Most cited
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Most cited
From articles published in Journal of Liver Cancer during the past two years (2022 ~ ).
Guideline
- 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):1-120. Published online December 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.11.07
- 7,732 Views
- 282 Downloads
- 29 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common cancer worldwide and the fourth most common cancer among men in South Korea, where the prevalence of chronic hepatitis B infection is high in middle and old age. The current practice guidelines will provide useful and sensible advice for the clinical management of patients with HCC. A total of 49 experts in the fields of hepatology, oncology, surgery, radiology, and radiation oncology from the Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center Korea Practice Guideline Revision Committee revised the 2018 Korean guidelines and developed new recommendations that integrate the most up-to-date research findings and expert opinions. These guidelines provide useful information and direction for all clinicians, trainees, and researchers in the diagnosis and treatment of HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Contrast-enhanced US for HCC: Finally out from the waiting list?
Richard G. Barr, Luigi Bolondi
Hepatology.2024; 79(2): 267. CrossRef - The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis
Log Young Kim, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Young Chang, Hoongil Jo, Young Youn Cho, Sangheun Lee, Dong Hyeon Lee, Jae Young Jang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential role of Fibrosis‐4 score in hepatocellular carcinoma screening: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Sujeong Shin, Won Sohn, Yoosoo Chang, Yoosun Cho, Min‐Jung Kwon, Sarah H. Wild, Christopher D. Byrne, Seungho Ryu
Hepatology Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress of lncRNA-ATB/miR-141-3p/GP73 Ax-is-Mediated EMT Promoting TACE Refractoriness
棋 耿
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(01): 903. CrossRef - Response to atezolizumab plus bevacizumab specific for lung and lymph node metastases affects survival of patients with HCC
Jiwon Yang, Jonggi Choi, Won‐Mook Choi, Kang Mo Kim, Han Chu Lee, Ju Hyun Shim
Liver International.2024; 44(4): 907. CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef - Management Consensus Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2023 Update on Surveillance, Diagnosis, Systemic Treatment, and Posttreatment Monitoring by the Taiwan Liver Cancer Association and the Gastroenterological Society of Taiwan
Wei Teng, Hung-Wei Wang, Shi-Ming Lin
Liver Cancer.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Complications of immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 9. CrossRef - Liver resection in selective hepatocellular carcinoma with Vp3 or Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis improves prognosis
Manuel Lim, Jongman Kim, Jinsoo Rhu, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 102. CrossRef - Comparison of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
Jeayeon Park, Yun Bin Lee, Yunmi Ko, Youngsu Park, Hyunjae Shin, Moon Haeng Hur, Min Kyung Park, Dae-Won Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Kyung-Hun Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Su Jong Yu, Tae-Yong Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Tae-You Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 81. CrossRef - Programmed Death 1 and Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Protein 4 Gene Expression in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Can Serve as Prognostic Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ji Ah Lee, Hei-Gwon Choi, Hyuk Soo Eun, Jiyoon Bu, Tae Min Jang, Jeongdong Lee, Chae Yeon Son, Min Seok Kim, Woo Sun Rou, Seok Hyun Kim, Byung Seok Lee, Ha Neul Kim, Tae Hee Lee, Hong Jae Jeon
Cancers.2024; 16(8): 1493. CrossRef - Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Steatotic Liver Disease and Its Newly Proposed Subclassification
Byeong Geun Song, Aryoung Kim, Myung Ji Goh, Wonseok Kang, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Dong Hyun Sinn
Liver Cancer.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Diagnostic performance of the 2022 KLCA-NCC criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma on magnetic resonance imaging with extracellular contrast and hepatobiliary agents: comparison with the 2018 KLCA-NCC criteria
Ja Kyung Yoon, Sunyoung Lee, Jeong Ah Hwang, Ji Eun Lee, Seung-seob Kim, Myeong-Jin Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 157. CrossRef - Radiologic features of hepatocellular carcinoma related to prognosis
Shin Hye Hwang, Hyungjin Rhee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 143. CrossRef - Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: a large-scale multicenter study
Sun Hong Yoo, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Han-Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim, Do Seon Song, Seong Hee Kang, Moon Young Kim, Young-Hwan Ahn, Jieun Han, Young Seok Kim, Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, J
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 189. CrossRef - Smoking Increases the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Man Young Park, Eun Ju Cho, Su Jong Yu, Sang Gyune Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Young Seok Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3336. CrossRef - Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2023 Expert Consensus-Based Practical Recommendations of the Korean Liver Cancer Association
Yuri Cho, Jin Woo Choi, Hoon Kwon, Kun Yung Kim, Byung Chan Lee, Hee Ho Chu, Dong Hyeon Lee, Han Ah Lee, Gyoung Min Kim, Jung Suk Oh, Dongho Hyun, In Joon Lee, Hyunchul Rhim
Korean Journal of Radiology.2023; 24(7): 606. CrossRef - Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2023 expert consensus-based practical recommendations of the Korean Liver Cancer Association
Yuri Cho, Jin Woo Choi, Hoon Kwon, Kun Yung Kim, Byung Chan Lee, Hee Ho Chu, Dong Hyeon Lee, Han Ah Lee, Gyoung Min Kim, Jung Suk Oh, Dongho Hyun, In Joon Lee, Hyunchul Rhim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 241. CrossRef - Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2023 Expert consensus-based practical recommendations of the Korean Liver Cancer Association
Yuri Cho, Jin Woo Choi, Hoon Kwon, Kun Yung Kim, Byung Chan Lee, Hee Ho Chu, Dong Hyeon Lee, Han Ah Lee, Gyoung Min Kim, Jung Suk Oh, Dongho Hyun, In Joon Lee, Hyunchul Rhim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(3): 521. CrossRef - Classification of microvascular invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with prognosis and magnetic resonance imaging
Yoon Jung Hwang, Jae Seok Bae, Youngeun Lee, Bo Yun Hur, Dong Ho Lee, Haeryoung Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(3): 733. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma using Sonazoid: a comprehensive review
Woo Kyoung Jeong
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 272. CrossRef - The Current Evidence of Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Won Il Jang, Sunmi Jo, Ji Eun Moon, Sun Hyun Bae, Hee Chul Park
Cancers.2023; 15(20): 4914. CrossRef - Clinical outcome of surgical resection for multifocal T2-T3 hepatocellular carcinoma up to 3 nodules: a comparative analysis with a single nodule
Sehyeon Yu, Hye-Sung Jo, Young-Dong Yu, Yoo jin Choi, Dong-Sik Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 377. CrossRef - Sonazoid contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: strengths and shortcomings
Sung Won Lee, Min Kyu Kang, Xiang Zhang
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 238. CrossRef - Sequential regorafenib or nivolumab therapy in recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma with sorafenib failure in liver transplant patients does not improve prognosis
Jieun Kwon, Jongman Kim, Jinsoo Rhu, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
Annals of Liver Transplantation.2023; 3(2): 104. CrossRef - Concurrent nivolumab and external beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A phase 2 study
Bo Hyun Kim, Hee Chul Park, Tae Hyun Kim, Young-Hwan Koh, Jung Yong Hong, Yuri Cho, Dong Hyun Sinn, Boram Park, Joong-Won Park
JHEP Reports.2023; : 100991. CrossRef - Regular Alpha-Fetoprotein Tests Boost Curative Treatment and Survival for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients in an Endemic Area
Joo Hyun Oh, Jonghyun Lee, Eileen L. Yoon, Soung Won Jeong, Soon Sun Kim, Young Eun Chon, Sang Bong Ahn, Dae Won Jun
Cancers.2023; 16(1): 150. CrossRef - Adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma
Arndt Vogel, Robert C. Grant, Tim Meyer, Gonzalo Sapisochin, Grainne M. O’Kane, Anna Saborowski
Hepatology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Contrast-enhanced US for HCC: Finally out from the waiting list?

Review Articles
- A clinical and pathological update on hepatocellular carcinoma
- Salvatore Lorenzo Renne, Luca Di Tommaso
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):14-22. Published online March 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.18

- 7,658 Views
- 496 Downloads
- 11 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It is estimated that more than 1 million individuals will be affected annually by hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by 2025. HCC can be broadly grouped into two major molecular subgroups, each of which is characterized by specific morphological and phenotypic features that mirror the genetic background. The use of these tissue biomarkers in the daily practice of pathologists promises to better allocate patients with HCC with adequate treatments. In turn, this will likely boost the attitude of clinicians toward obtaining a pre-treatment biopsy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sujin Koo, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Seungeun Ryoo, Jungeun Park, Dong Ah Park
Current Oncology.2024; 31(1): 324. CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef - Identification of gallbladder cancer by direct near-infrared measurement of raw bile combined with two-trace two-dimensional correlation analysis
Eunjin Jang, Woosuk Sohng, Dongho Choi, Hoeil Chung
The Analyst.2023; 148(2): 374. CrossRef - Measurement of Heavy Metal and Antioxidant-Oxidant Levels in Tissues Obtained From Three Different Localizations of Explant Hepatectomy of Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Cemalettin Koc, Sami Akbulut, Kemal Baris Sarici, Muhammed Mehdi Uremis, Ufuk Gunay Dogan, Zeynep Kucukakcali, Ibrahim Umar Garzali, Ertugrul Karabulut, Yusuf Turkoz, Sezai Yilmaz
Transplantation Proceedings.2023; 55(5): 1262. CrossRef - Adding MRI as a Surveillance Test for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis Can Improve Prognosis
Su Jong Yu, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Dong Ho Lee, Su Jin Kim, Eun Ju Cho, Se Hyung Kim, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Yoon Jun Kim, Jeong Min Lee, Jae Young Lee, Jung-Hwan Yoon
Biomedicines.2023; 11(2): 382. CrossRef - Development of a sorafenib-loaded solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system: Formulation optimization and characterization of enhanced properties
Chaemin Lim, Dayoon Lee, Mikyung Kim, Subin Lee, Yuseon Shin, Jacob D. Ramsey, Han-Gon Choi, Eun Seong Lee, Yu Seok Youn, Kyung Taek Oh
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2023; 82: 104374. CrossRef - Validation of MELD 3.0 scoring system in East Asian patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jong-In Chang, Ji Eun Moon, Dong Hyun Sinn, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Liver Transplantation.2023; 29(10): 1029. CrossRef - Higher Number of Tumor-Infiltrating PD-L1+ Cells Is Related to Better Response to Multikinase Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ji Won Han, Ji Hoon Kim, Dong Hyun Kim, Jeong Won Jang, Si Hyun Bae, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Jaegyoon Ahn, Hyun Yang, Pil Soo Sung
Diagnostics.2023; 13(8): 1453. CrossRef - Risk of dyslipidemia in chronic hepatitis B patients taking tenofovir alafenamide: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Eui Gwon Hwang, Eun-Ae Jung, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Hepatology International.2023; 17(4): 860. CrossRef - Recent application of artificial intelligence on histopathologic image-based prediction of gene mutation in solid cancers
Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Kyung Jin Seo, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Kwangil Yim, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang, Chan Kwon Jung, Yosep Chong
Briefings in Bioinformatics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of pelitinib in the regulation of migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via inhibition of Twist1
Sewoong Lee, Eunjeong Kang, Unju Lee, Sayeon Cho
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

- Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: what clinicians need to know
- Jin Woo Choi, Hyo-Cheol Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):4-13. Published online February 23, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.01.16

- 7,503 Views
- 421 Downloads
- 8 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transarterial radioembolization (TARE) with yttrium 90 (90Y) has been used in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) for more than 10 years in Korea. There are two types of 90Y radioactive microspheres available, namely, glass and resin microspheres, with comparable clinical outcomes. In general, TARE outperforms transarterial chemoembolization regarding post-embolization syndrome, time to progression, tumor downsizing for liver transplantation, and hospitalization stay. Although TARE is commonly recommended for patients with unresectable large HCCs, it can be an alternative to or performed in combination with ablation, surgical resection, and systemic treatment. This review aimed to address 90Y radioactive microspheres, patient selection, clinical outcomes, simulation tests, radioembolization procedures, follow-up imaging, and complications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unlocking Precision in Radioembolization: Navigating the Future of Holmium-166 Radioembolization Mapping and Lung Shunt Study by Implementing Scout Dosimetry
Peiman Habibollahi, Armeen Mahvash, Nima Kokabi, Nariman Nezami
CardioVascular and Interventional Radiology.2024; 47(4): 451. CrossRef - Feasibility of Liver Transplantation after 90Y Radioembolization: Lessons from a Radiation Protection Incident
Marine Soret, Jacques-Antoine Maisonobe, Philippe Maksud, Stéphane Payen, Manon Allaire, Eric Savier, Charles Roux, Charlotte Lussey-Lepoutre, Aurélie Kas
Health Physics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Liver-Directed Locoregional Therapies for Neuroendocrine Liver Metastases: Recent Advances and Management
Cody R. Criss, Mina S. Makary
Current Oncology.2024; 31(4): 2076. CrossRef - Transarterial chemoembolization as an alternative to radioembolization is associated with earlier tumor recurrence than in radioembolization-eligible patients
Sung Won Chung, Heejin Cho, Hyunjae Shin, Jeayeon Park, Ju Yeon Kim, Ji Hoon Hong, Moon Haeng Hur, Min Kyung Park, Yun Bin Lee, Su Jong Yu, Myungsu Lee, Yoon Jun Kim, Jin Chul Paeng, Jung-Hwan Yoon, Jin Wook Chung, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Hyo-Cheol Kim
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The evolution of immune checkpoint inhibitor combinations in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma – A systematic review
Brandon M. Meyers, Jennifer J. Knox, David M. Liu, Deanna McLeod, Ravi Ramjeesingh, Vincent C. Tam, Howard J. Lim
Cancer Treatment Reviews.2023; 118: 102584. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Image-Guided Locoregional Therapies for Primary Liver Tumors
Cody R. Criss, Mina S. Makary
Biology.2023; 12(7): 999. CrossRef - Multidisciplinary consensus recommendations for management of hepatocellular carcinoma in Middle East and North Africa region
Imam Waked, Sherif Alsammany, Sayed Hammad Tirmazy, Kakil Rasul, Jafar Bani‐Issa, Wael Abdel‐Razek, Ashraf Omar, Amr Shafik, Salem Eid, Amr Abdelaal, Ahmed Hosni, Gamal Esmat
Liver International.2023; 43(10): 2062. CrossRef - Impact of Low Skeletal Muscle Mass on Long-Term Outcomes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Trans-Arterial Radioembolization: A Retrospective Multi-Center Study
Heechul Nam, Hyun Yang, Ho Soo Chun, Han Ah Lee, Joon Yeul Nam, Jeong Won Jang, Yeon Seok Seo, Do Young Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Si Hyun Bae
Cancers.2023; 15(21): 5195. CrossRef
- Unlocking Precision in Radioembolization: Navigating the Future of Holmium-166 Radioembolization Mapping and Lung Shunt Study by Implementing Scout Dosimetry

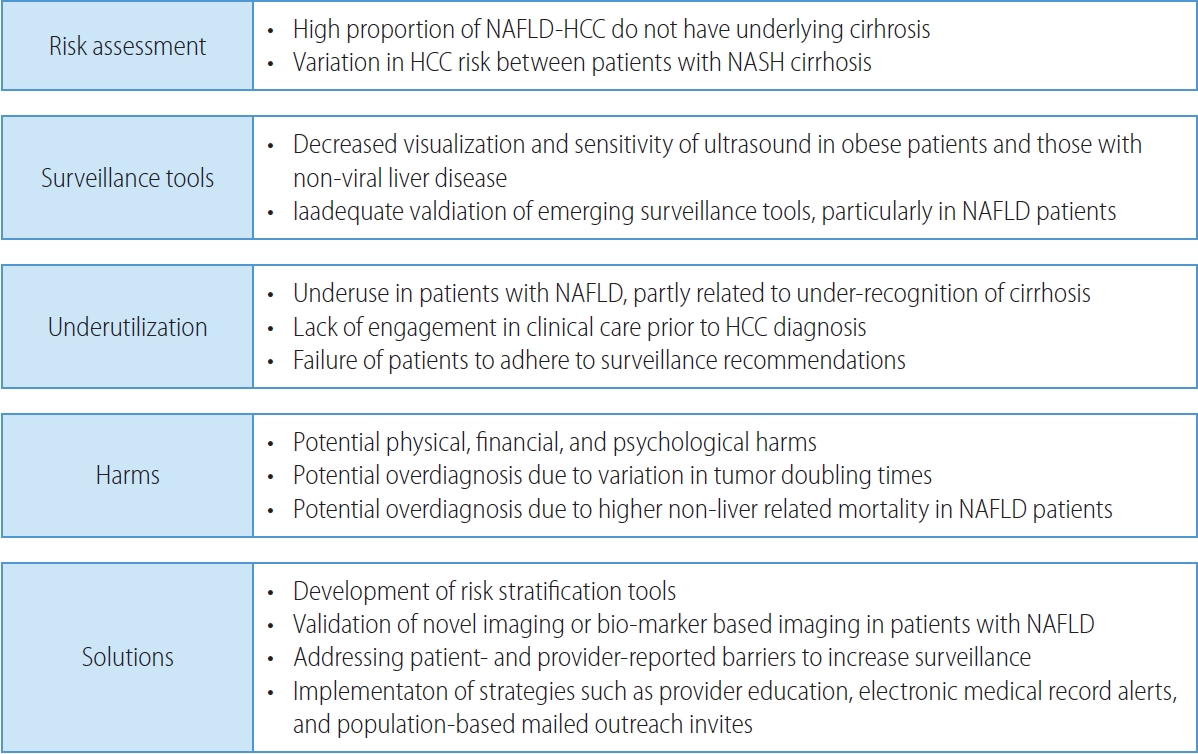
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma
- Darine Daher, Karim Seif El Dahan, Amit G. Singal
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):127-142. Published online February 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.12.30
- 3,188 Views
- 168 Downloads
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), one of the most common causes of liver disease, is an increasingly common cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Several demographic, clinical, and genetic factors contribute to HCC risk in NAFLD patients, which may inform risk stratification scores. Proven efficacious approaches to primary prevention approach in patients with non-viral liver disease remain an area of need. Semi-annual surveillance is associated with improved early tumor detection and reduced HCC-related mortality; however, patients with NAFLD have several challenges to effective surveillance, including under-recognition of at-risk patients, low surveillance utilization in clinical practice, and lower sensitivity of current tools for early-stage HCC detection. Treatment decisions are best made in a multidisciplinary fashion and are informed by several factors including tumor burden, liver dysfunction, performance status, and patient preferences. Although patients with NAFLD often have larger tumor burden and increased comorbidities compared to counterparts, they can achieve similar post-treatment survival with careful patient selection. Therefore, surgical therapies continue to provide a curative treatment option for patients diagnosed at an early stage. Although there has been debate about the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with NAFLD, current data are insufficient to change treatment selection based on liver disease etiology.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Overnutrition and Lipotoxicity: Impaired Efferocytosis and Chronic Inflammation as Precursors to Multifaceted Disease Pathogenesis
Vivek Mann, Alamelu Sundaresan, Shishir Shishodia
Biology.2024; 13(4): 241. CrossRef - Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Steatotic Liver Disease and Its Newly Proposed Subclassification
Byeong Geun Song, Aryoung Kim, Myung Ji Goh, Wonseok Kang, Geum-Youn Gwak, Yong-Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Dong Hyun Sinn
Liver Cancer.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Smoking Increases the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Man Young Park, Eun Ju Cho, Su Jong Yu, Sang Gyune Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Young Seok Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3336. CrossRef - Reply: Validation of MELD 3.0 scoring system in East Asian patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim
Liver Transplantation.2023; 29(11): E38. CrossRef - Unraveling the Janus-Faced Role of Autophagy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Implications for Therapeutic Interventions
Thi Ha Nguyen, Tuan Minh Nguyen, Dinh Thi Minh Ngoc, Taesik You, Mi Kyung Park, Chang Hoon Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(22): 16255. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter, Propensity Score Study
Ji Kim, Hee-Chul Nam, Chang-Wook Kim, Hee Cho, Jae-Sung Yoo, Ji Han, Jeong Jang, Jong Choi, Seung Yoon, Hyun Yang, Si Bae, Suho Kim, Jung Oh, Ho Chun, Chang Jeon, Jaegyoon Ahn, Pil Sung
Cancers.2023; 15(17): 4233. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Overnutrition and Lipotoxicity: Impaired Efferocytosis and Chronic Inflammation as Precursors to Multifaceted Disease Pathogenesis

Original Article
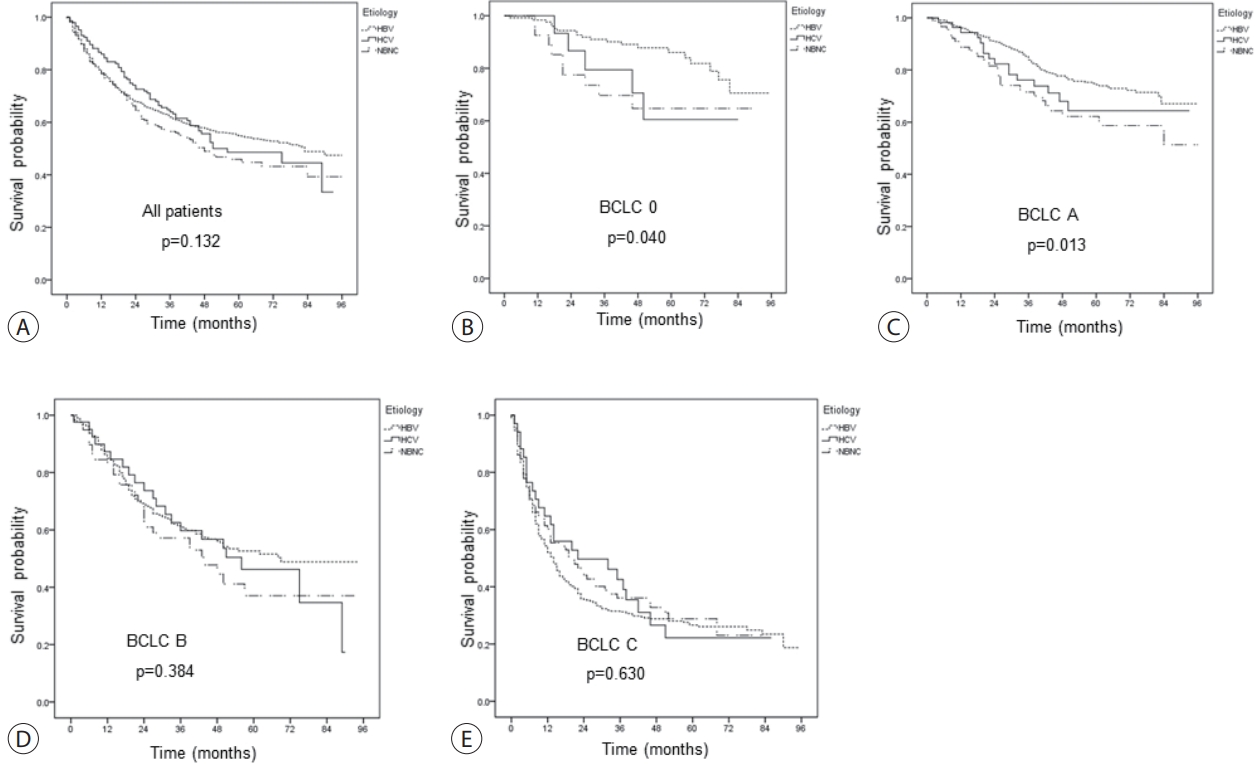
- Clinical characteristics and prognosis of Korean patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with respect to etiology
- Wonjoon Jang, Hye Won Lee, Jae Seung Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):158-166. Published online September 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.09.18
- 2,741 Views
- 65 Downloads
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
The profile of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has changed globally; the role of etiology in predicting prognosis of HCC patients remains unclear. We aimed to analyze the characteristics and prognosis of Korean patients with HCC according to disease etiology.
Methods
This retrospective observational study included patients diagnosed with HCC between 2010 and 2014 in a single center in Korea. Patients with HCC aged <19 years old, had coinfection with other viral hepatitis, had missing follow-up data, were Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage D, or died before 1 month were excluded.
Results
A total of 1,595 patients with HCC were analyzed; they were classified into the hepatitis B virus (HBV) group (1,183 [74.2%]), hepatitis C virus (HCV) group (146 [9.2%]), and non-B non-C (NBNC) group (266 [16.7%]). The median overall survival of all patients was 74 months. The survival rates at 1, 3, and 5 years were 78.8%, 62.0% and 54.9% in the HBV group; 86.0%, 64.0%, and 48.6% in the HCV group; and 78.4%, 56.5%, and 45.9% in the NBNC group, respectively. NBNC-HCC has a poorer prognosis than other causes of HCC. Survival was significantly longer in the HBV group with early-stage HCC than in the NBNC group. Furthermore, survival was shorter in patients with early-stage HCC and diabetes mellitus (DM) than in those without DM.
Conclusions
The etiology of HCC affected clinical characteristics and prognosis to some extent. NBNC-HCC patients showed shorter overall survival than viral-related HCC patients. Additionally, the presence of DM is an additional important prognostic factor in patients with early-stage HCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis
Log Young Kim, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Young Chang, Hoongil Jo, Young Youn Cho, Sangheun Lee, Dong Hyeon Lee, Jae Young Jang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef - Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis Followed by Acute Hepatitis A Infection: Case Report
Min-Woo An, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jin Kuk Kim, Ahrim Moon, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Medicina.2023; 59(5): 819. CrossRef - Validation of MELD 3.0 scoring system in East Asian patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jong-In Chang, Ji Eun Moon, Dong Hyun Sinn, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Liver Transplantation.2023; 29(10): 1029. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Statin use and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with chronic hepatitis B: an emulated target trial using longitudinal nationwide population cohort data
Dong Hyun Sinn, Danbee Kang, Yewan Park, Hyunsoo Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Juhee Cho, Geum-Youn Gwak
BMC Gastroenterology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Addition of Kidney Dysfunction Type to MELD-Na for the Prediction of Survival in Cirrhotic Patients Awaiting Liver Transplantation in Comparison with MELD 3.0 with Albumin
Kyeong-Min Yeom, Jong-In Chang, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Ji Eun Moon, Dong Hyun Sinn, Young Seok Kim, Sang Gyune Kim
Diagnostics.2023; 14(1): 39. CrossRef
- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis

Review Articles
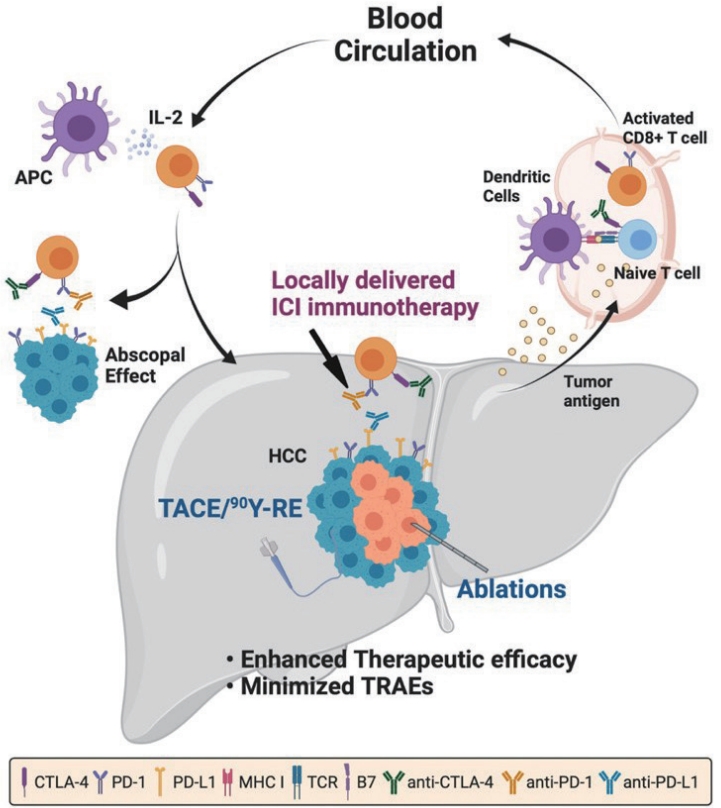
- Combination of interventional oncology local therapies and immunotherapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Dong-Hyun Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):93-102. Published online April 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.28
- 5,192 Views
- 165 Downloads
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Interventional oncology (IO) local therapies of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can activate anti-cancer immunity and it is potentially leading to an anti-cancer immunity throughout the body. For the development of an effective HCC treatment regime, great emphasis has been dedicated to different IO local therapy mediated immune modulation and possible combinations with immune checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. In this review paper, we summarize the status of combination of IO local therapy and immunotherapy, as well as the prospective role of therapeutic carriers and locally administered immunotherapy in advanced HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reduced-Dose or Discontinuation of Bevacizumab Might Be Considered after Variceal Bleeding in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab: Case Reports
Kyeong-Min Yeom, Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(1): 157. CrossRef - CT-guided high dose rate brachytherapy can induce multiple systemic proteins of proliferation and angiogenesis predicting outcome in HCC
Lukas Salvermoser, Shraga Nahum Goldberg, Marianna Alunni-Fabbroni, Philipp Maximilian Kazmierczak, Moritz Nikolaus Gröper, Jan Niklas Schäfer, Elif Öcal, Tanja Burkard, Stefanie Corradini, Najib Ben Khaled, Agnese Petrera, Moritz Wildgruber, Jens Ricke,
Translational Oncology.2024; 43: 101919. CrossRef - Complications of immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 9. CrossRef - Syngeneic N1-S1 Orthotopic Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Sprague Dawley Rat for the Development of Interventional Oncology-Based Immunotherapy: Survival Assay and Tumor Immune Microenvironment
Bongseo Choi, Jason Pe, Bo Yu, Dong-Hyun Kim
Cancers.2023; 15(3): 913. CrossRef - Preclinical Development and Validation of Translational Temperature Sensitive Iodized Oil Emulsion Mediated Transcatheter Arterial Chemo‐Immuno‐Embolization for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Heegon Kim, Bongseo Choi, Samdeep K. Mouli, Hyunjun Choi, Kathleen R. Harris, Laura M. Kulik, Robert J. Lewandowski, Dong‐Hyun Kim
Advanced Healthcare Materials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Current Evidence of Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Won Il Jang, Sunmi Jo, Ji Eun Moon, Sun Hyun Bae, Hee Chul Park
Cancers.2023; 15(20): 4914. CrossRef - Inducing the Abscopal Effect in Liver Cancer Treatment: The Impact of Microwave Ablation Power Levels and PD-1 Antibody Therapy
Changli Liao, Guiyuan Zhang, Ruotong Huang, Linyuan Zeng, Bin Chen, Haitao Dai, Keyu Tang, Run Lin, Yonghui Huang
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(12): 1672. CrossRef
- Reduced-Dose or Discontinuation of Bevacizumab Might Be Considered after Variceal Bleeding in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab: Case Reports

- Liquid biopsy for early detection and therapeutic monitoring of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Eun-Ji Choi, Young-Joon Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):103-114. Published online September 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.09.08
- 3,533 Views
- 138 Downloads
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
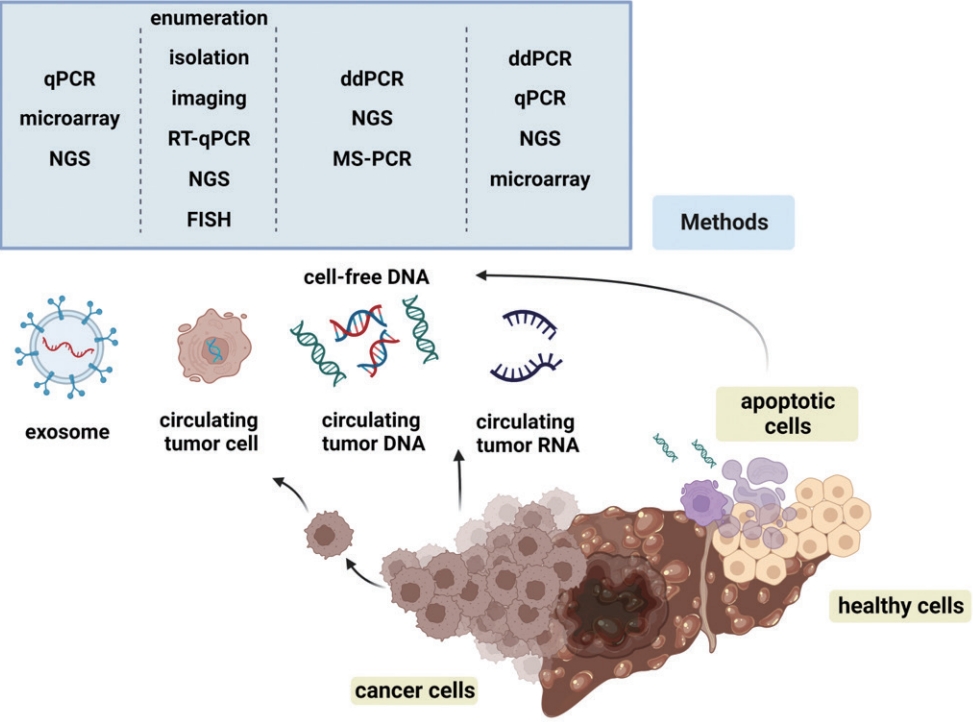
Supplementary Material - Advances in our knowledge of the molecular characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have enabled significant progress in the detection and therapeutic prediction of HCC. As a non-invasive alternative to tissue biopsy, liquid biopsy examines circulating cellular components such as exosomes, nucleic acids, and cell-free DNA found in body fluids (e.g., urine, saliva, ascites, and pleural effusions) and provides information about tumor characteristics. Technical advances in liquid biopsy have led to the increasing adoption of diagnostic and monitoring applications for HCC. This review summarizes the various analytes, ongoing clinical trials, and case studies of United States Food and Drug Administrationapproved in vitro diagnostic applications for liquid biopsy, and provides insight into its implementation in managing HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomarcatori tumorali: tra diagnostica clinica e medicina di precisione
Rossana FRANZIN
La Rivista Italiana della Medicina di Laboratorio.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - 16S rRNA Next-Generation Sequencing May Not Be Useful for Examining Suspected Cases of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
Chan Jin Yang, Ju Sun Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Keun Woo Park, Jina Yun, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(2): 289. CrossRef - Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: a large-scale multicenter study
Sun Hong Yoo, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Han-Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim, Do Seon Song, Seong Hee Kang, Moon Young Kim, Young-Hwan Ahn, Jieun Han, Young Seok Kim, Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, J
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 189. CrossRef - Correspondence on Letter regarding “Long-term prognosis and the need for histologic assessment of chronic hepatitis B in the serological immune tolerant phase”
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(2): 513. CrossRef - Exploring the Role of Circulating Cell-Free RNA in the Development of Colorectal Cancer
Chau-Ming Kan, Xiao Meng Pei, Martin Ho Yin Yeung, Nana Jin, Simon Siu Man Ng, Hin Fung Tsang, William Chi Shing Cho, Aldrin Kay-Yuen Yim, Allen Chi-Shing Yu, Sze Chuen Cesar Wong
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(13): 11026. CrossRef
- Biomarcatori tumorali: tra diagnostica clinica e medicina di precisione

Original Article
- Stereotactic body radiation therapy for elderly patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective observational study
- Jeong Yun Jang, Jinhong Jung, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Jin-hong Park, Sang Min Yoon
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):136-145. Published online September 16, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.08.18
- 2,943 Views
- 73 Downloads
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
We aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in elderly patients with small hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC).
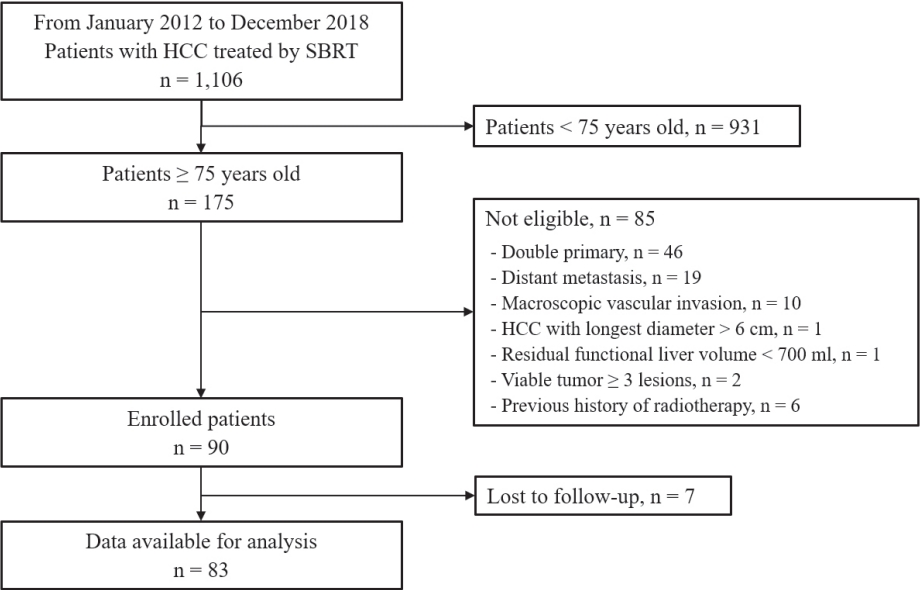
Methods
Eighty-three patients (89 lesions) with HCC who underwent SBRT between January 2012 and December 2018 were reviewed in this retrospective observational study. The key inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) age ≥75 years, 2) contraindications for hepatic resection or percutaneous ablative therapies, 3) no macroscopic vascular invasion, and 4) no extrahepatic metastasis.
Results
The patients were 75-90 years of age, and 49 (59.0%) of them were male. Most patients (94.0%) had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 or 1. Seventy-four patients (89.2%) had Child-Pugh class A hepatic function before SBRT. The median tumor size was 1.6 cm (range, 0.7-3.5). The overall median follow-up period was 34.8 months (range, 7.3-99.3). The 5-year local tumor control rate was 90.1%. The 3-year and 5-year overall survival rate was 57.1% and 40.7%, respectively. Acute toxicity grade ≥3 was observed in three patients (3.6%) with elevated serum hepatic enzymes; however, no patient experienced a worsening of the Child-Pugh score to ≥2 after SBRT. None of the patients developed late toxicity (grade ≥3).
Conclusions
SBRT is a safe treatment option with a high local control rate in elderly patients with small HCC who are not eligible for other curative treatments. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sujin Koo, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Seungeun Ryoo, Jungeun Park, Dong Ah Park
Current Oncology.2024; 31(1): 324. CrossRef - Radiotherapy trend in elderly hepatocellular carcinoma: retrospective analysis of patients diagnosed between 2005 and 2017
Bong Kyung Bae, Jeong Il Yu, Hee Chul Park, Myung Ji Goh, Yong-Han Paik
Radiation Oncology Journal.2023; 41(2): 98. CrossRef - Loco-regional therapies competing with radiofrequency ablation in potential indications for hepatocellular carcinoma: a network meta-analysis
Ha Il Kim, Jihyun An, Seungbong Han, Ju Hyun Shim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 1013. CrossRef - Has the growing evidence of radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma increased the use of radiotherapy in elderly patients?
Tae Hyun Kim
Radiation Oncology Journal.2023; 41(3): 141. CrossRef - Chronic Liver Disease in the Older Patient—Evaluation and Management
Daniel Anthony DiLeo, Tolga Gidener, Ayse Aytaman
Current Gastroenterology Reports.2023; 25(12): 390. CrossRef
- Radiofrequency Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Elderly Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

Review Article
- Management of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: challenges and strategies for optimal outcomes
- Jae Hyun Yoon, Sung Kyu Choi
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):300-315. Published online September 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.08.27
- 2,149 Views
- 144 Downloads
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
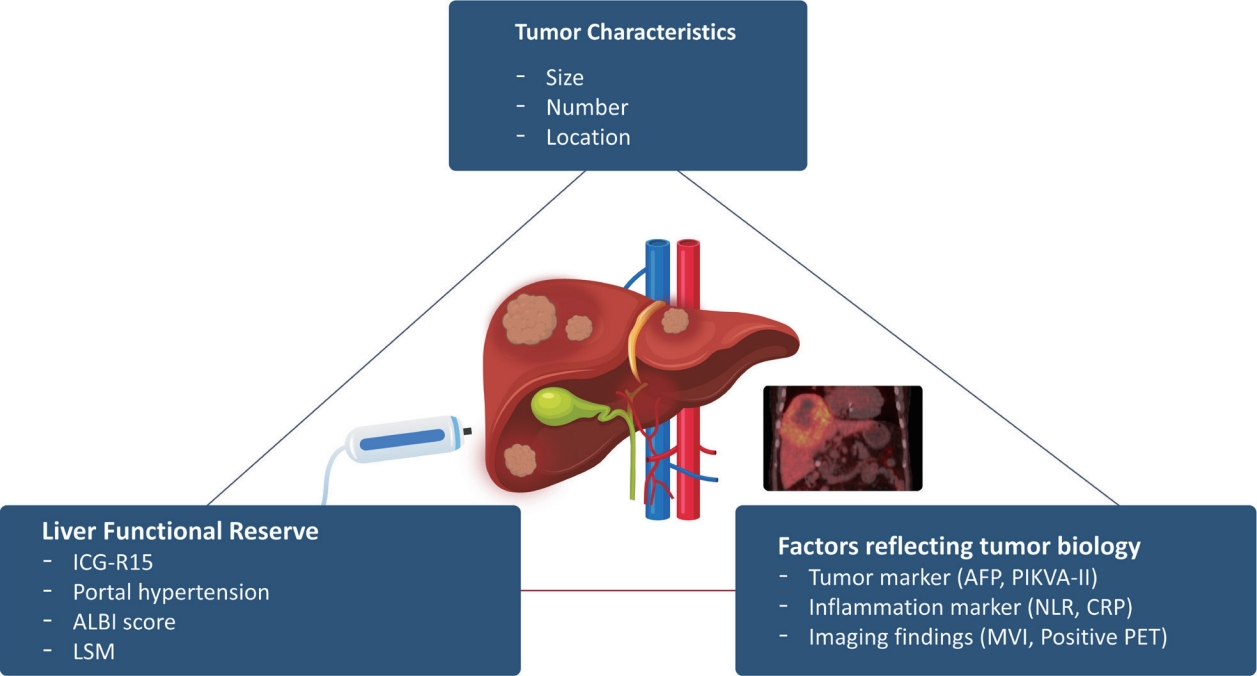
PDF - Although hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is associated with a poor prognosis, management of early-stage HCC is often successful with highly efficacious treatment modalities such as liver transplantation, surgical resection, and radiofrequency ablation. However, unfavorable clinical outcomes have been observed under certain circumstances, even after efficient treatment. Factors that predict unsuitable results after treatment include tumor markers, inflammatory markers, imaging findings reflecting tumor biology, specific outcome indicators for each treatment modality, liver functional reserve, and the technical feasibility of the treatment modalities. Various strategies may overcome these challenges, including the application of reinforced treatment indication criteria with predictive markers reflecting tumor biology, compensation for technical issues with up-to-date technologies, modification of treatment modalities, downstaging with locoregional therapies (such as transarterial chemotherapy or radiotherapy), and recently introduced combination immunotherapies. In this review, we discuss the challenges to achieving optimal outcomes in the management of early-stage HCC and suggest strategies to overcome these obstacles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diosgenin potentiates the anticancer effect of doxorubicin and volasertib via regulating polo-like kinase 1 and triggering apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Eman H. Yousef, Mohamed E. El-Mesery, Maha R. Habeeb, Laila A. Eissa
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef - Radiofrequency for hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 3 cm: potential for applications in daily practice
Ji Hoon Kim, Pil Soo Sung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Efficacy of Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) for Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Moonhyung Lee, Hyun Phil Shin
Medicina.2023; 59(12): 2174. CrossRef
- Diosgenin potentiates the anticancer effect of doxorubicin and volasertib via regulating polo-like kinase 1 and triggering apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells

Original Article
- Effect of direct-acting antivirals for hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence and death after curative treatment
- Young-Hwan Ahn, Heirim Lee, Ji Eun Han, Hyo Jung Cho, Jae Youn Cheong, Bumhee Park, Soon Sun Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):125-135. Published online June 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.05.24
- 2,960 Views
- 78 Downloads
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
There has been a long-standing debate about the association of directacting antiviral (DAA) therapy and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) recurrence. This study aimed to investigate the association between DAA therapy and HCC recurrence after curative therapy.
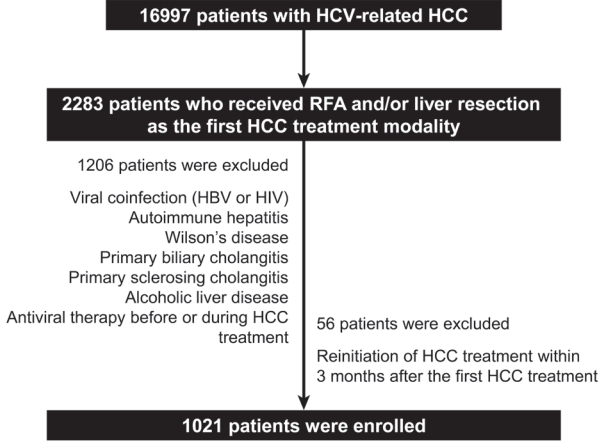
Methods
We retrospectively enrolled 1,021 patients with HCV-related (hepatitis C virus) HCC who underwent radiofrequency ablation (RFA), liver resection, or both as the first treatment modality from January 2007 to December 2016 and without a history of HCV therapy before HCC treatment from a nationwide database. The effect of HCV treatment on HCC recurrence and all-cause mortality was also investigated.
Results
Among the 1,021 patients, 77 (7.5%) were treated with DAA, 14 (1.4%) were treated with interferon-based therapy, and 930 (91.1%) did not receive HCV therapy. DAA therapy was an independent prognostic factor for lower HCC recurrence rate (hazard ratio [HR], 0.04; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.006-0.289; P=0.001 for landmarks at 6 months after HCC treatment and HR, 0.05; 95% CI, 0.007-0.354; P=0.003 for landmarks at 1 year). Furthermore, DAA therapy was associated with lower all-cause mortality (HR, 0.049; 95% CI, 0.007-0.349; P=0.003 for landmarks at 6 months and HR, 0.063; 95% CI, 0.009-0.451; P=0.006 for landmarks at 1 year).
Conclusions
DAA therapy after curative HCC treatment can decrease HCC recurrence and all-cause mortality compared to interferon-based therapy or no antiviral therapy. Therefore, clinicians should consider administering DAA therapy after curative HCC treatment in patients with HCV-related HCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef - Analyzing risk factors and developing a stratification system for hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after interferon-free direct-acting antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients
Chih-Hsuan Luan, Pin-Shuo Su, Chi-Jen Chu, Chung-Chi Lin, Chien-Wei Su, Jiing-Chyuan Luo, I-Cheng Lee, Chen-Ta Chi, Shou-Dong Lee, Yuan-Jen Wang, Fa-Yauh Lee, Yi-Hsiang Huang, Ming-Chih Hou
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2024; 87(4): 357. CrossRef - Addition of Kidney Dysfunction Type to MELD-Na for the Prediction of Survival in Cirrhotic Patients Awaiting Liver Transplantation in Comparison with MELD 3.0 with Albumin
Kyeong-Min Yeom, Jong-In Chang, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Ji Eun Moon, Dong Hyun Sinn, Young Seok Kim, Sang Gyune Kim
Diagnostics.2023; 14(1): 39. CrossRef - Is direct-acting antiviral treatment beneficial or harmful for patients with hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma?
Hye Won Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(2): 91. CrossRef
- Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma

Case Report
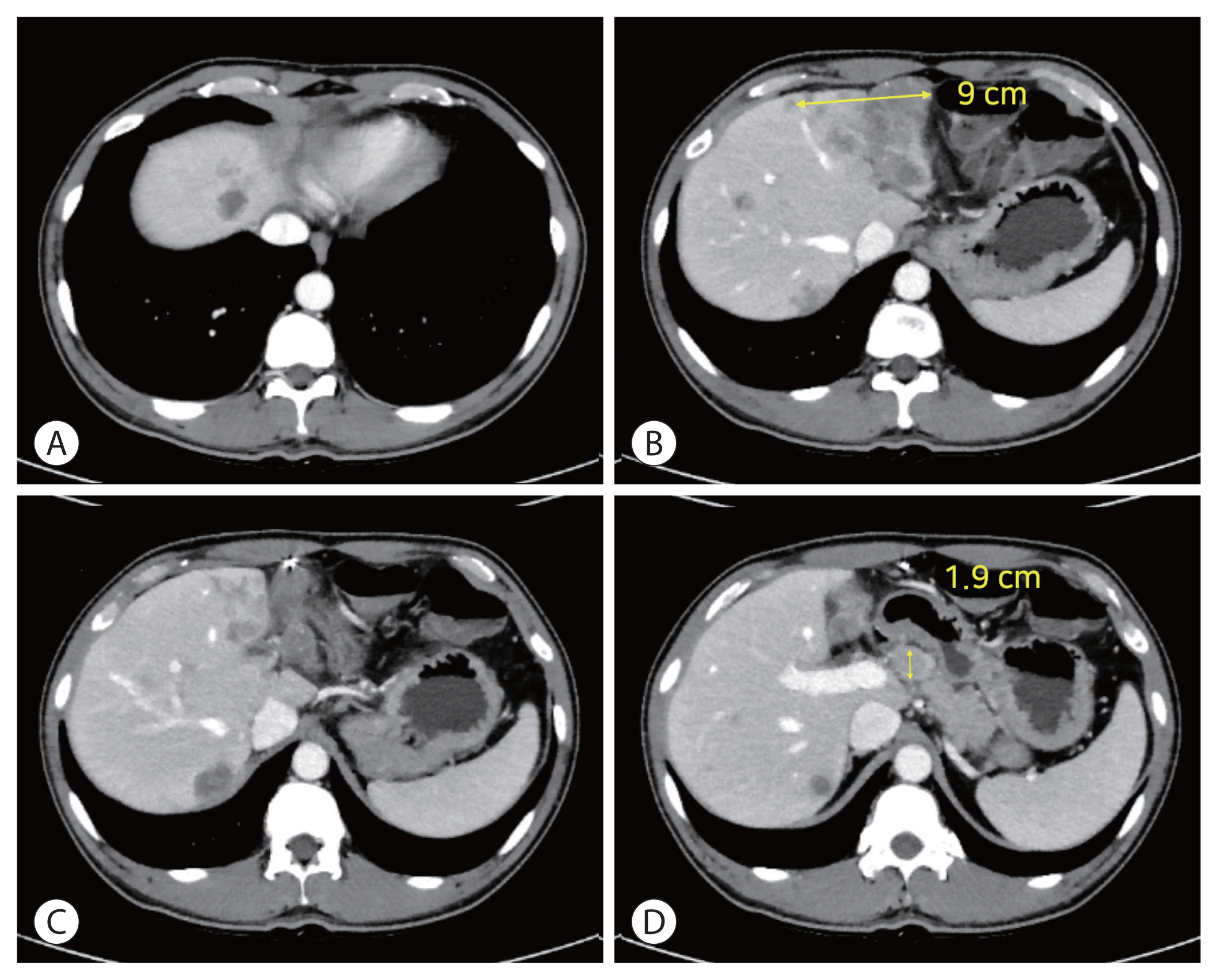
- Concurrent transarterial radioembolization and combination atezolizumab/ bevacizumab treatment of infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: a case report
- Min Kyung Park, Su Jong Yu
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):69-74. Published online March 21, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.09
- 3,259 Views
- 106 Downloads
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Treatment options for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have been rapidly evolving. Herein, we describe a patient with advanced HCC and portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) who responded decisively to a multidisciplinary approach. The patient had an ill-defined infiltrative HCC (diffuse subtype), with several intrahepatic metastasis and tumor invasion of left portal vein. Concurrent use of transarterial radioembolization (TARE) and systemic therapeutics (atezolizumab + bevacizumab) ultimately proved successful. There was marked reduction in tumor volume after TARE and an additional three cycles of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab. This concurrent treatment was well tolerated, without adverse events during immunotherapy. The impressive results achieved suggest that concurrent TARE and combination atezolizumab/bevacizumab is a promising treatment approach for advanced HCC with PVTT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biologics, Immunotherapies, and Cytotoxic Chemotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma following Current Recommendations by the BCLC: A Review of Agents
Rajangad S. Gurtatta, Sydney E. Whalen, Charles E. Ray
Seminars in Interventional Radiology.2024; 41(01): 084. CrossRef - Combining immunotherapy with transarterial radioembolization
ZeynepCeren Balaban Genc, Efe Soydemır, SevalAy Ersoy, Tunc Ones
Indian Journal of Nuclear Medicine.2023; 38(2): 145. CrossRef - The New Era of Systemic Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From the First Line to the Optimal Sequence
Maria Cerreto, Ferdinando Cardone, Lucia Cerrito, Leonardo Stella, Francesco Santopaolo, Maria Pallozzi, Antonio Gasbarrini, Francesca Romana Ponziani
Current Oncology.2023; 30(10): 8774. CrossRef - Is multidisciplinary treatment effective for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus?
Won Hyeok Choe
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef
- Biologics, Immunotherapies, and Cytotoxic Chemotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma following Current Recommendations by the BCLC: A Review of Agents

Original Article
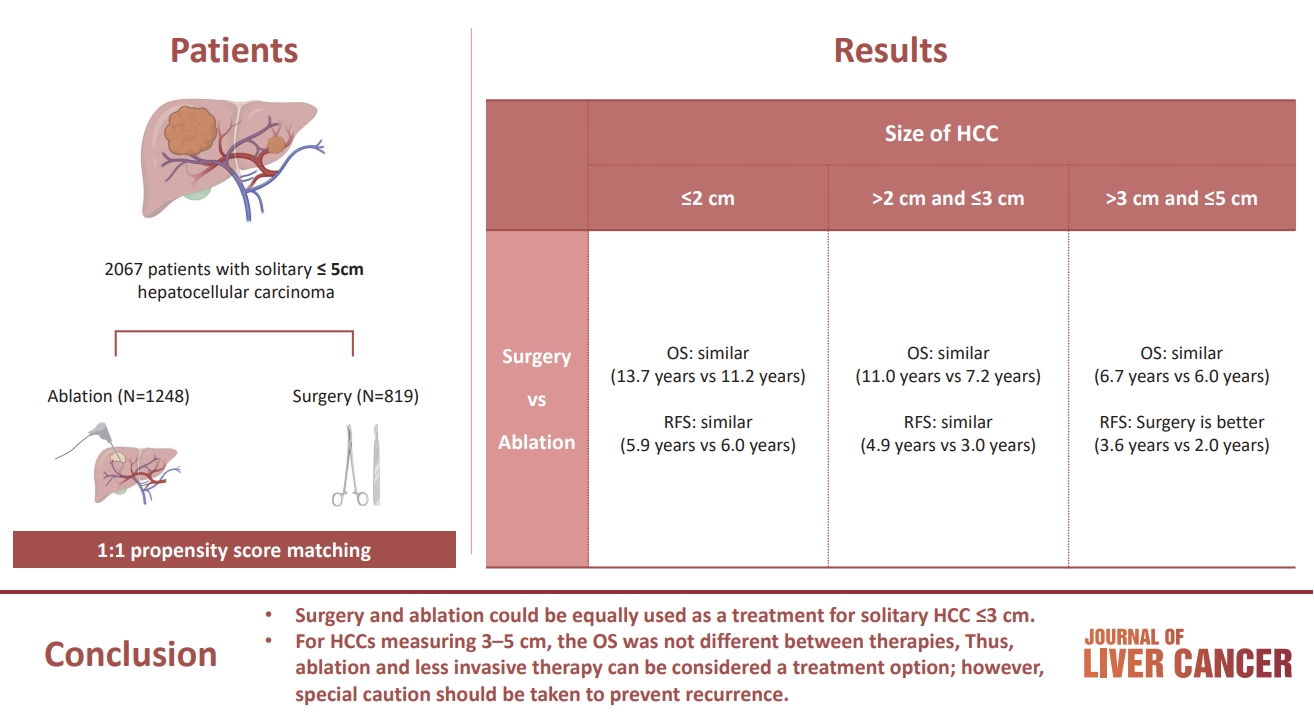
- Treatment options for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm: surgery vs. ablation: a multicenter retrospective study
- Kazuya Kariyama, Kazuhiro Nouso, Atsushi Hiraoka, Hidenori Toyoda, Toshifumi Tada, Kunihiko Tsuji, Toru Ishikawa, Takeshi Hatanaka, Ei Itobayashi, Koichi Takaguchi, Akemi Tsutsui, Atsushi Naganuma, Satoshi Yasuda, Satoru Kakizaki, Akiko Wakuta, Shohei Shiota, Masatoshi Kudo, Takashi Kumada
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):71-80. Published online November 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.09.11
- 914 Views
- 93 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
The aim of this study was to compare the therapeutic efficacy of ablation and surgery in solitary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) measuring ≤5 cm with a large HCC cohort database.
Methods
The study included consecutive 2,067 patients with solitary HCC who were treated with either ablation (n=1,248) or surgery (n=819). Th e patients were divided into three groups based on the tumor size and compared the outcomes of the two therapies using propensity score matching.
Results
No significant difference in recurrence-free survival (RFS) or overall survival (OS) was found between surgery and ablation groups for tumors measuring ≤2 cm or >2 cm but ≤3 cm. For tumors measuring >3 cm but ≤5 cm, RFS was significantly better with surgery than with ablation (3.6 and 2.0 years, respectively, P=0.0297). However, no significant difference in OS was found between surgery and ablation in this group (6.7 and 6.0 years, respectively, P=0.668).
Conclusion
The study suggests that surgery and ablation can be equally used as a treatment for solitary HCC no more than 3 cm in diameter. For HCCs measuring 3-5 cm, the OS was not different between therapies; thus, ablation and less invasive therapy can be considered a treatment option; however, special caution should be taken to prevent recurrence. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reply to the Letter regarding “Treatment options for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm: surgery vs. ablation: a multicenter retrospective study”
Kazuhiro Nouso, Kazuya Kariyama
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 5. CrossRef - Radiofrequency for hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 3 cm: potential for applications in daily practice
Ji Hoon Kim, Pil Soo Sung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Letter regarding “Treatment options for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm: surgery vs. ablation: a multicenter retrospective study”
Jongman Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 3. CrossRef
- Reply to the Letter regarding “Treatment options for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm: surgery vs. ablation: a multicenter retrospective study”

Recommendation and Guideline
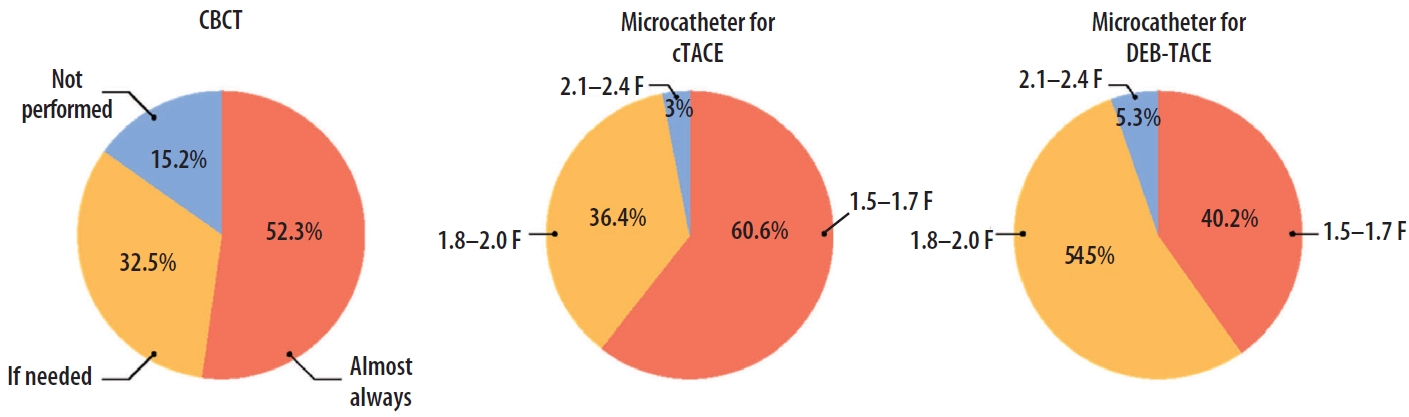
- Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2023 expert consensus-based practical recommendations of the Korean Liver Cancer Association
- Yuri Cho, Jin Woo Choi, Hoon Kwon, Kun Yung Kim, Byung Chan Lee, Hee Ho Chu, Dong Hyeon Lee, Han Ah Lee, Gyoung Min Kim, Jung Suk Oh, Dongho Hyun, In Joon Lee, Hyunchul Rhim
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):241-261. Published online July 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.05.22
- 2,204 Views
- 139 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) was introduced in 1977 with the administration of chemotherapeutic agent to gelatin sponge particles through the hepatic artery in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and was established as conventional TACE using Lipiodol in the 1980s. In the 2000s, drug-eluting beads were developed and applied clinically. Currently, TACE is a commonly used non-surgical treatment modality for patients with HCC who are unsuitable for curative treatment. Considering the vital role of TACE in the management of HCC, it is crucial to organize current knowledge and expert opinions regarding patient preparation, procedural techniques, and post-treatment care in TACE, which can enhance therapeutic efficacy and safety. A group of 12 experts in the fields of interventional radiology and hepatology, convened by the Research Committee of the Korean Liver Cancer Association (KLCA), has developed expert consensus-based practical recommendations in TACE. These recommendations have been endorsed by the Korean Society of Interventional Radiology and provide useful information and direction in performing TACE procedure as well as pre- and post- procedural patient care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Liver resection in selective hepatocellular carcinoma with Vp3 or Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis improves prognosis
Manuel Lim, Jongman Kim, Jinsoo Rhu, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 102. CrossRef - A refined prediction model for survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with transarterial chemoembolization
Hae Lim Lee, Seok Hwan Kim, Hee Yeon Kim, Sung Won Lee, Myeong Jun Song
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Implications of the first edition of the Korean expert consensus-based practice recommendations for transarterial chemoembolization in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Jin Wook Chung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 235. CrossRef
- Liver resection in selective hepatocellular carcinoma with Vp3 or Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis improves prognosis

Original Article
- Subclassification of advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: combined transarterial chemoembolization and radiotherapy as an alternative first-line treatment
- Sujin Jin, Won-Mook Choi, Ju Hyun Shim, Danbi Lee, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Jinhong Jung, Sang Min Yoon, Jonggi Choi
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):177-188. Published online March 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.03.04

- 1,479 Views
- 88 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
The Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) guidelines recommend systemic therapy as the only first-line treatment for patients with BCLC stage C hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) despite its heterogeneity of disease extent. We aimed to identify patients who might benefit from combined transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radiation therapy (RT) by subclassifying BCLC stage C.
Methods
A total of 1,419 treatment-naïve BCLC stage C patients with macrovascular invasion (MVI) who were treated with combined TACE and RT (n=1,115) or systemic treatment (n=304) were analyzed. The primary outcome was overall survival (OS). Factors associated with OS were identified and assigned points by the Cox model. The patients were subclassified into three groups based on these points.
Results
The mean age was 55.4 years, and 87.8% were male. The median OS was 8.3 months. Multivariate analysis revealed a significant association of Child-Pugh B, infiltrative-type tumor or tumor size ≥10 cm, main or bilateral portal vein invasion, and extrahepatic metastasis with poor OS. The sub-classification was categorized into low (point ≤1), intermediate (point=2), and high (point ≥3) risks based on the sum of points (range, 0–4). The OS in the low, intermediate, and high-risk groups was 22.6, 8.2, and 3.8 months, respectively. In the low and intermediate-risk groups, patients treated with combined TACE and RT exhibited significantly longer OS (24.2 and 9.5 months, respectively) than those who received systemic treatment (6.4 and 5.1 months, respectively; P<0.0001).
Conclusions
Combined TACE and RT may be considered as a first-line treatment option for HCC patients with MVI when classified into low- and intermediate-risk groups. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Liver resection in selective hepatocellular carcinoma with Vp3 or Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis improves prognosis
Manuel Lim, Jongman Kim, Jinsoo Rhu, Gyu-Seong Choi, Jae-Won Joh
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 102. CrossRef - Comparison of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
Jeayeon Park, Yun Bin Lee, Yunmi Ko, Youngsu Park, Hyunjae Shin, Moon Haeng Hur, Min Kyung Park, Dae-Won Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Kyung-Hun Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Su Jong Yu, Tae-Yong Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Tae-You Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 81. CrossRef - How to optimize the treatment strategy for advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion
Beom Kyung Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 121. CrossRef
- Liver resection in selective hepatocellular carcinoma with Vp3 or Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis improves prognosis

Case Report
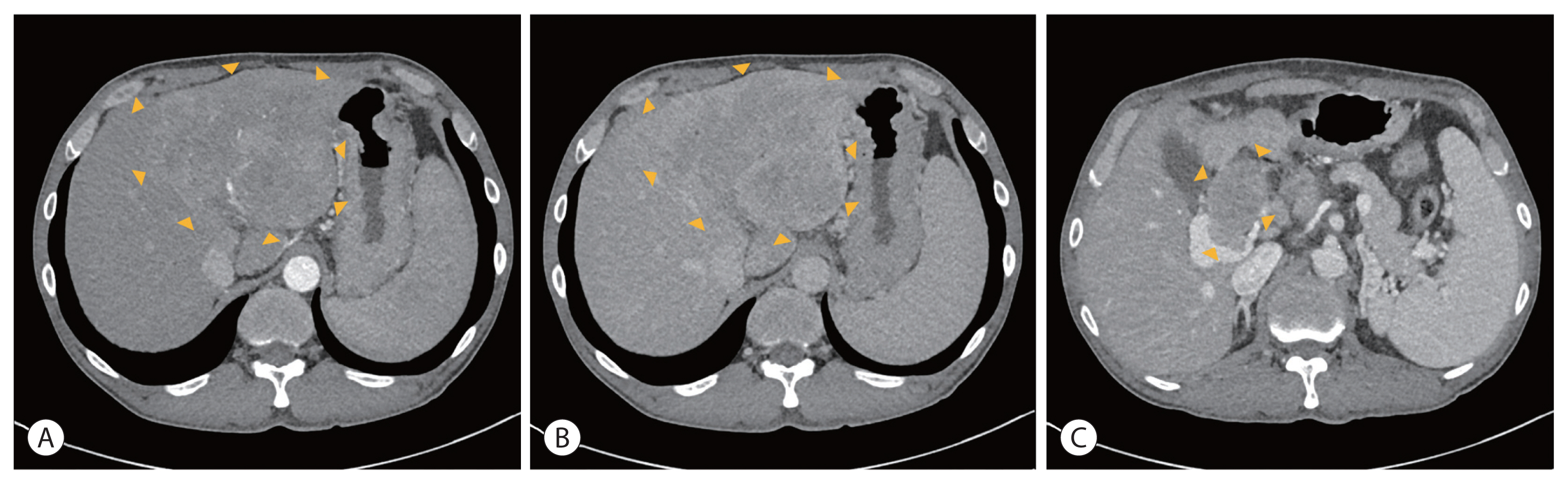
- Multidisciplinary treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma
- Ahlim Lee, Jaejun Lee, Hyun Yang, Soo-Yoon Sung, Chang Ho Jeon, Su Ho Kim, Moon Hyung Choi, Young Joon Lee, Ho Jong Chun, Si Hyun Bae
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(1):75-83. Published online March 18, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.03.04
- 3,944 Views
- 93 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a cytotoxic chemotherapy-resistant tumor and most HCCs arise in a background of liver cirrhosis of various causes. Although the IMBrave150 trial showed remarkable advancements in the treatment of unresectable HCC with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (AteBeva), therapeutic outcomes were unsatisfactory in more than half of the patients. Accordingly, many ongoing trials combine conventional modalities with new drugs such as immune checkpoint inhibitors for better treatment outcomes, and they are expected to benefit patients with limited responses to conventional treatment. Here, two patients with advanced stage HCC with preserved liver function and good performance status showed partial response after treatment with combination or sequential therapy of AteBeva, hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and transarterial chemoembolization. These findings indicate the efficacy of multidisciplinary treatment against advanced HCC. Additional studies are required to establish optimal treatment strategies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Complications of immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Young-Gi Song, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2024; 24(1): 9. CrossRef - Feasibility of additional radiotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab
Tae Hyun Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Yu Ri Cho, Young-Hwan Koh, Joong-Won Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 330. CrossRef - Is multidisciplinary treatment effective for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus?
Won Hyeok Choe
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef
- Complications of immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter