Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- A multidisciplinary approach with immunotherapies for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
- Yu Rim Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):316-329. Published online September 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.09.04

- 1,521 Views
- 101 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a highly aggressive disease that is usually diagnosed at an advanced stage. Advanced HCC has limited treatment options and often has a poor prognosis. For the past decade, tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been the only treatments approved for advanced HCC that have shown overall survival (OS) benefits; however, but their clinical efficacy has been limited. Recent trials have demonstrated promising advancements in survival outcomes through immunotherapy-based treatments, such as combinations of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) with other ICIs, antiangiogenic drugs, and locoregional therapies. The atezolizumab-bevacizumab and durvalumab-tremelimumab (STRIDE) regimen has significantly improved survival rates as a first-line treatment and has become the new standard of care. Therefore, combined treatments for advanced HCC can result in better treatment outcomes owing to their synergistic effects, which requires a multidisciplinary approach. Ongoing studies are examining other therapeutic innovations that can improve disease control and OS rates. Despite improvements in the treatment of advanced HCC, further studies on the optimal treatment selection and sequences, biomarker identification, combination approaches with other therapies, and development of novel immunotherapy agents are required. This review presents the current treatment options and clinical data of the ICI-based combination immunotherapies for advanced HCC from a multidisciplinary perspective.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reduced-Dose or Discontinuation of Bevacizumab Might Be Considered after Variceal Bleeding in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab: Case Reports
Kyeong-Min Yeom, Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(1): 157. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Advances in Systemic Therapy
Insija Ilyas Selene, Merve Ozen, Reema A. Patel
Seminars in Interventional Radiology.2024; 41(01): 056. CrossRef
- Reduced-Dose or Discontinuation of Bevacizumab Might Be Considered after Variceal Bleeding in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab: Case Reports

Case Report
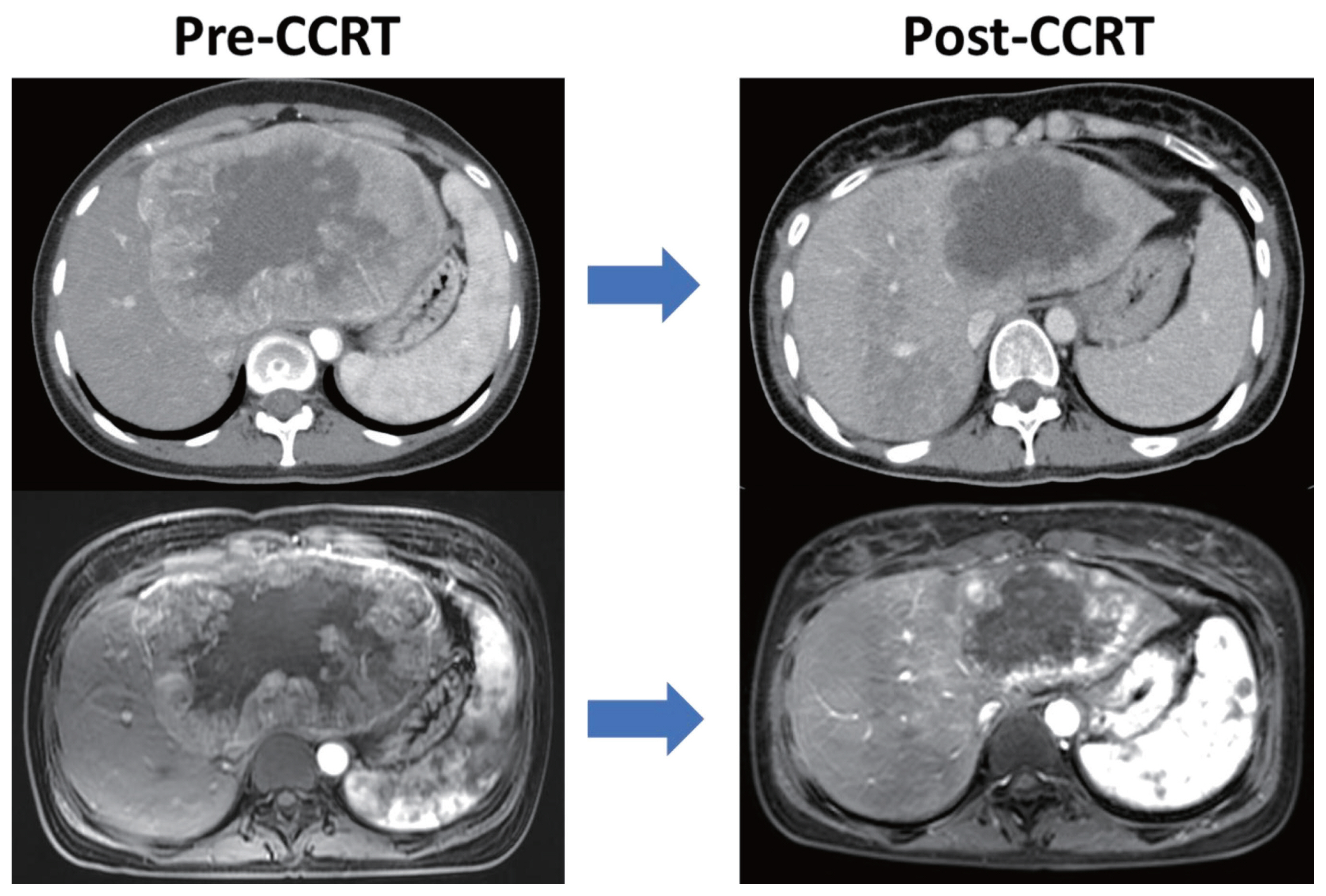
- Long-term survival after multimodal treatment involving radiotherapy for huge hepatocellular carcinoma with oligometastasis: a case report
- Byung Min Lee, Jinsil Seong
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):163-168. Published online September 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.08.06
- 2,546 Views
- 74 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The clinical efficacy of local ablative treatment for oligometastasis is widely accepted in most cancers. However, due to limited data, this has not been the case for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, we report a case of pulmonary oligometastasis of a huge HCC that was treated by multimodality with liver-directed concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) plus subsequent resection of the primary lesion and local ablative radiotherapy (RT) for subsequent lung oligometastatic lesions. In this patient, liver-directed CCRT induced significant tumor shrinkage with compensatory hypertrophy of the non-tumor liver, followed by curative resection. Surgical resection of the first and second pulmonary metastatic lesions as well as local ablative RT of the third lesion achieved complete tumor regression, which led to long-term survival of 6 years. Therefore, the active use of local ablative RT requires full consideration in cases of oligometastatic HCC.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter