Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Inter-reader Agreement for CT/MRI LI-RADS Category M Imaging Features: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Dong Hwan Kim, Sang Hyun Choi
- Received March 11, 2024 Accepted April 5, 2024 Published online April 15, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.04.05 [Accepted]
- 189 Views
- 8 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Backgrounds/Aims
To systematically evaluate inter-reader agreement in the assessment of individual Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) category M (LR-M) imaging features in computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging (CT/MRI) LI-RADS v2018, and to explore the causes of poor agreement in LR-M assignment.
Methods
Original studies reporting inter-reader agreement for LR-M features on multiphasic CT or MRI were identified using the MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases. The pooled kappa coefficient (κ) was calculated using the DerSimonian–Laird random-effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using Cochran’s Q test and I2 statistics. Subgroup meta-regression analyses were conducted to explore the study heterogeneity.
Results
In total, 24 eligible studies with 5,163 hepatic observations were included. The pooled κ values were 0.72 (95% confidence interval, 0.65–0.78) for rim arterial phase hyperenhancement, 0.52 (0.39–0.65) for peripheral washout, 0.60 (0.50–0.70) for delayed central enhancement, 0.68 (0.57–0.78) for targetoid restriction, 0.74 (0.65–0.83) for targetoid transitional phase/hepatobiliary phase appearance, 0.64 (0.49–0.78) for infiltrative appearance, 0.49 (0.30–0.68) for marked diffusion restriction, and 0.61 (0.48–0.73) for necrosis or severe ischemia. Substantial study heterogeneity was observed for all LR-M features (Cochran's Q test: p < 0.01; I2 ≥ 89.2%). Studies with a mean observation size of <3 cm, those performed using 1.5-T MRI, and those with multiple image readers, were significantly associated with poor agreement of LR-M features.
Conclusions
The agreement for peripheral washout and marked diffusion restriction was limited. The LI-RADS should focus on improving the agreement of LR-M features.

- Outcomes of Liver Resection and Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Multinodular BCLC-A Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jiwon Yang, Won-Mook Choi, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Deok-Bog Moon, Dong-Hwan Jung, Jonggi Choi
- Received March 3, 2024 Accepted March 25, 2024 Published online April 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.25 [Accepted]
- 328 Views
- 27 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to compare the outcomes of liver resection (LR) and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with multinodular hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) within the Milan criteria who were not eligible for liver transplantation.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 483 patients with multinodular HCC within the Milan criteria, who underwent either LR or TACE as an initial therapy between 2013 and 2022. The overall survival (OS) in the entire population and recurrence-free survival (RFS) in patients who underwent LR and TACE and achieved a complete response were analyzed. Propensity score (PS) matching analysis was also used for a fair comparison of outcomes between the two groups.
Results
Among the 483 patients, 107 (22.2%) and 376 (77.8%) underwent LR and TACE, respectively. The median size of the largest tumor was 2.0 cm, and 72.3% of the patients had two HCC lesions. The median OS and RFS were significantly longer in the LR group than in the TACE group (p <0.01 for both). In the multivariate analysis, TACE (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.81 and aHR, 2.41) and large tumor size (aHR, 1.43 and aHR, 1.44) were significantly associated with worse OS and RFS, respectively. The PS-matched analysis also demonstrated that the LR group had significantly longer OS and RFS than the TACE group (PS <0.05).
Conclusion
In this study, LR showed better OS and RFS than TACE in patients with multinodular Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A HCC. Therefore, LR can be considered an effective treatment option for these patients.

Review Articles
- Advancing Korean nationwide registry for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic sampling approach utilizing the Korea Central Cancer Registry database
- Bo Hyun Kim, E Hwa Yun, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Geun Hong, Jun Yong Park, Ju Hyun Shim, Eunyang Kim, Hyun-Joo Kong, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Suk Lim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):57-61. Published online March 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.03
- 324 Views
- 20 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
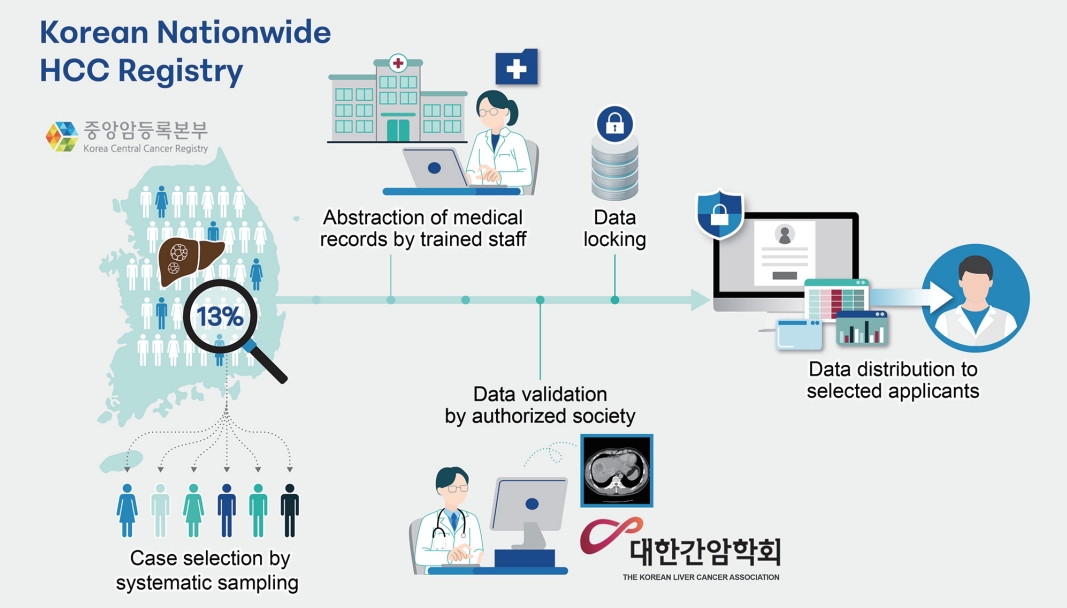
Supplementary Material - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presents a substantial public health challenge in South Korea as evidenced by 10,565 new cases annually (incidence rate of 30 per 100,000 individuals), in 2020. Cancer registries play a crucial role in gathering data on incidence, disease attributes, etiology, treatment modalities, outcomes, and informing health policies. The effectiveness of a registry depends on the completeness and accuracy of data. Established in 1999 by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, the Korea Central Cancer Registry (KCCR) is a comprehensive, legally mandated, nationwide registry that captures nearly all incidence and survival data for major cancers, including HCC, in Korea. However, detailed information on cancer staging, specific characteristics, and treatments is lacking. To address this gap, the KCCR, in partnership with the Korean Liver Cancer Association (KLCA), has implemented a systematic approach to collect detailed data on HCC since 2010. This involved random sampling of 10-15% of all new HCC cases diagnosed since 2003. The registry process encompassed four stages: random case selection, meticulous data extraction by trained personnel, expert validation, anonymization of personal data, and data dissemination for research purposes. This random sampling strategy mitigates the biases associated with voluntary reporting and aligns with stringent privacy regulations. This innovative approach positions the KCCR and KLCA as foundations for advancing cancer control and shaping health policies in South Korea.

- Changing etiology and epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: Asia and worldwide
- Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):62-70. Published online March 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.13
- 704 Views
- 58 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
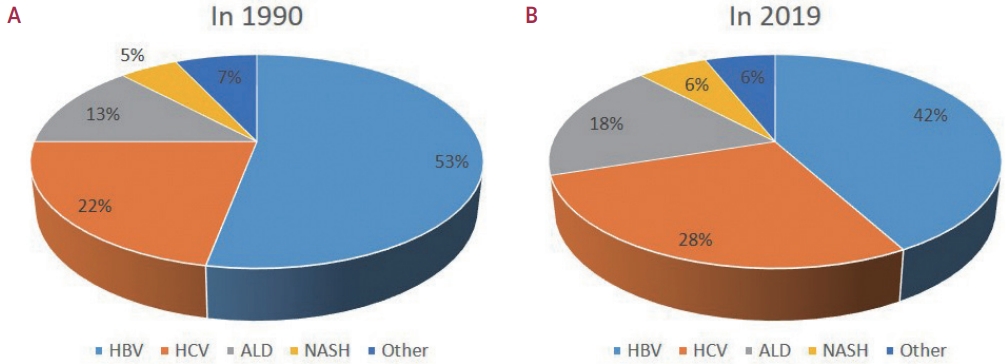
PDF - Approximately 80% of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cases arise in sub-Saharan Africa and Eastern Asia, following a similarly high prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) carriers in these regions. The etiology and epidemiology of HCC have recently changed worldwide. Although HBV infection is the main contributor to HCC development, a slow but continuous decline in HBV infection rates has been reported since 1990. Owing to the widespread use of direct-acting antivirals, the incidence of hepatitis C virus-related HCC has remarkably decreased in Japan and European countries. In Korea, Taiwan, and Singapore, the incidence of HBV-related HCC has significantly decreased owing to vaccination against HBV. Globally, while HBV accounted for more than half of HCCs in 1990, this had decreased to 42% in 2019. In contrast, the proportion of patients with alcoholic- and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) increased from 13% to 18% and from 5% to 6%, respectively. NASH-related HCC has characteristics that differ from those of virus-associated HCC. Compared with other etiologies, patients with NASHassociated HCC are older, have a higher body mass index, and have higher rates of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and cardiovascular disease. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)-associated HCC is also known to develop in the absence of cirrhosis, unlike alcohol-related and autoimmune liver diseases. Because patients with NAFLD usually have diabetes or obesity, surveying this population is challenging. Optimal selection of the target population and surveillance tools among patients with NAFLD needs to be determined.

- Multidisciplinary approach for hepatocellular carcinoma patients: current evidence and future perspectives
- Joo Hyun Oh, Dong Hyun Sinn
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):47-56. Published online March 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.02.27

- 478 Views
- 44 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Management of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is challenging due to the complex relationship between underlying liver disease, tumor burden, and liver function. HCC is also notorious for its high recurrence rate even after curative treatment for early-stage tumor. Liver transplantation can substantially alter patient prognosis, but donor availability varies by each patient which further complicates treatment decision. Recent advancements in HCC treatments have introduced numerous potentially efficacious treatment modalities. However, high level evidence comparing the risks and benefits of these options is limited. In this complex situation, multidisciplinary approach or multidisciplinary team care has been suggested as a valuable strategy to help cope with escalating complexity in HCC management. Multidisciplinary approach involves collaboration among medical and health care professionals from various academic disciplines to provide comprehensive care. Although evidence suggests that multidisciplinary care can enhance outcomes of HCC patients, robust data from randomized controlled trials are currently lacking. Moreover, the implementation of a multidisciplinary approach necessitates increased medical resources compared to conventional cancer care. This review summarizes the current evidence on the role of multidisciplinary approach in HCC management and explores potential future directions.

- Current perspectives on radiotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma management: a comprehensive review
- Dowook Kim, Jun-Sang Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):33-46. Published online March 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.02.26
- 485 Views
- 47 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
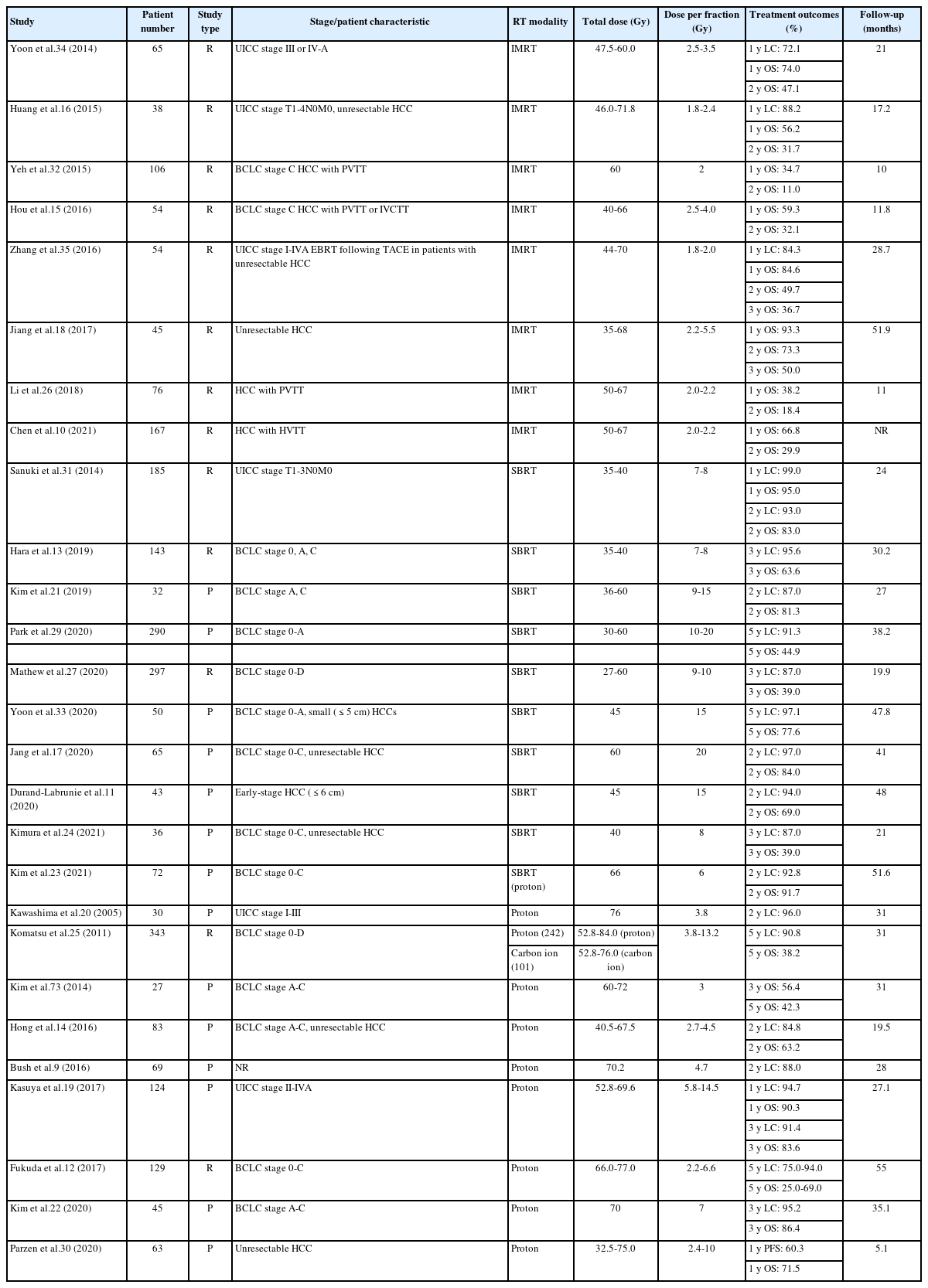
PDF - This review examines the transformative role of external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) in managing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), spotlighting the progression from traditional EBRT techniques to advanced modalities like intensity-modulated radiotherapy (RT), stereotactic body RT (SBRT), and innovative particle therapy, including proton beam therapy and carbon ion RT. These advancements have significantly improved the precision and efficacy of RT, marking a paradigm shift in the multimodal management of HCC, particularly in addressing complex cases and enhancing local tumor control. The review underscores the synergistic potential of integrating RT with other treatments like transarterial chemoembolization, systemic therapies such as sorafenib, and emerging immunotherapies, illustrating enhanced survival and disease control outcomes. The efficacy of RT is addressed for challenging conditions, including advanced HCC with macrovascular invasion, and RT modalities, like SBRT, are compared against traditional treatments like radiofrequency ablation for early-stage HCC. Additionally, the review accentuates the encouraging outcomes of particle therapy in enhancing local control and survival rates, minimizing treatment-related toxicity, and advocating for continued research and clinical trials. In conclusion, the integration of RT into multimodal HCC treatment strategies, coupled with the emergence of particle therapy, is crucial for advancing oncologic management, emphasizing the need for relentless innovation and personalized treatment approaches.

- Intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: refining substaging or shifting paradigm?
- Bernardo Stefanini, Luca Ielasi, Dante Pio Pallotta, Sofia Penazza, Mariarosaria Marseglia, Fabio Piscaglia
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):23-32. Published online March 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.02.21
- 564 Views
- 40 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
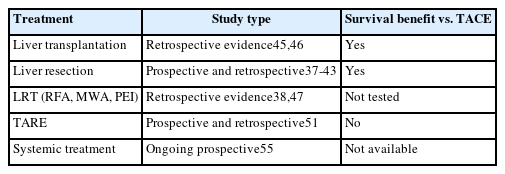
PDF - This review explores the evolution of cancer staging, focusing on intermediate hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and the challenges faced by physicians. The Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system, introduced in 1999, was designed to address the limitations associated with providing accurate prognostic information for HCC and allocating specific treatments, to avoid overtreatment. However, criticism has emerged, particularly regarding the intermediate stage of HCC (BCLC-B) and its heterogeneous patient population. To overcome this limitation, various subclassification systems, such as the Bolondi and Kinki criteria, have been proposed. These systems are aimed at refining categorizations within the intermediate stage and have demonstrated varying degrees of success in predicting outcomes through external validation. This study discusses the shift in treatment paradigms, emphasizing the need for a more personalized approach rather than strictly adhering to cancer stages, without dismissing the relevance of staging systems. It assesses the available treatment options for intermediate-stage HCC, highlighting the importance of considering surgical and nonsurgical options alongside transarterial chemoembolization for optimal outcomes. In conclusion, the text advocates for a paradigm shift in staging systems prioritizing treatment suitability over cancer stage. This reflects the evolving landscape of HCC management, where a multidisciplinary approach is crucial for tailoring treatments to individual patients, ultimately aiming to improve overall survival.

- Complications of immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
- Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):9-16. Published online November 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.11.21
- 972 Views
- 74 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
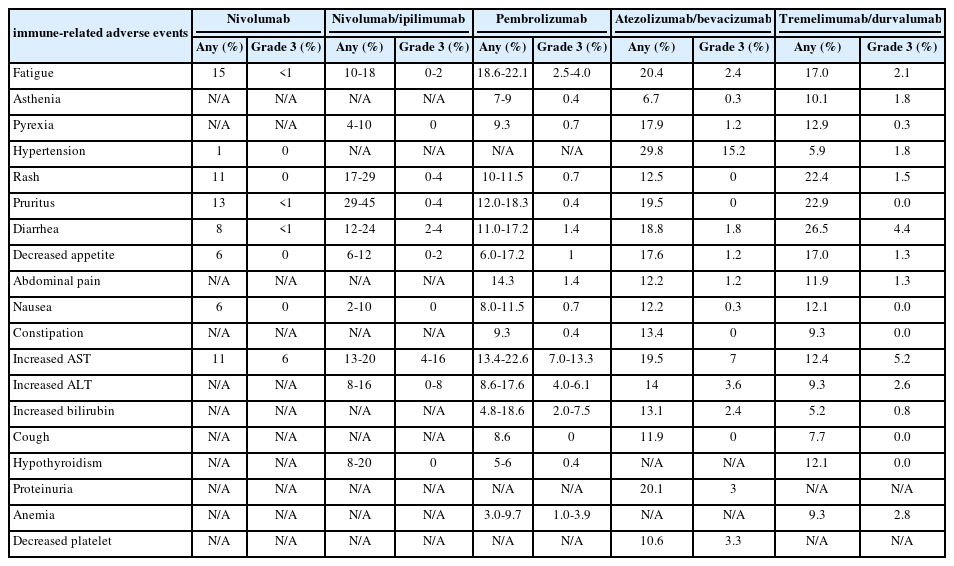
PDF - Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are highly effective in cancer treatment. However, the risks associated with the treatment must be carefully balanced against the therapeutic benefits. Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) are generally unpredictable and may persist over an extended period. In this review, we analyzed common irAEs reported in highly cited original articles and systematic reviews. The prevalent adverse reactions include fatigue, pyrexia, rash, pruritus, diarrhea, decreased appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, constipation, hepatitis, and hypothyroidism. Therefore, it is crucial to conduct evaluations not only of gastrointestinal organs but also of cardiac, neurologic, endocrine (including the frequently affected thyroid), and ophthalmic systems before commencing ICIs. This review further explores commonly reported types of irAEs, specific irAEs associated with each ICI agent, rare yet potentially fatal irAEs, and available treatment options for managing them.

Case Report
- Metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis confirmed on blind liver biopsy
- Hun Kim, Tae Hoon Roh, Jun Seop Lee, Min Seong Kim, Beom Kyung Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):113-117. Published online November 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.11.05
- 811 Views
- 80 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
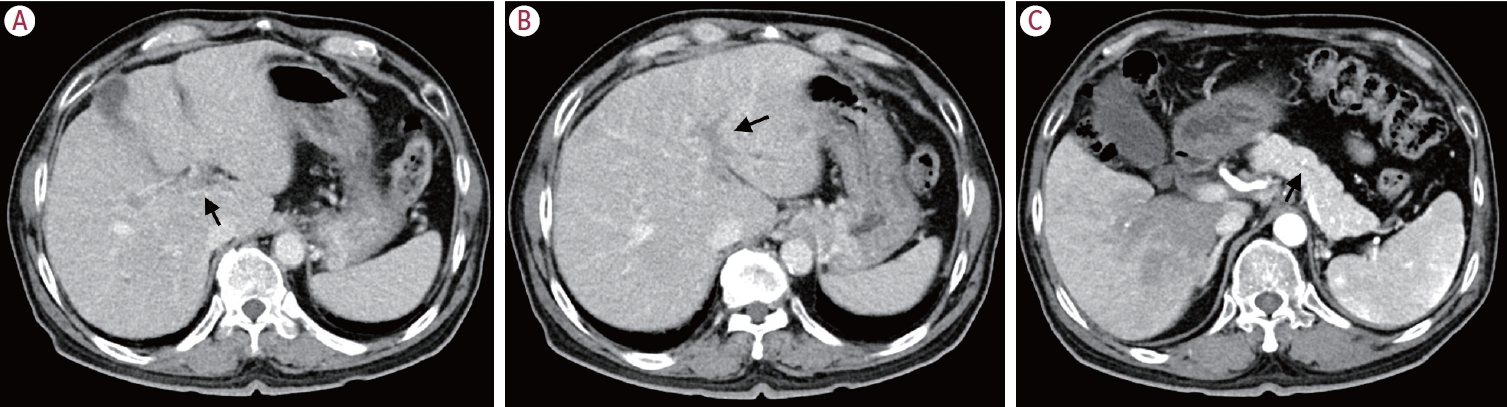
PDF - Portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) is an uncommon condition in which tumor cells expand into the vessels, causing blood clot formation in the portal vein. PVTT is mainly associated with hepatocellular carcinoma, leading to an unfavorable prognosis; however, it can also develop in patients with other cancer types. Herein, we report a case of metastatic renal cell carcinoma diagnosed by a blind liver biopsy in a patient with dynamic computed tomography-confirmed portal vein thrombosis and cholangiopathy. This case illustrates the importance of systematic surveillance with routine laboratory tests and contrast-enhanced imaging studies on patients with cancer to detect potential liver infiltration of metastatic cancer.

Original Article
- Treatment options for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm: surgery vs. ablation: a multicenter retrospective study
- Kazuya Kariyama, Kazuhiro Nouso, Atsushi Hiraoka, Hidenori Toyoda, Toshifumi Tada, Kunihiko Tsuji, Toru Ishikawa, Takeshi Hatanaka, Ei Itobayashi, Koichi Takaguchi, Akemi Tsutsui, Atsushi Naganuma, Satoshi Yasuda, Satoru Kakizaki, Akiko Wakuta, Shohei Shiota, Masatoshi Kudo, Takashi Kumada
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):71-80. Published online November 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.09.11
- 914 Views
- 93 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
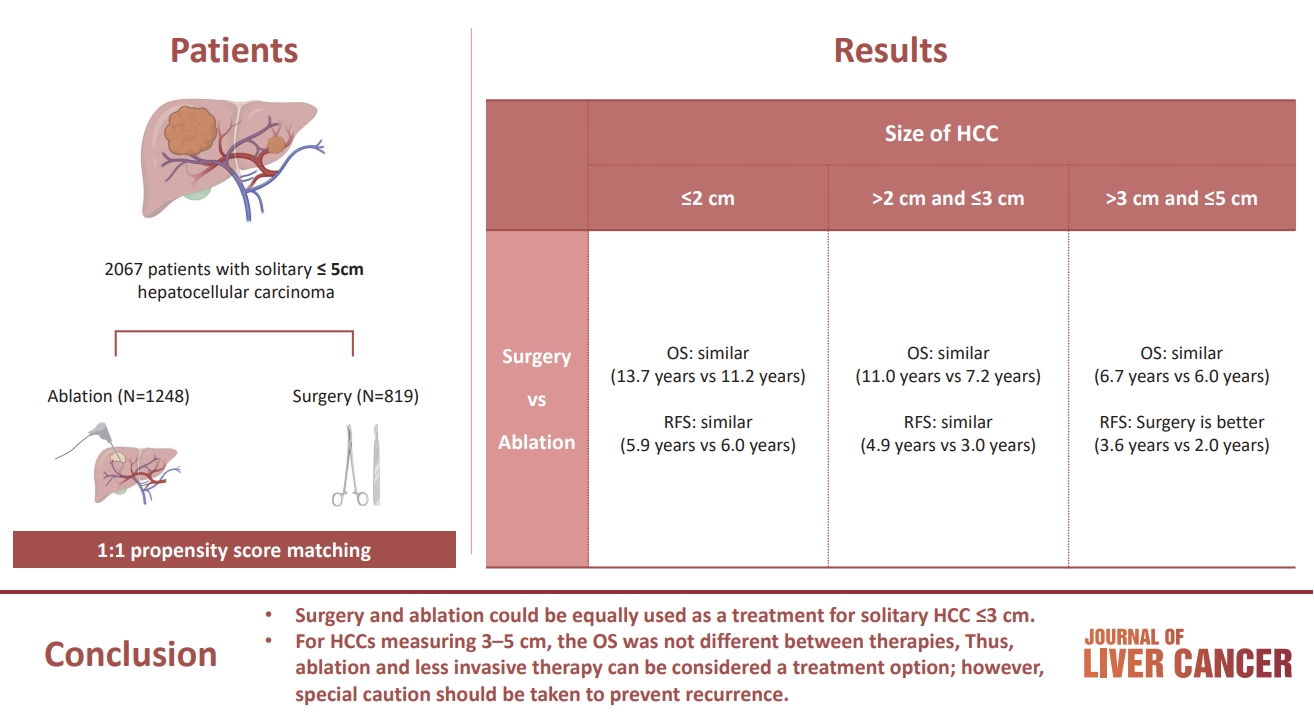
The aim of this study was to compare the therapeutic efficacy of ablation and surgery in solitary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) measuring ≤5 cm with a large HCC cohort database.
Methods
The study included consecutive 2,067 patients with solitary HCC who were treated with either ablation (n=1,248) or surgery (n=819). Th e patients were divided into three groups based on the tumor size and compared the outcomes of the two therapies using propensity score matching.
Results
No significant difference in recurrence-free survival (RFS) or overall survival (OS) was found between surgery and ablation groups for tumors measuring ≤2 cm or >2 cm but ≤3 cm. For tumors measuring >3 cm but ≤5 cm, RFS was significantly better with surgery than with ablation (3.6 and 2.0 years, respectively, P=0.0297). However, no significant difference in OS was found between surgery and ablation in this group (6.7 and 6.0 years, respectively, P=0.668).
Conclusion
The study suggests that surgery and ablation can be equally used as a treatment for solitary HCC no more than 3 cm in diameter. For HCCs measuring 3-5 cm, the OS was not different between therapies; thus, ablation and less invasive therapy can be considered a treatment option; however, special caution should be taken to prevent recurrence. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reply to the Letter regarding “Treatment options for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm: surgery vs. ablation: a multicenter retrospective study”
Kazuhiro Nouso, Kazuya Kariyama
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 5. CrossRef - Radiofrequency for hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 3 cm: potential for applications in daily practice
Ji Hoon Kim, Pil Soo Sung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Letter regarding “Treatment options for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm: surgery vs. ablation: a multicenter retrospective study”
Jongman Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 3. CrossRef
- Reply to the Letter regarding “Treatment options for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm: surgery vs. ablation: a multicenter retrospective study”

Review Articles
- A multidisciplinary approach with immunotherapies for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
- Yu Rim Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):316-329. Published online September 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.09.04

- 1,544 Views
- 101 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a highly aggressive disease that is usually diagnosed at an advanced stage. Advanced HCC has limited treatment options and often has a poor prognosis. For the past decade, tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been the only treatments approved for advanced HCC that have shown overall survival (OS) benefits; however, but their clinical efficacy has been limited. Recent trials have demonstrated promising advancements in survival outcomes through immunotherapy-based treatments, such as combinations of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) with other ICIs, antiangiogenic drugs, and locoregional therapies. The atezolizumab-bevacizumab and durvalumab-tremelimumab (STRIDE) regimen has significantly improved survival rates as a first-line treatment and has become the new standard of care. Therefore, combined treatments for advanced HCC can result in better treatment outcomes owing to their synergistic effects, which requires a multidisciplinary approach. Ongoing studies are examining other therapeutic innovations that can improve disease control and OS rates. Despite improvements in the treatment of advanced HCC, further studies on the optimal treatment selection and sequences, biomarker identification, combination approaches with other therapies, and development of novel immunotherapy agents are required. This review presents the current treatment options and clinical data of the ICI-based combination immunotherapies for advanced HCC from a multidisciplinary perspective.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reduced-Dose or Discontinuation of Bevacizumab Might Be Considered after Variceal Bleeding in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab: Case Reports
Kyeong-Min Yeom, Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(1): 157. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Advances in Systemic Therapy
Insija Ilyas Selene, Merve Ozen, Reema A. Patel
Seminars in Interventional Radiology.2024; 41(01): 056. CrossRef
- Reduced-Dose or Discontinuation of Bevacizumab Might Be Considered after Variceal Bleeding in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab: Case Reports

- Management of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: challenges and strategies for optimal outcomes
- Jae Hyun Yoon, Sung Kyu Choi
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):300-315. Published online September 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.08.27
- 2,148 Views
- 144 Downloads
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
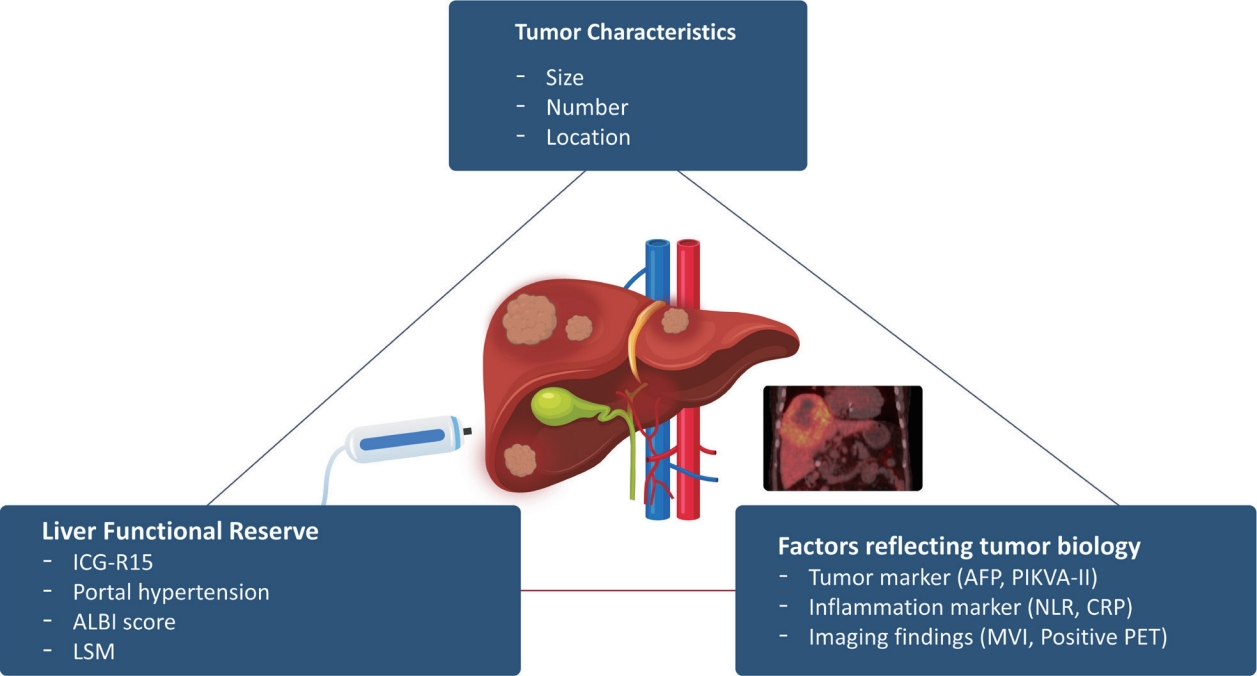
PDF - Although hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is associated with a poor prognosis, management of early-stage HCC is often successful with highly efficacious treatment modalities such as liver transplantation, surgical resection, and radiofrequency ablation. However, unfavorable clinical outcomes have been observed under certain circumstances, even after efficient treatment. Factors that predict unsuitable results after treatment include tumor markers, inflammatory markers, imaging findings reflecting tumor biology, specific outcome indicators for each treatment modality, liver functional reserve, and the technical feasibility of the treatment modalities. Various strategies may overcome these challenges, including the application of reinforced treatment indication criteria with predictive markers reflecting tumor biology, compensation for technical issues with up-to-date technologies, modification of treatment modalities, downstaging with locoregional therapies (such as transarterial chemotherapy or radiotherapy), and recently introduced combination immunotherapies. In this review, we discuss the challenges to achieving optimal outcomes in the management of early-stage HCC and suggest strategies to overcome these obstacles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diosgenin potentiates the anticancer effect of doxorubicin and volasertib via regulating polo-like kinase 1 and triggering apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Eman H. Yousef, Mohamed E. El-Mesery, Maha R. Habeeb, Laila A. Eissa
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef - Radiofrequency for hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 3 cm: potential for applications in daily practice
Ji Hoon Kim, Pil Soo Sung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Efficacy of Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) for Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Moonhyung Lee, Hyun Phil Shin
Medicina.2023; 59(12): 2174. CrossRef
- Diosgenin potentiates the anticancer effect of doxorubicin and volasertib via regulating polo-like kinase 1 and triggering apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells

- Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma using Sonazoid: a comprehensive review
- Woo Kyoung Jeong
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):272-283. Published online September 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.08.25
- 1,167 Views
- 82 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
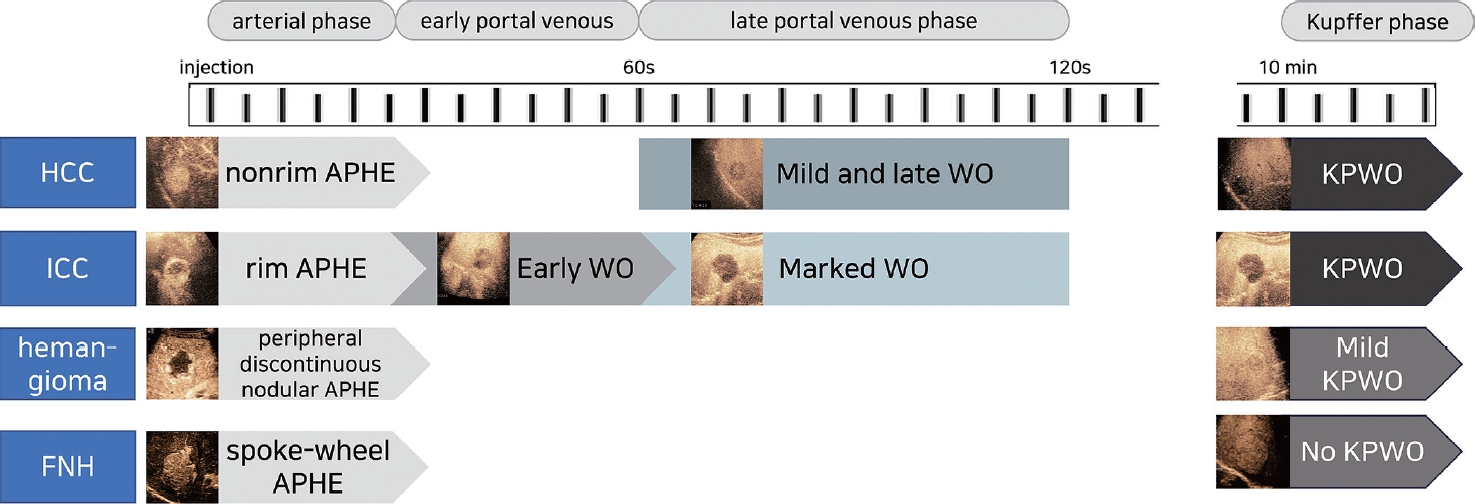
PDF - Sonazoid contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) is a promising technique for the detection and diagnosis of focal liver lesions, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recently, a collaborative effort between the Korean Society of Radiology and Korean Society of Abdominal Radiology resulted in the publication of guidelines for diagnosing HCC using Sonazoid CEUS. These guidelines propose specific criteria for identifying HCC based on the imaging characteristics observed during Sonazoid CEUS. The suggested diagnostic criteria include nonrim arterial phase hyperenhancement, and the presence of late and mild washout, or Kupffer phase washout under the premise that the early or marked washout should not occur during the portal venous phase. These criteria aim to improve the accuracy of HCC diagnosis using Sonazoid CEUS. This review offers a comprehensive overview of Sonazoid CEUS in the context of HCC diagnosis. It covers the fundamental principles of Sonazoid CEUS and its clinical applications, and introduces the recently published guidelines. By providing a summary of this emerging technique, this review contributes to a better understanding of the potential role of Sonazoid CEUS for diagnosing HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sonazoid contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: strengths and shortcomings
Sung Won Lee, Min Kyu Kang, Xiang Zhang
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 238. CrossRef
- Sonazoid contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: strengths and shortcomings

- Imaging prognostication and tumor biology in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Diana Kadi, Marilyn F. Yamamoto, Emily C. Lerner, Hanyu Jiang, Kathryn J. Fowler, Mustafa R. Bashir
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):284-299. Published online September 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.08.29

- 1,982 Views
- 110 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver malignancy, and represents a significant global health burden with rising incidence rates, despite a more thorough understanding of the etiology and biology of HCC, as well as advancements in diagnosis and treatment modalities. According to emerging evidence, imaging features related to tumor aggressiveness can offer relevant prognostic information, hence validation of imaging prognostic features may allow for better noninvasive outcomes prediction and inform the selection of tailored therapies, ultimately improving survival outcomes for patients with HCC.

Original Article
- Clinical outcome of surgical resection for multifocal T2-T3 hepatocellular carcinoma up to 3 nodules: a comparative analysis with a single nodule
- Sehyeon Yu, Hye-Sung Jo, Young-Dong Yu, Yoo jin Choi, Dong-Sik Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):377-388. Published online September 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.08.24

- 626 Views
- 35 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
s: Although the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging system seems to underestimate the impact of curative-intent surgical resection for multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), recent studies have indicated favorable results for the surgical resection of multiple HCC. This study aimed to assess clinical outcomes and feasibility of surgical resection for multifocal HCC with up to three nodules compared with single tumor cases.
Methods
Patients who underwent surgical resection for HCC with up to three nodules between 2009 and 2020 were included, and those with the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) 8th edition, T1 and T4 stages were excluded to reduce differences in disease distribution and severity. Finally, 81 and 52 patients were included in the single and multiple treatment groups, respectively. Short- and long-term outcomes including recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS), were evaluated.
Results
All patients were classified as Child-Pugh class A. RFS and OS were not significantly different between the two groups (P=0.176 and P=0.966, respectively). Multivariate analysis revealed that transfusion and intrahepatic metastasis were significantly associated with recurrence (P=0.046 and P=0.005, respectively). Additionally, intrahepatic metastasis was significantly associated with OS (hazard ratio, 1.989; 95% confidence interval, 1.040-3.802; P=0.038).
Conclusions
Since there was no significant difference in survival between the single and multiple groups among patients with AJCC 8th stage T2 and T3, surgical resection with curative intent could be considered with acceptable long-term survival for selected patients with multiple HCC of up to three nodules.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter