Hyewon Bang, Nam-Hee Kim, Seung Hye Choi, Si Hyun Bae, Eun Sun Jung, Ki Ouk Min, Yong Hwa Eom
Korean Journal of Clinical Oncology.2022; 18(2): 93. CrossRef - Current Status and Future Directions of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance Test Based on Cost-effective Analysis
Jihyun An
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 78(5): 255. CrossRef
- Concurrent nivolumab and external beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A phase II study

- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
- Young Eun Chon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Sik Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):135-147. Published online September 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.135
- 4,534 Views
- 158 Downloads
- 15 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
s: Considering the high prevalence and mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in Korea, accurate statistics for HCC are important. We evaluated the characteristics of Korean patients with newly diagnosed HCC.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated data from the Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry (KPLCR). The baseline characteristics, treatment modalities, and overall survival (OS) of 4,572 patients with HCC registered in the KPLCR between 2012 and 2014 were investigated.
Results
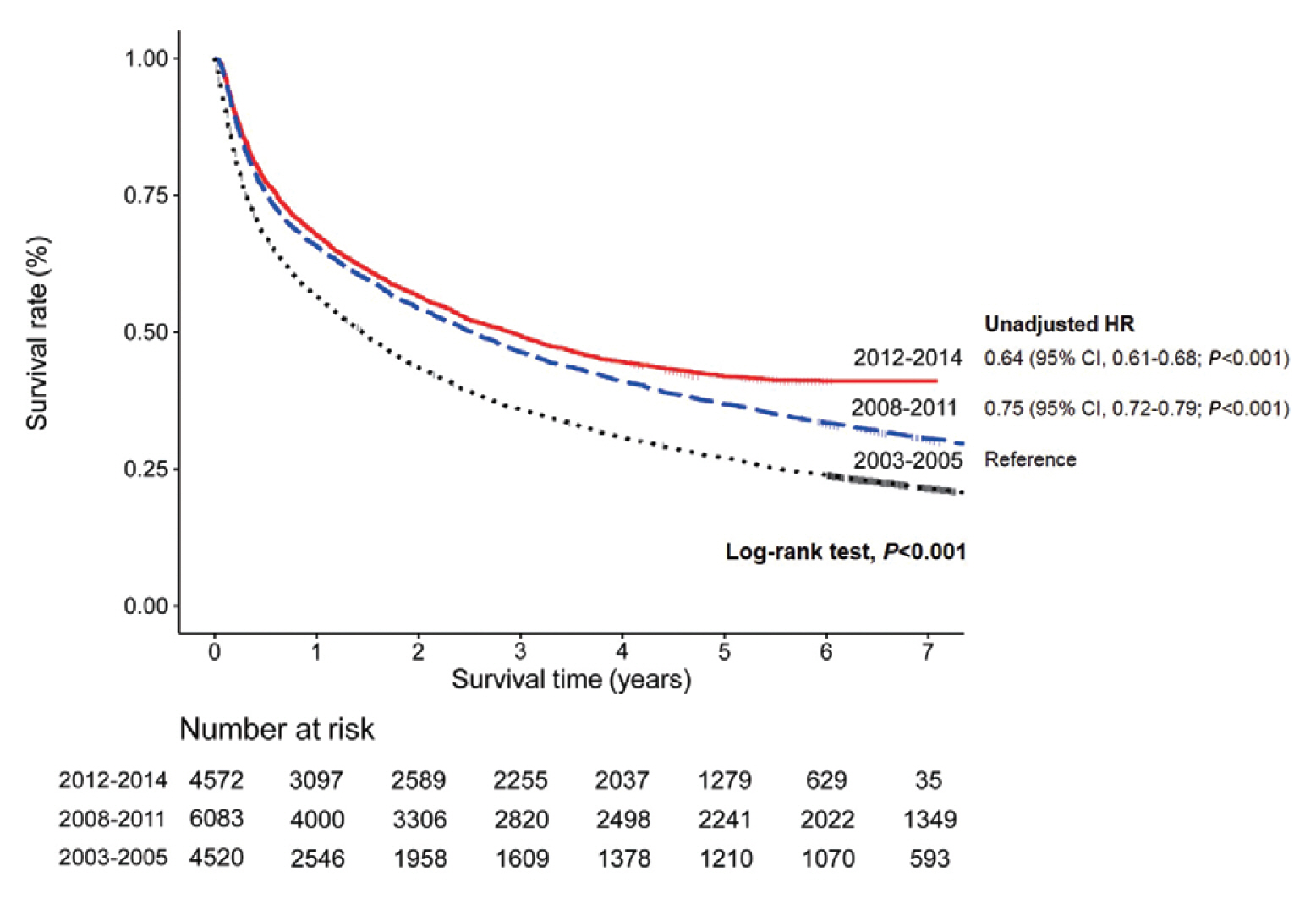
At the time of HCC diagnosis, the median age was 60.0 years, with male predominance (79.6%). Hepatitis B virus infection was the most common etiology (59.1%). The rates of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stages 0, A, B, C, and D at diagnosis were 3.9%, 36.9%, 12.5%, 39.4%, and 7.3%, respectively. The proportion of very early or early stage HCC at diagnosis (BCLC stage 0 or A) in the 2012-2014 cohort was significantly lower than that in the 2008-2011 cohort (40.8% vs. 48.3%, P<0.001). Transarterial therapy (37.5%) was the most commonly performed initial treatment, followed by surgical resection (19.8%), best supportive care (19.1%), and local ablation (10.6%). The median OS was 2.9 years, and the 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 67.7%, 49.3% and 41.9%, respectively. The OS rate of the 2012-2014 cohort was significantly higher than that of the 2008-2011 cohort (log-rank, P<0.001).
Conclusions
The OS of HCC patients registered in the KPLCR between 2012 and 2014 significantly improved. Nevertheless, as about half of the HCC patients were diagnosed at an advanced stage, vigorous and optimized HCC screening strategies should be implemented. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence is decreasing in Korea but increasing in the very elderly
Young Eun Chon, Seong Yong Park, Han Pyo Hong, Donghee Son, Jonghyun Lee, Eileen Yoon, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Bong Ahn, Soung Won Jeong, Dae Won Jun
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(1): 120. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Factors associated with the survival outcomes of patients with untreated hepatocellular carcinoma: An analysis of nationwide data
Min Jung Kwon, Soy Chang, Ji Hoon Kim, Ji Won Han, Jeong Won Jang, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Pil Soo Sung
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical practice guideline and real-life practice in hepatocellular carcinoma: A Korean perspective
Myung Ji Goh, Dong Hyun Sinn, Jong Man Kim, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ho Hyun, Jeong Il Yu, Jung Yong Hong, Moon Seok Choi
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(2): 197. CrossRef - Implications of the first edition of the Korean expert consensus-based practice recommendations for transarterial chemoembolization in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Jin Wook Chung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 235. CrossRef - Nomogram for predicting overall survival in patients with large (>5 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma based on real-world practice
Nalee Kim, Jeong Il Yu, Hee Chul Park, Jung Yong Hong, Ho Yeong Lim, Myung Ji Goh, Yong-Han Paik
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 350. CrossRef - Surgical resection versus ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma: The debate is still open
Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 174. CrossRef - A case report of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy and sorafenib combination therapy followed by metastasectomy of lung and muscle metastases
Sang Yi Moon, Sang Young Han, Yang-Hyun Baek
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 57. CrossRef - Cause of death and cause-specific mortality for primary liver cancer in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study in hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Bo Hyun Kim, Dahhay Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Joo Won, Hyunsoon Cho
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 242. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 583. CrossRef - Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: It is time to move forward
Bo Hyun Kim, Yuri Cho, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 810. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Korean Journal of Radiology.2022; 23(12): 1126. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Dong Ho Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Ju-Yeon Cho, Jonggi Choi, Young Chang, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 58. CrossRef - Cost-Effectiveness of Adjuvant Immunotherapy With Cytokine-Induced Killer Cell for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on a Randomized Controlled Trial and Real-World Data
Jeong-Yeon Cho, Sun-Hong Kwon, Eui-Kyung Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Hye-Lin Kim
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Refractory to Transarterial Chemoembolization and Vascular Variation: A Case Study
Sang Yi Moon, Sang Young Han, Yang-Hyun Baek
Kosin Medical Journal.2021; 36(2): 161. CrossRef
- Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence is decreasing in Korea but increasing in the very elderly

- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea Between 2008 and 2011: an Analysis of Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
- Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Young Eun Chon, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Young-Joo Won, Eunyang Kim, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):41-52. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.41

- 5,033 Views
- 193 Downloads
- 15 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Backgrounds/Aims
Backgrounds/Aims: In Korea, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cancer and results in the second-highest cancer death rate among all cancers. We aimed to describe the characteristics of patients who were newly diagnosed with HCC in Korea between 2008 and 2011.
Methods
The Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry (KPLCR) is a random sample consisting of approximately 15% of patients with newly diagnosed primary liver cancer registered in the Korean Central Cancer Registry. We investigated the baseline characteristics, treatment modalities, and overall survival (OS) of patients with HCC registered in the KPLCR between 2008 and 2011.
Results
A total of 6,083 patients were histologically or radiologically diagnosed with HCC. The hepatitis B virus was the predominant HCC etiology (72.0%). According to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system, stages 0, A, B, C, and D accounted for 8.6%, 39.7%, 11.5%, 33.8%, and 6.9%, respectively. Transarterial therapy (41.7%) was the most commonly performed initial treatment, followed by best supportive care (21.7%), surgical resection (16.7%), and local ablation therapies (10.6%). The overall rate of adherence to the BCLC treatment guideline was only 37.7%. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 65.6%, 46.2%, and 36.8%, respectively.
Conclusions
Between 2008 and 2011, approximately half of patients with HCC (48.3%) were candidates for curative treatment (BCLC stage 0 or A), but one-third of patients (33.8%) had advanced HCC (BCLC stage C). Transarterial therapy was the most commonly conducted initial treatment and the 5-year OS rate was 36.8% in this period. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adjuvant and neoadjuvant immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma
Josep M. Llovet, Roser Pinyol, Mark Yarchoan, Amit G. Singal, Thomas U. Marron, Myron Schwartz, Eli Pikarsky, Masatoshi Kudo, Richard S. Finn
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology.2024; 21(4): 294. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence is decreasing in Korea but increasing in the very elderly
Young Eun Chon, Seong Yong Park, Han Pyo Hong, Donghee Son, Jonghyun Lee, Eileen Yoon, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Bong Ahn, Soung Won Jeong, Dae Won Jun
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(1): 120. CrossRef - Implications of the first edition of the Korean expert consensus-based practice recommendations for transarterial chemoembolization in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Jin Wook Chung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 235. CrossRef - Surgical resection versus ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma: The debate is still open
Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 174. CrossRef - Cause of death and cause-specific mortality for primary liver cancer in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study in hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Bo Hyun Kim, Dahhay Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Joo Won, Hyunsoon Cho
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 242. CrossRef - Impact of expanding hepatitis B treatment guidelines: A modelling and economic impact analysis
Young‐Suk Lim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Jae‐Jun Shim, Homie Razavi, Devin Razavi‐Shearer, Dong Hyun Sinn
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2022; 56(3): 519. CrossRef - Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: It is time to move forward
Bo Hyun Kim, Yuri Cho, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 810. CrossRef - Therapeutic Decision Making in Hepatocellular Carcinoma According to Age and Child–Pugh Class: A Nationwide Cohort Analysis in South Korea
Sunmin Park, Chai Hong Rim, Young Kul Jung, Won Sup Yoon, Alessandro Granito
Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Outcome of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor and Molecular Target Agent Combination for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Beyond Sorafenib Era
Nae-Yun Heo
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 77(3): 145. CrossRef - Rare Case of Pyogenic Brain Abscess after Transarterial Chemoembolization in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Case Report and Literature Review
Jun-Ho Myeong, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 81. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Dong Ho Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Ju-Yeon Cho, Jonggi Choi, Young Chang, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 58. CrossRef - Glucose Variability and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Eun Ju Cho, Kyungdo Han, Soo Seong Heo, Bo-Yeon Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Su Jong Yu
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2021; 30(5): 974. CrossRef -
Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein improves diagnostic accuracy for hepatocellular carcinoma
Han Ah Lee, Yoo Ra Lee, Young-Sun Lee, Young Kul Jung, Ji Hoon Kim, Hyunggin An, Hyung Joon Yim, Yoon Tae Jeen, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun, Yeon Seok Seo
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(28): 4687. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Young Eun Chon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Sik Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(2): 135. CrossRef - Efficacy of Local Treatments for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Involving the Inferior Vena Cava and/or Right Atrium
Han Ah Lee, Chai Hong Rim
Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2020; Volume 7: 435. CrossRef
- Adjuvant and neoadjuvant immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma

- Discrepancy between the Actual Clinical Status of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Expectations from Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance: a Single-Center Study
- Nak Min Kim, Young Seok Doh, Ji Woong Jang, Seok-Hwan Kim, Hyuk Soo Eun, Jae Hyuck Jun, Sae Hee Kim, Il Hyun Baek, Sung Hee Jung
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(1):30-37. Published online March 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.1.30

- 4,436 Views
- 95 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: The National Liver Cancer Screening Program (NLCSP) has been implemented for the past 15 years in Korea. However, the actual clinical experience in Korea is inconsistent with the expectations of the hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) surveillance program. To evaluate the actual clinical situation of HCC diagnoses, we investigated disease severity in patients with HCC and the diagnostic environment.
Methods
From January 2011 to December 2015, all patients who were diagnosed with HCC in a single secondary hospital in Daejeon city were retrospectively enrolled in this study. Severity of HCC was evaluated according to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system.
Results
Over the course of 5 years, 298 participants were enrolled. The mean age of participants was 64.0 years. Positive hepatitis B surface antigen was confirmed in 134 patients (45.0%), 35 patients (11.7%) tested positive for anti-hepatitis C virus antibody, and 93 patients (32.2%) had more than 40 g/day of alcohol consumption. The proportions of patients according to BCLC stages were as follows: BCLC-0, 28 patients (9.4%); BCLC-A, 42 patients (14.1%); BCLC-B, 26 patients (8.7%); BCLC-C, 134 patients (45.0%); and BCLC-D, 68 patients (22.8%). The diagnostic environments were as follows: 19 patients were in the NLCSP group (6.4%), 114 in the group with presenting signs (38.3%), 110 in the regular outpatient care group (36.9%), and 55 patients in the incidental diagnosis group (18.5%).
Conclusions
Most patients (67.8%) had advanced stage HCC at diagnosis, and curative treatment was not indicated due to the severity disease. Thus, the actual situation is far worse than the theoretical expectation of HCC surveillance, suggesting that many high-risk patients for HCC are missed in surveillance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- NCA‐GA‐SVM: A new two‐level feature selection method based on neighborhood component analysis and genetic algorithm in hepatocellular carcinoma fatality prognosis
Wojciech Książek, Filip Turza, Paweł Pławiak
International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Imaging Modalities for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance: Expanding Horizons beyond Ultrasound
Hyo Jung Park, So Yeon Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(2): 99. CrossRef
- NCA‐GA‐SVM: A new two‐level feature selection method based on neighborhood component analysis and genetic algorithm in hepatocellular carcinoma fatality prognosis

- Epidemiologic Changes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A 10-year Single Center Experience in Gangneung, Korea
- Young Don Kim, Woo Sung Jang, Jang Hoon Kwon, Jong Sam Hong, Gab Jin Cheon
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2013;13(2):123-129. Published online September 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.13.2.123
- 978 Views
- 16 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is common cause of liver related death in Korea, and the importance of alcohol as an etiology of chronic liver disease including cirrhosis is emphasized recently. We investigated the epidemiologic changes of HCC during last 10 years in single tertiary center in Gangneung, Korea.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of admitted patients diagnosed as HCC in year 2002 and 2012 respectively, and their clinical characteristics were compared.
Results
A total of 214 patients were enrolled. Mean age was 60.1 years and 179 (83.6%) was male. Number of patient with cirrhosis was 160 (74.8%) and with viral hepatitis was 164 (74.8%). Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) was the most common cause of HCC patients with liver cirrhosis (61.9%), and alcohol was 14.4%. The possible curative group (by BCLC stage 0 or A) was only 36.4% (n=78), and had not decreased during the study periods (36.3 % vs. 36.6%, P=0.144), and other clinical variables also had no statistical differences.
Conclusions
The clinical characteristics of HCC including clinical stage at the time of diagnosis were not changed over the last 10 year period, and CHB was still the most common etiology of HCC in Gangneung, Korea.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter