Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- The Genomic Landscape and Its Clinical Implications in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Sun Young Yim, Ju-Seog Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):97-107. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.97

- 6,457 Views
- 253 Downloads
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a complex process. During the last decade, advances in genomic technologies enabled delineation of the genomic landscape of HCC, resulting in the identification of the common underlying molecular alterations. The tumor microenvironment, regulated by inflammatory cells, including cancer cells, stromal tissues, and the surrounding extracellular matrix, has been extensively studied using molecular data. The integration of molecular, immunological, histopathological, and clinical findings has provided clues to uncover predictive biomarkers to enhance responses to novel therapies. Herein, we provide an overview of the current HCC genomic landscape, previously identified gene signatures that are used routinely to predict prognosis, and an immune-specific class of HCC. Since biomarker-driven treatment is still an unmet need in HCC management, translation of these discoveries into clinical practice will lead to personalized therapies and improve patient care, especially in the era of targeted and immunotherapies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comprehensive clinicopathologic study of alpha fetoprotein‐expression in a large cohort of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Dirk Andreas Ridder, Arndt Weinmann, Mario Schindeldecker, Lana Louisa Urbansky, Kristina Berndt, Tiemo Sven Gerber, Hauke Lang, Johannes Lotz, Karl J. Lackner, Wilfried Roth, Beate Katharina Straub
International Journal of Cancer.2022; 150(6): 1053. CrossRef - Two distinct stem cell‐like subtypes of hepatocellular carcinoma with clinical significance and their therapeutic potentials
Sung Hwan Lee, Yun Seong Jeong, Sunyoung Lee, Bo Hwa Sohn, Ho Kyoung Hwang, Gi Hong Choi, Chang Moo Kang, Jin Sub Choi, Woo Jung Lee, Jae‐Ho Cheong, Hee Jin Jang, Ahmed Kaseb, Lewis Roberts, Sun Young Yim, Yun Shin Chun, Ju‐Seog Lee
Cancer Communications.2022; 42(2): 179. CrossRef - Activated TAZ induces liver cancer in collaboration with EGFR/HER2 signaling pathways
Hyuk Moon, Hyunjung Park, Min Jee Chae, Hye Jin Choi, Do Young Kim, Simon Weonsang Ro
BMC Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Tumor aggressiveness is independent of radiation quality in murine hepatocellular carcinoma and mammary tumor models
Eshwar B. Udho, Shane M. Huebner, Dawn M. Albrecht, Kristina A. Matkowskyj, Linda Clipson, Catigan A. Hedican, Rachel Koth, Santina M. Snow, Emily L. Eberhardt, Devon Miller, Rachel Van Doorn, Genti Gjyzeli, Erin K. Spengler, Douglas R. Storts, Douglas H.
International Journal of Radiation Biology.2021; 97(8): 1140. CrossRef - Infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with multiple lung metastasis completely cured using nivolumab: a case report
Ji Eun Han, Hyo Jung Cho, Soon Sun Kim, Jae Youn Cheong
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(2): 169. CrossRef - Update on Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Brief Review from Pathologist Standpoint
Nese Karadag Soylu
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2020; 51(4): 1176. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma: new provisions of the WHO classification, 5th edition, 2019
E.M. Nepomnyashchaya, A.V. Shaposhnikov, E.A. Yurieva
Arkhiv patologii.2020; 82(6): 36. CrossRef
- Comprehensive clinicopathologic study of alpha fetoprotein‐expression in a large cohort of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma

Case Report
- Sorafenib-induced Pancreatic Pseudocyst in a Patient with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Rare Adverse Event
- Dae-ha Kim, Minkoo Kim, Hyung Joon Yim, Sang Jun Suh, Young Kul Jung
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):154-158. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.154
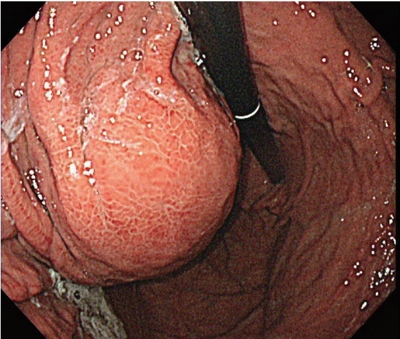
- 3,436 Views
- 47 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 54-year old man diagnosed with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma began treatment with sorafenib. After 3 weeks of treatment, he complained of abdominal pain and nausea. Abdominal sonography showed multiple hepatic lesions only. Serum amylase and lipase levels were 35 U/L and 191 U/L, respectively. The patient was diagnosed with sorafenib-induced acute pancreatitis. After 10 days of discontinuing sorafenib he still complained of nausea and loss of appetite. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed a large bulging lesion, which was suspected to cause extrinsic compression on the high body of the gastric anterior wall. Computed tomography scan revealed a cystic lesion, 8.3 cm in size, in the pancreatic tail, suggesting a pancreatic pseudocyst. After the withdrawal of sorafenib, systemic chemotherapy with Adriamycin and cisplatin was administered. Four months after the discontinuation of sorafenib, the size of the pancreatic pseudocyst decreased from 8.3 cm to 3 cm. The patient's symptoms were also relieved.

Original Article
- Sorafenib Combined with Transarterial-Chemoembolization in Child-Pugh Class B Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jong Sik Lee, Sun Young Moon, Kyung Ann Lee, Jae Ki Min, Sung Jin Jeon, In Ae Kim, Kang Hoon Lee, Won Hyeok Choe, Jeong Han Kim, So Young Kwon
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2014;14(1):31-36. Published online March 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.14.1.31
- 1,256 Views
- 8 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: The aim of the study is to investigate efficacy and safety of sorafenib combined with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in Child-Pugh (CP) class-B patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
A total of 12 CP class-B patients who were initially treated with sorafenib combined with TACE were retrospectively reviewed. At 14 days after the first TACE, patients were continuously treated with sorafenib until unacceptable adverse events (AEs) or diseaseprogression. Consecutive TACEs were also performed, if patients were tolerable.
Results
Of 12 patients, 8, 3 and 1 patients had CP-score 7, 8, and 9, respectively. The median overall survival was 85 days. Patients underwent median 2 sessions of TACE (range 1-4) and the median duration of sorafenib was 48days (range, 12-92 days). Three patients refused repeated TACEs and 4 patients required delay of the consecutive TACE due to AEs of sorafenib. Six patients required transient or permanent discontinuation of sorafenib, due to its AEs (grade 1/2 AEs, 2 patients; grade 3/4 AEs, 4 patients). High CP score (score 8/9 vs. 7) was tended to be association with interruption of sorafenib (P=0.061) and requirement of refusal/ delay of consecutive TACE (P=0.081).
Conclusions
Sorafenib combined with TACE were frequently interrupted or delayed in CP class-B patients, mostly because of its side effects, even though there were not serious. Our experiences suggest that combination with sorafenib and TACE might interface with each other due to its side effects in CP class-B patients, especially patients with CP score 8/9 liver cirrhosis.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter