Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Outcomes of Liver Resection and Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Multinodular BCLC-A Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jiwon Yang, Won-Mook Choi, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Deok-Bog Moon, Dong-Hwan Jung, Jonggi Choi
- Received March 3, 2024 Accepted March 25, 2024 Published online April 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.25 [Accepted]
- 323 Views
- 27 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to compare the outcomes of liver resection (LR) and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with multinodular hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) within the Milan criteria who were not eligible for liver transplantation.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 483 patients with multinodular HCC within the Milan criteria, who underwent either LR or TACE as an initial therapy between 2013 and 2022. The overall survival (OS) in the entire population and recurrence-free survival (RFS) in patients who underwent LR and TACE and achieved a complete response were analyzed. Propensity score (PS) matching analysis was also used for a fair comparison of outcomes between the two groups.
Results
Among the 483 patients, 107 (22.2%) and 376 (77.8%) underwent LR and TACE, respectively. The median size of the largest tumor was 2.0 cm, and 72.3% of the patients had two HCC lesions. The median OS and RFS were significantly longer in the LR group than in the TACE group (p <0.01 for both). In the multivariate analysis, TACE (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.81 and aHR, 2.41) and large tumor size (aHR, 1.43 and aHR, 1.44) were significantly associated with worse OS and RFS, respectively. The PS-matched analysis also demonstrated that the LR group had significantly longer OS and RFS than the TACE group (PS <0.05).
Conclusion
In this study, LR showed better OS and RFS than TACE in patients with multinodular Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A HCC. Therefore, LR can be considered an effective treatment option for these patients.

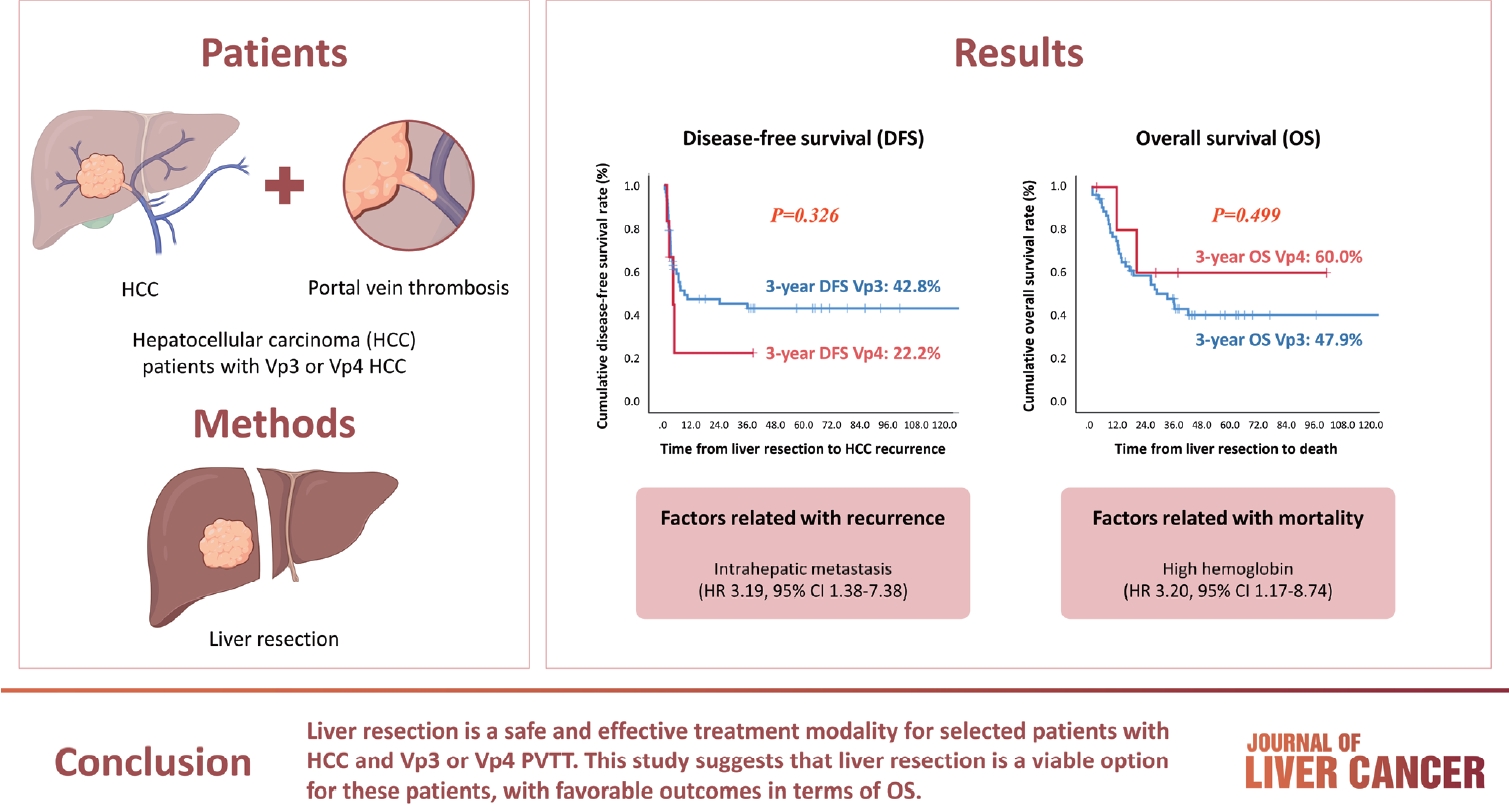
- Liver resection in selective hepatocellular carcinoma with Vp3 or Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis improves prognosis
- Manuel Lim, Jongman Kim, Jinsoo Rhu, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):102-112. Published online February 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.01.31
- 399 Views
- 38 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumor thrombi located in the first branch of the portal vein (Vp3) or in the main portal trunk (Vp4) are associated with poor prognosis. This study aimed to investigate the clinicopathological characteristics and risk factors for HCC recurrence and mortality following liver resection (LR) in patients with Vp3 or Vp4 HCC.
Methods
The study included 64 patients who underwent LR for HCC with Vp3 or Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT).
Results
Fifty-eight patients (90.6%) had Vp3 PVTT, whereas the remaining six patients exhibited Vp4 PVTT. The median tumor size measured 8 cm, with approximately 36% of patients presented with multiple tumors. Fifty-four patients (84.4%) underwent open LR, whereas 10 patients underwent laparoscopic LR. In the Vp4 cases, combined LR and tumor thrombectomy were performed. The 3-year cumulative disease-free survival rate was 42.8% for the Vp3 group and 22.2% for the Vp4 group. The overall survival (OS) rate at 3 years was 47.9% for the Vp3 group and 60.0% for the Vp4 group. Intrahepatic metastasis has been identified as an important contributor to HCC recurrence. High hemoglobin levels are associated with high mortality.
Conclusion
LR is a safe and effective treatment modality for selected patients with Vp3 or Vp4 HCC PVTT. This suggests that LR is a viable option for these patients, with favorable outcomes in terms of OS.

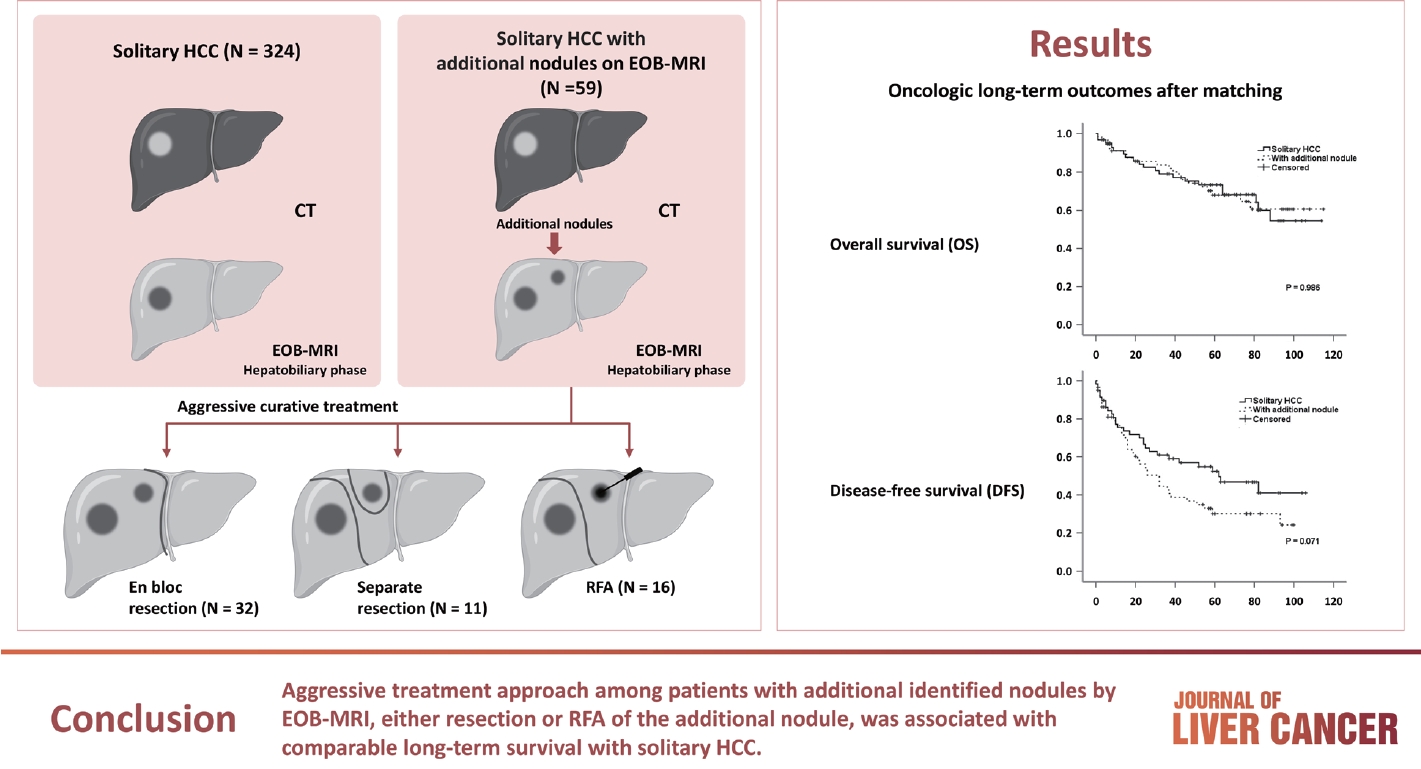
- Additional nodules detected using EOB-MRI in patients with resectable single hepatocellular carcinoma: an implication for active treatment strategy
- Na Reum Kim, Seoung Yoon Rho, Jonathan Navarro, Chansik An, Dai Hoon Han, Jin Sub Choi, Myeong-Jin Kim, Gi Hong Choi
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):92-101. Published online February 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.01.25
- 701 Views
- 41 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
Gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (EOBMRI) further enhances the identification of additional hepatic nodules compared with computed tomography (CT) alone; however, the optimal treatment for such additional nodules remains unclear. We investigated the long-term oncological effect of aggressive treatment strategies for additional lesions identified using EOB-MRI in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
Data from 522 patients diagnosed with solitary HCC using CT between January 2008 and December 2012 were retrospectively reviewed. Propensity score-matched (PSM) analysis was used to compare the oncologic outcomes between patients with solitary HCC and those with additional nodules on EOB-MRI after aggressive treatment (resection or radiofrequency ablation [RFA]).
Results
Among the 383 patients included, 59 had additional nodules identified using EOB-MRI. Compared with patients with solitary HCC, those with additional nodules on EOB-MRI had elevated total bilirubin, aspartate transaminase, and alanine transaminase; had a lower platelet count, higher MELD score, and highly associated with liver cirrhosis (P<0.05). Regarding long-term outcomes, 59 patients with solitary HCC and those with additional nodules after PSM were compared. Disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) were comparable between the two groups (DFS, 60.4 vs. 44.3 months, P=0.071; OS, 82.8 vs. 84.8 months, P=0.986).
Conclusion
The aggressive treatment approach, either resection or RFA, for patients with additional nodules identified on EOBMRI was associated with long-term survival comparable with that for solitary HCC. However, further studies are required to confirm these findings.

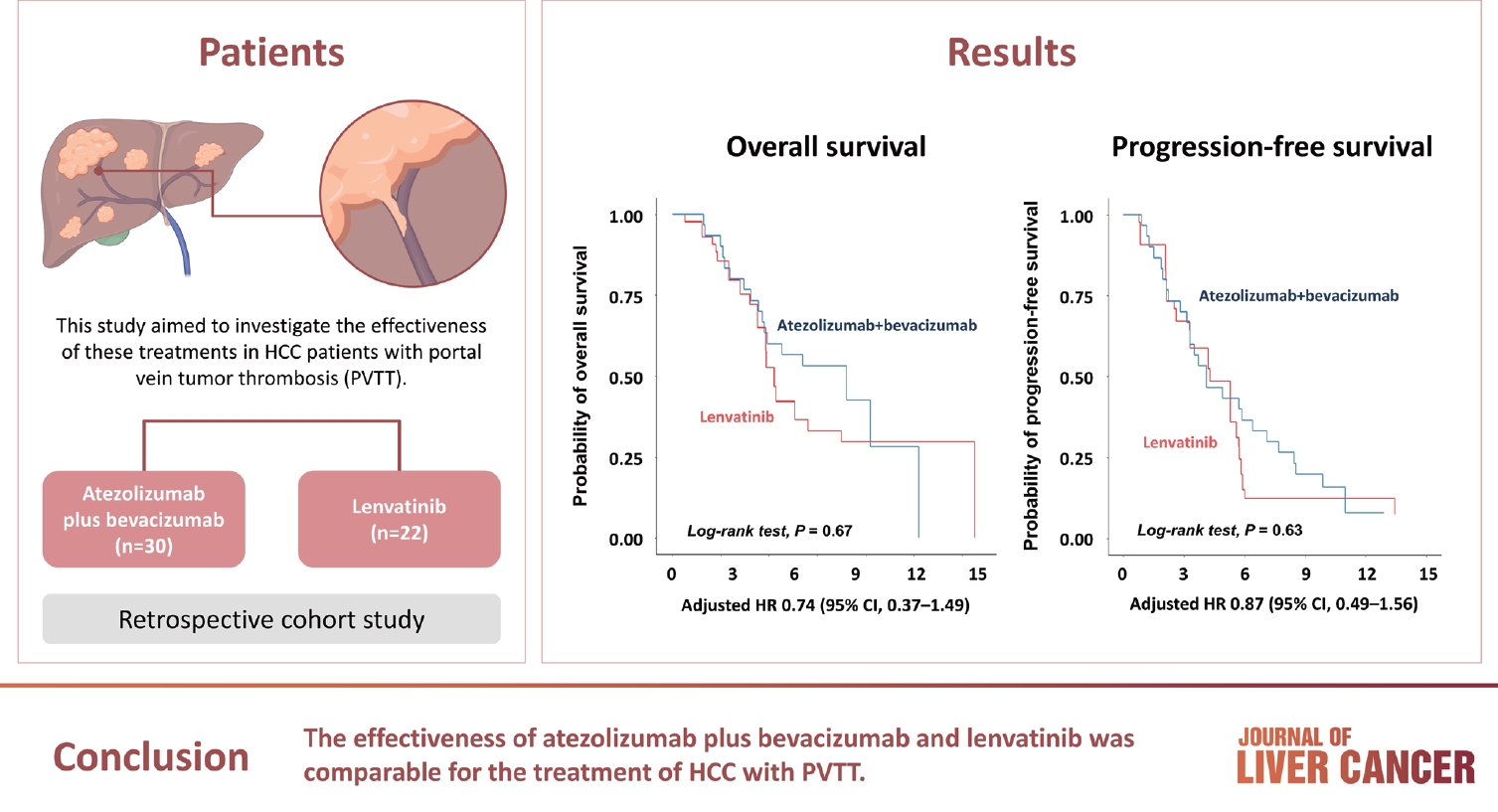
- Comparison of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
- Jeayeon Park, Yun Bin Lee, Yunmi Ko, Youngsu Park, Hyunjae Shin, Moon Haeng Hur, Min Kyung Park, Dae-Won Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Kyung-Hun Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Su Jong Yu, Tae-Yong Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Tae-You Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):81-91. Published online January 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.12.25
- 967 Views
- 132 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib are currently available as first-line therapy for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, comparative efficacy studies are still limited. This study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of these treatments in HCC patients with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT).
Methods
We retrospectively included patients who received either atezolizumab plus bevacizumab or lenvatinib as first-line systemic therapy for HCC with PVTT. Primary endpoint was overall survival (OS), and secondary endpoints included progressionfree survival (PFS) and disease control rate (DCR) determined by response evaluation criteria in solid tumors, version 1.1.
Results
A total of 52 patients were included: 30 received atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and 22 received lenvatinib. The median follow-up duration was 6.4 months (interquartile range, 3.9-9.8). The median OS was 10.8 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 5.7 to not estimated) with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and 5.8 months (95% CI, 4.8 to not estimated) with lenvatinib (P=0.26 by log-rank test). There was no statistically significant difference in OS (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.71; 95% CI, 0.34-1.49; P=0.37). The median PFS was similar (P=0.63 by log-rank test), with 4.1 months (95% CI, 3.3-7.7) for atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and 4.3 months (95% CI, 2.6-5.8) for lenvatinib (aHR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.51-1.69; P=0.80). HRs were similar after inverse probability treatment weighting. The DCRs were 23.3% and 18.2% in patients receiving atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib, respectively (P=0.74).
Conclusion
The effectiveness of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib was comparable for the treatment of HCC with PVTT.

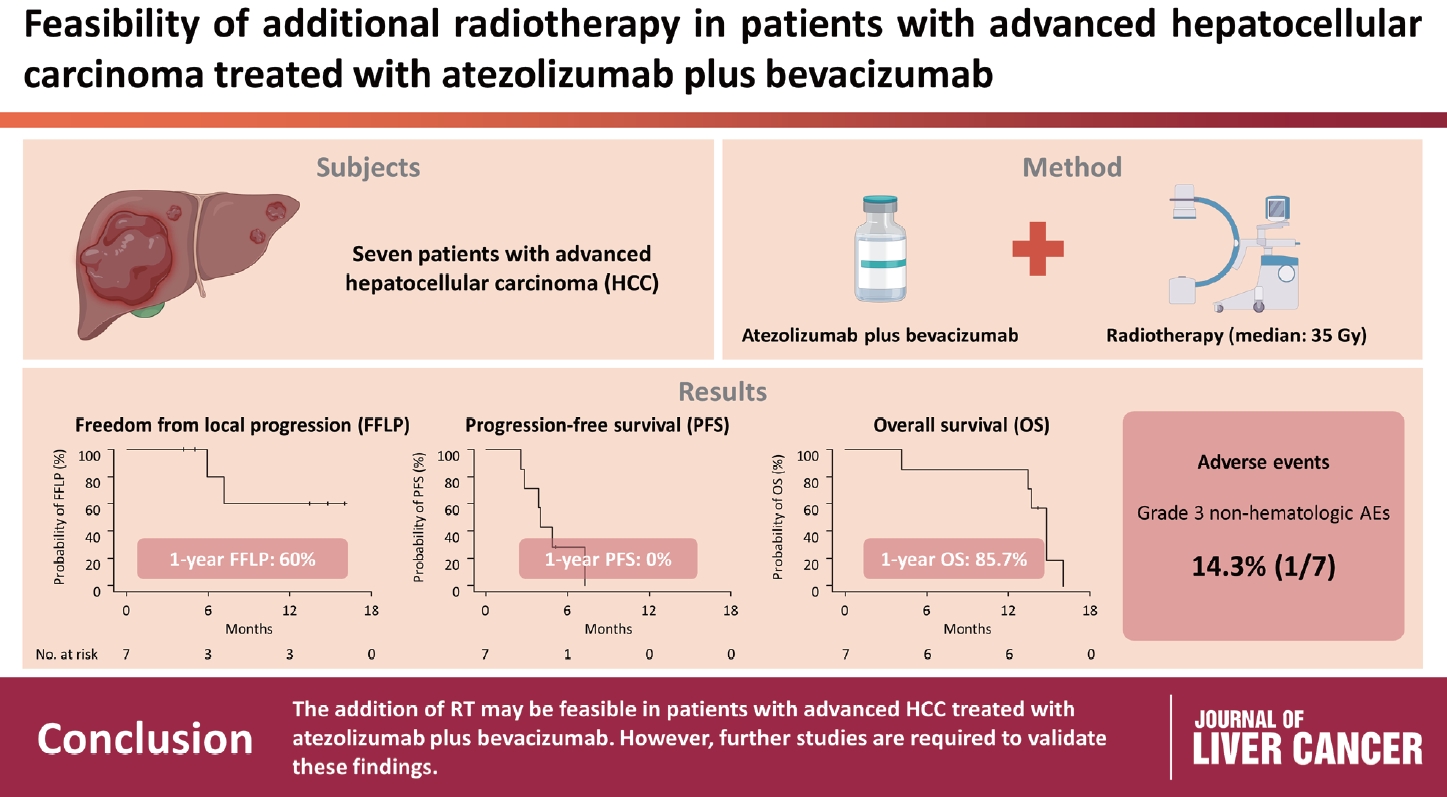
- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
- Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):330-340. Published online May 16, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.04.14
- 1,748 Views
- 112 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
Radiotherapy (RT) is an effective local treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, whether additional RT is safe and effective in patients with advanced HCC receiving atezolizumab plus bevacizumab remains unclear. This retrospective cohort study aimed to evaluate the feasibility of additional RT in these patients.
Methods
Between March and October 2021, we retrospectively analyzed seven patients with advanced HCC who received RT during treatment with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab. The median prescribed RT dose was 35 Gy (range, 33–66). Freedom from local progression (FFLP), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) after RT were analyzed.
Results
The median follow-up duration after RT was 14.2 months (range, 10.0–18.6). Of the seven patients, disease progression was noted in six (85.7%), the sites of disease progression were local in two (28.6%), intrahepatic in four (57.1%), and extrahepatic in four (57.1%). The median time of FFLP was not reached, and PFS and OS times were 4.0 (95% confidence interval [CI], 3.6–4.5) and 14.8% (95% CI, 12.5–17.2) months, respectively. The 1-year FFLP, PFS, and OS rates were 60% (95% CI, 43.8–76.2), 0%, and 85.7% (95% CI, 75.9–95.5), respectively. Grade 3 or higher hematologic adverse events (AEs) were not observed, but grade 3 nonhematologic AEs unrelated to RT were observed in one patient.
Conclusions
The addition of RT may be feasible in patients with advanced HCC treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab. However, further studies are required to validate these findings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Letter regarding “Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab”
Sun Hyun Bae, Hee Chul Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 402. CrossRef
- Letter regarding “Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab”

- Clinical characteristics and prognosis of Korean patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with respect to etiology
- Wonjoon Jang, Hye Won Lee, Jae Seung Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):158-166. Published online September 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.09.18
- 2,738 Views
- 65 Downloads
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
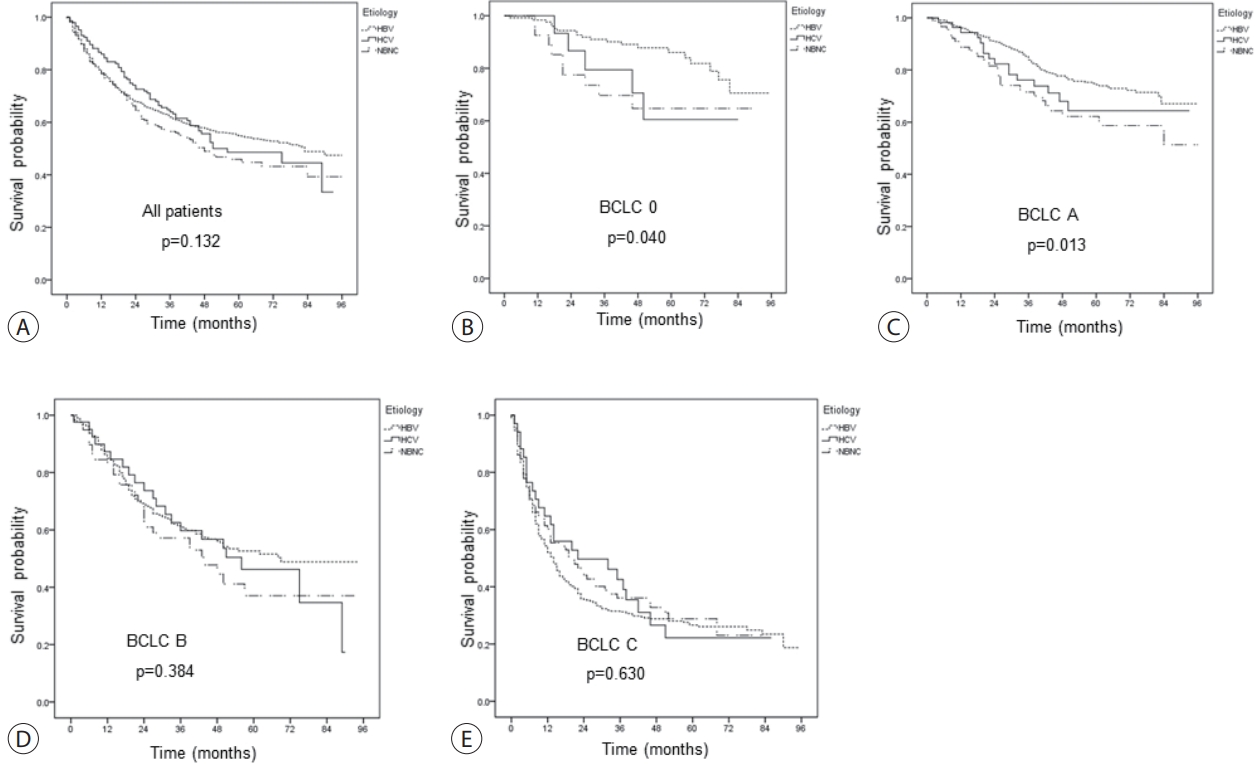
The profile of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has changed globally; the role of etiology in predicting prognosis of HCC patients remains unclear. We aimed to analyze the characteristics and prognosis of Korean patients with HCC according to disease etiology.
Methods
This retrospective observational study included patients diagnosed with HCC between 2010 and 2014 in a single center in Korea. Patients with HCC aged <19 years old, had coinfection with other viral hepatitis, had missing follow-up data, were Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage D, or died before 1 month were excluded.
Results
A total of 1,595 patients with HCC were analyzed; they were classified into the hepatitis B virus (HBV) group (1,183 [74.2%]), hepatitis C virus (HCV) group (146 [9.2%]), and non-B non-C (NBNC) group (266 [16.7%]). The median overall survival of all patients was 74 months. The survival rates at 1, 3, and 5 years were 78.8%, 62.0% and 54.9% in the HBV group; 86.0%, 64.0%, and 48.6% in the HCV group; and 78.4%, 56.5%, and 45.9% in the NBNC group, respectively. NBNC-HCC has a poorer prognosis than other causes of HCC. Survival was significantly longer in the HBV group with early-stage HCC than in the NBNC group. Furthermore, survival was shorter in patients with early-stage HCC and diabetes mellitus (DM) than in those without DM.
Conclusions
The etiology of HCC affected clinical characteristics and prognosis to some extent. NBNC-HCC patients showed shorter overall survival than viral-related HCC patients. Additionally, the presence of DM is an additional important prognostic factor in patients with early-stage HCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis
Log Young Kim, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Young Chang, Hoongil Jo, Young Youn Cho, Sangheun Lee, Dong Hyeon Lee, Jae Young Jang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef - Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis Followed by Acute Hepatitis A Infection: Case Report
Min-Woo An, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jin Kuk Kim, Ahrim Moon, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Medicina.2023; 59(5): 819. CrossRef - Validation of MELD 3.0 scoring system in East Asian patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jong-In Chang, Ji Eun Moon, Dong Hyun Sinn, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Liver Transplantation.2023; 29(10): 1029. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Statin use and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with chronic hepatitis B: an emulated target trial using longitudinal nationwide population cohort data
Dong Hyun Sinn, Danbee Kang, Yewan Park, Hyunsoo Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Juhee Cho, Geum-Youn Gwak
BMC Gastroenterology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Addition of Kidney Dysfunction Type to MELD-Na for the Prediction of Survival in Cirrhotic Patients Awaiting Liver Transplantation in Comparison with MELD 3.0 with Albumin
Kyeong-Min Yeom, Jong-In Chang, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Ji Eun Moon, Dong Hyun Sinn, Young Seok Kim, Sang Gyune Kim
Diagnostics.2023; 14(1): 39. CrossRef
- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis

- Stereotactic body radiation therapy for elderly patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective observational study
- Jeong Yun Jang, Jinhong Jung, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Jin-hong Park, Sang Min Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):136-145. Published online September 16, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.08.18
- 2,942 Views
- 73 Downloads
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
We aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in elderly patients with small hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC).
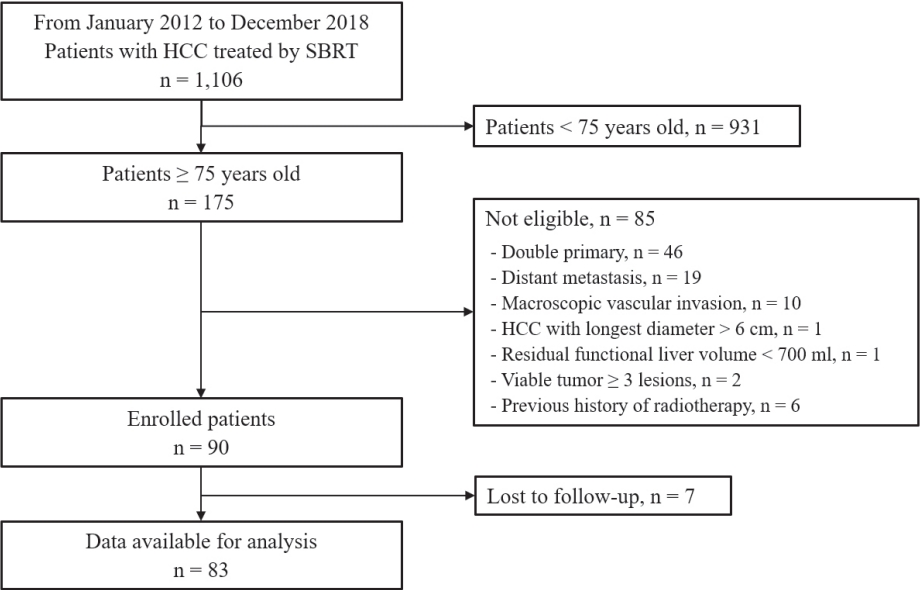
Methods
Eighty-three patients (89 lesions) with HCC who underwent SBRT between January 2012 and December 2018 were reviewed in this retrospective observational study. The key inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) age ≥75 years, 2) contraindications for hepatic resection or percutaneous ablative therapies, 3) no macroscopic vascular invasion, and 4) no extrahepatic metastasis.
Results
The patients were 75-90 years of age, and 49 (59.0%) of them were male. Most patients (94.0%) had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 or 1. Seventy-four patients (89.2%) had Child-Pugh class A hepatic function before SBRT. The median tumor size was 1.6 cm (range, 0.7-3.5). The overall median follow-up period was 34.8 months (range, 7.3-99.3). The 5-year local tumor control rate was 90.1%. The 3-year and 5-year overall survival rate was 57.1% and 40.7%, respectively. Acute toxicity grade ≥3 was observed in three patients (3.6%) with elevated serum hepatic enzymes; however, no patient experienced a worsening of the Child-Pugh score to ≥2 after SBRT. None of the patients developed late toxicity (grade ≥3).
Conclusions
SBRT is a safe treatment option with a high local control rate in elderly patients with small HCC who are not eligible for other curative treatments. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sujin Koo, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Seungeun Ryoo, Jungeun Park, Dong Ah Park
Current Oncology.2024; 31(1): 324. CrossRef - Radiotherapy trend in elderly hepatocellular carcinoma: retrospective analysis of patients diagnosed between 2005 and 2017
Bong Kyung Bae, Jeong Il Yu, Hee Chul Park, Myung Ji Goh, Yong-Han Paik
Radiation Oncology Journal.2023; 41(2): 98. CrossRef - Loco-regional therapies competing with radiofrequency ablation in potential indications for hepatocellular carcinoma: a network meta-analysis
Ha Il Kim, Jihyun An, Seungbong Han, Ju Hyun Shim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 1013. CrossRef - Has the growing evidence of radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma increased the use of radiotherapy in elderly patients?
Tae Hyun Kim
Radiation Oncology Journal.2023; 41(3): 141. CrossRef - Chronic Liver Disease in the Older Patient—Evaluation and Management
Daniel Anthony DiLeo, Tolga Gidener, Ayse Aytaman
Current Gastroenterology Reports.2023; 25(12): 390. CrossRef
- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
- Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Dong Ho Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Ju-Yeon Cho, Jonggi Choi, Young Chang, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):58-68. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.58
- 6,563 Views
- 265 Downloads
- 18 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
s: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related death in Korea. This study evaluated the characteristics of Korean patients newly diagnosed with HCC in 2015.
Methods
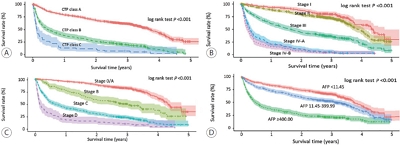
Data from the Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry (KPLCR), a representative sample of patients newly diagnosed with HCC in Korea, were analyzed. A total of 1,558 patients with HCC registered in the KPLCR in 2015 were investigated.
Results
The median age was 61.0 years (interquartile range, 54.0-70.0 years), and men accounted for 79.7% of the subjects. Hepatitis B virus infection was the most common underlying liver disease (58.1%). According to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system, stage 0, A, B, C, and D HCCs accounted for 14.2%, 31.5%, 7.6%, 39.0%, and 7.8% of patients, respectively. Transarterial therapy (32.1%) was the most commonly performed initial treatment, followed by surgical resection (23.2%), best supportive care (20.2%), and local ablation therapy (10.7%). Overall, 34.5% of patients were treated in accordance with the BCLC guidelines: 59.2% in stage 0/A, 48.4% in stage B, 18.1% in stage C, and 71.6% in stage D. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 67.1%, 50.9%, and 27.0%, respectively.
Conclusions
In 2015, approximately 45% of Korean HCC cases were diagnosed at a very early or early stage, and 35% of patients underwent potentially curative initial treatment. BCLC guidance was followed in 34.5% of patients; in patients with stage B or C disease, there was relatively low adherence. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concurrent nivolumab and external beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A phase II study
Bo Hyun Kim, Hee Chul Park, Tae Hyun Kim, Young-Hwan Koh, Jung Yong Hong, Yuri Cho, Dong Hyun Sinn, Boram Park, Joong-Won Park
JHEP Reports.2024; 6(4): 100991. CrossRef - Identification of patients with favorable prognosis after resection in intermediate-stage-hepatocellular carcinoma
Han Ah Lee, Minjong Lee, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Ho Soo Chun, Yewan Park, Hwi Young Kim, Tae Hun Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Dong Hyun Sinn
International Journal of Surgery.2024; 110(2): 1008. CrossRef - Factors associated with the survival outcomes of patients with untreated hepatocellular carcinoma: An analysis of nationwide data
Min Jung Kwon, Soy Chang, Ji Hoon Kim, Ji Won Han, Jeong Won Jang, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Pil Soo Sung
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The imitator of immune-tolerant chronic hepatitis B: A killer in disguise
Moon Haeng Hur, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(2): 363. CrossRef - Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: a large-scale multicenter study
Sun Hong Yoo, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Han-Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim, Do Seon Song, Seong Hee Kang, Moon Young Kim, Young-Hwan Ahn, Jieun Han, Young Seok Kim, Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, J
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 189. CrossRef - A Case of Transverse Myelitis Following Treatment with Atezolizumab for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Kyung Han Kim, Yang-Hyun Baek, Yeo Wool Kang, Byeol-A Yoon, Sang Yi Moon
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 82(1): 35. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter, Propensity Score Study
Ji Kim, Hee-Chul Nam, Chang-Wook Kim, Hee Cho, Jae-Sung Yoo, Ji Han, Jeong Jang, Jong Choi, Seung Yoon, Hyun Yang, Si Bae, Suho Kim, Jung Oh, Ho Chun, Chang Jeon, Jaegyoon Ahn, Pil Sung
Cancers.2023; 15(17): 4233. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Modeling the Risk of Liver Cancer in Adults: A Machine Learning Investigation into the Role of Obesity and Overweight
Bah Karamo, Bah Adama Ns , Jallow Amadou Wurry
Archives of Pathology and Clinical Research.2023; 7(1): 034. CrossRef - Surgical resection versus ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma: The debate is still open
Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 174. CrossRef - Cause of death and cause-specific mortality for primary liver cancer in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study in hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Bo Hyun Kim, Dahhay Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Joo Won, Hyunsoon Cho
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 242. CrossRef - Impact of tumor size on hepatectomy outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma: a nationwide propensity score matching analysis
Suk Kyun Hong, Kwang-Woong Lee, Sola Lee, Su young Hong, Sanggyun Suh, Eui Soo Han, YoungRok Choi, Nam-Joon Yi, Kyung-Suk Suh
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2022; 102(4): 193. CrossRef - Efficacy and feasibility of surgery and external radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal invasion: A meta-analysis
Han Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, In-Soo Shin, Won Sup Yoon, Hye Yoon Lee, Chai Hong Rim
International Journal of Surgery.2022; 104: 106753. CrossRef - Yoon et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(2): 207. CrossRef - Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: It is time to move forward
Bo Hyun Kim, Yuri Cho, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 810. CrossRef - Treatment patterns for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with Child–Pugh class B and their impact on survival: A Korean nationwide registry study
Dongsub Jeon, Gi‐Won Song, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim
Liver International.2022; 42(12): 2830. CrossRef - Metastatic breast cancer from a hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report
Hyewon Bang, Nam-Hee Kim, Seung Hye Choi, Si Hyun Bae, Eun Sun Jung, Ki Ouk Min, Yong Hwa Eom
Korean Journal of Clinical Oncology.2022; 18(2): 93. CrossRef - Current Status and Future Directions of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance Test Based on Cost-effective Analysis
Jihyun An
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 78(5): 255. CrossRef
- Concurrent nivolumab and external beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A phase II study

- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
- Young Eun Chon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Sik Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):135-147. Published online September 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.135
- 4,517 Views
- 158 Downloads
- 15 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
s: Considering the high prevalence and mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in Korea, accurate statistics for HCC are important. We evaluated the characteristics of Korean patients with newly diagnosed HCC.
Methods
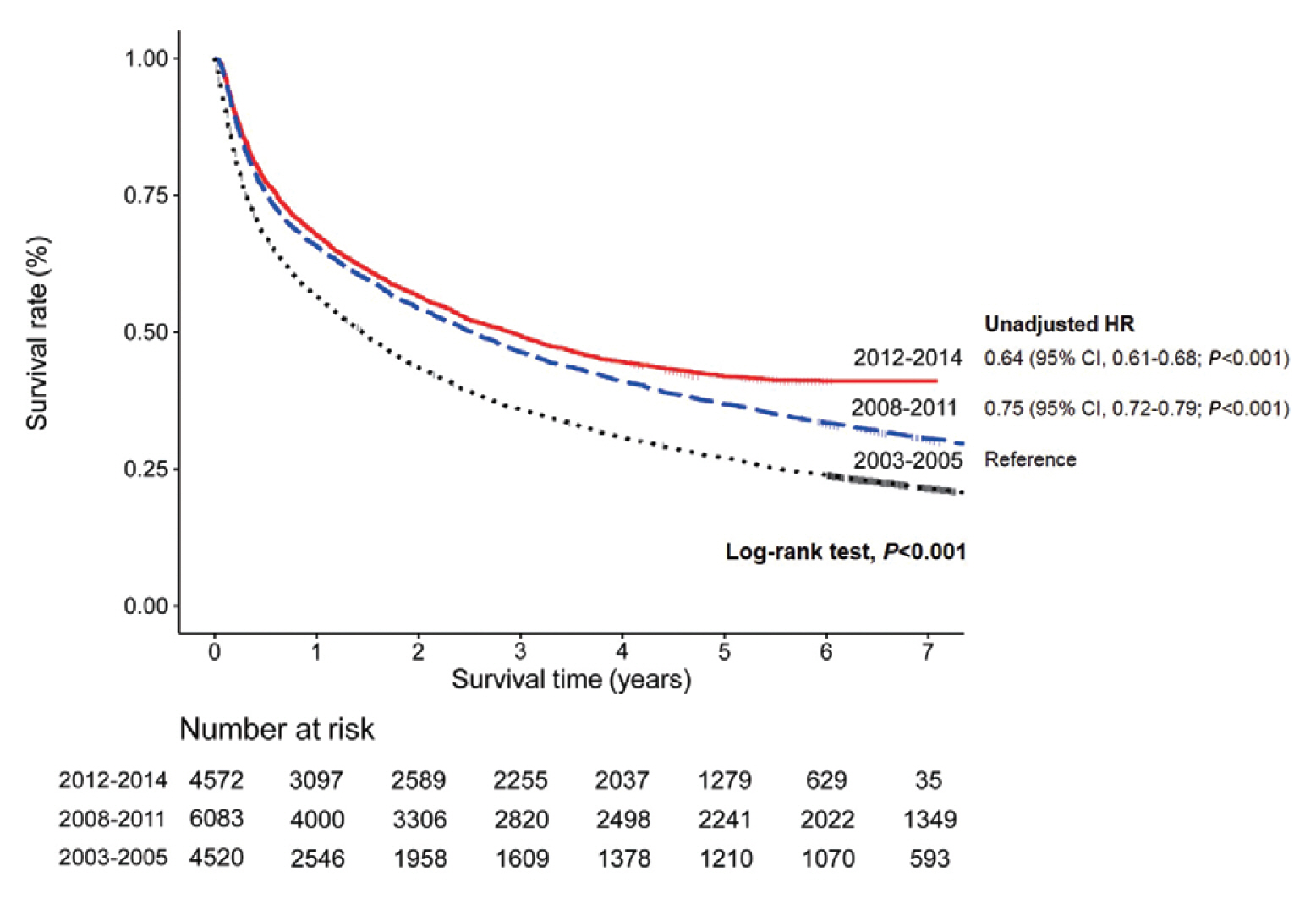
We retrospectively evaluated data from the Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry (KPLCR). The baseline characteristics, treatment modalities, and overall survival (OS) of 4,572 patients with HCC registered in the KPLCR between 2012 and 2014 were investigated.
Results
At the time of HCC diagnosis, the median age was 60.0 years, with male predominance (79.6%). Hepatitis B virus infection was the most common etiology (59.1%). The rates of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stages 0, A, B, C, and D at diagnosis were 3.9%, 36.9%, 12.5%, 39.4%, and 7.3%, respectively. The proportion of very early or early stage HCC at diagnosis (BCLC stage 0 or A) in the 2012-2014 cohort was significantly lower than that in the 2008-2011 cohort (40.8% vs. 48.3%, P<0.001). Transarterial therapy (37.5%) was the most commonly performed initial treatment, followed by surgical resection (19.8%), best supportive care (19.1%), and local ablation (10.6%). The median OS was 2.9 years, and the 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 67.7%, 49.3% and 41.9%, respectively. The OS rate of the 2012-2014 cohort was significantly higher than that of the 2008-2011 cohort (log-rank, P<0.001).
Conclusions
The OS of HCC patients registered in the KPLCR between 2012 and 2014 significantly improved. Nevertheless, as about half of the HCC patients were diagnosed at an advanced stage, vigorous and optimized HCC screening strategies should be implemented. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence is decreasing in Korea but increasing in the very elderly
Young Eun Chon, Seong Yong Park, Han Pyo Hong, Donghee Son, Jonghyun Lee, Eileen Yoon, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Bong Ahn, Soung Won Jeong, Dae Won Jun
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(1): 120. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Factors associated with the survival outcomes of patients with untreated hepatocellular carcinoma: An analysis of nationwide data
Min Jung Kwon, Soy Chang, Ji Hoon Kim, Ji Won Han, Jeong Won Jang, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Pil Soo Sung
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical practice guideline and real-life practice in hepatocellular carcinoma: A Korean perspective
Myung Ji Goh, Dong Hyun Sinn, Jong Man Kim, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ho Hyun, Jeong Il Yu, Jung Yong Hong, Moon Seok Choi
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(2): 197. CrossRef - Implications of the first edition of the Korean expert consensus-based practice recommendations for transarterial chemoembolization in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Jin Wook Chung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 235. CrossRef - Nomogram for predicting overall survival in patients with large (>5 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma based on real-world practice
Nalee Kim, Jeong Il Yu, Hee Chul Park, Jung Yong Hong, Ho Yeong Lim, Myung Ji Goh, Yong-Han Paik
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 350. CrossRef - Surgical resection versus ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma: The debate is still open
Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 174. CrossRef - A case report of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy and sorafenib combination therapy followed by metastasectomy of lung and muscle metastases
Sang Yi Moon, Sang Young Han, Yang-Hyun Baek
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 57. CrossRef - Cause of death and cause-specific mortality for primary liver cancer in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study in hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Bo Hyun Kim, Dahhay Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Joo Won, Hyunsoon Cho
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 242. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 583. CrossRef - Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: It is time to move forward
Bo Hyun Kim, Yuri Cho, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 810. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Korean Journal of Radiology.2022; 23(12): 1126. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Dong Ho Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Ju-Yeon Cho, Jonggi Choi, Young Chang, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 58. CrossRef - Cost-Effectiveness of Adjuvant Immunotherapy With Cytokine-Induced Killer Cell for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on a Randomized Controlled Trial and Real-World Data
Jeong-Yeon Cho, Sun-Hong Kwon, Eui-Kyung Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Hye-Lin Kim
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Refractory to Transarterial Chemoembolization and Vascular Variation: A Case Study
Sang Yi Moon, Sang Young Han, Yang-Hyun Baek
Kosin Medical Journal.2021; 36(2): 161. CrossRef
- Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence is decreasing in Korea but increasing in the very elderly

- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea Between 2008 and 2011: an Analysis of Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
- Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Young Eun Chon, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Young-Joo Won, Eunyang Kim, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):41-52. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.41

- 5,017 Views
- 193 Downloads
- 15 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Backgrounds/Aims
Backgrounds/Aims: In Korea, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cancer and results in the second-highest cancer death rate among all cancers. We aimed to describe the characteristics of patients who were newly diagnosed with HCC in Korea between 2008 and 2011.
Methods
The Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry (KPLCR) is a random sample consisting of approximately 15% of patients with newly diagnosed primary liver cancer registered in the Korean Central Cancer Registry. We investigated the baseline characteristics, treatment modalities, and overall survival (OS) of patients with HCC registered in the KPLCR between 2008 and 2011.
Results
A total of 6,083 patients were histologically or radiologically diagnosed with HCC. The hepatitis B virus was the predominant HCC etiology (72.0%). According to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system, stages 0, A, B, C, and D accounted for 8.6%, 39.7%, 11.5%, 33.8%, and 6.9%, respectively. Transarterial therapy (41.7%) was the most commonly performed initial treatment, followed by best supportive care (21.7%), surgical resection (16.7%), and local ablation therapies (10.6%). The overall rate of adherence to the BCLC treatment guideline was only 37.7%. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 65.6%, 46.2%, and 36.8%, respectively.
Conclusions
Between 2008 and 2011, approximately half of patients with HCC (48.3%) were candidates for curative treatment (BCLC stage 0 or A), but one-third of patients (33.8%) had advanced HCC (BCLC stage C). Transarterial therapy was the most commonly conducted initial treatment and the 5-year OS rate was 36.8% in this period. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adjuvant and neoadjuvant immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma
Josep M. Llovet, Roser Pinyol, Mark Yarchoan, Amit G. Singal, Thomas U. Marron, Myron Schwartz, Eli Pikarsky, Masatoshi Kudo, Richard S. Finn
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology.2024; 21(4): 294. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence is decreasing in Korea but increasing in the very elderly
Young Eun Chon, Seong Yong Park, Han Pyo Hong, Donghee Son, Jonghyun Lee, Eileen Yoon, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Bong Ahn, Soung Won Jeong, Dae Won Jun
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(1): 120. CrossRef - Implications of the first edition of the Korean expert consensus-based practice recommendations for transarterial chemoembolization in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Jin Wook Chung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 235. CrossRef - Surgical resection versus ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma: The debate is still open
Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 174. CrossRef - Cause of death and cause-specific mortality for primary liver cancer in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study in hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Bo Hyun Kim, Dahhay Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Joo Won, Hyunsoon Cho
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 242. CrossRef - Impact of expanding hepatitis B treatment guidelines: A modelling and economic impact analysis
Young‐Suk Lim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Jae‐Jun Shim, Homie Razavi, Devin Razavi‐Shearer, Dong Hyun Sinn
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2022; 56(3): 519. CrossRef - Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: It is time to move forward
Bo Hyun Kim, Yuri Cho, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 810. CrossRef - Therapeutic Decision Making in Hepatocellular Carcinoma According to Age and Child–Pugh Class: A Nationwide Cohort Analysis in South Korea
Sunmin Park, Chai Hong Rim, Young Kul Jung, Won Sup Yoon, Alessandro Granito
Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Outcome of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor and Molecular Target Agent Combination for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Beyond Sorafenib Era
Nae-Yun Heo
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 77(3): 145. CrossRef - Rare Case of Pyogenic Brain Abscess after Transarterial Chemoembolization in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Case Report and Literature Review
Jun-Ho Myeong, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 81. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Dong Ho Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Ju-Yeon Cho, Jonggi Choi, Young Chang, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 58. CrossRef - Glucose Variability and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Eun Ju Cho, Kyungdo Han, Soo Seong Heo, Bo-Yeon Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Su Jong Yu
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2021; 30(5): 974. CrossRef -
Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein improves diagnostic accuracy for hepatocellular carcinoma
Han Ah Lee, Yoo Ra Lee, Young-Sun Lee, Young Kul Jung, Ji Hoon Kim, Hyunggin An, Hyung Joon Yim, Yoon Tae Jeen, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun, Yeon Seok Seo
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(28): 4687. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Young Eun Chon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Sik Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(2): 135. CrossRef - Efficacy of Local Treatments for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Involving the Inferior Vena Cava and/or Right Atrium
Han Ah Lee, Chai Hong Rim
Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2020; Volume 7: 435. CrossRef
- Adjuvant and neoadjuvant immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma

- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Recurrent Peritoneal Metastasis after Hepatectomy Who Showed Complete Response by Surgical Resection
- Hyo Young Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Joon Yeul Nam, Young Chang, Hyeki Cho, Young Youn Cho, Eung Ju Cho, Su Jong Yu, Yoon Jun Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(2):153-157. Published online September 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.2.153
- 1,725 Views
- 15 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after hepatic resection is quite common. Peritoneal
recurrence has been considered incurable status and related to poor prognosis. Although
peritoneal metastasectomy is a therapeutic option for some selected patients with a few
peritoneal metastasis, the indication and therapeutic effect has not been clear. We report a
case
of a 61-year-old man achieving complete remission of recurrent peritoneal metastasis after repeated surgical resection by a multidisciplinary approach. Peritoneal metastasectomy might be a therapeutic option for selected patients with localized oligonodular peritoneal metastasis.

Case Report
- A Case of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Long-term Post-progression Survival under Repeated Transarterial Chemoembolization after Sorafenib Failure
- Jihyun Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Yong Jin Jung, Tae Hun Kim, Kwon Yu
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):82-87. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.82
- 1,630 Views
- 8 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma is the third leading cause of cancer related mortality worldwide. Only 30% of patients are eligible for curative surgical resection at diagnosis. For patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with accompanying portal vein tumor thrombosis, Sorafenib is recommended as first-line treatment. However, survival gain from sorafenib is unsatisfactory, and there is no standard therapy for patients who are intolerable or refractory to sorafenib. Here we report a case of a 52-year-old man who initially achieved partial response after sorafenib treatment, but eventually showed disease progression and was treated subsequently with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Multinodular recurrence occurred, but he was treated with repeated TACE, and has survived for 4 years so far.

Original Articles
- High-level Expression of Interleukin-17 and C-reactive Protein Predicts Tumor Progression in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated by Transarterial Chemoembolization
- Myeong Jun Song, Sung Won Lee, Eun-Jee Oh, Bohyun Jang, Jeong Won Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(2):108-117. Published online September 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.2.108
- 942 Views
- 9 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is the standard locoregional treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Angiogenesis and inflammation play important roles in tumor growth in HCC. In this study, we evaluated the associations between the levels of growth factors and inflammatory markers and clinical prognosis in patients with unresectable HCC treated with TACE.
Methods
The clinical outcomes of 58 HCC patients treated with TACE at the Catholic Medical Centers from January, 2012 to February 2015 were evaluated. Baseline levels of the growth factors vascular endothelial growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and hepatocyte growth factor and the inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-17 and high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) were compared with the treatment outcomes. The primary endpoint was time to progression (TTP); the secondary endpoint was overall survival (OS).
Results
During the 20.8 months of follow-up, TTP was significantly delayed in patients with low levels of hs-CRP (≤0.15) and IL-17 (≤0.94) and a maximal tumor diameter ≤5 cm (P =0.010, P =0.015, and 0.048, respectively). Patients with HCC with low hs-CRP and IL-17 levels had a longer survival than that of those with high hs-CRP levels and IL-17 (35.1 vs. 22.5 months, P =0.000; 41 vs. 21.8 months, P =0.000, respectively). However, any baseline growth factors were not significantly correlated with TTP and OS.
Conclusions
Elevated IL-17 and hs-CRP may be predictive of a poor outcome in patients with HCC treated with TACE. A better understanding of this relationship will require further investigation of the immune mechanisms underlying tumor progression.

- Characteristics and Survival of Korean Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Nationwide Random Sample Study
- Young-Suk Lim, Seung Hyung Kim, Seung Hyung Kim, Jae Seok Hwang, Kwang-Hyub Han
- J Liver Cancer. 2014;14(2):97-107. Published online September 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.14.2.97
- 1,275 Views
- 26 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Given the high incidence and mortality rate of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), ensuring high quality of registry data is important for the improvement of health service. Registries by voluntary reporting often lack case completeness and may cause selection bias. A statutory Korean Central Cancer Registry (KCCR) has case completeness and provides accurate information on HCC incidence, but provides limited information about HCC characteristics.
Methods
The Korean Liver Cancer Study Group (KLCSG) and the KCCR jointly built a nationwide cohort of patients who were diagnosed with HCC between 2003 and 2005. Out of 31,521 new HCC cases that were registered at the KCCR between 2003 and 2005, 4,630
case
s (14.7% of total HCC cases) were randomly selected and abstracted from 32 hospitals nationwide, and followed up until December 2011. After excluding 110 patients who met the exclusion criteria, a total of 4,520 HCC patients were analyzed.
Results
Mean age at the diagnosis of HCC was 57.1±10.8 years, and males comprised 81.0%. Hepatitis B was the predominant etiology (72%), and hepatitis C comprised 12%. Stage at diagnosis was 10%, 43%, 28%, 11% and 8% for modified International Union Against Cancer (mUICC) stages I, II, III, IV-A and IV-B, respectively. Initial treatment modalities were transarterial therapy in 53%, surgical resection in 10%, local ablation in 7%, and liver transplantation in 1%. The median survival was 1.4 years, and the 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates were 56%, 35% and 27%, respectively. Age, gender, Child-Pugh class, etiology, tumor stage at diagnosis, and treatment modality were factors independently related to survival.
Conclusions
About half of HCC patients are diagnosed at advanced stages in Korea. Curativeintent treatments are rarely applied to patients. This data provides unbiased information about the characteristics and outcome of HCC patients in Korea. (J Liver Cancer 2014;14:97- 107) -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Young Eun Chon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Sik Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(2): 135. CrossRef - Subclassification of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer B and C hepatocellular carcinoma: A cohort study of the multicenter registry database
Sangheun Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Kijun Song, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Seung Up Kim, Kwang‐Hyub Han, Do Young Kim
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2016; 31(4): 842. CrossRef
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry

- Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient and Associated Factors in Survival Prediction in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis and Early and Very Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Tae Yeob Kim, Moon Young Kim, Jae Young Jang, Ki Tae Suk, Soung Won Jeong, Dong Joon Kim, Joo Hyun Sohn, Soon Koo Baik
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2014;14(1):23-30. Published online March 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.14.1.23
- 825 Views
- 5 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: To analyze the usefulness of hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) in survival prediction in cirrhotic patients with early and very early hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
We consecutively collected data of 45 stable cirrhotic patients (male 41, median age 57.2 years, BCLC A 29) with early-stage HCC undergoing HVPG measurement. Prognostic accuracy of HVPG was analyzed by the area under curve (AUC). Survival curves and the associated factors of HVPG status were obtained using Kaplan-Meier method and logistic regression analysis, respectively.
Results
The AUC value for prediction of survival by HVPG were 0.754 (95% CI, 0.603-0.870, P=0.006). The cut-off value of HVPG to predict death was 12 mmHg. Among the 45 patients, 11 patients (24.4%) died: 11 of 28 patients in the high HVPG group and none of 17 patients in the low HVPG group during followup period (P=0.003). The survival rate with high HVPG group was higher than those of low HVPG group (log rank P=0.008). In Child-Turcott-Pugh (CTP) class, the survival rate with CTP A class was higher than that with CTP B class (log rank P<0.001). The only associated factor with HVPG ≥12 mmHg in CTP A class and early-stage HCC was the presence of medium or large sized esophageal varices (odds ratio 66.8, 95% CI, 1.3-3530.4, P=0.038).
Conclusions
HVPG ≥12 mmHg may be suggested a predictor of survival in cirrhotic patients with early-stage HCC. In CTP A class, the presence of medium or large sized esophageal varices were associated with high HVPG.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter