Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Letter to the Editor
- Letter regarding “Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab”
- Sun Hyun Bae, Hee Chul Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):402-404. Published online September 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.08.18
- 667 Views
- 32 Downloads

Original Article
- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
- Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):330-340. Published online May 16, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.04.14
- 1,754 Views
- 112 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
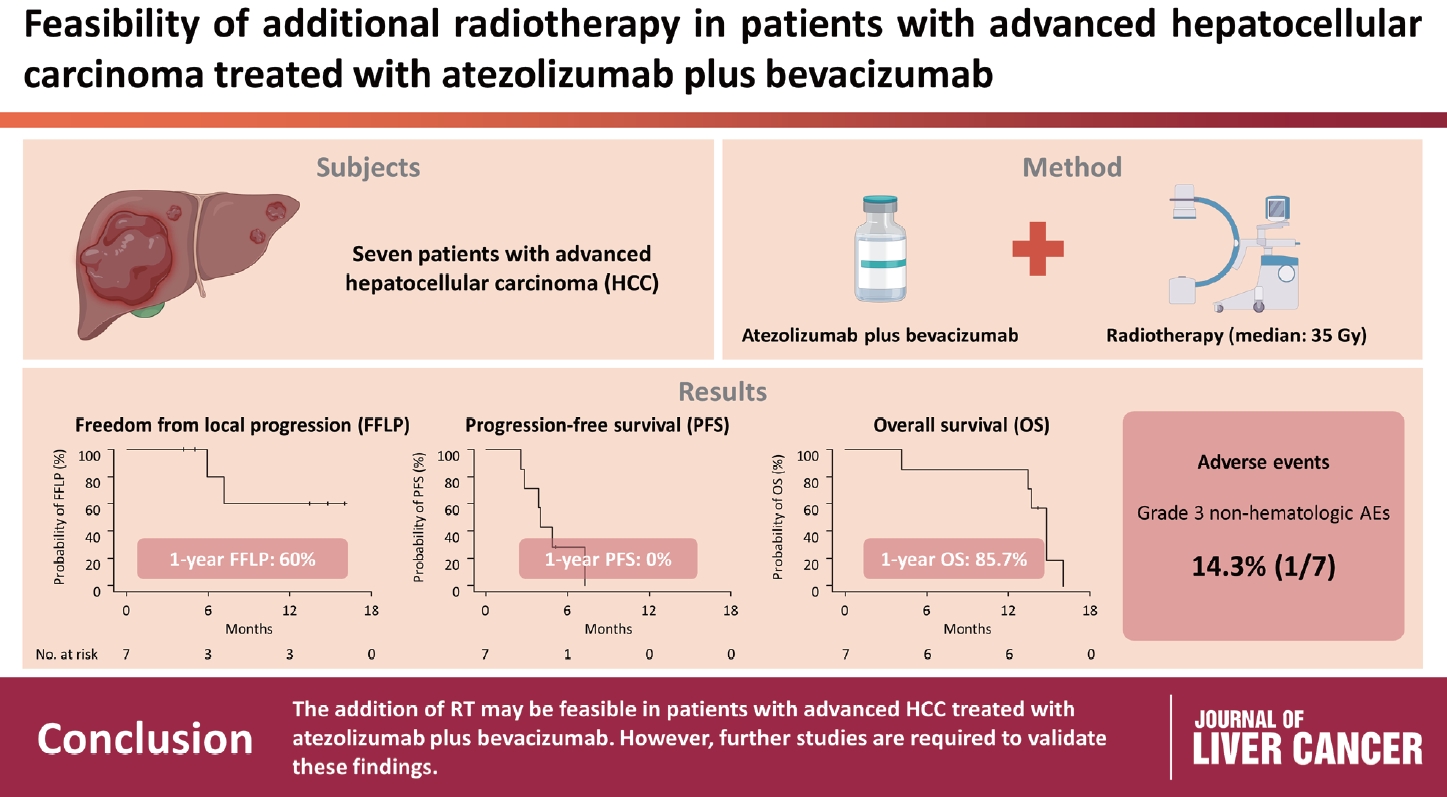
Radiotherapy (RT) is an effective local treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, whether additional RT is safe and effective in patients with advanced HCC receiving atezolizumab plus bevacizumab remains unclear. This retrospective cohort study aimed to evaluate the feasibility of additional RT in these patients.
Methods
Between March and October 2021, we retrospectively analyzed seven patients with advanced HCC who received RT during treatment with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab. The median prescribed RT dose was 35 Gy (range, 33–66). Freedom from local progression (FFLP), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) after RT were analyzed.
Results
The median follow-up duration after RT was 14.2 months (range, 10.0–18.6). Of the seven patients, disease progression was noted in six (85.7%), the sites of disease progression were local in two (28.6%), intrahepatic in four (57.1%), and extrahepatic in four (57.1%). The median time of FFLP was not reached, and PFS and OS times were 4.0 (95% confidence interval [CI], 3.6–4.5) and 14.8% (95% CI, 12.5–17.2) months, respectively. The 1-year FFLP, PFS, and OS rates were 60% (95% CI, 43.8–76.2), 0%, and 85.7% (95% CI, 75.9–95.5), respectively. Grade 3 or higher hematologic adverse events (AEs) were not observed, but grade 3 nonhematologic AEs unrelated to RT were observed in one patient.
Conclusions
The addition of RT may be feasible in patients with advanced HCC treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab. However, further studies are required to validate these findings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Letter regarding “Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab”
Sun Hyun Bae, Hee Chul Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 402. CrossRef
- Letter regarding “Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab”

Case Reports
- Favorable response of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis after radiotherapy combined with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
- Yong Tae Kim, Jina Kim, Jinsil Seong
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):225-229. Published online March 16, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.27

- 1,066 Views
- 69 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Recently, the superiority of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (AteBeva) over sorafenib was proven in the IMbrave150 trial, and AteBeva became the first-line systemic treatment for untreated, unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). While the results are encouraging, more than half of patients with advanced HCC are still being treated in a palliative setting. Radiotherapy (RT) is known to induce immunogenic effects that may enhance the therapeutic efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Herein, we report the case of a patient with advanced HCC with massive portal vein tumor thrombosis treated with a combination of RT and AteBeva, who showed near complete response in tumor thrombosis and favorable response to HCC. Although this is a rare case, it shows the importance of reducing the tumor burden via RT to combination immunotherapy in patients with advanced HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 330. CrossRef - Carbon Ion Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hwa Kyung Byun, Changhwan Kim, Jinsil Seong
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 945. CrossRef
- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab

- A case of nearly complete response in hepatocellular carcinoma with disseminated lung metastasis by combination therapy of nivolumab and ipilimumab after treatment failure of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
- Hyung Jun Kim, Sang Youn Hwang, Jung Woo Im, Ki Jeong Jeon, Wan Jeon
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):213-218. Published online March 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.23

- 945 Views
- 65 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Recently, the efficacy of immuno-oncologic agents for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been proven in several trials. In particular, atezolizumab with bevacizumab (AteBeva), as a first-line therapy for advanced HCC, has shown tremendous advances in the IMBrave150 study. However, second or third-line therapy after treatment failure with AteBeva has not been firmly established. Moreover, clinicians have continued their attempts at multidisciplinary treatment that includes other systemic therapy and radiotherapy (RT). Here, we report a case that showed a near complete response (CR) of lung metastasis to nivolumab with ipilimumab therapy after achieving a near CR of intrahepatic tumor using sorafenib and RT in a patient with advanced HCC who had experienced treatment failure of AteBeva.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Systemic Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: ASCO Guideline Update
John D. Gordan, Erin B. Kennedy, Ghassan K. Abou-Alfa, Eliza Beal, Richard S. Finn, Terence P. Gade, Laura Goff, Shilpi Gupta, Jennifer Guy, Hang T. Hoang, Renuka Iyer, Ishmael Jaiyesimi, Minaxi Jhawer, Asha Karippot, Ahmed O. Kaseb, R. Kate Kelley, Jerem
Journal of Clinical Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Systemic Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: ASCO Guideline Update

- A case of successful surgical treatment for peritoneal seeding of hepatocellular carcinoma after radiotherapy and atezolizumab plus bevacizumab combination treatment
- Yuri Cho, Bo Hyun Kim, Tae Hyun Kim, Young Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):206-212. Published online February 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.09
- 1,446 Views
- 58 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
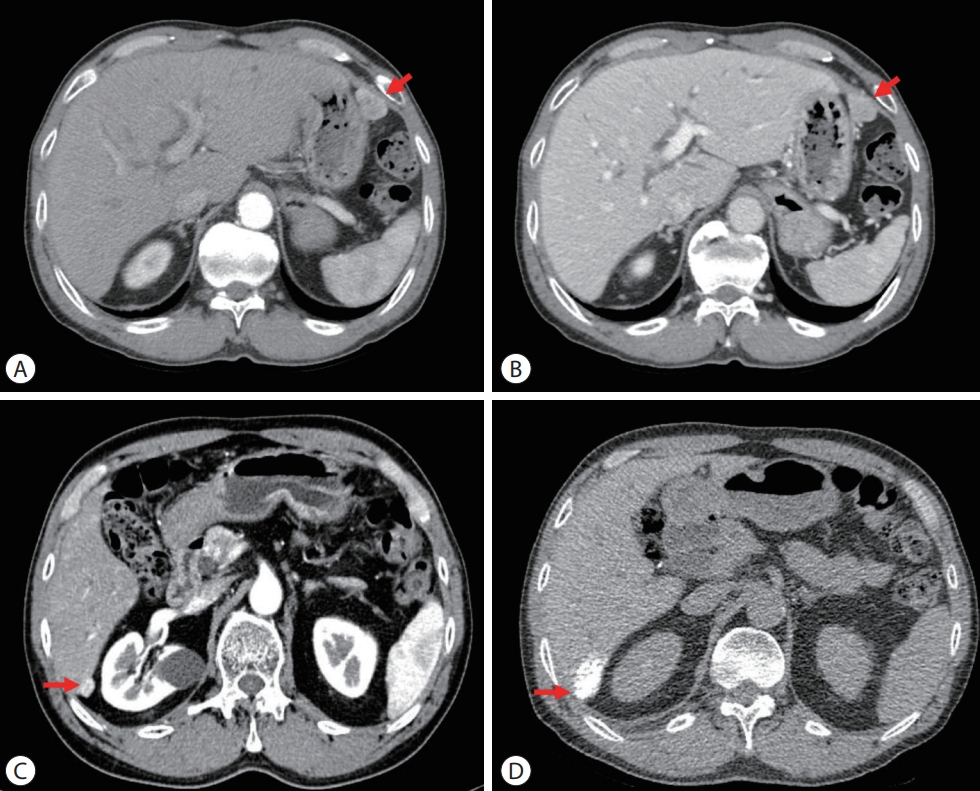
PDF - Peritoneal seeding of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is incurable and has poor prognosis. A 68-year-old man underwent surgical resection for a 3.5 cm single nodular HCC at the tip of segment 3 and transarterial chemoembolization for a 1.5 cm-sized recurrent HCC at the tip of segment 6. 3 months later, an increasing 1 cm pelvic nodule on the rectovesical pouch warranted radiotherapy. Although it stabilized, a new 2.7 cm-sized peritoneal nodule in the right upper quadrant (RUQ) omentum appeared 3.5 years after radiotherapy. Hence, omental mass and small bowel mesentery mass excision were performed. 3 years later, recurrent peritoneal metastases in the RUQ omentum and rectovesical pouch progressed. 33 cycles of atezolizumab and bevacizumab treatment elicited stable disease response. Finally, laparoscopic left pelvic peritonectomy was performed without tumor recurrence. Herein, we present a case of HCC with peritoneal seeding that was successfully treated with surgery after radiotherapy and systemic therapy, leading to complete remission.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 330. CrossRef
- Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab

- Multidisciplinary treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma
- Ahlim Lee, Jaejun Lee, Hyun Yang, Soo-Yoon Sung, Chang Ho Jeon, Su Ho Kim, Moon Hyung Choi, Young Joon Lee, Ho Jong Chun, Si Hyun Bae
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):75-83. Published online March 18, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.04
- 3,944 Views
- 93 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
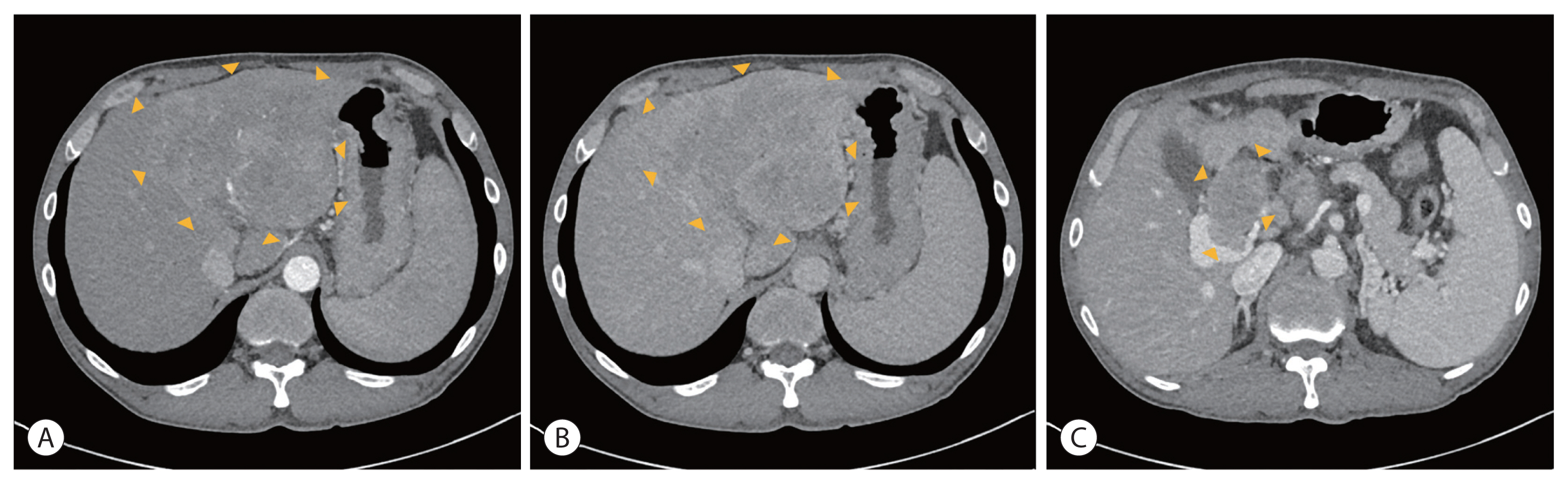
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a cytotoxic chemotherapy-resistant tumor and most HCCs arise in a background of liver cirrhosis of various causes. Although the IMBrave150 trial showed remarkable advancements in the treatment of unresectable HCC with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (AteBeva), therapeutic outcomes were unsatisfactory in more than half of the patients. Accordingly, many ongoing trials combine conventional modalities with new drugs such as immune checkpoint inhibitors for better treatment outcomes, and they are expected to benefit patients with limited responses to conventional treatment. Here, two patients with advanced stage HCC with preserved liver function and good performance status showed partial response after treatment with combination or sequential therapy of AteBeva, hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and transarterial chemoembolization. These findings indicate the efficacy of multidisciplinary treatment against advanced HCC. Additional studies are required to establish optimal treatment strategies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Complications of immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 9. CrossRef - Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 330. CrossRef - Is multidisciplinary treatment effective for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus?
Won Hyeok Choe
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef
- Complications of immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma

- Complete response in hepatocellular carcinoma with lymph node metastasis by combination therapy of atezolizumab and bevacizumab: a case report
- Sang Youn Hwang, Sun Mi Lee, Jeong Woo Lim, Gi Jung Jeon, Hye Won Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):177-180. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.10
- 3,054 Views
- 80 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
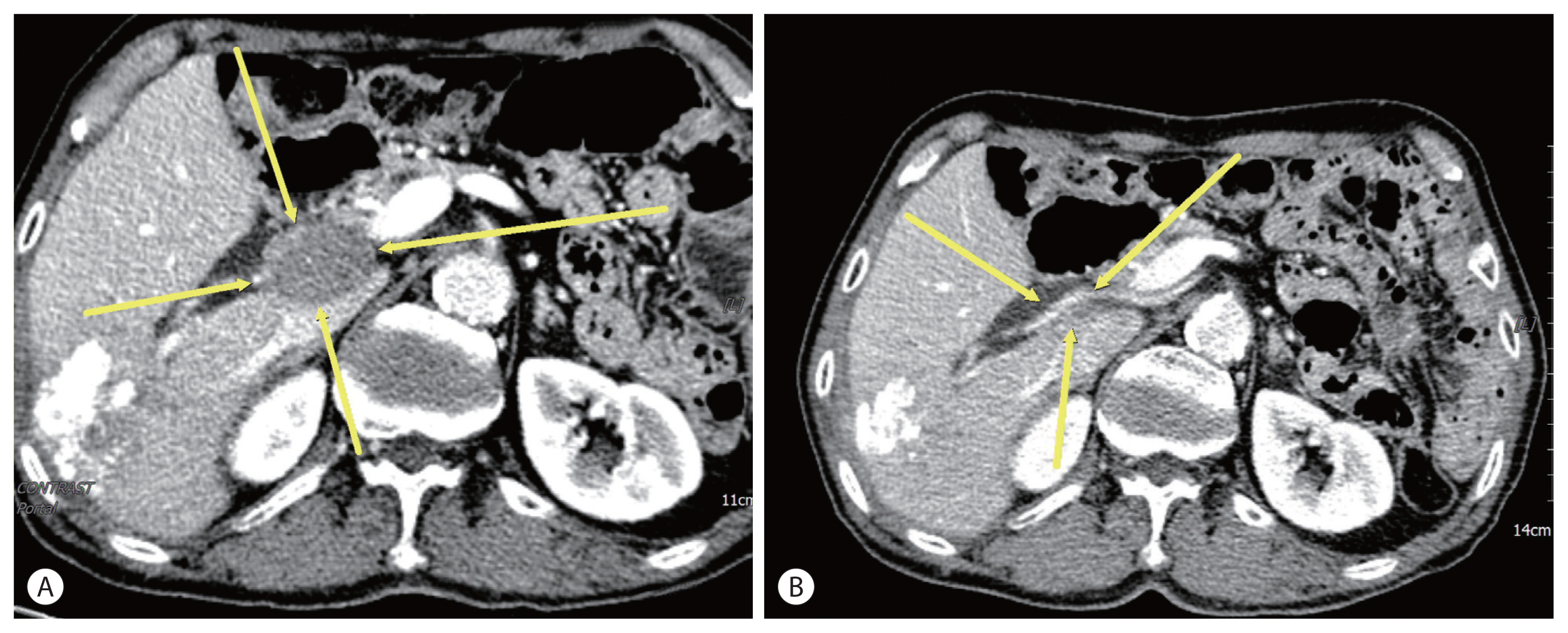
PDF - Sorafenib is the oldest first line systemic treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and has been used exclusively for nearly 10 years. The superiority of administering a combination of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (AteBeva) compared to sorafenib as first line systemic treatment for unresectable HCC was recently proven during the IMbrave150 Phase III randomized trial. While clinicians can expect improved responses and treatment outcomes due to the good results of the IMbrave 150 trial, they must also consider that atezolizumab can cause various immune-related adverse events (IrAEs). Based on the above suggestions, we herein present a case of HCC with lymph node metastasis who achieved complete remission following treatment with AteBeva and developed an IrAE (adrenal insufficiency). Further study of real-life data regarding combination therapy with AteBeva is needed to manage patients with advanced HCC.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter