Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Use of doxorubicin-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion: a prospective study
- Su Jong Yu, Yun Bin Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Hyo-Cheol Kim, Jin Wook Chung, Jung-Hwan Yoon, Yoon Jun Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):166-176. Published online March 3, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.08
- 2,064 Views
- 95 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
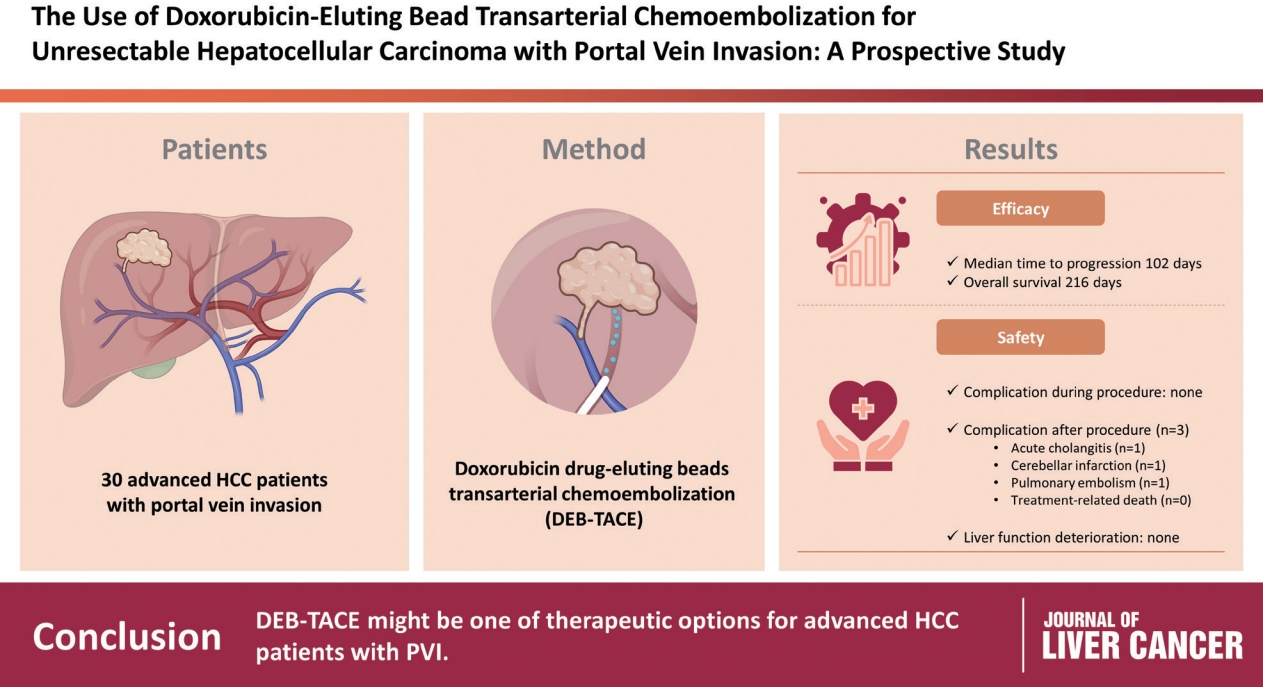
To evaluate the applicability of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) treatment with doxorubicin drug-eluting beads (DEBs) in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with portal vein invasion (PVI).
Methods
This prospective study was approved by the institutional review board and informed consent was obtained from all participants. A total of 30 HCC patients with PVI received DEB-TACE between 2015 and 2018. The following parameters were evaluated: complications during DEB-TACE, abdominal pain, fever, and laboratory outcomes, including liver function change. Overall survival (OS), time to progression (TTP), and adverse events were also analyzed and assessed.
Results
DEBs measuring 100–300 μm in diameter were loaded with doxorubicin (150 mg per procedure). There were no complications during DEB-TACE and no significant differences in the levels of prothrombin time, serum albumin, or total bilirubin at follow-up compared to baseline. The median TTP was 102 days (95% confidence interval [CI], 42–207 days) and the median OS was 216 days (95% CI, 160–336 days). Three patients (10%) had severe adverse reactions, including transient acute cholangitis (n=1), cerebellar infarction (n=1), and pulmonary embolism (n=1), but no treatment-related death occurred.
Conclusions
DEB-TACE may be a therapeutic option for advanced HCC patients with PVI.

Case Reports
- Sorafenib combined with radiation therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal and hepatic vein invasion extending to the inferior vena cava: a complete response case according to modified RECIST criteria
- Yuri Cho, Bo Hyun Kim, Tae Hyun Kim, Young Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):63-68. Published online February 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.01.18

- 2,743 Views
- 90 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The prognosis of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with tumor thrombus extending to the inferior vena cava (IVC) is extremely poor. Herein, we present a rare case of advanced HCC that was treated with sorafenib and radiotherapy, leading to complete remission. This patient had a 9 cm infiltrative HCC occupying almost the entire left lobe with a tumor thrombus extending through the hepatic vein, IVC, and left portal vein. The patient received 400 mg sorafenib twice daily. One year after the start of sorafenib, intensity-modulated radiation therapy for viable HCC and tumor thrombus was performed with a dose of 5,500 cGy. Twenty-seven months after the starting date of sorafenib, there was no intratumoral arterial enhancement, which suggested a complete response according to the modified RECIST criteria. This case suggests that the combination of sorafenib and radiotherapy might provide clinical benefits in patients with advanced HCC with IVC tumor thrombus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 330. CrossRef - Is multidisciplinary treatment effective for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus?
Won Hyeok Choe
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef
- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab

- Early Experience of Oncolytic Virus Injection Combined with Sorafenib in a Patient with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Portal Vein Thrombosis
- Hyun Ho Jo, Seong Joon Chun, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Min Hee Lee, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):177-182. Published online September 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.177

- 3,271 Views
- 69 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - JX-594 is a modified oncolytic poxvirus designed to selectively replicate in and destroy cancer cells. In a pilot study, JX-594 injection followed by sorafenib was well-tolerated in three patients and associated with objective tumor responses. In this study, we report a case in which a patient with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein thrombosis was treated with a combination of JX-594 and sorafenib.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent progress in combination therapy of oncolytic vaccinia virus
Seyedeh Nasim Mirbahari, Miles Da Silva, Abril Ixchel Muñoz Zúñiga, Nika Kooshki Zamani, Gabriel St-Laurent, Mehdi Totonchi, Taha Azad
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Recent progress in combination therapy of oncolytic vaccinia virus

- Advanced Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Successfully Treated with Transarterial Radioembolization and Multi-tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy
- Myung Ji Goh, Wonseok Kang, Dong Hyun Sinn, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):160-166. Published online September 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.160

- 3,547 Views
- 133 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transarterial radioembolization (TARE) with yttrium-90 microspheres has become widely utilized in managing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The utility of TARE is expanding with new insights through experiences from real-world practice and clinical trials, and recently published data suggest that TARE in combination with sorafenib may improve the overall survival in selected patients. Here, we report a case of advanced stage HCC that was successfully treated with TARE and sorafenib. The patient achieved complete response (CR) at 12 months after the initial treatment with TARE and sorafenib, followed by additional transarterial chemoembolization and proton beam therapy for local tumor recurrence at 19-month post-TARE. The patient was followed up every 3 months thereafter and still achieved CR both biochemically and radiologically for the following 12 months. A combination strategy of TARE and systemic therapy may be a useful alternative treatment option for selected patients with advanced stage HCC.

- Successful Sequential Therapy Involving Regorafenib after Failure of Sorafenib in a Patient with Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Liver Transplantation
- Soon Kyu Lee, Jeong Won Jang, Heechul Nam, Pil Soo Sung, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):84-89. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.84
- 3,333 Views
- 89 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
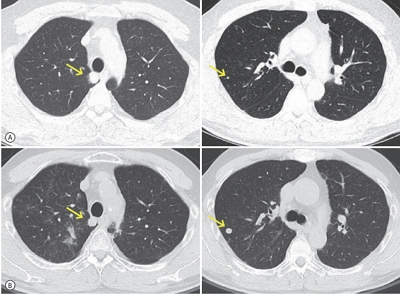
PDF - The efficacy and safety of sequential systemic therapy for the treatment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after liver transplantation (LT) are not well established. This study describes a successful experience where sequential therapy with sorafenib followed by regorafenib was used to treat recurrent HCC in a 54-year old male LT recipient. After HCC recurred in both lungs 10 months after LT, sorafenib was administered with radiation therapy to treat pulmonary metastases. However, after 4 months of sorafenib treatment showed progressive pulmonary metastases, sequential regorafenib treatment was started. After 3 months (cycles) of regorafenib treatment, tumor response was partial, and after 6 months (cycles), disease status remained stable without signs of progression or drug-related serious adverse events. This case suggests that sequential systemic therapy is feasible in patient with recurrent HCC after LT.

- Nivolumab for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Multiple Lung Metastases after Sorafenib Failure
- Jaewoong Kim, Jin Won Chang, Jun Yong Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):72-77. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.72
- 4,569 Views
- 137 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
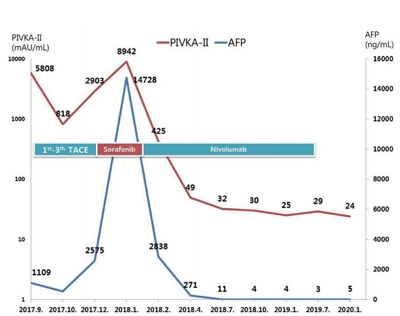
PDF - Over the past decade, standard first-line systemic treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been based on sorafenib, a multi-kinase inhibitor. Regorafenib, another tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is the only second-line therapy that has been globally approved after progression under sorafenib treatment. Recently, immunotherapeutic agents have emerged as promising treatment options in many different malignancies, including advanced HCC. Nivolumab is the first immunotherapy approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in HCC patients with advanced-stage second-line after sorafenib failure. In this report, a case of advanced HCC with multiple lung metastases in which a complete response and maintained progression-free status was achieved with nivolumab, following the failure of transarterial chemoembolization and sorafenib is presented. We hope this report may help expand the clinical application of second-line treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with multiple lung metastasis completely cured using nivolumab: a case report
Ji Eun Han, Hyo Jung Cho, Soon Sun Kim, Jae Youn Cheong
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(2): 169. CrossRef
- Infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with multiple lung metastasis completely cured using nivolumab: a case report

- Recurrent Coronary Artery Vasospasm in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sorafenib: a Case Report and Literature Review
- Dae Hyun Lim, Jai Hoon Yoon, Dae Won Jun, Oh Young Lee, Byung Chul Yoon, Hang Rak Lee, Kyung Soo Kim, Ho Soon Choi
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):67-71. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.67
- 4,341 Views
- 87 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
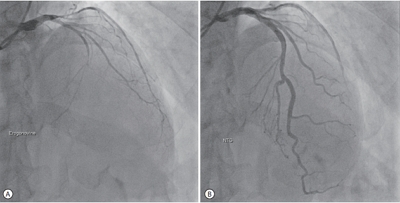
PDF - Tyrosine kinase inhibitors are widely used as targeted treatments for various malignancies. Sorafenib is an orally active tyrosine kinase inhibitor that blocks the signaling pathways of several growth factors. Its use is approved for various malignancies such as unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, and gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Several adverse effects have been reported in the literature; however, cardiotoxicity is rare. We present a case of recurrent coronary vasospasm caused by short-term administration (5 days) of sorafenib. Since it caused refractory ischemia after re-administration, we had no choice but to stop the treatment.

Review Article
- The Genomic Landscape and Its Clinical Implications in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Sun Young Yim, Ju-Seog Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):97-107. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.97

- 6,461 Views
- 253 Downloads
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a complex process. During the last decade, advances in genomic technologies enabled delineation of the genomic landscape of HCC, resulting in the identification of the common underlying molecular alterations. The tumor microenvironment, regulated by inflammatory cells, including cancer cells, stromal tissues, and the surrounding extracellular matrix, has been extensively studied using molecular data. The integration of molecular, immunological, histopathological, and clinical findings has provided clues to uncover predictive biomarkers to enhance responses to novel therapies. Herein, we provide an overview of the current HCC genomic landscape, previously identified gene signatures that are used routinely to predict prognosis, and an immune-specific class of HCC. Since biomarker-driven treatment is still an unmet need in HCC management, translation of these discoveries into clinical practice will lead to personalized therapies and improve patient care, especially in the era of targeted and immunotherapies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comprehensive clinicopathologic study of alpha fetoprotein‐expression in a large cohort of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Dirk Andreas Ridder, Arndt Weinmann, Mario Schindeldecker, Lana Louisa Urbansky, Kristina Berndt, Tiemo Sven Gerber, Hauke Lang, Johannes Lotz, Karl J. Lackner, Wilfried Roth, Beate Katharina Straub
International Journal of Cancer.2022; 150(6): 1053. CrossRef - Two distinct stem cell‐like subtypes of hepatocellular carcinoma with clinical significance and their therapeutic potentials
Sung Hwan Lee, Yun Seong Jeong, Sunyoung Lee, Bo Hwa Sohn, Ho Kyoung Hwang, Gi Hong Choi, Chang Moo Kang, Jin Sub Choi, Woo Jung Lee, Jae‐Ho Cheong, Hee Jin Jang, Ahmed Kaseb, Lewis Roberts, Sun Young Yim, Yun Shin Chun, Ju‐Seog Lee
Cancer Communications.2022; 42(2): 179. CrossRef - Activated TAZ induces liver cancer in collaboration with EGFR/HER2 signaling pathways
Hyuk Moon, Hyunjung Park, Min Jee Chae, Hye Jin Choi, Do Young Kim, Simon Weonsang Ro
BMC Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Tumor aggressiveness is independent of radiation quality in murine hepatocellular carcinoma and mammary tumor models
Eshwar B. Udho, Shane M. Huebner, Dawn M. Albrecht, Kristina A. Matkowskyj, Linda Clipson, Catigan A. Hedican, Rachel Koth, Santina M. Snow, Emily L. Eberhardt, Devon Miller, Rachel Van Doorn, Genti Gjyzeli, Erin K. Spengler, Douglas R. Storts, Douglas H.
International Journal of Radiation Biology.2021; 97(8): 1140. CrossRef - Infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with multiple lung metastasis completely cured using nivolumab: a case report
Ji Eun Han, Hyo Jung Cho, Soon Sun Kim, Jae Youn Cheong
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(2): 169. CrossRef - Update on Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Brief Review from Pathologist Standpoint
Nese Karadag Soylu
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2020; 51(4): 1176. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma: new provisions of the WHO classification, 5th edition, 2019
E.M. Nepomnyashchaya, A.V. Shaposhnikov, E.A. Yurieva
Arkhiv patologii.2020; 82(6): 36. CrossRef
- Comprehensive clinicopathologic study of alpha fetoprotein‐expression in a large cohort of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma

Case Reports
- Sorafenib-induced Pancreatic Pseudocyst in a Patient with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Rare Adverse Event
- Dae-ha Kim, Minkoo Kim, Hyung Joon Yim, Sang Jun Suh, Young Kul Jung
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):154-158. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.154
- 3,438 Views
- 47 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
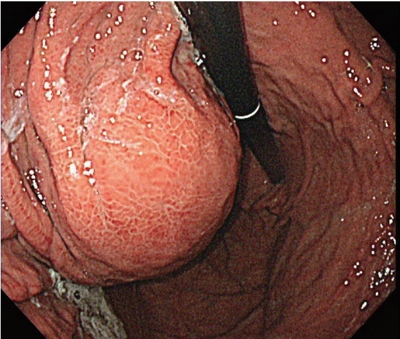
PDF - A 54-year old man diagnosed with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma began treatment with sorafenib. After 3 weeks of treatment, he complained of abdominal pain and nausea. Abdominal sonography showed multiple hepatic lesions only. Serum amylase and lipase levels were 35 U/L and 191 U/L, respectively. The patient was diagnosed with sorafenib-induced acute pancreatitis. After 10 days of discontinuing sorafenib he still complained of nausea and loss of appetite. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed a large bulging lesion, which was suspected to cause extrinsic compression on the high body of the gastric anterior wall. Computed tomography scan revealed a cystic lesion, 8.3 cm in size, in the pancreatic tail, suggesting a pancreatic pseudocyst. After the withdrawal of sorafenib, systemic chemotherapy with Adriamycin and cisplatin was administered. Four months after the discontinuation of sorafenib, the size of the pancreatic pseudocyst decreased from 8.3 cm to 3 cm. The patient's symptoms were also relieved.

- Radiation-induced Myositis after Proton Beam Therapy to Huge Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jihye Kim, Gyu Sang Yoo, Dong Hyun Sinn, Hee Chul Park, Kwang Cheol Koh
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):136-142. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.136
- 6,155 Views
- 119 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Proton beam therapy (PBT) is one of the advances in radiotherapy techniques, which enables dose escalation with lower probability of radiation-induced liver or gastrointestinal injuries. However, the chest wall proximal to the tumor can be affected by high dose irradiation. Here, we report on a 58-year-old male patient who presented with huge hepatocellular carcinoma, received treatment with transarterial chemoembolization and PBT, and developed severe chest wall pain due to radiation-induced myositis. The patient’s symptoms were controlled by oral steroids.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pectoralis Major Radiation Myonecrosis After Lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
Jason Gurewitz, Anand Mahadevan, Benjamin T. Cooper
Practical Radiation Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Current role of proton beam therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Gyu Sang Yoo, Jeong Il Yu, Hee Chul Park
International Journal of Gastrointestinal Intervention.2021; 10(4): 175. CrossRef
- Pectoralis Major Radiation Myonecrosis After Lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy

Original Article
- An Analysis for Survival Predictors for Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Who Failed to Sorafenib Treatment in Pre-regorafenib Era
- Chan Uk Lee, Young-Sun Lee, Ji Hoon Kim, Minjin Lee, Sehwa Kim, Young Kul Jung, Yeon Seok Seo, Hyung Joon Yim, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):117-127. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.117

- 4,208 Views
- 64 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Sorafenib is the standard treatment for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We aimed to investigate the prognosis predictors and the role of second-line cytotoxic systemic chemotherapy (CSC) in patients with advanced HCC after sorafenib discontinuation in the pre-regorafenib era.
Methods
From 2007 to 2015 in the pre-regorafenib era, the medical records of 166 HCC patients, who had permanently discontinued sorafenib, were retrospectively reviewed. For further analysis of survival factors after sorafenib treatment failure, we compared the survival of patients who had maintained liver function after second-line treatment with the best supportive care (BSC) group and selective BSC (SBSC) group.
Results
After discontinuation of sorafenib, median overall survival (OS) was 2.8 (1.9-3.7) months. The OS in patients who discontinued sorafenib due to adverse effect, progression, and poor clinical condition were 5.5 (2.4-8.6), 5.5 (2.2-8.9), and 0.9 (0.5-1.3) months, respectively (P<0.001). The independent predictive factors of survival after sorafenib failure were serum level of bilirubin and albumin, α-fetoprotein, discontinuation cause, and second-line CSC. In comparison with survival between second-line CSC and BSC group, the CSC group showed better survival outcome compared to the BSC group (10.6 vs. 1.6 months, P<0.001) and SBSC group (10.6 vs. 4.2 months, P=0.023).
Conclusions
The survival after sorafenib failure in patients who discontinued sorafenib due to progression and adverse effects was significantly better than in those who discontinued treatment due to clinical deterioration. In the pre-regorafenib era, patients who received second-line CSC showed better survival than those who received only supportive care after sorafenib failure.

Case Reports
- A Case of Achieving Partial Remission with the Combination of Sorafenib and Nivolumab in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Showing Disease Progression after Nivolumab Therapy
- Sang Youn Hwang, Seon-Mi Lee, Jung Woo Im, Ki Jeong Jeon, Cheol-Won Choi, Kyung-Su Kim, Wan Jeon
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(1):74-78. Published online March 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.1.74
- 3,255 Views
- 48 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
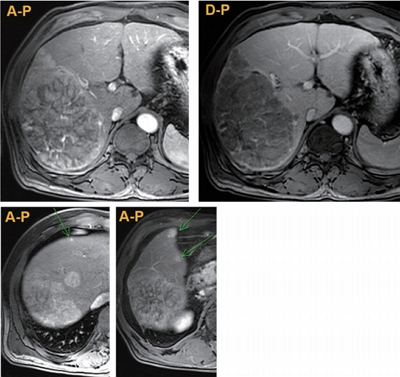
PDF - Sorafenib is a well-known approved systemic therapeutic agent used in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Regorafenib and nivolumab are approved as second-line therapeutic drugs in patients showing disease progression after sorafenib therapy. However, there is no established third- or fourth-line therapy in patients with progression after regorafenib or nivolumab treatment. Recently, the combination of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICPIs) has been attempted as a firstline treatment strategy in advanced HCC patients based on the hypothesis that combination therapy may overcome resistance in ICPI monotherapy. On the basis of this suggestion, we herein describe the case of an HCC patient demonstrating macrovascular invasion, whereby partial remission was achieved via the combination of sorafenib and nivolumab following disease progression after nivolumab therapy. Further studies on the combination of TKIs and ICPIs are necessary to determine ways to manage HCC patients showing disease progression after ICPI therapy.

- Sorafenib Treatment in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Tumor Thrombus Nearly Occupying the Entire Right Atrium
- Kang, Young Mo , Ryu, Soo Hyung , Lee, Bo Kyung , Ko, Kyoung Ho , Park, Tae Young , Moon, Jeong Seop , Cho, Seon Hwa
- J Liver Cancer. 2018;18(2):142-145. Published online September 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.18.2.142
- 2,420 Views
- 36 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
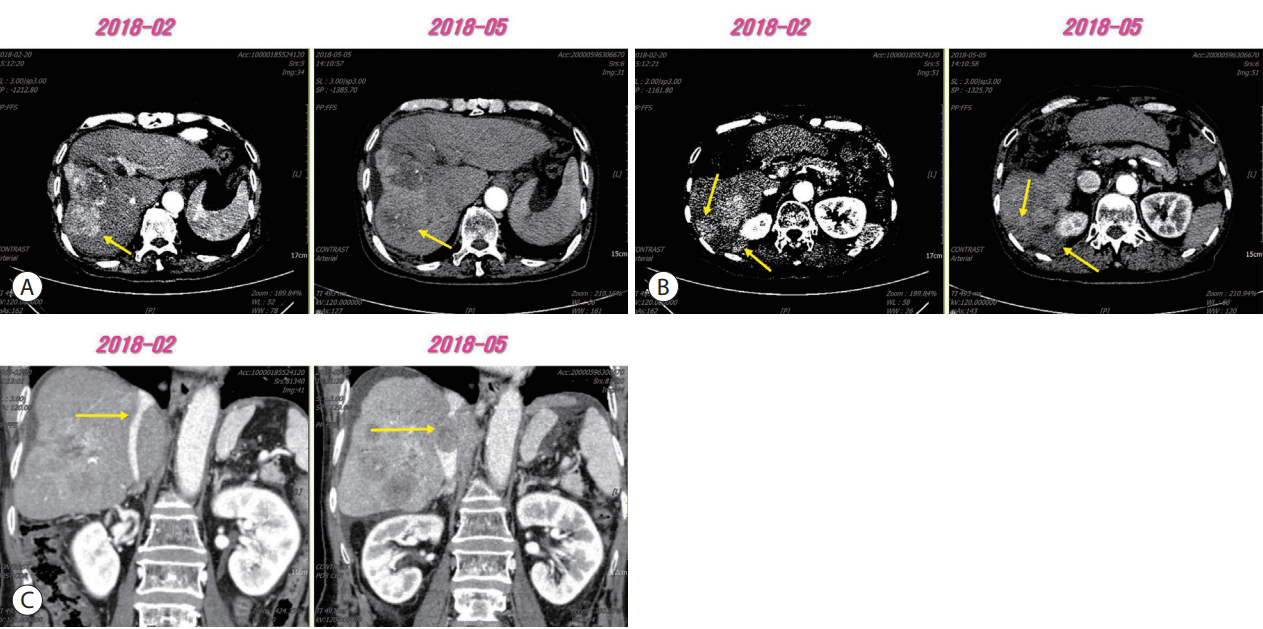
PDF - Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with tumor thrombus extending through the hepatic veins, inferior vena cava, and right atrium (RA) is very rare. However, whether active treatments such as radiation, transcatheter arterial chemoembolization, and sorafenib in advanced HCC with RA involvement prolong survival is uncertain. We present a rare case of advanced HCC with tumor thrombus nearly occupying the entire RA that was treated with sorafenib. The patient received 400 mg sorafenib twice daily. However, her liver enzyme levels continued to increase and abdominal computed tomography showed an increase in the tumor size in the liver and RA. In the present case, active treatment with sorafenib was ineffective; thus, palliative care may be more beneficial in advanced HCC with extensive RA involvement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Hepatic Vein and Inferior Vena Cava Invasion
Akash Shukla, Abhinav Jain
Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hepatology.2023; 13(5): 813. CrossRef - Clinical outcome and toxicity of radiotherapy for inferior vena cava tumor thrombus in HCC patients
So Jung Lee, Hong Seok Jang, Yoo Kyung Choi
Medicine.2021; 100(25): e26390. CrossRef - miR-4454 Promotes Hepatic Carcinoma Progression by Targeting Vps4A and Rab27A
Haoming Lin, Rui Zhang, Wenrui Wu, Liming Lei, Grzegorz Węgrzyn
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Hepatic Vein and Inferior Vena Cava Invasion

- A Case of Achieving Complete Remission with Combination of Sorafenib and Tegafur in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Progression of Disease after Sorafenib Therapy
- Sang Youn Hwang, Seon-Mi Lee, Jung Woo Im, Ki Jeong Jeon, Sang Bu Ahn, Jin-Young Park, Cheol-Won Choi, Kwang-Mo Yang
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):88-93. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.88
- 1,770 Views
- 9 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Sorafenib is the only approved targeted agent as the first line systemic therapy for treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the improvement of survival duration under 3 months is far from clinical satisfactory and most patients experience disease progression within 6 months after sorafenib therapy. Unfortunately, second line systemic therapy after treatment failure of sorafenib was not established and there were no clear guidelines for salvage treatment modalities. Recently, studies suggests that combination of sorafenib and single cytotoxic agent can be relatively effective and safe strategy that achieves promising rates of local and systemic control in advanced HCC patients. Based on above suggestions, we herein offer our experience of a case achieved complete remission by combination therapy of sorafenib and tegafur in the patient with progressed disease after sorafenib therapy.

- A Case of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Long-term Post-progression Survival under Repeated Transarterial Chemoembolization after Sorafenib Failure
- Jihyun Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Yong Jin Jung, Tae Hun Kim, Kwon Yu
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):82-87. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.82
- 1,631 Views
- 8 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma is the third leading cause of cancer related mortality worldwide. Only 30% of patients are eligible for curative surgical resection at diagnosis. For patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with accompanying portal vein tumor thrombosis, Sorafenib is recommended as first-line treatment. However, survival gain from sorafenib is unsatisfactory, and there is no standard therapy for patients who are intolerable or refractory to sorafenib. Here we report a case of a 52-year-old man who initially achieved partial response after sorafenib treatment, but eventually showed disease progression and was treated subsequently with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Multinodular recurrence occurred, but he was treated with repeated TACE, and has survived for 4 years so far.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter