Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Reports
- Metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis confirmed on blind liver biopsy
- Hun Kim, Tae Hoon Roh, Jun Seop Lee, Min Seong Kim, Beom Kyung Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):113-117. Published online November 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.11.05
- 813 Views
- 80 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
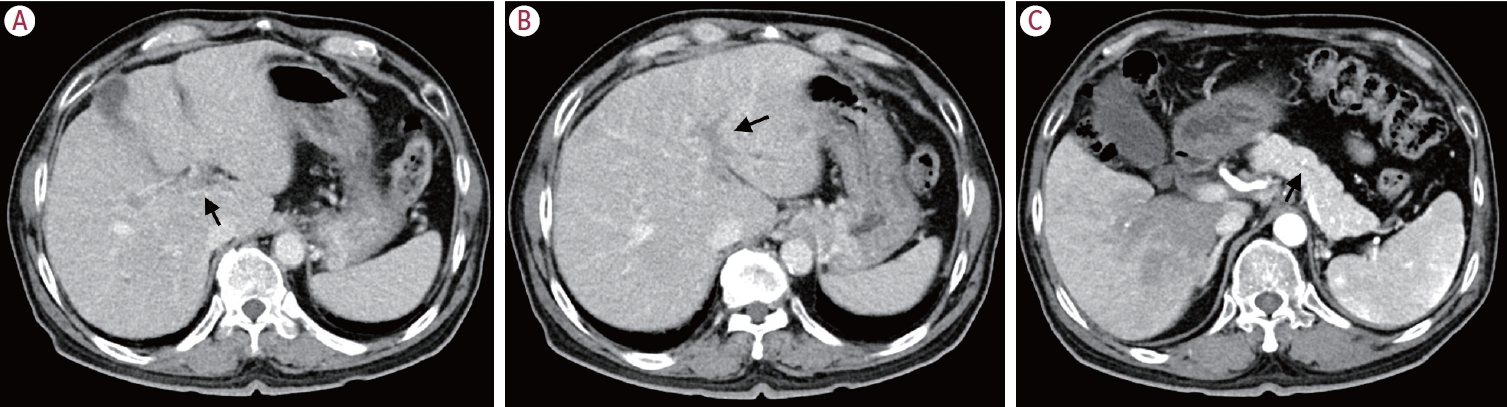
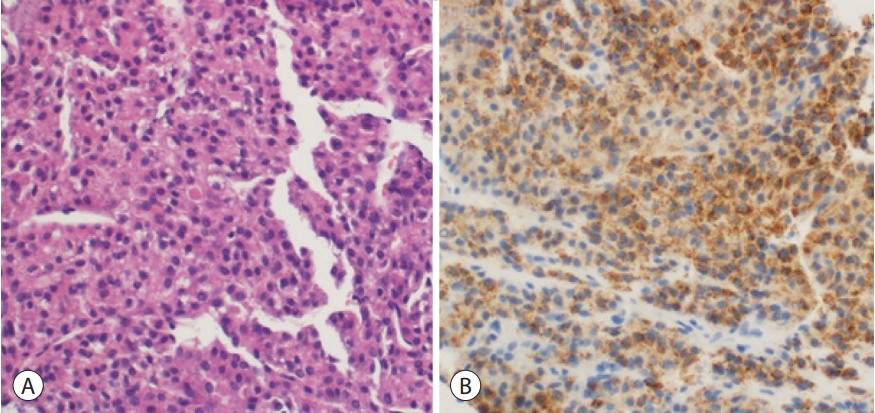
PDF - Portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) is an uncommon condition in which tumor cells expand into the vessels, causing blood clot formation in the portal vein. PVTT is mainly associated with hepatocellular carcinoma, leading to an unfavorable prognosis; however, it can also develop in patients with other cancer types. Herein, we report a case of metastatic renal cell carcinoma diagnosed by a blind liver biopsy in a patient with dynamic computed tomography-confirmed portal vein thrombosis and cholangiopathy. This case illustrates the importance of systematic surveillance with routine laboratory tests and contrast-enhanced imaging studies on patients with cancer to detect potential liver infiltration of metastatic cancer.

- Curative liver transplantation after lung resection for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with lung metastasis and inferior vena cava tumor thrombosis: a case report
- Dong Jin Joo, Do Young Kim, Jinsil Seong, Hyun Jeong Kim, Jae Geun Lee, Dai Hoon Han, Gi Hong Choi, Myoung Soo Kim, Jin Sub Choi, Soon Il Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):181-186. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.08

- 3,606 Views
- 91 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with distant metastasis is an absolute contraindication for liver transplantation (LT). However, it is still unclear whether LT is feasible or acceptable in such patients, albeit after being treated with a multidisciplinary approach and after any metastatic lesion is ruled out. We report one such successful treatment with living donor LT (LDLT) after completely controlling far-advanced HCC with inferior vena cava tumor thrombosis and multiple lung metastases. The patient has been doing well without HCC recurrence for eight years since LDLT. The current patient could be an anecdotal case, but provides a case for expanding LDLT indications in the context of advanced HCC and suchlike.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inferior Vena Cava Thrombectomy and Stenting as Bridge to Liver Transplantation After Radiotherapy-Induced Thrombosis
Raphael PH Meier, Shani Kamberi, Josue Alvarez-Casas, Barton F. Lane, Chandra S. Bhati, Saad Malik, William Twaddell, Kirti Shetty, Adam Fang, Hyun S. Kim, Daniel G. Maluf
Progress in Transplantation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inferior Vena Cava Thrombectomy and Stenting as Bridge to Liver Transplantation After Radiotherapy-Induced Thrombosis

- Combination Therapy of Angiotherapy, Radiation Therapy, and Radiofrequency Ablation for Pulmonary Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Accompanied by Nontuberculous Mycobacteria
- Sang Hyun Park, Seul Ki Kim, Ji Hye Kim, Seokgyo Seo, Hyun Pyo Hong, Soo-Youn Ham, Byung Ik Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(1):79-84. Published online March 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.1.79
- 3,279 Views
- 52 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - With the advances in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treatment, the lung metastasis of HCC is becoming increasingly important. In treating the lung metastasis of HCC, a multidisciplinary approach can lead to better results than systemic chemotherapy alone. Here, we report on a patient who presented with pulmonary masses, while the HCC was being controlled in the abdominal cavity. The presence of nontuberculous mycobacteria was identified during the diagnosis of the pulmonary masses. The pulmonary metastases of HCC were treated with a combination of angiotherapy, radiation therapy, and radiofrequency ablation. The patient showed a satisfactory progress with this multidisciplinary localized treatment. We report the clinical progress and review the recent literature regarding the treatment of pulmonary metastasis without intrahepatic HCC herein.

- A Case of a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Lung Metastasis Who Failed Sorafenib Treatment and Achieved Complete Remission after Lung Resection and Radiation Therapy
- Jung Hwan Yu, Jung Il Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):77-81. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.77
- 1,475 Views
- 17 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), sorafenib is the only approved systemic chemotherapy, and has been applied for those with advanced HCC especially with systemic metastasis. However, the treatment results are suboptimal leaving many cases with disease progression despite the use of optimum dose. There is no established guideline for those that fail to respond to sorafenib treatment. In this case, a 46-years-old male with metastatic lung cancer from HCC experienced progression despite sorafenib treatment. Then, the patient received surgical resection of the metastatic lung mass followed by radiation therapy and achieved complete remission for 10 months after the surgical treatment and radiation therapy. Alpha-fetoprotein level was normalized and complete remission has been maintained.

- Long Term Survival in Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Surgical Resection of Brain Metastasis: A Case Report
- Jeong-Ho Lee, Hyung-Min Yu, Sung-Bum Cho
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(1):38-41. Published online March 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.1.38
- 999 Views
- 35 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Brain metastasis is a rare condition of extraheptaic metastases in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and brain metastasis have rapidly worsened neurologic signs and symptoms, therefore it is regarded to oncologic emergency. Current recommended treatments for brain metastasis are surgical resection or gamma-knife surgery with/without whole brain radiation therapy (RT). However, patients with brain metastasis have a very poor prognosis after adequate treatment. Here, we report a 62-year-old man with HCC and brain metastasis who had long term survival after surgical resection and whole brain RT. (J Liver Cancer 2016;16:38-41)

- A Case of Extrahepatic Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma to the Pronator Quadratus Muscle of Right Wrist
- Yonng Wook Song, Byung seok Lee, Seok Hyun Kim, Eaum seok Lee, Heon Young Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2015;15(1):41-45. Published online March 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.15.1.41
- 961 Views
- 3 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is usually associated with chronic liver disease such as liver cirrhosis. Primary HCC lesions and even recurrent intrahepatic lesions can be treated successfully by using variable modalities applicable to intrahepatic lesions. HCC can cause intrahepatic multiple occurrence and extrahepatic metastasis. Extrahepatic metastasis occurs in up to about 60% of patients of HCC, and a major of patients with extrahepatic HCC had late intrahepatic stage of tumor. Themost frequent site of extrahepatic metastasis of HCC was the lung. HCC metastasized to soft tissues was unusually reported. Extrahepatic metastasis of HCC, especially to unusual site, should not be overlooked and must be able to be controlled. We experienced a case that HCC was metastasized to the pronator quadratus muscle of right wrist and chould be removed surgically.

Review Article
- Emergencies in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Chang Wook Kim, Chang Don Lee
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2013;13(1):1-7. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.13.1.1
- 862 Views
- 13 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) may be suffered by various emergency conditions such as spontaneous rupture of HCC with intraperitoneal hemorrhage, variceal bleeding with portal vein tumor thrombus, hemobilia, obstructive jaundice, distant metastasis of HCC in central nervous system, spinal bone metastasis of HCC with cord compression and so on. These emergencies can be categorized into 4 types, conditions with spontaneous rupture of HCC, distant metastasis of HCC, direct invasion of HCC and paraneoplastic syndrome. According to HCC status and liver function, some these patients showed more beneficial effects with active palliative treatments than with best supportive cares. Various palliative treatments can be used such as surgical resection, transarterial chemoembolization, radiotherapy, systemic chemotherapy and combination of above therapies. We reviewed the emergencies in patients with HCC for improving survival and quality of life.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter